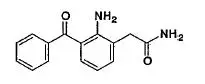
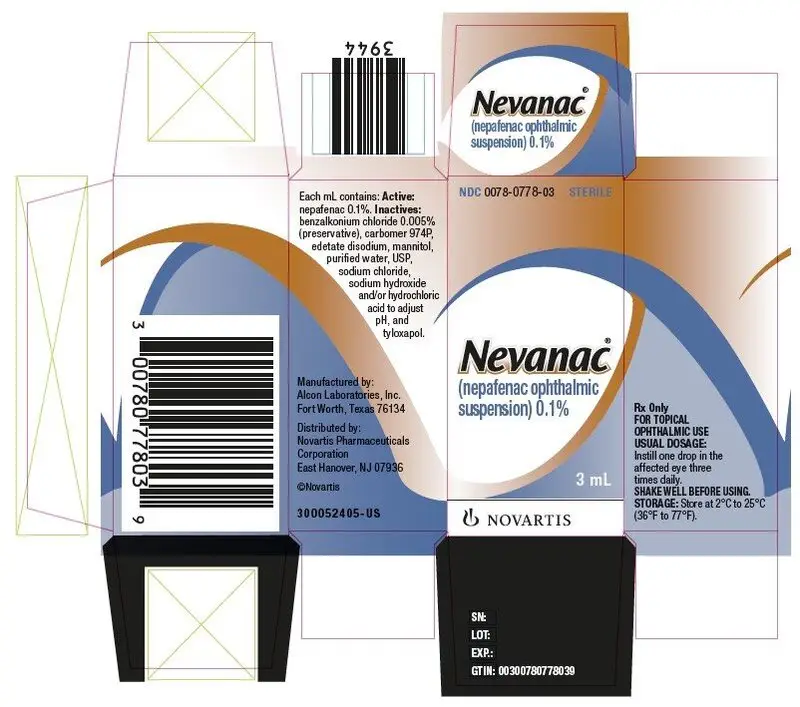
Drug Detail:Nevanac (Nepafenac ophthalmic [ ne-pa-fan-ak-off-thal-mik ])
Drug Class: Ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NEVANAC® (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension) 0.1%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2005
Indications and Usage for Nevanac
NEVANAC is a nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory prodrug indicated for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery. (1)
Nevanac Dosage and Administration
One drop of NEVANAC should be applied to the affected eye three times daily beginning 1 day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery and through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Sterile ophthalmic suspension 0.1%
3 mL in a 4 mL bottle (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formula or to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation (5.1)
- Delayed Healing (5.2)
- Corneal effects, including keratitis (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (5% to 10%) are capsular opacity, decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, increased intraocular pressure (IOP), and sticky sensation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2021
Related/similar drugs
diclofenac ophthalmic, dexamethasone ophthalmic, ketorolac ophthalmic, prednisolone ophthalmic, Lotemax, Durezol, IlevroFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Nevanac
NEVANAC® 0.1% is indicated for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery.
2. Nevanac Dosage and Administration
4. Contraindications
NEVANAC 0.1% is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formula or to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, including NEVANAC 0.1%, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied NSAIDs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphema) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that NEVANAC 0.1% be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies, or who are receiving other medications, which may prolong bleeding time.
5.2 Delayed Healing
Topical NSAIDs, including NEVANAC 0.1%, may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
5.3 Corneal Effects
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs, including NEVANAC 0.1%, and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events, which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 1 day prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk and severity of corneal adverse events.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Increased Bleeding Time [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Delayed Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Corneal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most frequently reported ocular adverse reactions following cataract surgery were capsular opacity, decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, increased intraocular pressure (IOP), and sticky sensation. These reactions occurred in approximately 5% to 10% of patients.
Other ocular adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of approximately 1% to 5% included conjunctival edema, corneal edema, dry eye, lid margin crusting, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia, ocular pain, ocular pruritus, photophobia, tearing, and vitreous detachment.
Some of these reactions may be the consequence of the cataract surgical procedure.
Non-ocular adverse reactions reported at an incidence of 1% to 4% included headache, hypertension, nausea/vomiting, and sinusitis.
| NEVANAC
nepafenac suspension/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |