Drug Detail:Monoferric (Ferric derisomaltose [ fer-ik-der-eye-soe-mawl-tose ])
Drug Class: Iron products
Highlights of Prescribing Information
MONOFERRIC (ferric derisomaltose) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Indications and Usage for Monoferric
MONOFERRIC is an iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients:
- who have intolerance to oral iron or have had unsatisfactory response to oral iron. ( 1)
- who have non-hemodialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. ( 1)
Monoferric Dosage and Administration
- For patients weighing 50 kg or more: Administer 1,000 mg of Monoferric as an intravenous infusion.
- For patients weighing less than 50 kg: Administer Monoferric as 20 mg/kg actual body weight as an intravenous infusion.
- Repeat Monoferric treatment if iron deficiency anemia reoccurs. ( 2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 1,000 mg iron /10 mL (100 mg/mL) single-dose vial ( 3)
- Injection: 500 mg iron/5 mL (100 mg/mL) single-dose vial ( 3)
- Injection: 100 mg iron/mL single-dose vial ( 3)
Contraindications
Serious hypersensitivity to Monoferric or any of its components. ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Monoferric administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of the infusion. ( 5.1)
- Iron Overload: Do not administer Monoferric to patients with iron overload. ( 5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥1%) are rash and nausea. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pharmacosmos at 1-888-828-0655 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2022
Related/similar drugs
ferrous sulfate, Venofer, FeroSul, AuryxiaFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Monoferric
Monoferric is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in adult patients:
- who have intolerance to oral iron or have had unsatisfactory response to oral iron
- who have non-hemodialysis dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD)
2. Monoferric Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
For patients weighing 50 kg or more: Administer 1,000 mg of Monoferric by intravenous infusion over at least 20 minutes as a single dose. Repeat dose if iron deficiency anemia reoccurs.
For patients weighing less than 50 kg: Administer Monoferric as 20 mg/kg actual body weight by intravenous infusion over at least 20 minutes as a single dose. Repeat dose if iron deficiency anemia reoccurs.
The dosage of Monoferric is expressed in mg of elemental iron. Each mL of Monoferric contains 100 mg of elemental iron.
Only administer Monoferric when personnel and therapies are immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions ( Warnings and Precautions (5.1)) .
2.2 Preparation and Administration
Inspect parenteral drug products visually for the absence of particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The product contains no preservatives.
Each vial of Monoferric is single-dose only. Discard unused portion.
- Withdraw the appropriate volume of Monoferric and dilute in 100 mL to 500 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Final diluted concentration should be more than 1 mg iron/mL.
- Compatibility of Monoferric with other drugs has not been established. Monoferric should not be mixed with or physically added to solutions containing other drugs.
- Administer the prepared solution via intravenous infusion over at least 20 minutes.
- Following dilution with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, Monoferric solution may be stored at room temperature for up to 8 hours.
- Extravasation of Monoferric may cause brown discoloration at the extravasation site which may be long lasting. Monitor for extravasation. If extravasation occurs, discontinue the Monoferric administration at that site.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Monoferric is a sterile, dark brown, non-transparent aqueous solution available as:
- Injection: 1,000 mg iron/10 mL (100 mg/mL) single-dose vial
- Injection: 500 mg iron/5 mL (100 mg/mL) single-dose vial
- Injection: 100 mg iron/mL single-dose vial
4. Contraindications
Monoferric is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity to Monoferric or any of its components (see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Description (11)) . Reactions have included shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving Monoferric. Patients may present with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Monoferric administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of the infusion. Only administer Monoferric when personnel and therapies are immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions. Monoferric is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity reactions to Monoferric or any of its components ( see Contraindications (4)). In clinical trials in patients with IDA and CKD, serious or severe hypersensitivity were reported in 0.3% (6/2008) of the Monoferric treated subjects. These included 3 events of hypersensitivity in 3 patients; 2 events of infusion-related reactions in 2 patients and 1 event of asthma in one patient.
5.2 Iron Overload
Excessive therapy with parenteral iron can lead to excess iron storage and possibly iatrogenic hemosiderosis or hemochromatosis. Monitor the hematologic response (hemoglobin and hematocrit) and iron parameters (serum ferritin and transferrin saturation) during parenteral iron therapy. Do not administer Monoferric to patients with iron overload (see Overdosage (10)) .
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions (see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)) .
- Iron Overload (see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)) .
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of Monoferric was evaluated in 3008 patients with iron deficiency anemia enrolled in two randomized, actively-controlled trials. Trial 1 enrolled adult patients with iron deficiency anemia with intolerance to oral iron or had an unsatisfactory response to oral iron with a clinical need for repletion of iron stores. Eligible subjects were required to have a baseline hemoglobin of ≤11g/dl, transferrin saturation (TSAT) of less than 20% and serum ferritin level of <100 ng/mL. Trial 2 enrolled adult patients with non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease (CKD) with iron deficiency anemia ( see Clinical Studies (14)). Eligible subjects also had to have serum ferritin ≤100 ng/mL or ≤300 ng/mL if TSAT ≤30%.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following adverse reactions have been most commonly reported from the post-marketing spontaneous reports with Monoferric:
Cardiac disorders: Tachycardia
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, constipation, diarrhea
General disorders and administration site conditions: Fatigue, pyrexia, chest pain, chills, Fishbane reaction, extravasation, influenza like symptoms, injection site reactions, malaise, pain
Immune System disorders: Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction, hypersensitivity
Investigations: Hepatic enzymes increased
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Back pain, muscle spasms, arthralgia, myalgia
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness, headache, paresthesia, dysgeusia, seizure, loss of consciousness, syncope
Psychiatric disorders: Anxiety
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnea, cough, bronchospasm
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Erythema, urticaria, discoloration skin, rash, pruritus, skin exfoliation, angioedema, sweating
Vascular disorders: Hypertension, hypotension, flushing, phlebitis
Extravasation of Monoferric at the injection site that may lead to irritation of the skin and potentially long lasting brown discoloration at the site of injection has also been reported.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 3934 patients in clinical studies of Monoferric, 29% were 65 years and over, while 13% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
10. Overdosage
Excessive dosages of Monoferric may lead to accumulation of iron in storage sites potentially leading to hemosiderosis and hemochromatosis. Avoid use of Monoferric in patients with iron overload (see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)) .
11. Monoferric Description
Monoferric is an iron replacement product containing ferric derisomaltose for intravenous infusion. Ferric derisomaltose is an iron carbohydrate complex with a matrix structure composed of interchanging layers of ferric hydroxide and the carbohydrate derisomaltose. Derisomaltose consists of linear, hydrogenated isomaltooligosaccharides with an average molecular weight of 1000 Da and a narrow molecular weight distribution that is almost devoid of mono- and disaccharides.
Ferric derisomaltose has an average molecular weight of 155,000 Da and has the following empirical formula:
{FeO (1-3X) (OH) (1+3X) (C 6H 5O 73-) X}, (H 20) T, -
(C 6H 10O 6) R(-C 6H 10O 5-) Z(C 6H 13O 5) R, (NaCl) Y
X = 0.0311; T = 0.25; R = 0.14; Z = 0.49; Y = 0.14
Iron atoms placed in the electronegative cavities of the 3-D structure between and within the derisomaltose molecules. A schematic representation is presented below
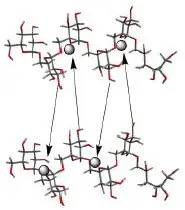
Monoferric is a sterile, dark brown, non-transparent aqueous solution with pH 5.0-7.0, containing ferric derisomaltose dissolved in water for injections and filled into Type I glass vials.
Each 1 mL of solution contains 100 mg of elemental iron as ferric derisomaltose in water for injection, hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide may be used to adjust pH.
12. Monoferric - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ferric derisomaltose is a complex of iron (III) hydroxide and derisomaltose, an iron carbohydrate oligosaccharide that releases iron. Iron binds to transferrin for transport to erythroid precursor cells to be incorporated into hemoglobin.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Serum ferritin peaks approximately 7 days after an intravenous dose of Monoferric and slowly returns to stable levels after about 4 weeks.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of total iron (derisomaltose-bound plus transferrin-bound iron) were evaluated in adult patients with IDA.
After a single dose of Monoferric, maximum concentration (C max) and area under the concentration time curve (AUC) of serum total iron increased approximately proportionally over the 100 to 1000 mg dose range. After a 1000 mg single dose, the C max and AUC inf of total iron (geometric mean and CV%) of serum total iron were 408 (10.5) μg/mL and 17730 (22.1) μg.h /mL.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted.
Iron oligosaccharide, an earlier formulation of ferric derisomaltose, was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, an in vitro chromosomal aberrations test and an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats, ferric derisomaltose was administered intravenously to male rats 28 days prior to mating and through cohabitation and to female rats 14 days prior to cohabitation and through GD 17. Doses administered were 2, 6, or 19 mg Fe/kg/day in males and 3, 11, or 32 mg Fe/kg/day in females. There was no effect on male or female fertility in rats at up to 19 mg Fe/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the MRHD of 1000 mg, based on BSA) in males and up to 32 mg Fe/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the MRHD of 1000 mg based on BSA) in females.
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of Monoferric for treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) were evaluated in two randomized, open-label, actively-controlled clinical trials performed in a total of 3050 patients with IDA of different etiology. Trial 1 included patients with IDA who had intolerance to oral iron or who had had unsatisfactory response to oral iron or for whom there was a clinical need for rapid repletion of iron stores. Trial 2 included patients with IDA who had non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD). In these two 8-Week trials, patients were randomized 2:1 to treatment with Monoferric or iron sucrose. Monoferric was intravenously administered as a single dose of 1000 mg.
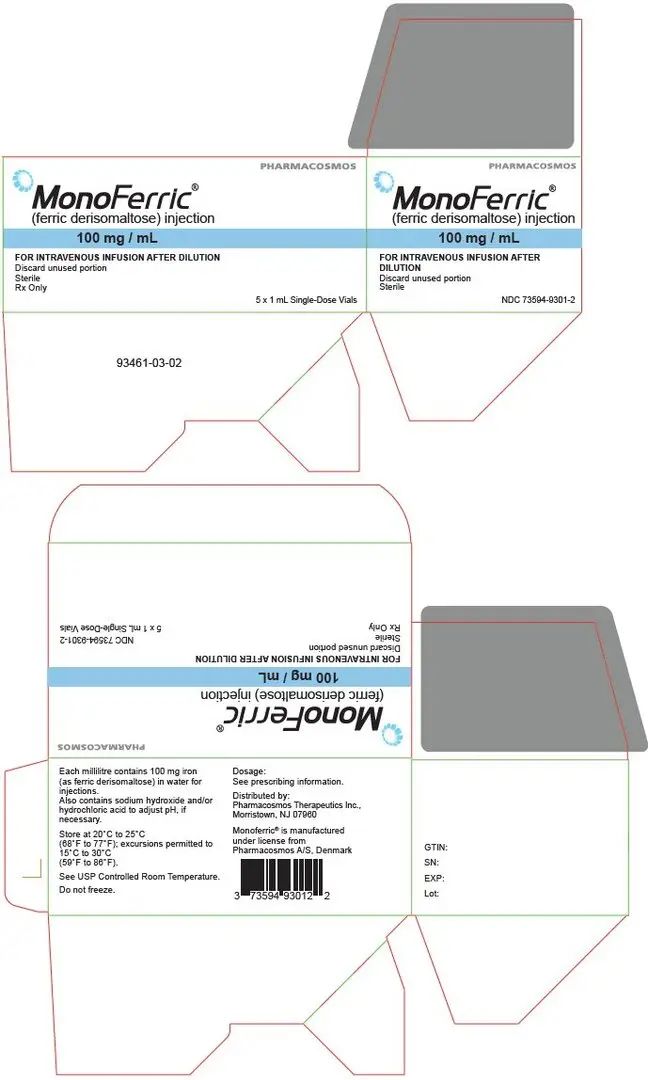
16. How is Monoferric supplied
16.1 How Supplied
Monoferric injection is a sterile, dark brown, non-transparent aqueous solution supplied in cartons as single-dose vials (10 mL, 5 mL or 1 mL) in the following configurations:
| Vial size | Number of vials per carton | NDC |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 mg/10 mL | 1 | 73594-9310-1 |
| 500 mg/5 mL | 1 | 73594-9305-1 |
| 100 mg/mL | 5 | 73594-9301-2 |
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). See the USP controlled room temperature.
Do not freeze.
When added to an infusion bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, Monoferric solution may be stored for up to 8 hours at room temperature.
| MONOFERRIC
ferric derisomaltose injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MONOFERRIC
ferric derisomaltose injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MONOFERRIC
ferric derisomaltose injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pharmacosmos Therapeutics Inc. (117344166) |