Drug Detail:Nimbex (Cisatracurium [ sis-at-ra-kure-ee-um ])
Drug Class: Neuromuscular blocking agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NIMBEX (cisatracurium besylate) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1995
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Nimbex
NIMBEX is a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker indicated:
- as an adjunct to general anesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation in adults and in pediatric patients 1 month to 12 years of age (1)
- to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery in adults and in pediatric patients 2 to 12 years of age as a bolus or infusion maintenance (1)
- for mechanical ventilation in the ICU in adults (1)
Limitations of Use:
NIMBEX is not recommended for rapid sequence endotracheal intubation due to the time required for its onset of action (1)
Nimbex Dosage and Administration
- Administer intravenously only by or under the supervision of experienced clinicians familiar with drug’s actions and possible complications (2.1)
- Use only if personnel and facilities for resuscitation and life support, and a NIMBEX antagonist are immediately available (2.1)
- Use a peripheral nerve stimulator to determine adequacy of blockade (e.g., need for additional doses), minimize risk of overdosage or underdosage, assess extent of recovery from blockade, potentially limit exposure to toxic metabolites through dose titration, and facilitate more rapid reversal of NIMBEX-induced paralysis (2.1)
- See the Full Prescribing Information for:
- Dosage and administration instructions in adults, pediatric patients, geriatric patients, patients with neuromuscular disease, burns, end-stage renal disease, and patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery with induced hypothermia (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5)
- Continuous infusion rates (2.6)
- Preparation instructions (2.7)
- Drug compatibility (2.8)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection:
- 10 mg/5 mL (2 mg/mL) in single-dose vials (3)
- 20 mg/10 mL (2 mg/mL) and benzyl alcohol as a preservative in multiple-dose vials (3)
- 200 mg/20 mL (10 mg/mL) in single-dose vials (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to cisatracurium (4)
- 10 mL multiple-dose vials contain benzyl alcohol and are contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 1 month of age and low birth-weight infants (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Residual Paralysis: Patients with neuromuscular diseases are at higher risk. Use a lower initial bolus dose and consider using a reversal agent in these patients. (2.2, 5.1)
- Benzyl Alcohol: Consider combined daily load of benzyl alcohol from all sources when the 10 mL multiple dose vials are used in infants (4, 5.2)
- Risk of Seizure: Monitor level of neuromuscular blockade during long-term administration to limit exposure to toxic metabolites (5.3)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis: Severe hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions have been reported. Consider cross-reactivity among neuromuscular blocking agents, both depolarizing and non-depolarizing. (4, 5.4)
- Risk of Death due to Medication Errors: Accidental administration can cause death. (5.5)
- Inadequate Anesthesia: Use NIMBEX in the presence of appropriate sedation or general anesthesia and monitor patients to ensure level of anesthesia is adequate (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (0.1% to 0.4%) were bradycardia, hypotension, flushing, bronchospasm, and rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Succinylcholine: May decrease time to onset of maximum neuromuscular blockade (7.1)
- Inhalational anesthetics, antibiotics, local anesthetics, magnesium salts, procainamide, lithium, quinidine: May potentiate or prolong neuromuscular blockade action of NIMBEX. Use peripheral nerve stimulator and monitor clinical signs of neuromuscular blockade. (5.8, 7.1)
- Phenytoin and Carbamazepine: May shorten duration of neuromuscular blockade. Use peripheral nerve stimulator and monitor clinical signs of neuromuscular blockade. (5.9, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Patients with Hemiparesis or Paraparesis: Perform neuromuscular monitoring on non-paretic limb (8.9)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Nimbex
- as an adjunct to general anesthesia to facilitate tracheal intubation in adults and in pediatric patients 1 month to 12 years of age
- to provide skeletal muscle relaxation in adults during surgical procedures or during mechanical ventilation in the ICU
- to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgical procedures via infusion in pediatric patients 2 years and older
2. Nimbex Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Important administration instructions include:
- NIMBEX is for intravenous use only.
- Administer NIMBEX in carefully adjusted dosage by or under the supervision of experienced clinicians who are familiar with the drug’s actions and the possible complications.
- Use NIMBEX only if the following are immediately available: personnel and facilities for resuscitation and life support (tracheal intubation, artificial ventilation, oxygen therapy); and an antagonist of NIMBEX [see Overdosage (10)].
- The dosage information which follows is intended to serve as an initial guide for individual patients; base subsequent NIMBEX dosage on the patients’ responses to the initial doses.
- Use a peripheral nerve stimulator to:
- Determine the adequacy of neuromuscular blockade (e.g., need for additional NIMBEX doses, reduction of the infusion rate).
- Minimize risk of overdosage or underdosage.
- Assess the extent of recovery from neuromuscular blockade (e.g., spontaneous recovery or recovery after administration of a reversal agent, e.g., neostigmine).
- Appropriately titrate doses to potentially limit exposure to toxic metabolites.
- Facilitate more rapid reversal of the NIMBEX-induced paralysis.
2.2 Recommended NIMBEX Dose for Performing Tracheal Intubation
Patients with Neuromuscular Disease
Geriatric Patients and Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Tracheal Intubation in Pediatric Patients
2.3 Recommended Maintenance Bolus NIMBEX Doses in Adult Surgical Procedures
- 40 to 50 minutes after an initial dose of NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg;
- 50 to 60 minutes after an initial dose of NIMBEX 0.2 mg/kg.
2.5 Dosage for Continuous Infusion
Continuous Infusion for Surgical Procedures in Adults and Pediatric Patients
Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Continuous Infusion for Mechanical Ventilation in the Intensive Care Unit in Adults
2.6 Rate Tables for Continuous Infusion
| Drug Delivery Rate (mcg/kg/minute) | |||||
| 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| Patient Weight | Infusion Delivery Rate (mL/hour) | ||||
| 10 kg | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 30 |
| 45 kg | 27 | 41 | 54 | 81 | 135 |
| 70 kg | 42 | 63 | 84 | 126 | 210 |
| 100 kg | 60 | 90 | 120 | 180 | 300 |
| Drug Delivery Rate (mcg/kg/minute) | |||||
| 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| Patient Weight | Infusion Delivery Rate (mL/hour) | ||||
| 10 kg | 1.5 | 2.3 | 3 | 4.5 | 7.5 |
| 45 kg | 6.8 | 10.1 | 13.5 | 20.3 | 33.8 |
| 70 kg | 10.5 | 15.8 | 21 | 31.5 | 52.5 |
| 100 kg | 15 | 22.5 | 30 | 45 | 75 |
2.7 Preparation of NIMBEX
Discard unused portion of the 5 mL and 20 mL single-dose vials.
NIMBEX may be diluted to 0.1 mg/mL in the following solutions:
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or
- 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
NIMBEX also may be diluted to 0.1 mg/mL or 0.2 mg/mL in the following solution:
- Lactated Ringer’s and 5% Dextrose Injection
Store this diluted NIMBEX solution under refrigeration for no more than 24 hours.
Do not dilute NIMBEX in Lactated Ringer’s Injection, USP due to chemical instability.
2.8 Drug Compatibility
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- Sufentanil Citrate Injection, diluted as directed
- Alfentanil Hydrochloride Injection, diluted as directed
- Fentanyl Citrate Injection, diluted as directed
- Midazolam Hydrochloride Injection, diluted as directed
- Droperidol Injection, diluted as directed
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
NIMBEX injection is available as a clear solution in the following strengths:
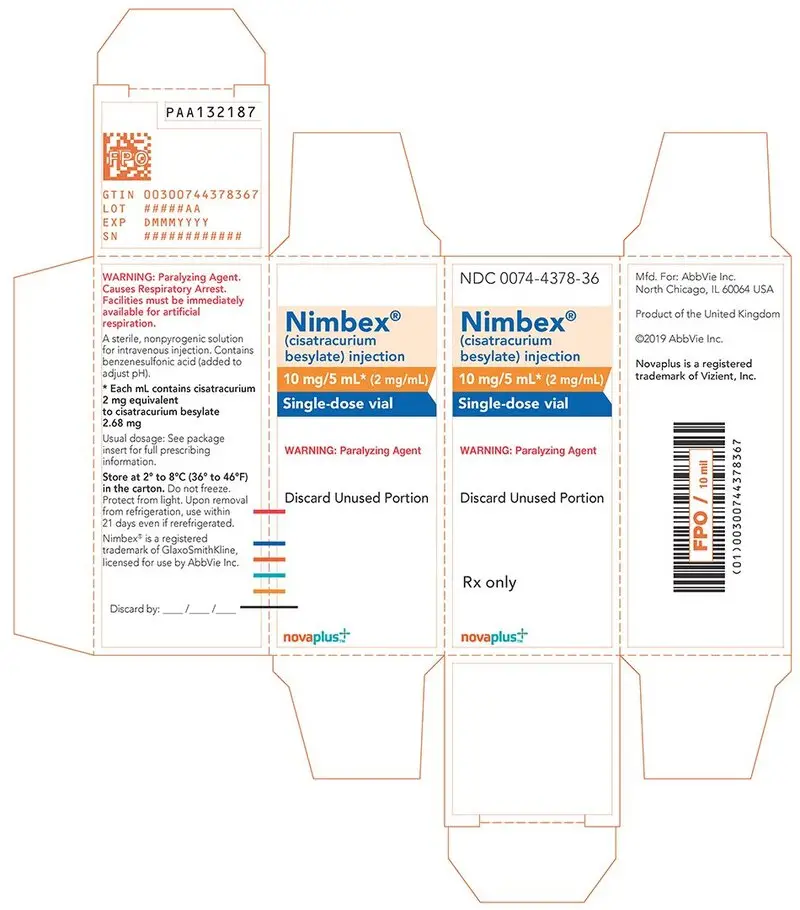
- 10 mg of cisatracurium per 5 mL (2 mg/mL) in single-dose vials (equivalent to 2.68 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate)
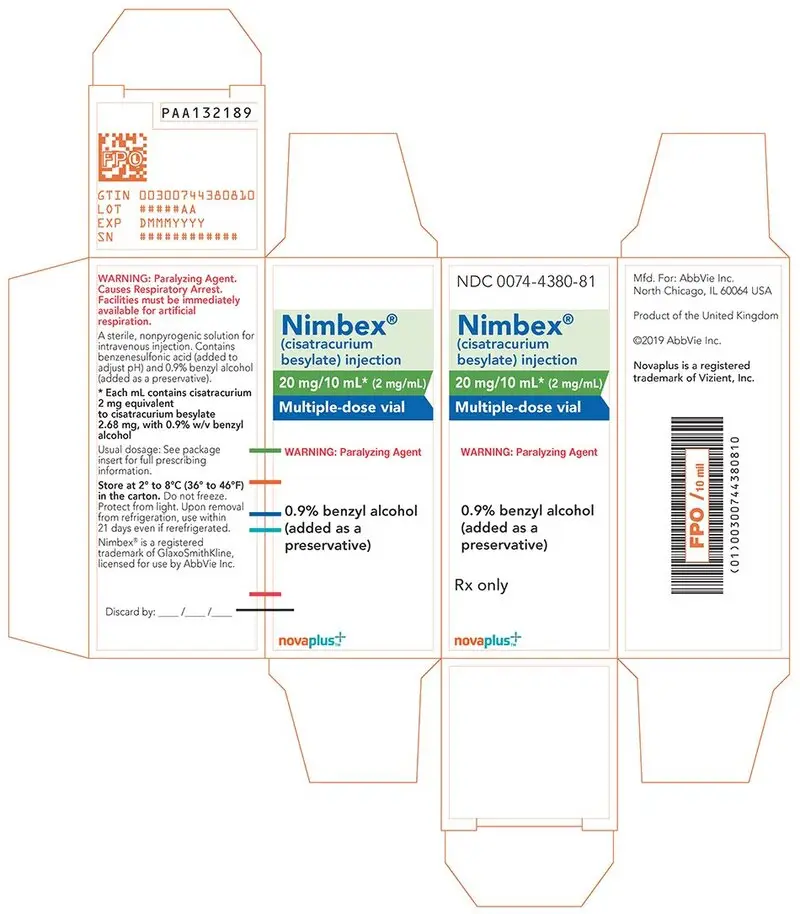
- 20 mg of cisatracurium per 10 mL (2 mg/mL) and benzyl alcohol as a preservative in multiple-dose vials (equivalent to 2.68 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate).
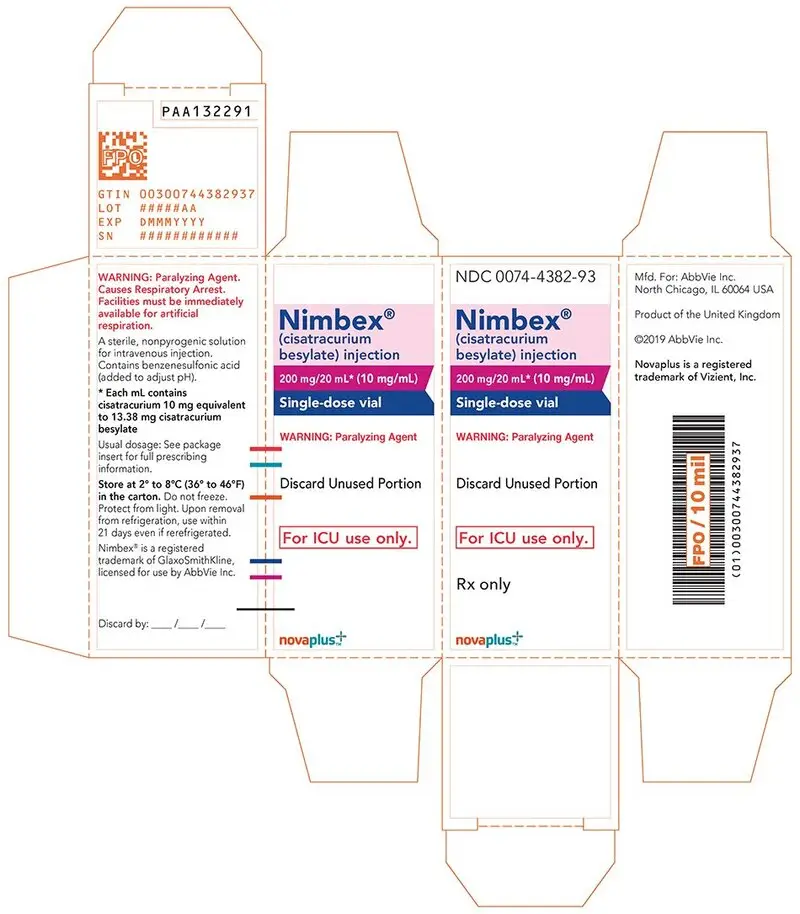
- 200 mg of cisatracurium per 20 mL (10 mg/mL) in single-dose vials (equivalent to 13.38 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate); intended only for administration as an infusion in a single patient in the ICU.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.2 Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative in 10 mL Multiple-Dose Vials
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of NIMBEX in Surgical Patients
Table 3 displays adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of less than 1%.
| Adverse Reaction | Incidence |
| Bradycardia | 0.4% |
| Hypotension | 0.2% |
| Flushing | 0.2% |
| Bronchospasm | 0.2% |
| Rash | 0.1% |
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of NIMBEX in Intensive Care Unit Patients
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Clinically Significant Drug Interactions
Table 4 displays clinically significant drug interactions with NIMBEX.
| Drug or Drug Class | Clinical Implications* |
| Succinylcholine | The use of succinylcholine prior to NIMBEX administration may decrease the time to onset of maximum neuromuscular blockade but has no effect on the duration of neuromuscular blockade. |
| Inhalational Anesthetics | Administration of inhalational anesthetics with nitrous oxide/oxygen for greater than 30 minutes to achieve 1.25 Minimum Alveolar Concentration (MAC) may prolong the duration of action of initial and maintenance doses of NIMBEX. This may potentiate the neuromuscular blockade. |
| Antibiotics† Local anesthetics Magnesium salts Procainamide Lithium Quinidine | May prolong the neuromuscular blockade action of NIMBEX |
| Phenytoin, Carbamazepine | May increase resistance to the neuromuscular blockade action of NIMBEX resulting in shorter durations of neuromuscular blockade and infusion rate requirements may be higher. |
| * The use of peripheral nerve stimulator is strongly recommended to evaluate the level of neuromuscular blockade, to assess the need for additional doses of NIMBEX, and to determine whether adjustments need to be made to the dose with subsequent administration. † Examples: aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, bacitracin, polymyxins, lincomycin, clindamycin, colistin, sodium colistimethate |
|
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Skeletal Muscle Relaxation During Surgery
Serious Adverse Reactions in Infants Due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative in 10 mL Multiple-Dose Vials
10. Overdosage
- Neostigmine: Administration of 0.04 to 0.07 mg/kg of neostigmine at approximately 10% recovery from neuromuscular blockade (range: 0 to 15%) produced 95% recovery of the muscle twitch response and a T4:T1 ratio ≥ 70% in an average of 9 to 10 minutes. The times from 25% recovery of the muscle twitch response to a T4:T1 ratio ≥ 70% following these doses of neostigmine averaged 7 minutes. The mean 25% to 75% recovery index following reversal was 3 to 4 minutes.
- Edrophonium: Administration of 1 mg/kg of edrophonium at approximately 25% recovery from neuromuscular blockade (range: 16% to 30%) produced 95% recovery and a T4:T1 ratio ≥ 70% in an average of 3 to 5 minutes.
For providers treating patients treated with cholinesterase inhibitors:
- Use a peripheral nerve stimulator to evaluate recovery and antagonism of neuromuscular blockade.
- Evaluate for evidence of adequate clinical recovery (e.g., 5-second head lift and grip strength).
- Support ventilation until adequate spontaneous ventilation has resumed.
11. Nimbex Description
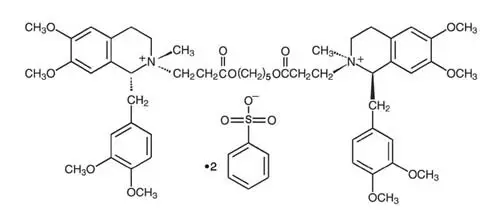
- The 5 mL single-dose vials contain 2 mg/mL cisatracurium, equivalent to 2.68 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate.
- The 10 mL multiple-dose vials contain 2 mg/mL cisatracurium, equivalent to 2.68 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate, and 0.9% benzyl alcohol as a preservative.
- The 20 mL single-dose vials contain 10 mg/mL cisatracurium, equivalent to 13.38 mg/mL cisatracurium besylate.
12. Nimbex - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
- Fifteen to 30 minutes of exposure to 1.25 MAC isoflurane or enflurane had minimal effects on the duration of action of initial doses of NIMBEX.
- In surgical procedures during enflurane or isoflurane anesthesia greater than 30 minutes, less frequent maintenance dosing, lower maintenance doses, or reduced infusion rates of NIMBEX were required. The average infusion rate requirement was decreased by as much as 30% to 40% [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
| NIMBEX Dose | Time to 90% Block in minutes | Time to Maximum Block in minutes | 5% Recovery in minutes | 25% Recovery† in minutes | 95% Recovery in minutes | T4:T1
Ratioೠ70% in minutes | 25%-75% Recovery Index in minutes |
| Adults | |||||||
| 0.1 mg/kg (2 × ED95) (n§= 98) | 3.3 (1.0-8.7) | 5.0 (1.2-17.2) | 33 (15-51) | 42 (22-63) | 64 (25-93) | 64 (32-91) | 13 (5-30) |
| 0.15|| mg/kg (3 × ED95) (n = 39) | 2.6 (1.0-4.4) | 3.5 (1.6-6.8) | 46 (28-65) | 55 (44-74) | 76 (60-103) | 75 (63-98) | 13 (11-16) |
| 0.2 mg/kg (4 × ED95) (n = 30) | 2.4 (1.5-4.5) | 2.9 (1.9-5.2) | 59 (31-103) | 65 (43-103) | 81 (53-114) | 85 (55-114) | 12 (2-30) |
| 0.25 mg/kg (5 × ED95) (n = 15) | 1.6 (0.8-3.3) | 2.0 (1.2-3.7) | 70 (58-85) | 78 (66-86) | 91 (76-109) | 97 (82-113) | 8 (5-12) |
| 0.4 mg/kg (8 × ED95) (n = 15) | 1.5 (1.3-1.8) | 1.9 (1.4-2.3) | 83 (37-103) | 91 (59-107) | 121 (110-134) | 126 (115-137) | 14 (10-18) |
| Infants (1-23 months of age) | |||||||
| 0.15 mg/kg** (n = 18-26) | 1.5 (0.7-3.2) | 2.0 (1.3-4.3) | 36 (28-50) | 43 (34-58) | 64 (54-84) | 59 (49-76) | 11.3 (7.3-18.3) |
| Pediatric Patients 2-12 years | |||||||
| 0.08 mg/kg ¶
(2 × ED95) (n = 60) | 2.2 (1.2-6.8) | 3.3 (1.7-9.7) | 22 (11-38) | 29 (20-46) | 52 (37-64) | 50 (37-62) | 11 (7-15) |
| 0.1 mg/kg (n = 16) | 1.7 (1.3-2.7) | 2.8 (1.8-6.7) | 21 (13-31) | 28 (21-38) | 46 (37-58) | 44 (36-58) | 10 (7-12) |
| 0.15 mg/kg ** (n = 23-24) | 2.1 (1.3-2.8) | 3.0 (1.5-8.0) | 29 (19-38) | 36 (29-46) | 55 (45-72) | 54 (44-66) | 10.6 (8.5-17.7) |
| * Values shown are the median values from the means from individual studies. Values in parentheses are ranges of individual patient values. † Clinically effective duration of block ‡ Train-of-four ratio § n=the number of patients with Time to Maximum Block data || Propofol anesthesia ¶ Halothane anesthesia ** Thiopentone, alfentanil, N2O/O2 anesthesia |
|||||||
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
| Parameter | Estimate† | Magnitude of Interpatient Variability (CV)‡ |
| CL (mL/min/kg) | 4.57 | 16% |
| Vss (mL/kg)§ | 145 | 27% |
| keo (min-1)ll | 0.0575 | 61% |
| EC50 (ng/mL)¶ | 141 | 52% |
| * Healthy male non-obese patients 19-64 years of age with creatinine clearance values greater than 70 mL/minute who received NIMBEX during opioid anesthesia and had venous samples collected † The percent standard error of the mean (%SEM) ranged from 3% to 12% indicating good precision for the PK/PD estimates. ‡ Expressed as a coefficient of variation; the %SEM ranged from 20% to 35% indicating adequate precision for the estimates of interpatient variability. § Vss is the volume of distribution at steady state estimated using a two-compartment model with elimination from both compartments. Vss is equal to the sum of the volume in the central compartment (Vc) and the volume in the peripheral compartment (Vp); interpatient variability could only be estimated for Vc. ll Rate constant describing the equilibration between plasma concentrations and neuromuscular block ¶ Concentration required to produce 50% T1 suppression; an index of patient sensitivity. |
||
| Parameter | Healthy Elderly Patients | Healthy Young Adult Patients |
| Elimination Half-Life (t½β, min) | 25.8 ± 3.6† | 22.1 ± 2.5 |
| Volume of Distribution at Steady State‡ (mL/kg) | 156 ± 17† | 133 ± 15 |
| Plasma Clearance (mL/min/kg) | 5.7 ± 1.0 | 5.3 ± 0.9 |
| * Values presented are mean ± SD. † P < 0.05 for comparisons between healthy elderly and healthy young adult patients ‡ Volume of distribution is underestimated because elimination from the peripheral compartment is ignored. |
||
| Parameter | Liver Transplant Patients | Healthy Adult Patients |
| Elimination Half-Life (t½β, min) | 24.4 ± 2.9 | 23.5 ± 3.5 |
| Volume of Distribution at Steady State‡ (mL/kg) | 195 ± 38† | 161 ± 23 |
| Plasma Clearance (mL/min/kg) | 6.6 ± 1.1† | 5.7 ± 0.8 |
| * Values presented are mean ± SD. † P < 0.05 for comparisons between liver transplant patients and healthy adult patients ‡ Volume of distribution is underestimated because elimination from the peripheral compartment is ignored. |
||
| Parameter | Healthy Adult Patients | ESRD Patients |
| Elimination Half-Life (t½β, min) | 29.4 ± 4.1 | 32.3 ± 6.3 |
| Volume of Distribution at Steady State† (mL/kg) | 149 ± 35 | 160 ± 32 |
| Plasma Clearance (mL/min/kg) | 4.66 ± 0.86 | 4.26 ± 0.62 |
| * Values presented are mean ± SD. † Volume of distribution is underestimated because elimination from the peripheral compartment is ignored. |
||
| Parameter | Cisatracurium (n = 6) | |
| Parent Compound | CL (mL/min/kg) | 7.45 ± 1.02 |
| t½ β(min) | 26.8 ± 11.1 | |
| Vβ (mL/kg)† | 280 ± 103 | |
| Laudanosine | Cmax (ng/mL) | 707 ± 360 |
| t½β (hrs) | 6.6 ± 4.1 | |
| MQA metabolite | Cmax (ng/mL) | 152-181‡ |
| t½β (min) | 26-31‡ | |
| * Presented as mean ± standard deviation † Volume of distribution during the terminal elimination phase, an underestimate because elimination from the peripheral compartment is ignored. ‡ n = 2, range presented |
||
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Skeletal Muscle Relaxation for Intubation of Adult Patients
- NIMBEX doses between 0.15 and 0.2 mg/kg were evaluated in 240 adults. Maximum neuromuscular blockade generally occurred in within 4 minutes for this dose range.
- When administered during induction using thiopental or propofol and co-induction agents (i.e., fentanyl and midazolam), excellent to good intubating conditions were generally achieved within 2 minutes (excellent intubation conditions most frequently achieved with the 0.2 mg/kg dose of NIMBEX).
- Following the induction of general anesthesia with propofol, nitrous oxide/oxygen, and co-induction agents (e.g., fentanyl and midazolam), good or excellent conditions for tracheal intubation occurred in 96/102 (94%) patients in 1.5 to 2 minutes following NIMBEX doses of 0.15 mg/kg and in 97/110 (88%) patients in 1.5 minutes following NIMBEX doses of 0.2 mg/kg.
| NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg (n = 26) | NIMBEX 0.20 mg/kg (n = 25) |
|
| Excellent and Good | 88% | 96% |
| 95% CI | 76,100 | 88,100 |
| Excellent | 31% | 60% |
| Good | 58% | 36% |
| *Excellent: Easy passage of tube without coughing. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. Good: Passage of tube with slight coughing and/or bucking. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. |
||
| Intubating Condition | NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg with Propofol (n = 31) | NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg with Thiopental (n= 31) | NIMBEX 0.20 mg/kg with Propofol (n= 30) | NIMBEX 0.20 mg/kg with Thiopental (n = 28) |
| Excellent and Good | 94% | 90% | 93% | 96% |
| 95% CI | 85,100 | 80,100 | 84,100 | 90,100 |
| Excellent | 58% | 55% | 70% | 57% |
| Good | 35% | 35% | 20% | 39% |
| * Excellent: Easy passage of tube without coughing. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. Good: Passage of tube with slight coughing and/or bucking. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. |
||||
14.2 Skeletal Muscle Relaxation for Intubation of Pediatric Patients
| NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg
1-11 mo. | NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg
1- 4 years | NIMBEX 0.15 mg/kg
5-12 years |
||||
| Halothane
Anesthesia (n=30) | Thiopentone/
Fentanyl Anesthesia (n=30) | Halothane
Anesthesia (n=30) | Thiopentone/
Fentanyl Anesthesia (n=30) | Halothane
Anesthesia (n=30) | Thiopentone/
Fentanyl Anesthesia (n=30) |
|
| Excellent and Good | 100% | 100% | 97% | 87% | 97% | 97% |
| Excellent | 100% | 83% | 90% | 63% | 73% | 70% |
| Good | 0% | 17% | 7% | 23% | 23% | 27% |
| Poor | 0% | 0% | 3% | 13% | 3% | 3% |
| *Excellent: Easy passage of the tube without coughing. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. Good: Passage of tube with slight coughing and/or bucking. Vocal cords relaxed and abducted. Poor: Passage of tube with moderate coughing and/or bucking. Vocal cords moderately adducted. Response of patient requires adjustment of ventilation pressure and/or rate. |
||||||
16. How is Nimbex supplied
NIMBEX (cisatracurium besylate) injection is a clear solution supplied as follows:
| Strength
(mg of cisatracurium) | Containers | NDC# | Preservative |
| 10 mg/5 mL (2 mg/mL) | Single-dose vials | 0074-4378-36 | Does not contain benzyl alcohol |
| 20 mg/10 mL (2 mg/mL) | Multiple-dose vials | 0074-4380-81 | Contains 0.9% w/v benzyl alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] |
| 200 mg/20 mL (10 mg/mL) | Single-dose vials | 0074-4382-93 | Does not contain benzyl alcohol |
Discard unused portion of the 5 mL and 20 mL single-dose vials.
17. Patient Counseling Information
| NIMBEX
cisatracurium besylate injection |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| NIMBEX
cisatracurium besylate injection |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| NIMBEX
cisatracurium besylate injection |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370) |