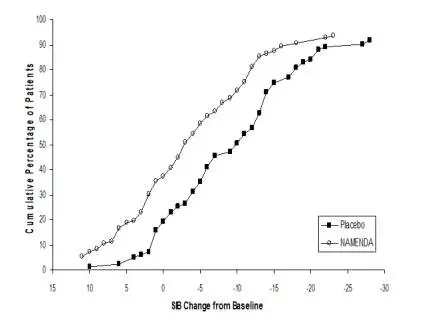
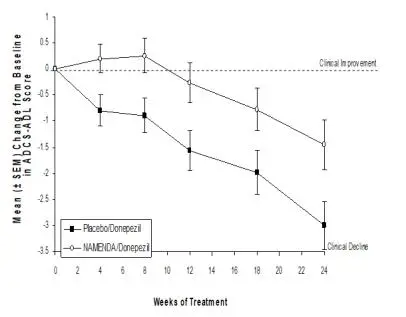
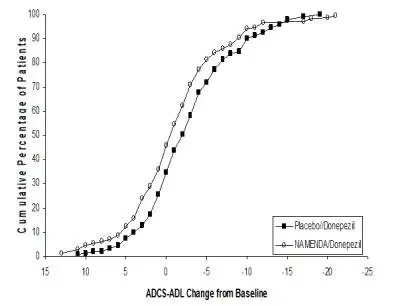
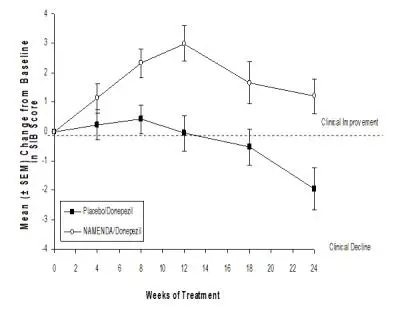
Drug Detail:Namenda (Memantine [ meh-man-teen ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous central nervous system agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NAMENDA® (memantine hydrochloride) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2003
Indications and Usage for Namenda
NAMENDA is a N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. (1)
Namenda Dosage and Administration
- May be taken with or without food. (2)
- Initial dose is 5 mg once daily. Increase dose in 5 mg increments to a maintenance dose of 10 mg twice daily. A minimum of 1 week of treatment with the previous dose should be observed before increasing the dose. (2)
- Severe renal impairment: recommended dose is 5 mg twice daily. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 5 mg and 10 mg (3)
Contraindications
- NAMENDA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to memantine hydrochloride or to any excipients used in the formulation. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Conditions that raise urine pH may decrease the urinary elimination of memantine, resulting in increased plasma levels of memantine. (5.1, 7.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5% and greater than placebo) are dizziness, headache, confusion and constipation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2018
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Namenda
NAMENDA (memantine hydrochloride) is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type.
2. Namenda Dosage and Administration
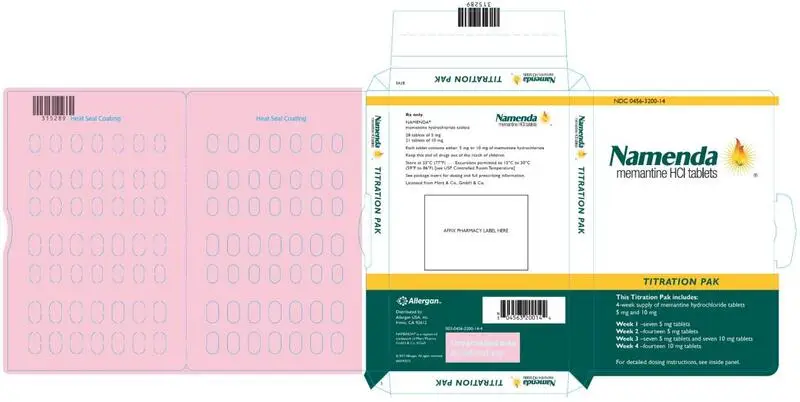
The recommended starting dose of NAMENDA is 5 mg once daily. The dose should be increased in 5 mg increments to 10 mg/day (5 mg twice daily), 15 mg/day (5 mg and 10 mg as separate doses), and 20 mg/day (10 mg twice daily). The minimum recommended interval between dose increases is one week. The dosage shown to be effective in controlled clinical trials is 20 mg/day.
NAMENDA can be taken with or without food. If a patient misses a single dose of NAMENDA, that patient should not double up on the next dose. The next dose should be taken as scheduled.
If a patient fails to take NAMENDA for several days, dosing may need to be resumed at lower doses and retitrated as described above.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
A target dose of 5 mg twice daily is recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 5 – 29 mL/min based on the Cockcroft-Gault equation).
Hepatic Impairment
NAMENDA should be administered with caution to patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
NAMENDA 5 mg Tablet: capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets are tan, with the strength “5” debossed on one side and “FL” on the other side.
NAMENDA 10 mg Tablet: capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets are gray, with the strength “10” debossed on one side and “FL” on the other side.
4. Contraindications
NAMENDA (memantine hydrochloride) is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to memantine hydrochloride or to any excipients used in the formulation.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
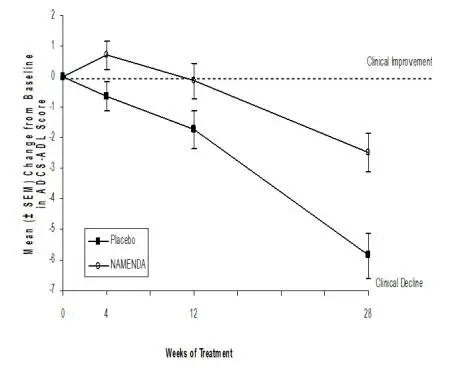
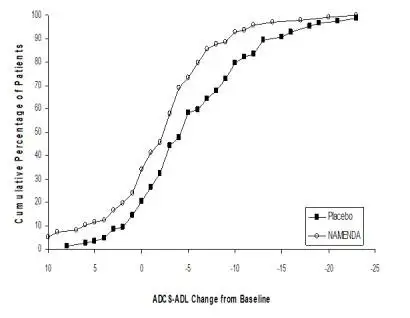
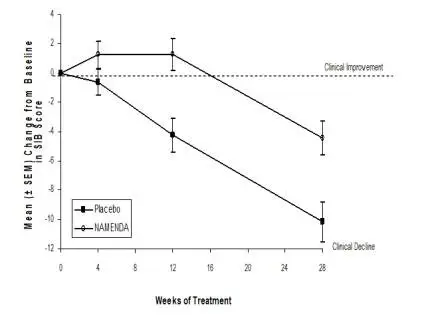
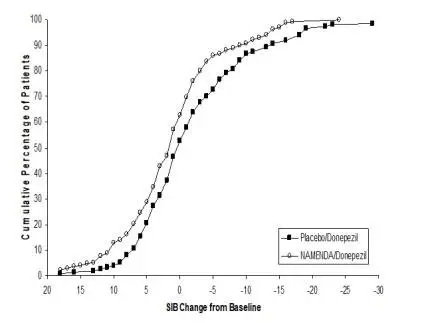
NAMENDA was evaluated in eight double-blind placebo-controlled trials involving a total of 1862 dementia (Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia) patients (940 patients treated with NAMENDA and 922 patients treated with placebo) for a treatment period up to 28 weeks.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation
In placebo-controlled trials in which dementia patients received doses of NAMENDA up to 20 mg/day, the likelihood of discontinuation because of an adverse reaction was the same in the NAMENDA group (10.1%) as in the placebo group (11.5%). No individual adverse reaction was associated with the discontinuation of treatment in 1% or more of NAMENDA-treated patients and at a rate greater than placebo.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
In double-blind placebo-controlled trials involving dementia patients, the most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and higher than placebo) in patients treated with NAMENDA were dizziness, headache, confusion and constipation. Table 1 lists all adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with NAMENDA and at an incidence greater than placebo.
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo
(N=922) % |
NAMENDA
(N=940) % |
| Body as a Whole | ||
| Fatigue | 1 | 2 |
| Pain | 1 | 3 |
| Cardiovascular System | ||
| Hypertension | 2 | 4 |
| Central and Peripheral Nervous System | ||
| Dizziness | 5 | 7 |
| Headache | 3 | 6 |
| Gastrointestinal System | ||
| Constipation | 3 | 5 |
| Vomiting | 2 | 3 |
| Musculoskeletal System | ||
| Back pain | 2 | 3 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Confusion | 5 | 6 |
| Somnolence | 2 | 3 |
| Hallucination | 2 | 3 |
| Respiratory System | ||
| Coughing | 3 | 4 |
| Dyspnea | 1 | 2 |
The overall profile of adverse reactions and the incidence rates for individual adverse reactions in the subpopulation of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease were not different from the profile and incidence rates described above for the overall dementia population.
Seizures
NAMENDA has not been systematically evaluated in patients with a seizure disorder. In clinical trials of NAMENDA, seizures occurred in 0.2% of patients treated with NAMENDA and 0.5% of patients treated with placebo.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs that Make Urine Alkaline
The clearance of memantine was reduced by about 80% under alkaline urine conditions at pH 8. Therefore, alterations of urine pH towards the alkaline condition may lead to an accumulation of the drug with a possible increase in adverse effects. Urine pH is altered by diet, drugs (e.g. carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sodium bicarbonate) and clinical state of the patient (e.g. renal tubular acidosis or severe infections of the urinary tract). Hence, memantine should be used with caution under these conditions.
12. Namenda - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration memantine is highly absorbed with peak concentrations reached in about 3-7 hours. Memantine has linear pharmacokinetics over the therapeutic dose range. Food has no effect on the absorption of memantine.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of memantine is 9-11 L/kg and the plasma protein binding is low (45%).
Metabolism
Memantine undergoes partial hepatic metabolism. The hepatic microsomal CYP450 enzyme system does not play a significant role in the metabolism of memantine.
Elimination
Memantine is excreted predominantly (about 48%) unchanged in urine and has a terminal elimination half-life of about 60-80 hours.
The remainder is converted primarily to three polar metabolites which possess minimal NMDA receptor antagonistic activity: the N-glucuronide conjugate, 6-hydroxy memantine, and 1-nitroso-deaminated memantine. A total of 74% of the administered dose is excreted as the sum of the parent drug and the N-glucuronide conjugate. Renal clearance involves active tubular secretion moderated by pH dependent tubular reabsorption.
Specific Populations
Gender
Following multiple dose administration of NAMENDA 20 mg daily, females had about 45% higher exposure than males, but there was no difference in exposure when body weight was taken into account.
Elderly
The pharmacokinetics of NAMENDA in young and elderly subjects are similar.
Renal Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following single oral administration of 20 mg memantine hydrochloride in 8 subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance, CLcr, > 50 – 80 mL/min), 8 subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 – 49 mL/min), 7 subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr 5 – 29 mL/min) and 8 healthy subjects (CLcr > 80 mL/min) matched as closely as possible by age, weight and gender to the subjects with renal impairment. Mean AUC0-∞ increased by 4%, 60%, and 115% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. The terminal elimination half-life increased by 18%, 41%, and 95% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects.
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild and moderate renal impairment. Dosage should be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Hepatic Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following the administration of single oral doses of 20 mg in 8 subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) and 8 subjects who were age-, gender-, and weight-matched to the hepatically-impaired subjects. There was no change in memantine exposure (based on Cmax and AUC) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. However, terminal elimination half-life increased by about 16% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment. Memantine should be administered with caution to patients with severe hepatic impairment as the pharmacokinetics of memantine have not been evaluated in that population.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Use with Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Coadministration of memantine with the AChE inhibitor donepezil hydrochloride did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either compound. Furthermore, memantine did not affect AChE inhibition by donepezil. In a 24-week controlled clinical study in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, the adverse event profile observed with a combination of NAMENDA and donepezil was similar to that of donepezil alone.
Effect of NAMENDA on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
In vitro studies conducted with marker substrates of CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, -2A6, -2C9, -2D6, -2E1, -3A4) showed minimal inhibition of these enzymes by memantine. In addition, in vitro studies indicate that at concentrations exceeding those associated with efficacy, memantine does not induce the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP1A2, -2C9, -2E1 and -3A4/5. No pharmacokinetic interactions with drugs metabolized by these enzymes are expected.
Pharmacokinetic studies evaluated the potential of memantine for interaction with warfarin, and bupropion. Memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics of the CYP2B6 substrate bupropion or its metabolite hydroxy-bupropion. Furthermore, memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of warfarin as assessed by the prothrombin INR.
Effect of Other Drugs on NAMENDA
Memantine is predominantly renally eliminated, and drugs that are substrates and/or inhibitors of the CYP450 system are not expected to alter the metabolism of memantine.
Drugs Eliminated via Renal Mechanisms
Because memantine is eliminated in part by tubular secretion, coadministration of drugs that use the same renal cationic system, including hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), triamterene (TA), metformin, cimetidine, ranitidine, quinidine, and nicotine, could potentially result in altered plasma levels of both agents. However, coadministration of NAMENDA and HCTZ/TA did not affect the bioavailability of either memantine or TA, and the bioavailability of HCTZ decreased by 20%. In addition, coadministration of memantine with the antihyperglycemic drug Glucovance® (glyburide and metformin hydrochloride) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of memantine, metformin and glyburide. Furthermore, memantine did not modify the serum glucose lowering effect of Glucovance®, indicating the absence of a pharmacodynamic interaction.
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Proteins
Because the plasma protein binding of memantine is low (45%), an interaction with drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins, such as warfarin and digoxin, is unlikely.
Patient Information
NAMENDA® [Nuh-MEN-dah]
(memantine hydrochloride)
Tablets
Read this Patient Information that comes with NAMENDA before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is NAMENDA?
NAMENDA® is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia in people with Alzheimer’s disease. NAMENDA belongs to a class of medicines called N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) inhibitors.
It is not known if NAMENDA is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take NAMENDA?
Do not take NAMENDA if you are allergic to memantine or any of the ingredients in NAMENDA tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in NAMENDA tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking NAMENDA?
Before you take NAMENDA, tell your doctor if you:
- have or have had seizures
- have or have had problems passing urine
- have or have had bladder or kidney problems
- have liver problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if NAMENDA will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if memantine passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take NAMENDA.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking NAMENDA with certain other medicines may affect each other. Taking NAMENDA with other medicines can cause serious side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other NMDA antagonists such as amantadine, ketamine, and dextromethorphan
- medicines that make your urine alkaline such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and sodium bicarbonate
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take NAMENDA?
- Your doctor will tell you how much NAMENDA to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- NAMENDA can be taken with food or without food.
- Do not use any tablets of NAMENDA that are damaged or show signs of tampering.
- If you forget to take one dose of NAMENDA, do not double up on the next dose. You should take only the next dose as scheduled.
- If you have forgotten to take NAMENDA for several days, you should not take the next dose until you talk to your doctor.
- If you take too much NAMENDA, call your doctor or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of NAMENDA?
NAMENDA may cause side effects, including:
The most common side effects of NAMENDA include:
- dizziness
- headache
- confusion
- constipation
These are not all the possible side effects of NAMENDA. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store NAMENDA?
- Store NAMENDA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
What are the ingredients in NAMENDA?
NAMENDA tablets:
Active ingredient: memantine hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose/colloidal silicon dioxide, talc, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate
Inactive ingredients of tablet film coating: hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 400, FD&C yellow #6 and FD&C blue #2 (5 mg tablets), and hypromellose, titanium dioxide, macrogol/polyethylene glycol 400 and iron oxide black (10 mg tablets)
Keep NAMENDA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of NAMENDA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not take NAMENDA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NAMENDA to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about NAMENDA. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about NAMENDA that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about NAMENDA, go to www.namenda.com, or call Allergan at 1-800-678-1605.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Made in Ireland
Distributed by:
Allergan USA, Inc.
Madison, NJ 07940
Licensed from Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbH
NAMENDA® is a registered trademark of Merz Pharma GmbH & Co KGaA
Allergan® and its design are trademarks of Allergan, Inc.

© 2019 Allergan. All rights reserved.
Content updated: November 2018
v1.1PPI3205
| NAMENDA
memantine hydrochloride tablet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMENDA
memantine hydrochloride tablet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMENDA
memantine hydrochloride kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |