Drug Detail:Monjuvi (Tafasitamab [ ta-fa-sit-a-mab ])
Drug Class: CD19 monoclonal antibodies
Highlights of Prescribing Information
MONJUVI® (tafasitamab-cxix) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Indications and Usage for Monjuvi
MONJUVI is a CD19-directed cytolytic antibody indicated in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1)
Monjuvi Dosage and Administration
- Administer premedications prior to starting MONJUVI. (2.2)
- The recommended dosage of MONJUVI is 12 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion according to the following dosing schedule: (2.1)
- Cycle 1: Days 1, 4, 8, 15 and 22 of the 28-day cycle.
- Cycles 2 and 3: Days 1, 8, 15 and 22 of each 28-day cycle.
- Cycle 4 and beyond: Days 1 and 15 of each 28-day cycle.
- Administer MONJUVI in combination with lenalidomide for a maximum of 12 cycles and then continue MONJUVI as monotherapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.3, 2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
For injection: 200 mg of tafasitamab-cxix as lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution.(3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Monitor patients frequently during infusion. Interrupt or discontinue infusion based on severity. (2.3, 5.1)
- Myelosuppression: Monitor complete blood counts. Manage using dose modifications and growth factor support. Interrupt or discontinue MONJUVI based on severity. (2.3, 5.2)
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal and viral infections can occur during and following MONJUVI. Monitor patients for infections. (2.3, 5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, pyrexia, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact MORPHOSYS US INC. at 1-844-667-1992 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Monjuvi
MONJUVI, in combination with lenalidomide, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
2. Monjuvi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of MONJUVI is 12 mg/kg based on actual body weight administered as an intravenous infusion according to the dosing schedule in Table 1.
Administer MONJUVI in combination with lenalidomide 25 mg for a maximum of 12 cycles, then continue MONJUVI as monotherapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Refer to the lenalidomide prescribing information for lenalidomide dosage recommendations.
| Cycle* | Dosing Schedule |
|---|---|
|
|
| Cycle 1 | Days 1, 4, 8, 15 and 22 |
| Cycles 2 and 3 | Days 1, 8, 15 and 22 |
| Cycle 4 and beyond | Days 1 and 15 |
MONJUVI should be administered by a healthcare professional with immediate access to emergency equipment and appropriate medical support to manage infusion-related reactions (IRRs) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Premedications
Administer premedications 30 minutes to 2 hours prior to starting MONJUVI infusion to minimize infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Premedications may include acetaminophen, histamine H1 receptor antagonists, histamine H2 receptor antagonists, and/or glucocorticosteroids.
For patients not experiencing infusion-related reactions during the first 3 infusions, premedication is optional for subsequent infusions.
If a patient experiences an infusion-related reaction, administer premedications before each subsequent infusion.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are summarized in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 2 (moderate) |
|
| Grade 3 (severe) |
|
|
| Grade 4 (life-threatening) |
|
|
| Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Platelet count of 50,000/ mcL or less |
|
| Neutrophil count of 1,000/ mcL or less for at least 7 days OR Neutrophil count of 1,000/ mcL or less with an increase of body temperature to 100.4°F (38°C) or higher OR Neutrophil count less than 500/mcL |
|
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
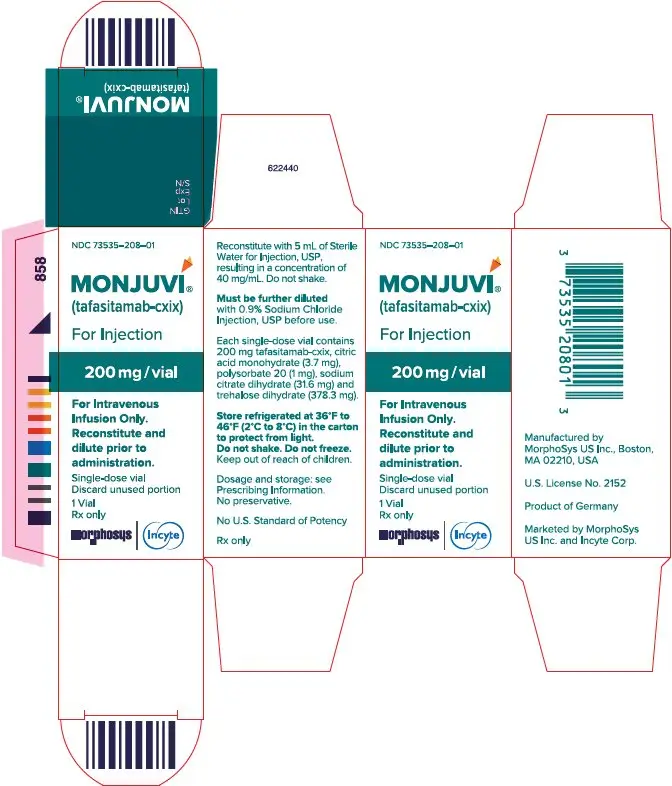
For injection: 200 mg of tafasitamab-cxix as white to slightly yellowish lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution and further dilution.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
MONJUVI can cause infusion-related reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In L-MIND, infusion-related reactions occurred in 6% of the 81 patients. Eighty percent of infusion-related reactions occurred during cycle 1 or 2. Signs and symptoms included chills, flushing, dyspnea, and hypertension. These reactions were managed with temporary interruption of the infusion and/or with supportive medication.
Premedicate patients prior to starting MONJUVI infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Monitor patients frequently during infusion. Based on the severity of the infusion-related reaction, interrupt or discontinue MONJUVI [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Institute appropriate medical management.
5.2 Myelosuppression
MONJUVI can cause serious or severe myelosuppression, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In L-MIND, Grade 3 neutropenia occurred in 25% of patients, thrombocytopenia in 12%, and anemia in 7%. Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 25% and thrombocytopenia in 6%. Neutropenia led to treatment discontinuation in 3.7% of patients.
Monitor CBC prior to administration of each treatment cycle and throughout treatment. Monitor patients with neutropenia for signs of infection. Consider granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration. Withhold MONJUVI based on the severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Refer to the lenalidomide prescribing information for dosage modifications.
5.3 Infections
Fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, occurred in patients during treatment with MONJUVI and following the last dose [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In L-MIND, 73% of the 81 patients developed an infection. The most frequent infections were respiratory tract infection (24%), urinary tract infection (17%), bronchitis (16%), nasopharyngitis (10%) and pneumonia (10%). Grade 3 or higher infection occurred in 30% of the 81 patients. The most frequent grade 3 or higher infection was pneumonia (7%). Infection-related deaths were reported in 2.5% of the 81 patients.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection and manage infections as appropriate.
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, MONJUVI may cause fetal B-cell depletion when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MONJUVI and for at least 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
MONJUVI is initially administered in combination with lenalidomide. The combination of MONJUVI with lenalidomide is contraindicated in pregnant women because lenalidomide can cause birth defects and death of the unborn child. Refer to the lenalidomide prescribing information on use during pregnancy.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is the potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assays. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other tafasitamab products may be misleading.
Overall, no treatment-emergent or treatment-boosted anti-tafasitamab antibodies were observed. No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, or safety profile of tafasitamab-cxix were observed in 2.5% of 81 patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL with pre-existing anti-tafasitamab antibodies in L-MIND.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
MONJUVI can cause fetal B-cell depletion when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MONJUVI in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Among 81 patients who received MONJUVI and lenalidomide in L-MIND, 72% were 65 years and older, while 38% were 75 years and older. Clinical studies of MONJUVI did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and older to determine whether effectiveness differs compared to that of younger subjects. Patients 65 years and older had more serious adverse reactions (57%) than younger patients (39%).
11. Monjuvi Description
Tafasitamab-cxix is a humanized CD19-directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody that contains an IgG1/2 hybrid Fc-domain with 2 amino acid substitutions to modify the Fc-mediated functions of the antibody. It is produced by recombinant DNA technology in mammalian cells (Chinese hamster ovary). Tafasitamab-cxix has a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa.
MONJUVI (tafasitamab-cxix) for injection is supplied as a sterile, preservative-free, white to slightly yellowish lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for intravenous use after reconstitution and further dilution. After reconstitution with 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the resulting concentration is 40 mg/mL with a pH of 6.0. Each single-dose vial contains 200 mg tafasitamab-cxix, citric acid monohydrate (3.7 mg), polysorbate 20 (1 mg), sodium citrate dihydrate (31.6 mg) and trehalose dihydrate (378.3 mg).
12. Monjuvi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tafasitamab-cxix is an Fc-modified monoclonal antibody that binds to CD19 antigen expressed on the surface of pre-B and mature B lymphocytes and on several B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Upon binding to CD19, tafasitamab-cxix mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanisms, including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
In studies conducted in vitro in DLBCL tumor cells, tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide resulted in increased ADCC activity compared to tafasitamab-cxix or lenalidomide alone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Tafasitamab-cxix reduced peripheral blood B cell counts by 97% after eight days of treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL. Nadir, with a reduction of 100%, was reached within 16 weeks of treatment.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mean trough concentrations (± standard deviation) were 179 (± 53) μg/mL following administration of MONJUVI at 12 mg/kg on Days 1, 8, 15, and 22 in Cycle 1-3 (plus an additional dose on Cycle 1 Day 4), and 153 (± 68) μg/mL following administration of MONJUVI at 12 mg/kg on Days 1 and 15 from Cycle 4 onwards. Overall maximum tafasitamab-cxix serum concentrations were 483 (±109) μg/mL.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and genotoxicity studies have not been conducted with tafasitamab-cxix.
Fertility studies have not been conducted with tafasitamab-cxix.
In the 13-week repeat-dose general toxicity study in cynomolgus monkeys, no adverse effects on male and female reproductive organs were observed up to the highest dose tested, 100 mg/kg/week (approximately 9 times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose of 12 mg/kg/week).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of MONJUVI in combination with lenalidomide followed by MONJUVI as monotherapy was evaluated in L-MIND, an open-label, multicenter, single arm trial (NCT02399085). Eligible patients had relapsed or refractory DLBCL after 1 to 3 prior systemic therapies, including a CD20-directed cytolytic antibody, and were not candidates for high dose chemotherapy (HDC) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Patients received MONJUVI 12 mg/kg intravenously in combination with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on Days 1 to 21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by MONJUVI as monotherapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity as follows:
- Cycle 1: Days 1, 4, 8, 15 and 22 of the 28-day cycle;
- Cycles 2 and 3: Days 1, 8, 15 and 22 of each 28-day cycle;
- Cycles 4 and beyond: Days 1 and 15 of each 28-day cycle.
Of the 71 patients with DLBCL confirmed by central laboratory who received the combination therapy, the median age was 71 years (range: 41 to 86 years); 55% were males, and 100% had received a prior CD20-containing therapy. Race was collected in 92% of patients; of these, 95% were White, and 3% were Asian. The median number of prior therapies was two; 49% had one prior line of treatment, and 51% had 2 to 4 prior lines. Thirty-two patients (45%) were refractory to their last prior therapy and 30 (42%) were refractory to rituximab. Nine patients (13%) had received prior ASCT. The primary reasons patients were not candidates for ASCT included age (47%), refractoriness to salvage chemotherapy (27%), comorbidities (13%) and refusal of high dose chemotherapy/ASCT (13%).
Efficacy was established based on best overall response rate, defined as the proportion of complete and partial responders, and duration of response, as assessed by an Independent Review Committee using the International Working Group Response Criteria (Cheson, 2007). Results are summarized in Table 5.
| N = 71 | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Best overall response rate, n (%) | 39 (55%) |
| (95% CI) | (43%, 67%) |
| Complete response rate | 37% |
| Partial response rate | 18% |
| Duration of Response | |
| Median (range) in months* | 21.7 (0, 24) |
16. How is Monjuvi supplied
MONJUVI (tafasitamab-cxix) for injection is a sterile, preservative-free, white to slightly yellowish lyophilized powder for reconstitution supplied as a 200 mg single-dose vial.
Each 200 mg vial is individually packaged in a carton (NDC 73535–208–01).
| MONJUVI
tafasitamab-cxix injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - MorphoSys US Inc. (100556743) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG | 340700520 | API MANUFACTURE(73535-208) , MANUFACTURE(73535-208) , ANALYSIS(73535-208) , PACK(73535-208) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioReliance Ltd | 505004556 | ANALYSIS(73535-208) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific BioLabs | 797419769 | ANALYSIS(73535-208) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Millmount Healthcare Limited (known as PCI Pharma Services) | 989237516 | LABEL(73535-208) , PACK(73535-208) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Commercialization Solutions, LLC | 832820588 | REPACK(73535-208) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphosys US Inc | 100556743 | ANALYSIS(73535-208) | |