Drug Detail:Ofloxacin (eent) (monograph) (Ocuflox)
Drug Class:
Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution Description
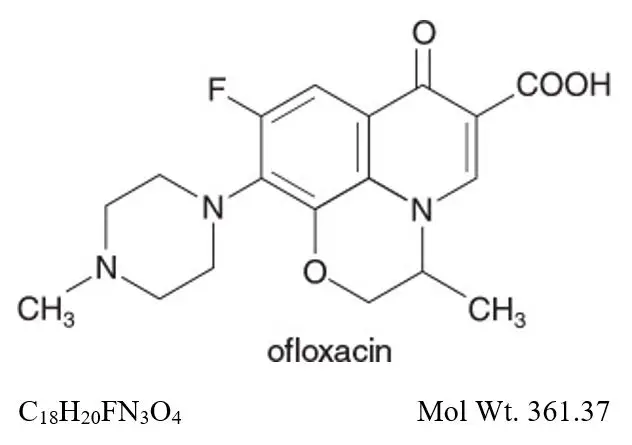
Chemical Name:
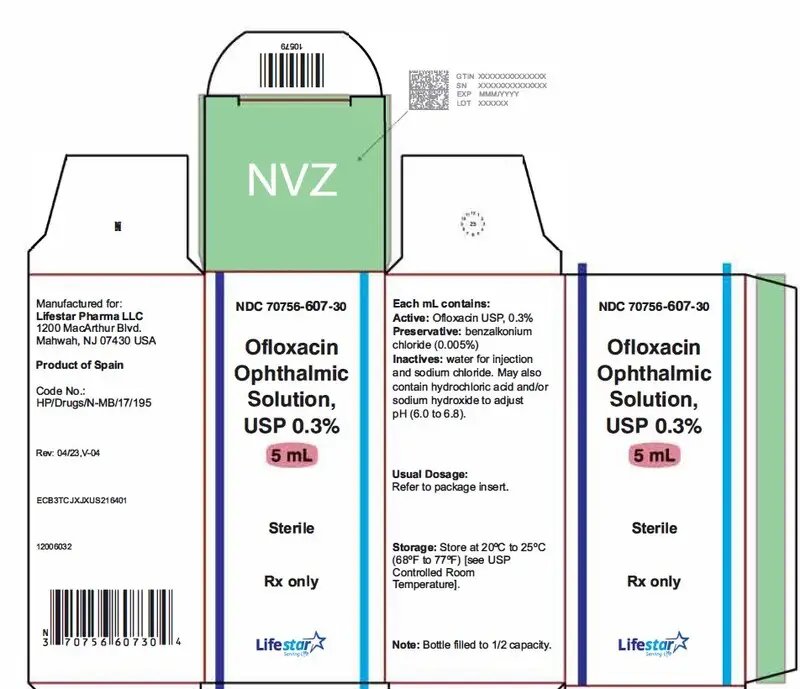
Contains: Active: ofloxacin 0.3% (3 mg/mL). Preservative: benzalkonium chloride (0.005%).
Inactives: sodium chloride and water for injection. May also contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution, USP is unbuffered and formulated with a pH of 6.4 (range - 6.0 to 6.8). It has an osmolality of 300 mOsm/kg. Ofloxacin is a fluorinated 4-quinolone which differs from other fluorinated 4-quinolones in that there is a six member (pyridobenzoxazine) ring from positions 1 to 8 of the basic ring structure.
Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Tear ofloxacin concentrations ranged from 5.7 to 31 mcg/g during the 40 minute period following the last dose on day 11. Mean tear concentration measured four hours after topical ophthalmic dosing was 9.2 mcg/g.
Corneal tissue concentrations of 4.4 mcg/mL were observed four hours after beginning topical ocular application of two drops of ofloxacin ophthalmic solution every 30 minutes. Ofloxacin was excreted in the urine primarily unmodified.
Microbiology
Cross-resistance has been observed between ofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones. There is generally no cross-resistance between ofloxacin and other classes of antibacterial agents such as beta-lactams or aminoglycosides.
Ofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following organisms both in vitro and clinically, in conjunctival and/or corneal ulcer infections (see Indications and Usage).
|
*Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections |
|
| AEROBES, GRAM-POSITIVE:
| AEROBES, GRAM-NEGATIVE:
|
| Staphylococcus aureus
| Enterobacter cloacae
|
| Staphylococcus epidermidis
| Haemophilus influenzae
|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae
| Proteus mirabilis
|
| ANAEROBIC SPECIES:
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
| Propionibacterium acnes
| Serratia marcescens*
|
| AEROBES, GRAM-POSITIVE:
| |
| Enterococcus faecalis
| Staphylococcus hominus
|
| Listeria monocytogenes
| Staphylococcus simulans
|
| Staphylococcus capitis
| Streptococcus pyogenes
|
| AEROBES, GRAM-NEGATIVE:
| |
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus
| Klebsiella pneumoniae
|
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. lwoffii
| Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis
|
| Citrobacter diversus
| Moraxella lacunata
|
| Citrobacter freundii
| Morganella morganii
|
| Enterobacter aerogenes
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
| Enterobacter agglomerans
| Pseudomonas acidovorans
|
| Escherichia coli
| Pseudomonas fluorescens
|
| Haemophilus parainfluenzae
| Shigella sonnei
|
| Klebsiella oxytoca
| |
| OTHER:
| |
| Chlamydia trachomatis
|
Indications and Usage for Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution
|
*Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections |
|
| CONJUNCTIVITIS:
| |
| Gram-positive bacteria:
| Gram-negative bacteria:
|
| Staphylococcus aureus
| Enterobacter cloacae
|
| Staphylococcus epidermidis
| Haemophilus influenzae
|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae
| Proteus mirabilis
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
| CORNEAL ULCERS:
| |
| Gram-positive bacteria:
| Gram-negative bacteria:
|
| Staphylococcus aureus
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
| Staphylococcus epidermidis
| Serratia marcescens*
|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae
| Anaerobic species:
|
| Propionibacterium acnes
|
|
Warnings
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution should not be injected subconjunctivally, nor should it be introduced directly into the anterior chamber of the eye.
There are rare reports of anaphylactic reaction/shock and fatal hypersensitivity reactions in patients receiving systemic quinolones, some following the first dose, including ofloxacin. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, angioedema (including laryngeal, pharyngeal or facial edema), airway obstruction, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. A rare occurrence of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, which progressed to toxic epidermal necrolysis, has been reported in a patient who was receiving topical ophthalmic ofloxacin. If an allergic reaction to ofloxacin occurs, discontinue the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require immediate emergency treatment. Oxygen and airway management, including intubation should be administered as clinically indicated.
Precautions
General
The systemic administration of quinolones, including ofloxacin, has led to lesions or erosions of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. Ofloxacin, administered systemically at 10 mg/kg/day in young dogs (equivalent to 110 times the maximum recommended daily adult ophthalmic dose) has been associated with these types of effects.
Information for Patients
Avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the eye, fingers or other source.
Systemic quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose. Discontinue use immediately and contact your physician at the first sign of a rash or allergic reaction.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long term studies to determine the carcinogenic potential of ofloxacin have not been conducted.
Ofloxacin was not mutagenic in the Ames test, in vitro and in vivo cytogenic assay, sister chromatid exchange assay (Chinese hamster and human cell lines), unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) assay using human fibroblasts, the dominant lethal assay, or mouse micronucleus assay. Ofloxacin was positive in the UDS test using rat hepatocyte, and in the mouse lymphoma assay.
In fertility studies in rats, ofloxacin did not affect male or female fertility or morphological or reproductive performance at oral dosing up to 360 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 4000 times the maximum recommended daily ophthalmic dose).
Pregnancy
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in infants below the age of one year have not been established.
Quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals after oral administration; however, topical ocular administration of ofloxacin to immature animals has not shown any arthropathy. There is no evidence that the ophthalmic dosage form of ofloxacin has any effect on weight bearing joints.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is:
| Days 1 and 2 | Instill one to two drops every two to four hours in the affected eye(s). |
| Days 3 through 7 | Instill one to two drops four times daily. |
| The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of bacterial corneal ulcer is: |
|
| Days 1 and 2 | Instill one to two drops into the affected eye every 30 minutes, while awake. Awaken at approximately four and six hours after retiring and instill one to two drops. |
| Days 3 through 7 to 9 | Instill one to two drops hourly, while awake. |
| Days 7 to 9 through | |
| treatment completion | Instill one to two drops, four times daily. |
How is Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution supplied
5 mL in 10 mL bottle -NDC 70756-607-30
10 mL in 10 mL bottle- NDC 70756-650-30
Note: Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Rx only
Manufactured for:
Lifestar Pharma LLC
1200 MacArthur Blvd.
Mahwah, NJ 07430 USA
Product of Spain
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Revised: June 2023, V-05
| OFLOXACIN
ofloxacin solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| OFLOXACIN
ofloxacin solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Lifestar Pharma LLC (080268943) |
| Registrant - Mankind Pharma Limited (915834068) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mankind Pharma Limited | 916512493 | MANUFACTURE(70756-607, 70756-650) , ANALYSIS(70756-607, 70756-650) , PACK(70756-607, 70756-650) | |