Drug Detail:Nizoral (Ketoconazole (oral) [ kee-toe-kon-a-zole ])
Drug Class: Azole antifungals
WARNING
NIZORAL® Tablets should be used only when other effective antifungal therapy is not available or tolerated and the potential benefits are considered to outweigh the potential risks.
Hepatotoxicity
Serious hepatotoxicity, including cases with a fatal outcome or requiring liver transplantation has occurred with the use of oral ketoconazole. Some patients had no obvious risk factors for liver disease. Patients receiving this drug should be informed by the physician of the risk and should be closely monitored. See WARNINGS section.
QT Prolongation and Drug Interactions Leading to QT Prolongation
Co-administration of the following drugs with ketoconazole is contraindicated: dofetilide, quinidine, pimozide, cisapride, methadone, disopyramide, dronedarone, ranolazine. Ketoconazole can cause elevated plasma concentrations of these drugs and may prolong QT intervals, sometimes resulting in life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias such as torsades de pointes. See CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions sections.
Nizoral Description
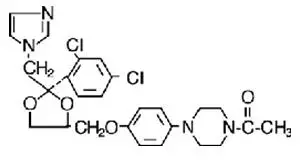
NIZORAL® is a synthetic broad-spectrum antifungal agent available in scored white tablets, each containing 200 mg ketoconazole base for oral administration. Inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and povidone. Ketoconazole is cis-1- acetyl-4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxyl]phenyl] piperazine and has the following structural formula:
Ketoconazole is a white to slightly beige, odorless powder, soluble in acids, with a molecular weight of 531.44.
Warnings
NIZORAL® Tablets should be used only when other effective antifungal therapy is not available or tolerated and the potential benefits are considered to outweigh the potential risks.
Precautions
General
NIZORAL® Tablets have been demonstrated to lower serum testosterone. Once therapy with NIZORAL® Tablets has been discontinued, serum testosterone levels return to baseline values. Testosterone levels are impaired with doses of 800 mg per day and abolished by 1600 mg per day. Clinical manifestations of decreased testosterone concentrations may include gynecomastia, impotence and oligospermia.
Information for Patients
Patients should be instructed to report any signs and symptoms which may suggest liver dysfunction so that appropriate biochemical testing can be done. Such signs and symptoms may include unusual fatigue, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine or pale stools (see WARNINGS section).
Drug Interactions
Ketoconazole is mainly metabolized through CYP3A4. Other substances that either share this metabolic pathway or modify CYP3A4 activity may influence the pharmacokinetics of ketoconazole. Similarly, ketoconazole may modify the pharmacokinetics of other substances that share this metabolic pathway. Ketoconazole is a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor and a P-glycoprotein inhibitor. When using concomitant medication, the corresponding label should be consulted for information on the route of metabolism and the possible need to adjust dosages.
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults. The relevance of the results from these studies in pediatric patients is unknown.
Drugs that may decrease ketoconazole plasma concentrations
Drugs that reduce the gastric acidity (e.g. acid neutralizing medicines such as aluminum hydroxide, or acid secretion suppressors such as H2-receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors) impair the absorption of ketoconazole from NIZORAL® Tablets. These drugs should be used with caution when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets:
- NIZORAL® Tablets should be administered with an acidic beverage (such as non-diet cola) upon co-treatment with drugs reducing gastric acidity.
- Acid neutralizing medicines (e.g. aluminum hydroxide) should be administered at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after the intake of NIZORAL® Tablets.
- Upon coadministration, the antifungal activity should be monitored and the NIZORAL® Tablets dose increased as deemed necessary.
Coadministration of NIZORAL® Tablets with potent enzyme inducers of CYP3A4 may decrease the bioavailability of ketoconazole to such an extent that efficacy may be reduced. Examples include:
- Antibacterials: isoniazid, rifabutin (see also under 'Drugs that may have their plasma concentrations increased'), rifampicin.
- Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine (see also under 'Drugs that may have their plasma concentrations increased'), phenytoin.
- Antivirals: efavirenz, nevirapine.
Therefore, administration of potent enzyme inducers of CYP3A4 with NIZORAL® Tablets is not recommended. The use of these drugs should be avoided from 2 weeks before and during treatment with NIZORAL® Tablets, unless the benefits outweigh the risk of potentially reduced ketoconazole efficacy. Upon coadministration, the antifungal activity should be monitored and the NIZORAL® Tablets dose increased as deemed necessary.
Drugs that may have their plasma concentrations increased by ketoconazole
Ketoconazole can inhibit the metabolism of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 and can inhibit the drug transport by P-glycoprotein, which may result in increased plasma concentrations of these drugs and/or their active metabolite(s) when they are administered with ketoconazole. These elevated plasma concentrations may increase or prolong both therapeutic and adverse effects of these drugs. CYP3A4-metabolized drugs known to prolong the QT interval may be contraindicated with NIZORAL® Tablets, since the combination may lead to ventricular tachyarrhythmias, including occurrences of torsade de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia.
Examples of drugs that may have their plasma concentrations increased by ketoconazole presented by drug class with advice regarding coadministration with NIZORAL® Tablets:
| Drug Class | Contraindicated | Not Recommended | Use with Caution | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under no circumstances should the drug be coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets, and up to one week after discontinuation of treatment with ketoconazole. | The use of the drug should be avoided during and up to one week after discontinuation of treatment with NIZORAL® Tablets, unless the benefits outweigh the potentially increased risks of side effects. If coadministration cannot be avoided, clinical monitoring for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged effects or side effects of the interacting drug is recommended, and its dosage should be reduced or interrupted as deemed necessary. When appropriate, plasma concentrations should be measured. The label of the coadministered drug should be consulted for information on dose adjustment and adverse effects. | Careful monitoring is recommended when the drug is coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets. Upon coadministration, patients should be monitored closely for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged effects or side effects of the interacting drug, and its dosage should be reduced as deemed necessary. When appropriate, plasma concentrations should be measured. The label of the coadministered drug should be consulted for information on dose adjustment and adverse effects. | ||
| Alpha Blockers | tamsulosin | |||
| Analgesics | methadone | alfentanil, buprenorphine IV and sublingual, fentanyl, oxycodone, sufentanil |
Methadone: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of methadone when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events including QT prolongation and torsade de pointes, or respiratory or CNS depression. [See CONTRAINDICATIONS.] Fentanyl: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of fentanyl when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of potentially fatal respiratory depression. Sufentanil: No human pharmacokinetic data of an interaction with ketoconazole are available. In vitro data suggest that sufentanil is metabolized by CYP3A4 and so potentially increased sufentanil plasma concentrations would be expected when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets. |
|
| Antiarrhythmics | disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine | digoxin |
Disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of these drugs when coadministered with ketoconazole may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events including QT prolongation. Digoxin: Rare cases of elevated plasma concentrations of digoxin have been reported. It is not clear whether this was due to the combination of therapy. It is, therefore, advisable to monitor digoxin concentrations in patients receiving ketoconazole. |
|
| Antibacterials | rifabutin | telithromycin |
Rifabutin: see also under 'Drugs that may decrease ketoconazole plasma concentrations'. Telithromycin: A multiple-dose interaction study with ketoconazole showed that Cmax of telithromycin was increased by 51% and AUC by 95%. |
|
| Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs | rivaroxaban | cilostazol, coumarins, dabigatran |
Cilostazol: Concomitant administration of single doses of cilostazol 100 mg and ketoconazole 400 mg approximately doubled cilostazol concentrations and altered (increase/decrease) the concentrations of the active metabolites of cilostazol. Coumarins: Ketoconazole may enhance the anticoagulant effect of coumarin-like drugs, thus the anticoagulant effect should be carefully titrated and monitored. Dabigatran: In patients with moderate renal impairment (CrCL 50 mL/min to ≤ 80 mL/min), consider reducing the dose of dabigatran to 75 mg twice daily when it is coadministered with ketoconazole. |
|
| Anticonvulsants | carbamazepine | Carbamazepine: In vivo studies have demonstrated an increase in plasma carbamazepine concentrations in subjects concomitantly receiving ketoconazole. In addition, the bioavailability of ketoconazole may be reduced by carbamazepine. | ||
| Antidiabetics | repaglinide, saxagliptin | |||
| Antihelmintics and Antiprotozoals | praziquantel | |||
| Antimigraine Drugs | ergot alkaloids, such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine) | eletriptan |
Ergot alkaloids: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of ergot alkaloids when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of ergotism, i.e., a risk for vasospasm potentially leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities. Eletriptan: Eletriptan should be used with caution with ketoconazole, and specifically, should not be used within at least 72 hours of treatment with ketoconazole. |
|
| Antineoplastics | irinotecan | dasatinib, lapatinib, nilotinib | bortezomib, busulphan, docetaxel, erlotinib, imatinib, ixabepilone, paclitaxel, trimetrexate, vinca alkaloids |
Irinotecan: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of irinotecan when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of potentially fatal adverse events. Docetaxel: In the presence of ketoconazole, the clearance of docetaxel in cancer patients was shown to decrease by 50%. |
| Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics and Hypnotics | alprazolam, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam | aripiprazole, buspirone, haloperidol, midazolam IV, quetiapine, ramelteon, risperidone |
Alprazolam, midazolam, triazolam: Coadministration of NIZORAL® Tablets with oral midazolam or triazolam, or alprazolam may cause several-fold increases in plasma concentrations of these drugs. This may potentiate and prolong hypnotic and sedative effects, especially with repeated dosing or chronic administration of these agents. Pimozide: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of pimozide when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events including QT prolongation and torsade de pointes. Aripiprazole: Coadministration of ketoconazole (200 mg/day for 14 days) with a 15 mg single dose of aripiprazole increased the AUC of aripiprazole and its active metabolite by 63% and 77%, respectively. The effect of a higher ketoconazole dose (400 mg/day) has not been studied. When ketoconazole is given concomitantly with aripiprazole, the aripiprazole dose should be reduced to one-half of the recommended dose. Buspirone: Ketoconazole is expected to inhibit buspirone metabolism and increase plasma concentrations of buspirone. If a patient has been titrated to a stable dosage on buspirone, a dose reduction of buspirone may be necessary to avoid adverse events attributable to buspirone or diminished anxiolytic activity. |
|
| Antivirals | indinavir, maraviroc, saquinavir | |||
| Beta Blockers | nadolol | |||
| Calcium Channel Blockers | felodipine, nisoldipine | other dihydropyridines, verapamil |
Calcium channel blockers can have a negative inotropic effect which may be additive to those of ketoconazole. The potential increase in plasma concentrations of calcium channel blockers when co-administered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of edema and congestive heart failure. Dihydropyridines: Concomitant administration of NIZORAL® Tablets may cause several-fold increases in plasma concentrations of dihydropyridines. |
|
| Cardiovascular Drugs, Miscellaneous | ranolazine | aliskiren, bosentan |
Ranolazine: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of ranolazine when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events including QT prolongation. Bosentan: Coadministration of bosentan 125 mg twice daily and ketoconazole, increased the plasma concentrations of bosentan by approximately 2-fold in normal volunteers. No dose adjustment of bosentan is necessary, but patients should be monitored for increased pharmacologic effects and adverse reactions of bosentan. |
|
| Diuretics | eplerenone | The potential increase in plasma concentrations of eplerenone when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of hyperkalemia and hypotension. | ||
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | cisapride | aprepitant | Cisapride: Oral ketoconazole potently inhibits the metabolism of cisapride resulting in a mean eight-fold increase in AUC of cisapride, which can lead to serious cardiovascular events including QT prolongation. | |
| Immunosuppressants | everolimus, rapamycin (also known as sirolimus), temsirolimus | budesonide, ciclesonide, cyclosporine, dexamethasone, fluticasone, methylprednisolone, tacrolimus |
Rapamycin (sirolimus): NIZORAL® Tablets 200 mg daily for 10 days increased the Cmax and AUC of a single 5-mg dose of sirolimus by 4.3-fold and 10.9-fold, respectively in 23 healthy subjects. Fluticasone: Coadministration of fluticasone propionate and ketoconazole is not recommended unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects. |
|
| Lipid Regulating Drugs | lovastatin, simvastatin | atorvastatin | The potential increase in plasma concentrations of atorvastatin, lovastatin and simvastatin when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of skeletal muscle toxicity, including rhabdomyolysis. | |
| Respiratory Drugs | salmeterol | |||
| Urological Drugs | fesoterodine, sildenafil, solifenacin, tadalafil, tolterodine, vardenafil | Vardenafil: A single dose of 5 mg of vardenafil should not be exceeded when coadministered with ketoconazole. | ||
| Other | colchicine, in subjects with renal or hepatic impairment; tolvaptan | colchicine | alcohol, cinacalcet |
Colchicine: The potential increase in plasma concentrations of colchicine when coadministered with NIZORAL® Tablets may increase the risk of potentially fatal adverse events. Tolvaptan: Ketoconazole 200 mg administered with tolvaptan increased tolvaptan exposure by 5-fold. Larger doses would be expected to produce larger increases in tolvaptan exposure. There is not adequate experience to define the dose adjustment that would be needed to allow safe use of tolvaptan with strong CYP3A inhibitors such as ketoconazole. Alcohol: Exceptional cases have been reported of a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol, characterized by flushing, rash, peripheral edema, nausea and headache. All symptoms completely resolved within a few hours. |
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Ketoconazole did not show any signs of mutagenic potential when evaluated using the dominant lethal mutation test or the Ames Salmonella microsomal activator assay. Ketoconazole was not carcinogenic in an 18-month, oral study in Swiss albino mice or a 24-month oral carcinogenicity study in Wistar rats at dose levels of 5, 20 and 80 mg/kg/day. The high dose in these studies was approximately 1× (mouse) or 2× (rat) the clinical dose in humans based on a mg/m2 comparison.
Pregnancy
Nonteratogenic Effects
Ketoconazole has also been found to be embryotoxic in the rat when given in the diet at doses higher than 80 mg/kg during the first trimester of gestation.
In addition, dystocia (difficult labor) was noted in rats administered oral ketoconazole during the third trimester of gestation. This occurred when ketoconazole was administered at doses higher than 10 mg/kg (about one fourth the maximum human dose, based on body surface area comparison).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following adverse reactions were reported in clinical trials:
Immune System Disorders: anaphylactoid reaction
Endocrine Disorders: gynecomastia
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: alcohol intolerance, anorexia, hyperlipidemia, increased appetite
Psychiatric Disorders: insomnia, nervousness
Nervous System Disorders: headache, dizziness, paresthesia, somnolence
Eye Disorders: photophobia
Vascular Disorders: orthostatic hypotension
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: epistaxis
Gastrointestinal Disorders: vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, constipation, abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, dry mouth, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, flatulence, tongue discoloration
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatitis, jaundice, hepatic function abnormal
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues Disorders: erythema multiforme, rash, dermatitis, erythema, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, xeroderma
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myalgia
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: menstrual disorder
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: asthenia, fatigue, hot flush, malaise, edema peripheral, pyrexia, chills
Investigations: platelet count decreased.
Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of NIZORAL® Tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions were reported during post-marketing experience:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: thrombocytopenia
Immune System Disorders: allergic conditions including anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reaction, angioneurotic edema
Endocrine Disorders: adrenocortical insufficiency
Nervous System Disorders: reversible intracranial pressure increased (e.g. papilloedema, fontanelle bulging in infants)
Hepatobiliary Disorders: serious hepatotoxicity including hepatitis cholestatic, biopsy-confirmed hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, hepatic failure including cases resulting in transplantation or death
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, photosensitivity
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: arthralgia
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: erectile dysfunction; with doses higher than the recommended therapeutic dose of 200 or 400mg daily, azoospermia.
|
MEDICATION GUIDE |
|
What is the most important information I should know about NIZORAL® Tablets? NIZORAL® Tablets is not the only medicine available to treat fungal infections and should only be used when other medicines are not right for you. Talk to your healthcare provider to find out if NIZORAL® Tablets are right for you. NIZORAL® Tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
What are NIZORAL® Tablets?
|
|
Who should not take NIZORAL® Tablets?
|
|
Before you take NIZORAL® Tablets, tell your healthcare provider if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Using NIZORAL® Tablets with certain other medicines may affect each other. Using NIZORAL® Tablets with other medicines can cause serious side effects. |
|
How should I take NIZORAL® Tablets?
|
|
What should I avoid while taking NIZORAL® Tablets?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of NIZORAL® Tablets? NIZORAL® Tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of NIZORAL® Tablets include nausea, headache, diarrhea, stomach pain, and abnormal liver function tests. These are not all the possible side effects of NIZORAL® Tablets. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store NIZORAL® Tablets?
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of NIZORAL® Tablets. Medications are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NIZORAL® Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NIZORAL® Tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about NIZORAL® Tablets. If you would like more information, talk to your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NIZORAL® Tablets that is written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in NIZORAL® Tablets? Active ingredient: ketoconazole. Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and povidone. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Titusville, New Jersey 08560, ©Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2014 |
| NIZORAL
ketoconazole tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Beerse, Belgium | 370005019 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Geel, Belgium | 374747970 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noramco, Inc., Athens, USA | 057234486 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson & Johnson Limited (DBA Pharmaceutical Product, Analytical and Pharmaceutical Development Center), Mumbai – Maharshtra, India | 650447175 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Cilag SPA Via C. Janssen 04010 Borgo San Michele Latina, Italy | 542797928 | MANUFACTURE(50458-220) , ANALYSIS(50458-220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Ortho, LLC State Road 933, Km 0.1 Mamey Ward Gurabo, PR 00778-9629 | 805887986 | PACK(50458-220) | |