Drug Detail:Namzaric (Donepezil and memantine [ doe-nep-e-zil-and-mem-an-teen ])
Drug Class: Cholinesterase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NAMZARIC (memantine and donepezil hydrochlorides) extended-release capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
Indications and Usage for Namzaric
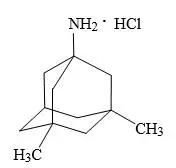
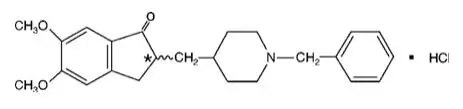
NAMZARIC is a combination of memantine hydrochloride, an NMDA receptor antagonist, and donepezil hydrochloride, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type in patients stabilized on 10 mg of donepezil hydrochloride once daily. (1)
Namzaric Dosage and Administration
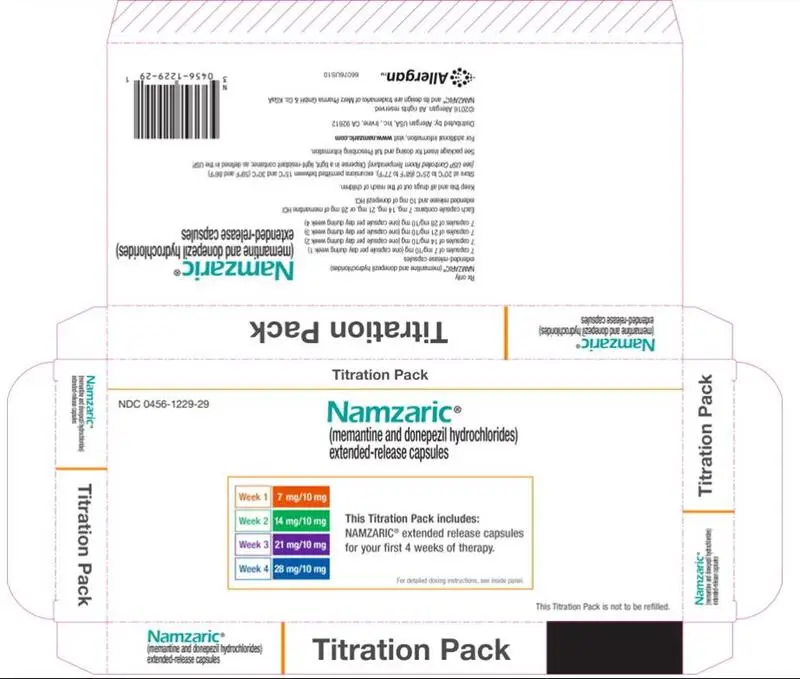
- For patients on donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg only, the recommended starting dose of NAMZARIC is 7 mg/10 mg, taken once daily in the evening. The dose should be increased in 7 mg increments to the recommended maintenance dose of 28 mg/10 mg. The minimum recommended interval between dose increases is one week. (2.1)
- Patients on memantine hydrochloride (10 mg twice daily or 28 mg extended- release once daily) and donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg once daily can be switched to NAMZARIC 28 mg/10 mg, taken once daily in the evening. (2.1)
- NAMZARIC can be taken with or without food, whole or sprinkled on applesauce; do not divide, chew, or crush. (2.2)
- Severe renal impairment: the recommended maintenance dose for NAMZARIC is 14 mg/10 mg once daily in the evening. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
-Extended-Release Capsules:
- 7 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride (3)
- 14 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride (3)
- 21 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride (3)
- 28 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride (3)
Contraindications
NAMZARIC is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to memantine hydrochloride, donepezil hydrochloride, piperidine derivatives, or to any excipients used in the formulation. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- NAMZARIC is likely to exaggerate succinylcholine-type muscle relaxation during anesthesia. (5.1)
- NAMZARIC may have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes manifesting as bradycardia or heart block. (5.2)
- Monitor patients for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers. (5.3)
- NAMZARIC can cause diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. (5.4)
- NAMZARIC may cause bladder outflow obstructions. (5.5)
- Conditions that raise urine pH may decrease the urinary elimination of memantine, resulting in increased plasma levels of memantine. (5.5, 7.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse reactions, occurring at a frequency of at least 5% and greater than placebo with memantine hydrochloride extended-release 28 mg/day, were headache, diarrhea, and dizziness. (6.1)
- The most common adverse reactions, occurring at a frequency of at least 5% in patients receiving donepezil hydrochloride and at twice or more the placebo rate, include diarrhea, anorexia, vomiting, nausea, and ecchymosis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Combined use with NMDA antagonists: use with caution. (7.2)
- NAMZARIC may interfere with anticholinergic medications. (7.4)
- Concomitant administration of succinylcholine, similar neuromuscular blocking agents, or cholinergic agonists may lead to synergistic effect. (7.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Namzaric
NAMZARIC is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type in patients stabilized on 10 mg of donepezil hydrochloride once daily.
2. Namzaric Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended dose of NAMZARIC is 28 mg/10 mg once daily.
For patients stabilized on donepezil and not currently on memantine:
For patients stabilized on donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg and not currently on memantine hydrochloride, the recommended starting dose of NAMZARIC is 7 mg/10 mg, taken once a day in the evening. The dose should be increased in 7 mg increments of the memantine hydrochloride component to the recommended maintenance dose of 28 mg/10 mg once daily. The minimum recommended interval between dose increases is one week. The dose should only be increased if the previous dose has been well tolerated. The maximum dose is 28 mg/10 mg once daily.
For patients stabilized on both donepezil and memantine:
Patients stabilized on memantine hydrochloride (10 mg twice daily or 28 mg extended-release once daily) and donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg once daily can be switched to NAMZARIC 28 mg/10 mg, taken once a day in the evening. Patients should start NAMZARIC the day following the last dose of memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride administered separately.
If a patient misses a single dose of NAMZARIC, the next dose should be taken as scheduled, without doubling up the dose.
2.2 Administration Information
NAMZARIC can be taken with or without food. NAMZARIC capsules can be taken intact or may be opened, sprinkled on applesauce, and swallowed without chewing. The entire contents of each NAMZARIC capsule should be consumed; the dose should not be divided.
Except when opened and sprinkled on applesauce, as described above, NAMZARIC capsules should be swallowed whole. NAMZARIC capsules should not be divided, chewed, or crushed.
2.3 Dosing in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
For patients stabilized on donepezil and not currently on memantine:
For patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 5-29 mL/min, based on the Cockcroft-Gault equation) stabilized on donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg once daily and not currently on memantine hydrochloride, the recommended starting dose of NAMZARIC is 7mg/10 mg taken once a day in the evening. The dose should be increased to the recommended maintenance dose of 14 mg/10 mg once daily in the evening after a minimum of one week [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
For patients stabilized on both donepezil and memantine:
Patients with severe renal impairment, stabilized on memantine hydrochloride (5 mg twice daily or 14 mg extended-release once daily) and donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg once daily, can be switched to NAMZARIC 14 mg/10 mg, taken once daily in the evening.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-Release Capsules:
- 7 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride: light green opaque body and an orange opaque cap with a black “FL 7/10” radial imprint
- 14 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride: light green opaque capsules with a black “FL 14/10” radial imprint
- 21 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride: white opaque body and an orange opaque cap with a black “FL 21/10” radial imprint
- 28 mg memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg donepezil hydrochloride: blue opaque capsules with a black “FL 28/10” radial imprint
4. Contraindications
NAMZARIC is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to memantine hydrochloride, donepezil hydrochloride, piperidine derivatives, or to any excipients used in the formulation.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Anesthesia
Donepezil hydrochloride, an active ingredient in NAMZARIC, as a cholinesterase inhibitor, is likely to exaggerate succinylcholine-type muscle relaxation during anesthesia.
5.2 Cardiovascular Conditions
Because of their pharmacological action, cholinesterase inhibitors may have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This effect may manifest as bradycardia or heart block in patients both with and without known underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride, an active ingredient in NAMZARIC.
5.3 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Through their primary action, cholinesterase inhibitors may be expected to increase gastric acid secretion due to increased cholinergic activity. Clinical studies of donepezil hydrochloride in a dose of 5 mg/day to 10 mg/day have shown no increase, relative to placebo, in the incidence of either peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients treated with NAMZARIC should be monitored closely for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers, e.g., those with a history of ulcer disease or those receiving concurrent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
5.4 Nausea and Vomiting
Donepezil hydrochloride, an active ingredient in NAMZARIC, when initiated, as a predictable consequence of its pharmacological properties, has been shown to produce diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Although in most cases, these effects have been mild and transient, sometimes lasting one to three weeks, and have resolved during continued use of donepezil hydrochloride, patients should be observed closely at the initiation of treatment.
5.5 Genitourinary Conditions
Although not observed in clinical trials of donepezil hydrochloride, an active ingredient in NAMZARIC, cholinomimetics may cause bladder outflow obstruction.
Conditions that raise urine pH may decrease the urinary elimination of memantine, an active ingredient in NAMZARIC, resulting in increased plasma levels of memantine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling.
- Cardiovascular Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Peptic Ulcer Disease and Gastrointestinal Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Nausea and Vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Genitourinary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Pulmonary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Memantine Hydrochloride
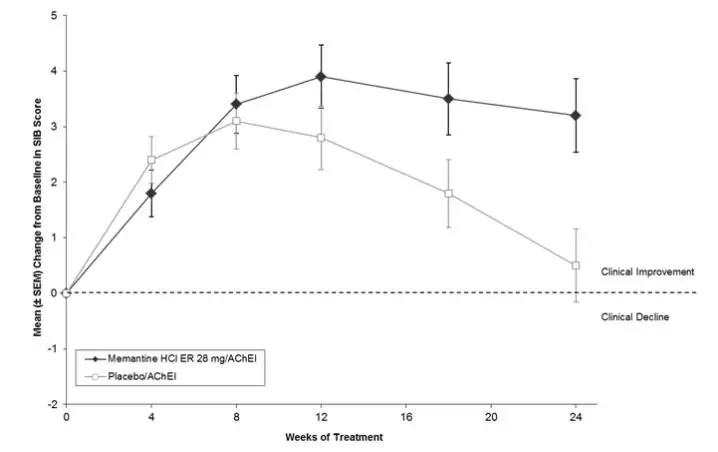
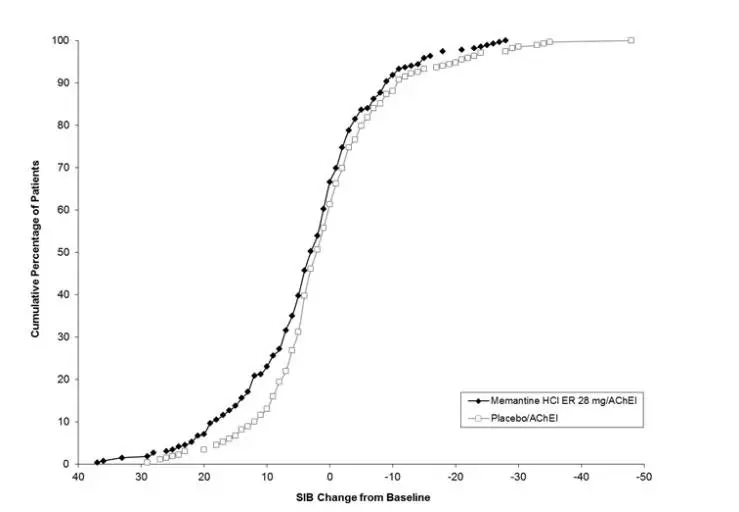
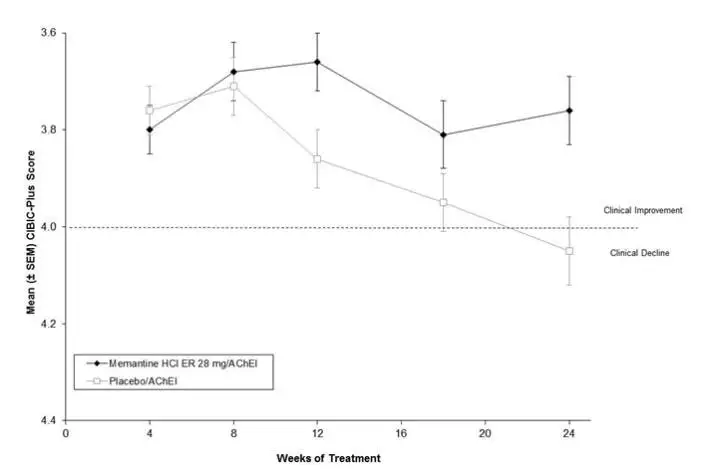
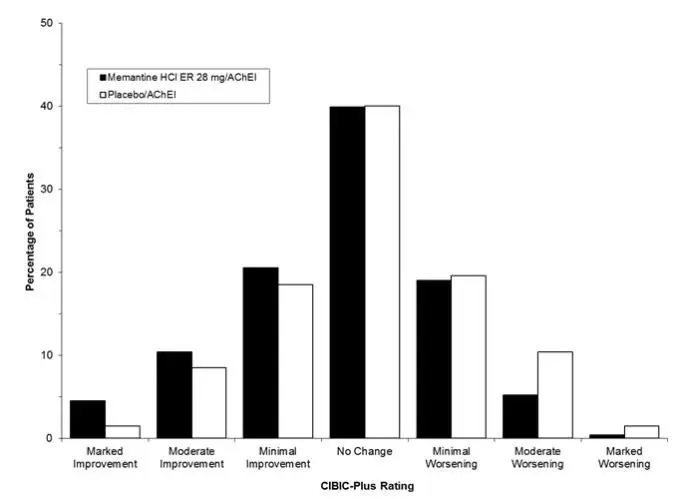
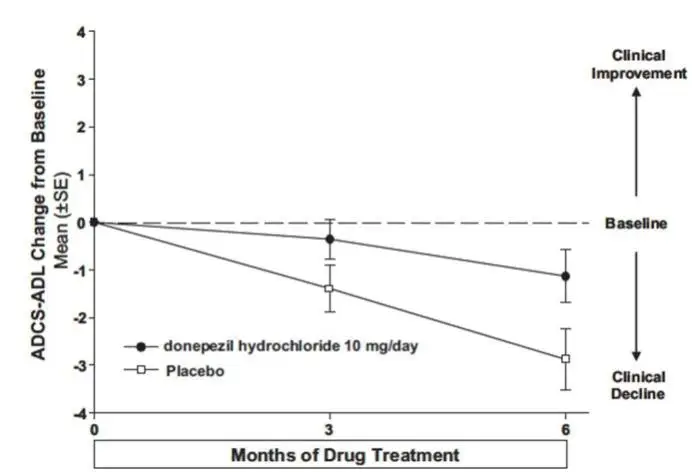
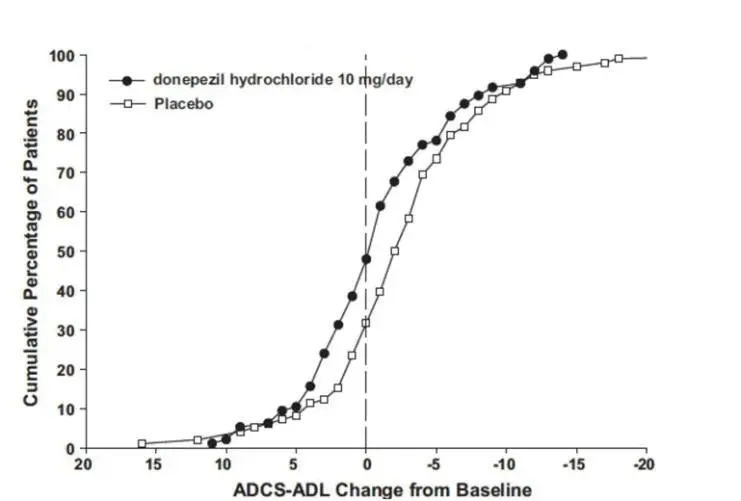
Memantine hydrochloride extended-release was evaluated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 676 patients with moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type (341 patients treated with memantine 28 mg/day dose and 335 patients treated with placebo) for a treatment period up to 24 weeks. Of the patients randomized, 236 treated with memantine 28 mg/day and 227 treated with placebo were on a stable dose of donepezil for 3 months prior to screening.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation with Memantine Hydrochloride
In the placebo-controlled clinical trial of memantine hydrochloride extended-release, the proportion of patients in the memantine hydrochloride extended-release 28 mg/day dose group and in the placebo group who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 10% and 6%, respectively. The most common adverse reaction in the memantine hydrochloride extended- release treated group that led to treatment discontinuation was dizziness, at a rate of 1.5%.
Most Common Adverse Reactions with Memantine Hydrochloride
The most common adverse reactions with memantine hydrochloride extended-release in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, defined as those occurring at a frequency of at least 5% in the memantine hydrochloride extended-release group and at a higher frequency than placebo, were headache, diarrhea, and dizziness.
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred at an incidence of ≥ 2% in the memantine hydrochloride extended-release treated group and occurred at a rate greater than placebo.
|
Adverse Reaction | Placebo (n = 335)
% | Memantine hydrochloride extended-release
28 mg (n = 341) % |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 4 | 5 |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 |
| Abdominal pain | 1 | 2 |
| Vomiting | 1 | 2 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||
| Influenza | 3 | 4 |
| Investigations | ||
| Increased weight | 1 | 3 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Back pain | 1 | 3 |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 5 | 6 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 5 |
| Somnolence | 1 | 3 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Anxiety | 3 | 4 |
| Depression | 1 | 3 |
| Aggression | 1 | 2 |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | ||
| Urinary incontinence | 1 | 2 |
| Vascular Disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 2 | 4 |
| Hypotension | 1 | 2 |
Donepezil hydrochloride
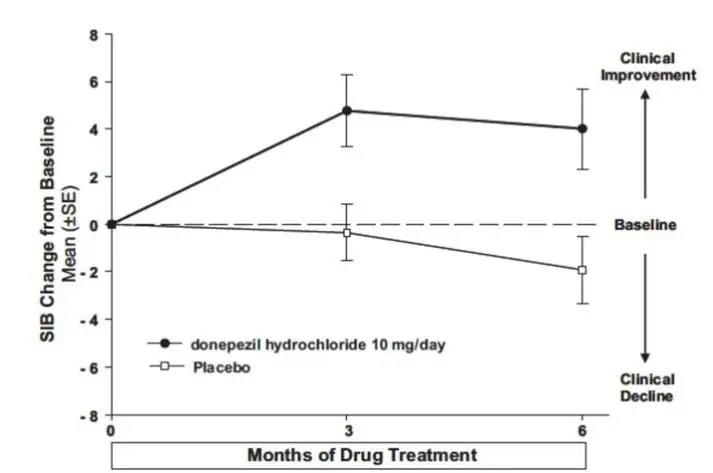
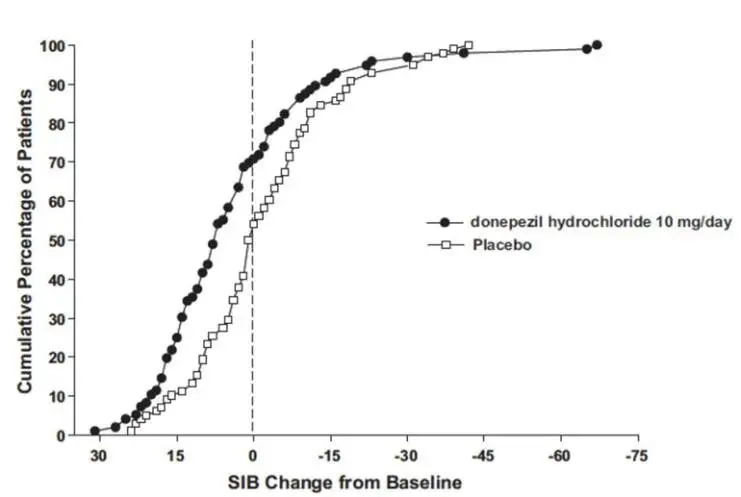
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation with Donepezil Hydrochloride
In controlled clinical trials of donepezil hydrochloride, the rate of discontinuation due to adverse reactions for patients treated with donepezil hydrochloride was approximately 12%, compared to 7% for patients treated with placebo. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation, defined as those occurring in at least 2% of donepezil hydrochloride patients and at twice or more the incidence seen with placebo, were anorexia (2%), nausea (2%), diarrhea (2%) and urinary tract infection (2%).
Most Common Adverse Reactions with Donepezil Hydrochloride
The most common adverse reactions reported with donepezil hydrochloride in controlled clinical trials in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease, defined as those occurring at a frequency of at least 5% in the donepezil hydrochloride group and at twice or more the placebo rate, were diarrhea, anorexia, vomiting, nausea, and ecchymosis. The most common adverse reactions reported with donepezil hydrochloride in controlled clinical trials in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease were insomnia, muscle cramp, and fatigue.
Table 2 lists adverse reactions that occurred at an incidence of ≥ 2% in the donepezil hydrochloride group and at a rate greater than placebo in controlled trials in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease.
| Table 2: Adverse reactions with donepezil hydrochloride in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease | ||
|
Body System/Adverse Event | Placebo (n = 392)
% | Donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg/day
(n = 501) % |
| Percent of Patients with any Adverse Event | 73 | 81 |
| Body as a Whole | ||
| Accident | 12 | 13 |
| Infection | 9 | 11 |
| Headache | 3 | 4 |
| Pain | 2 | 3 |
| Back pain | 2 | 3 |
| Fever | 1 | 2 |
| Chest pain | < 1 | 2 |
| Cardiovascular System | ||
| Hypertension | 2 | 3 |
| Hemorrhage | 1 | 2 |
| Syncope | 1 | 2 |
| Digestive System | ||
| Diarrhea | 4 | 10 |
| Vomiting | 4 | 8 |
| Anorexia | 4 | 8 |
| Nausea | 2 | 6 |
| Hemic and Lymphatic System | ||
| Ecchymosis | 2 | 5 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Systems | ||
| Increased creatine phosphokinase | 1 | 3 |
| Dehydration | 1 | 2 |
| Hyperlipemia | < 1 | 2 |
| Nervous System | ||
| Insomnia | 4 | 5 |
| Hostility | 2 | 3 |
| Nervousness | 2 | 3 |
| Hallucinations | 1 | 3 |
| Somnolence | 1 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 2 |
| Depression | 1 | 2 |
| Confusion | 1 | 2 |
| Emotional lability | 1 | 2 |
| Personality disorder | 1 | 2 |
| Skin and Appendages | ||
| Eczema | 2 | 3 |
| Urogenital System | ||
| Urinary incontinence | 1 | 2 |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Use of Memantine with Drugs That Make the Urine Alkaline
The clearance of memantine was reduced by about 80% under alkaline urine conditions at pH 8. Therefore, alterations of urine pH towards the alkaline condition may lead to an accumulation of the drug with a possible increase in adverse reactions. Urine pH is altered by diet, drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sodium bicarbonate) and clinical state of the patient (e.g., renal tubular acidosis or severe infections of the urinary tract). Hence, memantine should be used with caution under these conditions.
7.2 Use of Memantine with Other N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) Antagonists
The combined use of memantine hydrochloride with other NMDA antagonists (amantadine, ketamine, and dextromethorphan) has not been systematically evaluated and such use should be approached with caution.
7.4 Use of Donepezil with Anticholinergics
Because of their mechanism of action, cholinesterase inhibitors, including donepezil hydrochloride, have the potential to interfere with the activity of anticholinergic medications.
7.5 Use of Donepezil with Cholinomimetics and Other Cholinesterase Inhibitors
A synergistic effect may be expected when cholinesterase inhibitors, including donepezil hydrochloride, are given concurrently with succinylcholine, similar neuromuscular blocking agents, or cholinergic agonists such as bethanechol.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of NAMZARIC or its active ingredients (memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride) in pregnant women.
Adverse developmental effects (mortality and decreased body weight and skeletal ossification) were observed in the offspring of rats administered memantine or donepezil during pregnancy at doses associated with minimal maternal toxicity. These doses are higher than those used in humans at the recommended daily dose of NAMZARIC [see Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Memantine Hydrochloride
Oral administration of memantine (2, 6, or 18 mg/kg/day) to rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in decreased skeletal ossification in fetuses at the highest dose tested. The higher no-effect dose for adverse developmental effects (6 mg/kg) is 2 times the dose of memantine at the recommended human daily dose (RHD) of NAMZARIC (28 mg memantine/10 mg donepezil) on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis.
Oral administration of memantine to rabbits (3, 10, or 30 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis resulted in no adverse developmental effects. The highest dose tested is approximately 20 times the dose of memantine at the RHD of NAMZARIC on a mg/m2 basis.
In rats, memantine (2, 6, or 18 mg/kg/day) was administered orally prior to and throughout mating and, in females, through the period of organogenesis or continuing throughout lactation to weaning. Decreased skeletal ossification in fetuses and decreased body weight in pups were observed at the highest dose tested. The higher no-effect dose for adverse developmental effects (6 mg/kg/day) is 2 times the dose of memantine at the RHD of NAMZARIC on a mg/m2 basis.
Oral administration of memantine (2, 6, or 18 mg/kg/day) to rats from late gestation throughout lactation to weaning, resulted in decreased pup weights at the highest dose tested. The higher no-effect dose (6 mg/kg/day) is approximately 2 times the dose of memantine at the RHD of NAMZARIC on a mg/m2 basis.
Donepezil Hydrochloride
Oral administration of donepezil to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in no adverse developmental effects. The highest doses (16 and 10 mg/kg/day, respectively) were approximately 15 and 7 times, respectively, the dose of donepezil at the RHD of NAMZARIC on a mg/m2 basis.
Oral administration of donepezil (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day) to rats during late gestation and throughout lactation to weaning resulted in an increase in stillbirths and offspring mortality at the highest dose tested. The higher no-effect dose (3 mg/kg/day) is approximately 3 times the dose of donepezil at the RHD of NAMZARIC on a mg/m2 basis.
12. Namzaric - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
NAMZARIC
NAMZARIC was bioequivalent to co-administration of individual memantine hydrochloride extended-release and donepezil hydrochloride.
Exposure (AUC and Cmax) of memantine and donepezil following NAMZARIC administration in the fed or fasted state was similar. Further, exposure of memantine and donepezil following NAMZARIC administration as intact capsule or capsule contents sprinkled on applesauce was similar in healthy subjects.
Memantine Hydrochloride
Memantine is well absorbed after oral administration and has linear pharmacokinetics over the therapeutic dose range. It is excreted predominantly unchanged in urine and has a terminal elimination half-life of about 60-80 hours. In a study comparing 28 mg once-daily memantine hydrochloride extended-release to 10 mg twice-daily memantine hydrochloride, Cmax and AUC0-24 values were 48% and 33% higher for the memantine hydrochloride extended-release dosage regimen, respectively.
Absorption
After multiple dose administration of memantine hydrochloride extended-release, memantine peak concentrations occur around 9-12 hours postdose. There is no difference in the absorption of memantine hydrochloride extended-release when the capsule is taken intact or when the contents are sprinkled on applesauce.
After single-dose administration, there is no difference in memantine exposure, based on Cmax or AUC, for memantine hydrochloride extended-release when the drug product is administered with food or on an empty stomach. However, peak plasma concentrations are achieved about 18 hours after administration with food versus approximately 25 hours after administration on an empty stomach.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of memantine is 9-11 L/kg and the plasma protein binding is low (45%).
Metabolism
Memantine undergoes partial hepatic metabolism. The hepatic microsomal CYP450 enzyme system does not play a significant role in the metabolism of memantine.
Elimination
Memantine is excreted predominantly in the urine, unchanged, and has a terminal elimination half-life of about 60-80 hours. About 48% of administered drug is excreted unchanged in urine; the remainder is converted primarily to three polar metabolites which possess minimal NMDA receptor antagonistic activity: the N-glucuronide conjugate, 6-hydroxy memantine, and 1-nitroso-deaminated memantine. A total of 74% of the administered dose is excreted as the sum of the parent drug and the N-glucuronide conjugate. Renal clearance involves active tubular secretion moderated by pH dependent tubular reabsorption.
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Renal Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following single oral administration of 20 mg memantine hydrochloride in 8 subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance, CLcr, > 50 – 80 mL/min), 8 subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 – 49 mL/min), 7 subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr 5 – 29 mL/min) and 8 healthy subjects (CLcr > 80 mL/min) matched as closely as possible by age, weight and gender to the subjects with renal impairment. Mean AUC0-∞ increased by 4%, 60%, and 115% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. The terminal elimination half-life increased by 18%, 41%, and 95% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following the administration of single oral doses of 20 mg in 8 subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7-9) and 8 subjects who were age-, gender-, and weight-matched to the hepatically-impaired subjects.
There was no change in memantine exposure (based on Cmax and AUC) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. However, terminal elimination half-life increased by about 16% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of memantine has not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Gender
Following multiple dose administration of memantine hydrochloride 20 mg daily, females had about 45% higher exposure than males, but there was no difference in exposure when body weight was taken into account.
Elderly
The pharmacokinetics of memantine in young and elderly subjects are similar.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Use with Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Coadministration of memantine with the AChE inhibitor donepezil hydrochloride did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either compound. Furthermore, memantine did not affect AChE inhibition by donepezil. In a 24-week controlled clinical study in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, the adverse event profile observed with a combination of memantine immediate-release and donepezil was similar to that of donepezil alone.
Effect of Memantine on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
In vitro studies conducted with marker substrates of CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, -2A6, -2C9, -2D6, -2E1, -3A4) showed minimal inhibition of these enzymes by memantine. In addition, in vitro studies indicate that at concentrations exceeding those associated with efficacy, memantine does not induce the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP1A2, -2C9, -2E1 and -3A4/5. No pharmacokinetic interactions with drugs metabolized by these enzymes are expected.
Pharmacokinetic studies evaluated the potential of memantine for interaction with warfarin and bupropion. Memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics of the CYP2B6 substrate bupropion or its metabolite hydroxybupropion. Furthermore, memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of warfarin as assessed by prothrombin INR.
Effect of Other Drugs on Memantine
Memantine is predominantly renally eliminated, and drugs that are substrates and/or inhibitors of the CYP450 system are not expected to alter the pharmacokinetics of memantine. A single dose of bupropion did not affect the pharmacokinetics of memantine at steady state.
Drugs Eliminated via Renal Mechanisms
Because memantine is eliminated in part by tubular secretion, coadministration of drugs that use the same renal cationic system, including hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), triamterene (TA), metformin, cimetidine, ranitidine, quinidine, and nicotine, could potentially result in altered plasma levels of both agents. However, coadministration of memantine hydrochloride and HCTZ/TA did not affect the bioavailability of either memantine or TA, and the bioavailability of HCTZ decreased by 20%. In addition, coadministration of memantine hydrochloride with the antihyperglycemic drug Glucovance® (glyburide and metformin hydrochloride) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of memantine, metformin, and glyburide. Furthermore, memantine did not modify the serum glucose lowering effect of Glucovance®, indicating the absence of a pharmacodynamic interaction.
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Proteins
Because the plasma protein binding of memantine is low (45%), an interaction with drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins, such as warfarin and digoxin, is unlikely.
Donepezil Hydrochloride
Pharmacokinetics of donepezil are linear over a dose range of 1-10 mg given once daily. The rate and extent of absorption of donepezil hydrochloride tablets are not influenced by food.
Donepezil is absorbed with a relative oral bioavailability of 100% and reaches peak plasma concentrations in 3 to 4 hours.
The elimination half-life of donepezil is about 70 hours, and the mean apparent plasma clearance (Cl/F) is 0.13 – 0.19 L/hr/kg. Following multiple dose administration, donepezil accumulates in plasma by 4-7 fold, and steady state is reached within 15 days. The steady-state volume of distribution is 12 - 16 L/kg. Donepezil is approximately 96% bound to human plasma proteins, mainly to albumins (about 75%) and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (about 21%) over the concentration range of 2-1000 ng/mL.
Donepezil is both excreted in the urine intact and extensively metabolized to four major metabolites, two of which are known to be active, and a number of minor metabolites, not all of which have been identified. Donepezil is metabolized by CYP 450 isoenzymes 2D6 and 3A4 and undergoes glucuronidation. Following administration of 14C-labeled donepezil, plasma radioactivity, expressed as a percent of the administered dose, was present primarily as intact donepezil (53%) and as 6-O-desmethyl donepezil (11%), which has been reported to inhibit AChE to the same extent as donepezil in vitro and was found in plasma at concentrations equal to about 20% of donepezil. Approximately 57% and 15% of the total radioactivity was recovered in urine and feces, respectively, over a period of 10 days, while 28% remained unrecovered, with about 17% of the donepezil dose recovered in the urine as unchanged drug. Examination of the effect of CYP2D6 genotype in Alzheimer’s patients showed differences in clearance values among CYP2D6 genotype subgroups. When compared to the extensive metabolizers, poor metabolizers had a 31.5% slower clearance and ultra-rapid metabolizers had a 24% faster clearance. These results suggest CYP2D6 has a minor role in the metabolism of donepezil.
Renal Impairment
In a study of 11 patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (CLcr < 18 mL/min/ 1.73 m2) the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride did not differ from 11 age- and sex-matched healthy subjects.
Hepatic Disease
In a study of 10 patients with stable alcoholic cirrhosis, the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride was decreased by 20% relative to 10 healthy age- and sex-matched subjects.
Age
No formal pharmacokinetic study was conducted to examine age-related differences in the pharmacokinetics of donepezil hydrochloride. Population pharmacokinetic analysis suggested that the clearance of donepezil in patients decreases with increasing age. When compared with 65-year old, subjects, 90-year old subjects have a 17% decrease in clearance, while 40-year old subjects have a 33% increase in clearance. The effect of age on donepezil clearance may not be clinically significant.
Gender and Race
No specific pharmacokinetic study was conducted to investigate the effects of gender and race on the disposition of donepezil hydrochloride. However, retrospective pharmacokinetic analysis and population pharmacokinetic analysis of plasma donepezil concentrations measured in patients with Alzheimer’s disease indicate that gender and race (Japanese and Caucasians) did not affect the clearance of donepezil hydrochloride to an important degree.
Body weight
There was a relationship noted between body weight and clearance. Over the range of body weight from 50 kg to 110 kg, clearance increased from 7.77 L/h to 14.04 L/h, with a value of 10 L/h for 70 kg individuals.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Effect of Donepezil hydrochloride on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
No in vivo clinical trials have investigated the effect of donepezil hydrochloride on the clearance of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., cisapride, terfenadine) or by CYP2D6 (e.g., imipramine). However, in vitro studies show a low rate of binding to these enzymes (mean Ki about 50-130 µM), that, given the therapeutic plasma concentrations of donepezil (164 nM), indicates little likelihood of interference. Based on in vitro studies, donepezil shows little or no evidence of direct inhibition of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP2C19 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Whether donepezil hydrochloride has any potential for enzyme induction is not known. Formal pharmacokinetic studies evaluated the potential of donepezil hydrochloride for interaction with theophylline, cimetidine, warfarin, digoxin, and ketoconazole. No effects of donepezil hydrochloride on the pharmacokinetics of these drugs were observed.
Effect of Other Drugs on the Metabolism of Donepezil hydrochloride
A small effect of CYP2D6 inhibitors was identified in a population pharmacokinetic analysis of plasma donepezil concentrations measured in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Donepezil clearance was reduced by approximately 17% in patients taking 10 or 23 mg in combination with a known CYP2D6 inhibitor. This result is consistent with the conclusion that CYP2D6 is a minor metabolic pathway of donepezil.
Formal pharmacokinetic studies demonstrated that the metabolism of donepezil hydrochloride is not significantly affected by concurrent administration of digoxin or cimetidine.
An in vitro study showed that donepezil was not a substrate of P-glycoprotein.
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Proteins
Drug displacement studies have been performed in vitro between this highly bound drug (96%) and other drugs such as furosemide, digoxin, and warfarin. Donepezil hydrochloride at concentrations of 0.3-10 micrograms/mL did not affect the binding of furosemide (5 micrograms/mL), digoxin (2 ng/mL), and warfarin (3 micrograms/mL) to human albumin. Similarly, the binding of donepezil hydrochloride to human albumin was not affected by furosemide, digoxin, and warfarin.
| PATIENT INFORMATION
NAMZARIC [nam-ZAIR-ick] (memantine and donepezil hydrochlorides) extended release capsules |
What is NAMZARIC?
|
| Do not take NAMZARIC if you have an allergy to memantine HCl, donepezil HCl, medicines that contains piperidines, or any of the ingredients in NAMZARIC. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in NAMZARIC. |
Before taking NAMZARIC, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
How should I take NAMZARIC?
|
What are the possible side effects of NAMZARIC? NAMZARIC may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of memantine HCl include: • headache • diarrhea • dizziness The most common side effects of donepezil HCl include: • diarrhea • not wanting to eat (anorexia) • bruising These are not all the possible side effects of NAMZARIC. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
| How should I store NAMZARIC? |
| Store NAMZARIC at room temperature, about 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Capsules should be stored in the original prescription container or other light resistant container. |
| General information about the safe and effective use of NAMZARIC.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use NAMZARIC for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NAMZARIC to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about NAMZARIC that is written for health professionals. |
| What are the ingredients in NAMZARIC?
Active ingredient: memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, ethylcellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, medium chain triglycerides, microcrystalline cellulose, oleic acid, polyethylene glycol, povidone, sugar spheres, and talc. The capsule shells contain gelatin and titanium dioxide and are imprinted with shellac glaze and black iron oxide. Colorants are FD&C Blue No. 1 (7 mg/10 mg, 14 mg/10 mg, 28 mg/10 mg) FD&C Yellow No. 6 (7 mg/10 mg, 21 mg/10 mg), red iron oxide (7 mg/10 mg, 21 mg/10 mg) and yellow iron oxide (7 mg/10 mg, 14 mg/10 mg, 21 mg/10 mg). Distributed by: Allergan USA, Inc., Madison, NJ 07940 Licensed from Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA and Adamas Pharmaceuticals, Inc. NAMZARIC® and its design are trademarks of Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA. |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 01/2019
v1.1PP11207
| NAMZARIC
memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMZARIC
memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMZARIC
memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMZARIC
memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NAMZARIC
memantine hydrochloride and donepezil hydrochloride kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |