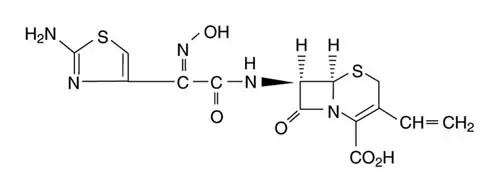
Drug Detail:Omnicef (Cefdinir [ sef-dih-neer ])
Drug Class: Third generation cephalosporins
Omnicef - Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism
Absorption
Cefdinir Capsules
Cefdinir plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameter values following administration of single 300- and 600-mg oral doses of cefdinir to adult subjects are presented in the following table:
| Dose | Cmax
(µg/mL) | tmax
(hr) | AUC (µg•hr/mL) |
| 300 mg | 1.60 (0.55) | 2.9 (0.89) | 7.05 (2.17) |
| 600 mg | 2.87 (1.01) | 3.0 (0.66) | 11.1 (3.87) |
Cefdinir Suspension
Cefdinir plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameter values following administration of single 7- and 14-mg/kg oral doses of cefdinir to pediatric subjects (age 6 months-12 years) are presented in the following table:
| Dose | Cmax
(µg/mL) | tmax
(hr) | AUC (µg•hr/mL) |
| 7 mg/kg | 2.30 (0.65) | 2.2 (0.6) | 8.31 (2.50) |
| 14 mg/kg | 3.86 (0.62) | 1.8 (0.4) | 13.4 (2.64) |
Microbiology
As with other cephalosporins, bactericidal activity of cefdinir results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Cefdinir is stable in the presence of some, but not all, β-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms resistant to penicillins and some cephalosporins are susceptible to cefdinir.
Cefdinir has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in INDICATIONS AND USAGE.
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method(1) (broth or agar) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of cefdinir powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For organisms other than Haemophilus spp. and Streptococcus spp:
| MIC (µg/mL) | Interpretation |
| ≤ 1 | Susceptible (S) |
| 2 | Intermediate (I) |
| ≥ 4 | Resistant (R) |
For Haemophilus spp:a
| MIC (µg/mL) | Interpretation b |
|
a These interpretive standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Haemophilus spp. using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).(1) b The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than "Susceptible." Strains yielding MIC results suggestive of a "nonsusceptible" category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing. |
|
| ≤ 1 | Susceptible (S) |
For Streptococcus spp:
Streptococcus pneumoniae that are susceptible
to penicillin (MIC ≤ 0.06 µg/mL), or streptococci other
than S. pneumoniae that are
susceptible to penicillin (MIC ≤ 0.12 µg/mL),
can be considered susceptible to cefdinir. Testing of cefdinir against
penicillin-intermediate or penicillin-resistant isolates is not recommended.
Reliable interpretive criteria for cefdinir are not available.
A report of "Susceptible" indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentration usually achievable. A report of "Intermediate" indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of "Resistant" indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable; other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of laboratory procedures. Standard cefdinir powder should provide the following MIC values:
| Microorganism | MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
c This quality control range is applicable only to H. influenzae ATCC 49766 tested by a broth microdilution procedure using HTM. |
|
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 0.12-0.5 |
| Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49766c | 0.12-0.5 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 0.12-0.5 |
Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. One such standardized procedure(2) requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 5-µg cefdinir to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to cefdinir.
Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 5-µg cefdinir disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For organisms other than Haemophilus spp. and Streptococcus spp:d
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation |
|
d Because certain strains of Citrobacter, Providencia , and Enterobacter spp. have been reported to give false susceptible results with the cefdinir disk, strains of these genera should not be tested and reported with this disk. |
|
| ≥ 20 | Susceptible (S) |
| 17-19 | Intermediate (I) |
| ≤ 16 | Resistant (R) |
For Haemophilus spp:e
| Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretation f |
|
e These zone diameter standards are applicable only to tests with Haemophilus spp. using HTM.(2) f The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than "Susceptible." Strains yielding MIC results suggestive of a "nonsusceptible" category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing. |
|
| ≥ 20 | Susceptible (S) |
For Streptococcus spp:
Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae should be tested against a 1-µg oxacillin disk. Isolates with
oxacillin zone sizes ≥ 20 mm are susceptible to penicillin
and can be considered susceptible to cefdinir. Streptococci other
than S. pneumoniae should be
tested with a 10-unit penicillin disk. Isolates with penicillin zone
sizes ≥ 28 mm are susceptible to penicillin and can be
considered susceptible to cefdinir.
As with standardized dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 5-µg cefdinir disk should provide the following zone diameters in these laboratory quality control strains:
| Organism | Zone Diameter (mm) |
|
g This quality control range is applicable only to testing of H. influenzae ATCC 49766 using HTM. |
|
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 24-28 |
| Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49766g | 24-31 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 25-32 |
Indications and Usage for Omnicef
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of OMNICEF and other antibacterial drugs, OMNICEF should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
OMNICEF (cefdinir) capsules and OMNICEF (cefdinir) for oral suspension are indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Clinical Trials - OMNICEF Capsules (Adult and Adolescent Patients)
In clinical trials, 5093 adult and adolescent patients (3841 US and 1252 non-US) were treated with the recommended dose of cefdinir capsules (600 mg/day). Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities were attributed to cefdinir. One hundred forty-seven of 5093 (3%) patients discontinued medication due to adverse events thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely associated with cefdinir therapy. The discontinuations were primarily for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea or nausea. Nineteen of 5093 (0.4%) patients were discontinued due to rash thought related to cefdinir administration.
In the US, the following adverse events were thought by investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to cefdinir capsules in multiple-dose clinical trials (N = 3841 cefdinir-treated patients):
| ADVERSE EVENTS
ASSOCIATED WITH CEFDINIR CAPSULES US TRIALS IN ADULT AND ADOLESCENT PATIENTS (N = 3841)a |
||
|
a 1733 males, 2108 females |
||
| Incidence ≥ 1% | Diarrhea | 15% |
| Vaginal moniliasis | 4% of women | |
| Nausea | 3% | |
| Headache | 2% | |
| Abdominal pain | 1% | |
| Vaginitis | 1% of women |
|
| Incidence < 1% but > 0.1% | Rash | 0.9% |
| Dyspepsia | 0.7% | |
| Flatulence | 0.7% | |
| Vomiting | 0.7% | |
| Abnormal stools | 0.3% | |
| Anorexia | 0.3% | |
| Constipation | 0.3% | |
| Dizziness | 0.3% | |
| Dry mouth | 0.3% | |
| Asthenia | 0.2% | |
| Insomnia | 0.2% | |
| Leukorrhea | 0.2% of women | |
| Moniliasis | 0.2% | |
| Pruritus | 0.2% | |
| Somnolence | 0.2% | |
The following laboratory value changes of possible clinical significance, irrespective of relationship to therapy with cefdinir, were seen during clinical trials conducted in the US:
| LABORATORY
VALUE CHANGES OBSERVED WITH CEFDINIR CAPSULES US TRIALS IN ADULT AND ADOLESCENT PATIENTS (N = 3841) |
||
|
a N < 3841 for these parameters |
||
| Incidence ≥ 1% | ↑Urine leukocytes | 2% |
| ↑Urine protein | 2% | |
| ↑Gamma-glutamyltransferasea | 1% | |
| ↓Lymphocytes, ↑Lymphocytes | 1%, 0.2% | |
| ↑Microhematuria | 1% | |
| Incidence < 1% but > 0.1% | ↑Glucosea | 0.9% |
| ↑Urine glucose | 0.9% | |
| ↑White blood cells, ↓White blood cells | 0.9%, 0.7% | |
| ↑Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | 0.7% | |
| ↑Eosinophils | 0.7% | |
| ↑Urine specific gravity, ↓Urine specific gravitya | 0.6%, 0.2% | |
| ↓Bicarbonatea | 0.6% | |
| ↑Phosphorus, ↓Phosphorusa | 0.6%, 0.3% | |
| ↑Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | 0.4% | |
| ↑Alkaline phosphatase | 0.3% | |
| ↑Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) | 0.3% | |
| ↓Hemoglobin | 0.3% | |
| ↑Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), ↓PMNs | 0.3%, 0.2% | |
| ↑Bilirubin | 0.2% | |
| ↑Lactate dehydrogenasea | 0.2% | |
| ↑Platelets | 0.2% | |
| ↑Potassiuma | 0.2% | |
| ↑Urine pHa | 0.2% | |
Clinical Trials - OMNICEF for Oral Suspension (Pediatric Patients)
In clinical trials, 2289 pediatric patients (1783 US and 506 non-US) were treated with the recommended dose of cefdinir suspension (14 mg/kg/day). Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities were attributed to cefdinir. Forty of 2289 (2%) patients discontinued medication due to adverse events considered by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely associated with cefdinir therapy. Discontinuations were primarily for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea. Five of 2289 (0.2%) patients were discontinued due to rash thought related to cefdinir administration.
In the US, the following adverse events were thought by investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to cefdinir suspension in multiple-dose clinical trials (N = 1783 cefdinir-treated patients):
| ADVERSE EVENTS
ASSOCIATED WITH CEFDINIR SUSPENSION US TRIALS IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS (N = 1783)a |
||
|
a 977 males, 806 females b Laboratory changes were occasionally reported as adverse events. |
||
| Incidence ≥ 1% | Diarrhea | 8% |
| Rash | 3% | |
| Vomiting | 1% |
|
| Incidence < 1% but > 0.1% | Cutaneous moniliasis | 0.9% |
| Abdominal pain | 0.8% | |
| Leukopeniab | 0.3% | |
| Vaginal moniliasis | 0.3% of girls | |
| Vaginitis | 0.3% of girls | |
| Abnormal stools | 0.2% | |
| Dyspepsia | 0.2% | |
| Hyperkinesia | 0.2% | |
| Increased ASTb | 0.2% | |
| Maculopapular rash | 0.2% | |
| Nausea | 0.2% | |
NOTE: In both cefdinir- and control-treated patients, rates of diarrhea and rash were higher in the youngest pediatric patients. The incidence of diarrhea in cefdinir-treated patients ≤ 2 years of age was 17% (95/557) compared with 4% (51/1226) in those >2 years old. The incidence of rash (primarily diaper rash in the younger patients) was 8% (43/557) in patients ≤ 2 years of age compared with 1% (8/1226) in those >2 years old.
The following laboratory value changes of possible clinical significance, irrespective of relationship to therapy with cefdinir, were seen during clinical trials conducted in the US:
| LABORATORY
VALUE CHANGES OF POSSIBLE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OBSERVED WITH CEFDINIR
SUSPENSION US TRIALS IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS (N = 1783) |
||
|
a N=1387 for these parameters |
||
| Incidence ≥1% | ↑Lymphocytes, ↓ Lymphocytes | 2%, 0.8% |
| ↑Alkaline phosphatase | 1% | |
| ↓Bicarbonatea | 1% | |
| ↑Eosinophils | 1% | |
| ↑Lactate dehydrogenase | 1% | |
| ↑Platelets | 1% | |
| ↑PMNs, ↓PMNs | 1%, 1% | |
| ↑Urine protein | 1% | |
| Incidence < 1% but > 0.1% | ↑Phosphorus, ↓Phosphorus | 0.9%, 0.4% |
| ↑Urine pH | 0.8% | |
| ↓White blood cells, ↑White blood cells | 0.7%, 0.3% | |
| ↓Calciuma | 0.5% | |
| ↓Hemoglobin | 0.5% | |
| ↑Urine leukocytes | 0.5% | |
| ↑Monocytes | 0.4% | |
| ↑AST | 0.3% | |
| ↑Potassiuma | 0.3% | |
| ↑Urine specific gravity, ↓Urine specific gravity | 0.3%, 0.1% | |
| ↓Hematocrita | 0.2% | |
Omnicef Dosage and Administration
(see INDICATIONS AND USAGE for Indicated Pathogens)
Capsules
The recommended dosage and duration of treatment for infections in adults and adolescents are described in the following chart; the total daily dose for all infections is 600 mg. Once-daily dosing for 10 days is as effective as BID dosing. Once-daily dosing has not been studied in pneumonia or skin infections; therefore, OMNICEF Capsules should be administered twice daily in these infections. OMNICEF Capsules may be taken without regard to meals.
| Type of Infection | Dosage | Duration |
| Community-Acquired Pneumonia | 300 mg q12h | 10 days |
| Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis | 300 mg q12h or 600 mg q24h | 5 to 10 days 10 days |
| Acute Maxillary Sinusitis | 300 mg q12h or 600 mg q24h | 10 days 10 days |
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis | 300 mg q12h or 600 mg q24h | 5 to 10 days 10 days |
| Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 300 mg q12h | 10 days |
Powder for Oral Suspension
The recommended dosage and duration of treatment for infections in pediatric patients are described in the following chart; the total daily dose for all infections is 14 mg/kg, up to a maximum dose of 600 mg per day. Once-daily dosing for 10 days is as effective as BID dosing. Once-daily dosing has not been studied in skin infections; therefore, OMNICEF for Oral Suspension should be administered twice daily in this infection. OMNICEF for Oral Suspension may be administered without regard to meals.
| Type of Infection | Dosage | Duration |
| Acute Bacterial Otitis Media | 7 mg/kg q12h or 14 mg/kg q24h | 5 to 10 days 10 days |
| Acute Maxillary Sinusitis | 7 mg/kg q12h or 14 mg/kg q24h | 10 days 10 days |
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis | 7 mg/kg q12h or 14 mg/kg q24h | 5 to 10 days 10 days |
| Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 7 mg/kg q12h | 10 days |
| Weight | 125 mg/5 mL | 250 mg/5 mL |
|
a Pediatric patients who weigh ≥ 43 kg should receive the maximum daily dose of 600 mg. |
||
| 9 kg/20 lbs | 2.5 mL q12h or 5 mL q24h | Use 125 mg/5 mL product |
| 18 kg/40 lbs | 5 mL q12h or 10 mL q24h | 2.5 mL q12h or 5 mL q24h |
| 27 kg/60 lbs | 7.5 mL q12h or 15 mL q24h | 3.75 mL q12h or 7.5 mL q24h |
| 36 kg/80 lbs | 10 mL q12h or 20 mL q24h | 5 mL q12h or 10 mL q24h |
| ≥43 kga/95 lbs | 12 mL q12h or 24 mL q24h | 6 mL q12h or 12 mL q24h |
Patients With Renal Insufficiency
For adult patients with creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min, the dose of cefdinir should be 300 mg given once daily.
Creatinine clearance is difficult to measure in outpatients. However, the following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance (CLcr) in adult patients. For estimates to be valid, serum creatinine levels should reflect steady-state levels of renal function.
| Males: | CLcr = | (weight) (140 – age) |
| (72) (serum creatinine) |
||
| Females: | CLcr = | 0.85 × above value |
where creatinine clearance is in mL/min, age is in years, weight is in kilograms, and serum creatinine is in mg/dL.(3)
The following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance in pediatric patients:
| CLcr = K × | body length or height | |
| serum creatinine |
where K = 0.55 for pediatric patients older than 1 year(4) and 0.45 for infants (up to 1 year)(5).
In the above equation, creatinine clearance is in mL/min/1.73 m2, body length or height is in centimeters, and serum creatinine is in mg/dL.
For pediatric patients with a creatinine clearance of < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, the dose of cefdinir should be 7 mg/kg (up to 300 mg) given once daily.
Patients on Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis removes cefdinir from the body. In patients maintained on chronic hemodialysis, the recommended initial dosage regimen is a 300-mg or 7-mg/kg dose every other day. At the conclusion of each hemodialysis session, 300 mg (or 7 mg/kg) should be given. Subsequent doses (300 mg or 7 mg/kg) are then administered every other day.
| Final Concentration | Final Volume(mL) | Amount of Water | Directions |
| 125 mg/5 mL | 60 100 | 38 mL 63 mL | Tap bottle to loosen powder, then add water in 2 portions. Shake well after each aliquot. |
| 250 mg/5 mL | 60 100 | 38 mL 63 mL | Tap bottle to loosen powder, then add water in 2 portions. Shake well after each aliquot. |
After mixing, the suspension can be stored at room temperature (25°C/77°F). The container should be kept tightly closed, and the suspension should be shaken well before each administration. The suspension may be used for 10 days, after which any unused portion must be discarded.
Clinical Studies
Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia
In a controlled, double-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted in the US, cefdinir BID was compared with cefaclor 500 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
| Cefdinir BID | Cefaclor TID | Outcome | |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 150/187 (80%) | 147/186 (79%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
| Eradication Rates
Overall |
177/195 (91%) |
184/200 (92%) |
Cefdinir equivalent to control |
|
S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis H. parainfluenzae |
31/31 (100%) 55/65 (85%) 10/10 (100%) 81/89 (91%) |
35/35 (100%) 60/72 (83%) 11/11 (100%) 78/82 (95%) |
In a second controlled, investigator-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted primarily in Europe, cefdinir BID was compared with amoxicillin/clavulanate 500/125 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
| Cefdinir BID | Amoxicillin/ Clavulanate TID | Outcome | |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 83/104 (80%) | 86/97 (89%) | Cefdinir not equivalent to control |
| Eradication Rates
Overall |
85/96 (89%) |
84/90 (93%) |
Cefdinir equivalent to control |
|
S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis H. parainfluenzae |
42/44 (95%) 26/35 (74%) 6/6 (100%) 11/11 (100%) |
43/44 (98%) 21/26 (81%) 8/8 (100%) 12/12 (100%) | |
Streptococcal Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis
In four controlled studies conducted in the United States, cefdinir was compared with 10 days of penicillin in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients. Two studies (one in adults and adolescents, the other in pediatric patients) compared 10 days of cefdinir QD or BID to penicillin 250 mg or 10 mg/kg QID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/ clinical response criteria 5 to 10 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
| Study | Efficacy Parameter | Cefdinir QD | Cefdinir BID | Penicillin QID | Outcome |
| Adults/ Adolescents | Eradication of S. pyogenes | 192/210 (91%) | 199/217 (92%) | 181/217 (83%) | Cefdinir superior to control |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 199/210 (95%) | 209/217 (96%) | 193/217 (89%) | Cefdinir superior to control | |
| Pediatric Patients | Eradication of S. pyogenes | 215/228 (94%) | 214/227 (94%) | 159/227 (70%) | Cefdinir superior to control |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 222/228 (97%) | 218/227 (96%) | 196/227 (86%) | Cefdinir superior to control |
Two studies (one in adults and adolescents, the other in pediatric patients) compared 5 days of cefdinir BID to 10 days of penicillin 250 mg or 10 mg/kg QID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 4 to 10 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
| Study | Efficacy Parameter | Cefdinir BID | Penicillin QID | Outcome |
| Adults/ Adolescents | Eradication of S. pyogenes | 193/218 (89%) | 176/214 (82%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 194/218 (89%) | 181/214 (85%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control | |
| Pediatric Patients | Eradication of S. pyogenes | 176/196 (90%) | 135/193 (70%) | Cefdinir superior to control |
| Clinical Cure Rates | 179/196 (91%) | 173/193(90%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
| OMNICEF
cefdinir capsule |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMNICEF
cefdinir powder, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMNICEF
cefdinir powder, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Abbott Laboratories |