Drug Detail:Nexlizet (Bempedoic acid and ezetimibe (tablets))
Drug Class: Antihyperlipidemic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NEXLIZET (bempedoic acid and ezetimibe) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Indications and Usage for Nexlizet
NEXLIZET, which contains an adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor and a cholesterol absorption inhibitor, is indicated as an adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering of LDL-C. (1)
Limitations of Use: The effect of NEXLIZET on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined. (1)
Nexlizet Dosage and Administration
- Administer one tablet (180 mg bempedoic acid and 10 mg ezetimibe) orally once daily with or without food. (2.1)
- Swallow the tablet whole. (2.1)
- Coadministration with Bile Acid Sequestrants: Administer at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after bile acid sequestrants. (2.2, 7)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 180 mg bempedoic acid/10 mg ezetimibe (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to ezetimibe tablets. (4, 6.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hyperuricemia: Elevations in serum uric acid have occurred. Assess uric acid levels periodically as clinically indicated. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia, and initiate treatment with urate-lowering drugs as appropriate. (5.1)
- Tendon Rupture: Tendon rupture has occurred. Discontinue NEXLIZET at the first sign of tendon rupture. Avoid NEXLIZET in patients who have a history of tendon disorders or tendon rupture. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) adverse reactions are upper respiratory tract infection, muscle spasms, hyperuricemia, back pain, abdominal pain or discomfort, bronchitis, pain in extremity, anemia, elevated liver enzymes, diarrhea, arthralgia, sinusitis, fatigue, and influenza. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Esperion at 833-377-7633 (833 ESPRMED) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Simvastatin: Avoid concomitant use of NEXLIZET with simvastatin greater than 20 mg. (7)
- Pravastatin: Avoid concomitant use of NEXLIZET with pravastatin greater than 40 mg. (7)
- Cyclosporine: Monitor cyclosporine concentrations. (7)
- Fibrates: If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving NEXLIZET and fenofibrate, consider alternative lipid-lowering therapy. (6.2, 7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on mechanism of action, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended with NEXLIZET. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2023
Related/similar drugs
atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, Lipitor, ezetimibe, CrestorFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Nexlizet
NEXLIZET is indicated as an adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering of LDL-C.
2. Nexlizet Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of NEXLIZET, in combination with maximally tolerated statin therapy, is one tablet orally once daily. One tablet of NEXLIZET contains 180 mg of bempedoic acid and 10 mg of ezetimibe.
Swallow the tablet whole. NEXLIZET can be taken with or without food.
After initiation of NEXLIZET, analyze lipid levels within 8 to 12 weeks.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
NEXLIZET is available as:
- Tablets: 180 mg/10 mg, blue, oval shaped, debossed with "818" on one side and "ESP" on the other side.
4. Contraindications
NEXLIZET is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to ezetimibe tablets [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash and urticaria have been reported with ezetimibe.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hyperuricemia
Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET, inhibits renal tubular OAT2 and may increase blood uric acid levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In clinical trials, 26% of bempedoic acid-treated patients with normal baseline uric acid values (versus 9.5% placebo) experienced hyperuricemia one or more times, and 3.5% of patients experienced clinically significant hyperuricemia reported as an adverse reaction (versus 1.1% placebo). Increases in uric acid levels usually occurred within the first 4 weeks of treatment initiation and persisted throughout treatment. After 12 weeks of treatment, the mean placebo-adjusted increase in uric acid compared to baseline was 0.8 mg/dL for patients treated with bempedoic acid.
Elevated blood uric acid may lead to the development of gout. In clinical trials, gout was reported in 1.5% of patients treated with bempedoic acid versus 0.4% of patients treated with placebo. The risk for gout events was higher in patients with a prior history of gout (11.2% bempedoic acid versus 1.7% placebo), although gout also occurred more frequently than placebo in patients treated with bempedoic acid who had no prior gout history (1.0% bempedoic acid versus 0.3% placebo).
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if symptoms of hyperuricemia occur. Assess serum uric acid when clinically indicated. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia, and initiate treatment with urate-lowering drugs as appropriate.
5.2 Tendon Rupture
Bempedoic acid, a component of NEXLIZET, is associated with an increased risk of tendon rupture or injury. In clinical trials, tendon rupture occurred in 0.5% of patients treated with bempedoic acid versus 0% of placebo-treated patients and involved the rotator cuff (the shoulder), biceps tendon, or Achilles tendon. Tendon rupture occurred within weeks to months of starting bempedoic acid. Tendon rupture may occur more frequently in patients over 60 years of age, in those taking corticosteroid or fluoroquinolone drugs, in patients with renal failure, and in patients with previous tendon disorders.
Discontinue NEXLIZET immediately if the patient experiences rupture of a tendon. Consider discontinuing NEXLIZET if the patient experiences joint pain, swelling, or inflammation. Advise patients to rest at the first sign of tendinitis or tendon rupture and to contact their healthcare provider if tendinitis or tendon rupture symptoms occur. Consider alternative therapy in patients with a history of tendon disorders or tendon rupture.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hyperuricemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Tendon Rupture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in postmarketing experience for ezetimibe:
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria; erythema multiforme; myalgia; elevated creatine phosphokinase; myopathy/rhabdomyolysis; elevations in liver transaminases; hepatitis; abdominal pain; thrombocytopenia; pancreatitis; nausea; dizziness; paresthesia; depression; headache; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in postmarketing experience for bempedoic acid:
Hypersensitivity: angioedema, wheezing, rash, and urticaria.
7. Drug Interactions
No specific pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with NEXLIZET have been conducted. Drug interactions that have been identified in studies with bempedoic acid or ezetimibe determine the interactions that may occur with NEXLIZET.
| Simvastatin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NEXLIZET with simvastatin causes an increase in simvastatin concentration and may increase the risk of simvastatin-related myopathy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of NEXLIZET with simvastatin greater than 20 mg. |
| Pravastatin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NEXLIZET with pravastatin causes an increase in pravastatin concentration and may increase the risk of pravastatin-related myopathy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of NEXLIZET with pravastatin greater than 40 mg. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NEXLIZET and cyclosporine increases ezetimibe and cyclosporine concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Monitor cyclosporine concentrations in patients receiving NEXLIZET and cyclosporine. In patients treated with cyclosporine, the potential effects of the increased exposure to ezetimibe from concomitant use should be carefully weighed against the benefits of alterations in lipid levels provided by NEXLIZET. |
| Fibrates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Both fenofibrate and ezetimibe may increase cholesterol excretion into the bile, leading to cholelithiasis. Coadministration of NEXLIZET with fibrates other than fenofibrate is not recommended. |
| Intervention: | If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving NEXLIZET and fenofibrate, gallbladder studies are indicated and alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered. |
| Cholestyramine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NEXLIZET and cholestyramine decreases ezetimibe concentration. This may result in a reduction of efficacy. |
| Intervention: | Administer NEXLIZET either at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after bile acid sequestrants [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of NEXLIZET have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 301 patients in the clinical trial of NEXLIZET, 149 (50%) were 65 and over, while 49 (16%) were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. However, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. There is limited experience with bempedoic acid in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2), and bempedoic acid has not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) receiving dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. NEXLIZET is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) due to the unknown effects of the increased exposure to ezetimibe [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
There is no clinical experience with NEXLIZET overdosage. In the event of overdose, contact Poison Control (1-800-222-1222) for latest recommendations.
11. Nexlizet Description
NEXLIZET tablets, for oral use, contain bempedoic acid, an adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor, and ezetimibe, a dietary cholesterol absorption inhibitor.
The chemical name for bempedoic acid is 8-hydroxy-2,2,14,14-tetramethyl-pentadecanedioic acid. The molecular formula is C19H36O5, and the molecular weight is 344.5 grams per mole. Bempedoic acid is a white to off-white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in ethanol, isopropanol and pH 8.0 phosphate buffer, and insoluble in water and aqueous solutions below pH 5.
Structural formula:
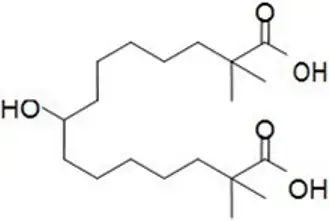
The chemical name for ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]-4(S)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone. The molecular formula is C24H21F2NO3 and the molecular weight is 409.4 grams per mole. Ezetimibe is a white, crystalline powder that is freely to very soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetone and practically insoluble in water.
Structural formula:
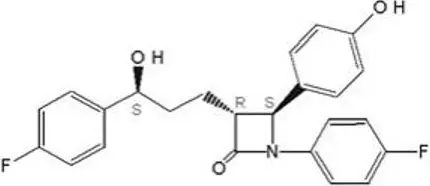
Each film-coated tablet of NEXLIZET contains 180 mg of bempedoic acid and 10 mg of ezetimibe, and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxy propyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate. The film coating comprises of FD&C Blue #1/Brilliant Blue FCF Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, glyceryl monocaprylocaprate, partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Nexlizet - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
NEXLIZET contains bempedoic acid and ezetimibe. NEXLIZET reduces elevated LDL-C through inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the liver and absorption in the intestine.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Administration of bempedoic acid and ezetimibe in combination with maximally tolerated statins, with or without other lipid modifying agents, decreases LDL-C, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and total cholesterol (TC) in patients with hyperlipidemia.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Specific Populations
Drug Interaction Studies
Bempedoic acid
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of NEXLIZET was investigated in a single, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial that enrolled 301 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease on maximally tolerated statin therapy. The efficacy of NEXLIZET in patients with multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease has not been established.
Study 1 (NCT03337308) was a 4-arm, 12-week trial that assessed the efficacy of NEXLIZET in 301 patients randomized 2:2:2:1 to receive either NEXLIZET (180 mg of bempedoic acid and 10 mg of ezetimibe) (n = 86), bempedoic acid 180 mg (n = 88), ezetimibe 10 mg (n = 86), or placebo (n = 41) once daily as add-on to maximally tolerated statin therapy. Patients were stratified by cardiovascular risk and baseline statin intensity. Patients on simvastatin 40 mg per day or higher and patients taking non-statin lipid-lowering therapy (including fibrates, niacin, bile acid sequestrants, ezetimibe, and PCSK9 inhibitors) were excluded from the trial.
Overall, the mean age at baseline was 64 years (range: 30 to 87 years), 50% were ≥ 65 years old, 50% were women, 12% Hispanic, 81% White, 17% Black, and 1% Asian. Sixty-two percent (62%) of patients had clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and/or a diagnosis of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). The mean baseline LDL-C was 149.7 mg/dL. At the time of randomization, 65% of patients were receiving statin therapy; and 35% were receiving high intensity statin therapy.
The primary efficacy outcome measure of the study was the percent change from baseline to Week 12 in LDL-C. The difference between NEXLIZET and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -38% (95% CI: -47%, -30%; p < 0.001). High-density lipoprotein (HDL) and triglycerides (TG) were examined as exploratory endpoints and were not included in the statistical hierarchy. The difference between NEXLIZET and placebo in mean percent change from baseline to Week 12 was -5% for HDL and median percent change from baseline to Week 12 was -11% for TG. The maximum LDL-C lowering effect was observed at Week 4. For additional results see Table 3.
| LDL-C LS Mean | non-HDL-C LS Mean | apo B LS Mean | TC LS Mean |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| apo B = apolipoprotein B; HDL-C = high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LS = least squares; SE = standard error; TC = total cholesterol. | ||||
| Background statin: atorvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin. | ||||
|
||||
| NEXLIZET (180 mg/10 mg; n = 86†) | -36 | -32 | -25 | -26 |
| Bempedoic acid (180 mg; n = 88† | -17 | -14 | -12 | -12 |
| Ezetimibe (10 mg; n = 86†) | -23 | -20 | -15 | -16 |
| Placebo (n = 41†) | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
| Mean Difference of NEXLIZET versus Placebo (95% CI) | -38 (-47, -30) | -34 (-44, -23) | -30 (-40, -20) | -27 (-35, -19) |
Examination of age, gender, and race subgroups did not identify differences in response to NEXLIZET among these subgroups in any of the trials.
| NEXLIZET
bempedoic acid and ezetimibe tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Esperion Therapeutics, Inc. (029516312) |





