Drug Detail:Oncaspar (Pegaspargase [ peg-ah-spar-jase ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ONCASPAR (pegaspargase) injection, for intramuscular or intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1994
Indications and Usage for Oncaspar
ONCASPAR is an asparagine specific enzyme indicated as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen for treatment of pediatric and adult patients with:
- First-line acute lymphoblastic leukemia (1.1)
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia and hypersensitivity to asparaginase (1.2)
Oncaspar Dosage and Administration
- Administered intramuscularly or intravenously no more frequently than every 14 days. (2.1)
- Patients ages 21 years and younger: 2,500 International Units/m2. (2.1)
- Patients ages over 21 years: 2,000 International Units/m2. (2.1)
- For intramuscular administration, limit the volume at a single injection site to 2 mL; if greater than 2 mL, use multiple injection sites. (2.3)
- For intravenous administration, give over a period of 1 to 2 hours in 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP through an infusion that is already running. (2.3)
- Do not administer ONCASPAR if drug has been frozen, stored at room temperature for more than 48 hours, or shaken or vigorously agitated. (16)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 3,750 International Units/5 mL (750 International Units/mL) solution in a single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
- History of serious hypersensitivity reactions to ONCASPAR. (4)
- History of serious thrombosis with prior L-asparaginase therapy. (4)
- History of pancreatitis with prior L-asparaginase therapy. (4)
- History of serious hemorrhagic events with prior L-asparaginase therapy. (4)
- Severe hepatic impairment. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Anaphylaxis or serious hypersensitivity reactions: Observe patients for 1 hour after administration. Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients with serious hypersensitivity reactions. (5.1)
- Thrombosis: Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients with serious thrombotic events. (5.2)
- Pancreatitis: Evaluate patients with abdominal pain for pancreatitis. Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients with pancreatitis. (5.3)
- Glucose intolerance: Monitor serum glucose. (5.4)
- Hemorrhage: Discontinue ONCASPAR for severe or life-threatening hemorrhage. Evaluate for etiology and treat. (5.5)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor for toxicity through recovery from cycle. Discontinue ONCASPAR for severe liver toxicity. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (>5%) grade >3 adverse reactions with ONCASPAR are hypoalbuminemia, elevated transaminase, febrile neutropenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, bilirubin increased, pancreatitis, abnormal clotting studies, embolic and thrombotic events, hypersensitivity, sepsis, and infections. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Servier Pharmaceuticals, at 1-800-807-6124 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2022
Related/similar drugs
Blincyto, methotrexate, imatinib, doxorubicin, mercaptopurine, Sprycel, GleevecFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Oncaspar
2. Oncaspar Dosage and Administration
2.2 Recommended Premedication
Premedicate patients with acetaminophen, an H-1 receptor blocker (such as diphenhydramine), and an H-2 receptor blocker (such as famotidine) 30-60 minutes prior to administration of ONCASPAR to decrease the risk and severity of both infusion and hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.3 Recommended Monitoring and Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Monitor patients at least weekly, with bilirubin, transaminases, glucose and clinical examinations until recovery from the cycle of therapy. If an adverse reaction should occur, modify treatment according to Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity* | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Infusion Reaction/Hypersensitivity Reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 1 |
|
| Grade 2 |
|
|
| Grade 3 to 4 |
|
|
| Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis |
|
| Severe or life-threatening thrombosis |
|
|
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grades 3 to 4 |
|
| Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | Grade 3 to 4 |
|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | Total bilirubin more than 3 times to no more than 10 times the ULN |
|
| Total bilirubin more than 10 times the ULN |
|
|
2.4 Preparation and Administration
Administer ONCASPAR in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical support and resuscitation equipment to manage hypersensitivity reactions, should they occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
ONCASPAR is a clear and colorless solution. Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter, cloudiness, or discoloration prior to administration. If any of these are present, discard the vial.
When ONCASPAR is administered intramuscularly:
- Limit the volume at a single injection site to 2 mL.
- If the volume to be administered is greater than 2 mL, use multiple injection sites.
When ONCASPAR is administered intravenously:
- Dilute ONCASPAR with 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, using aseptic technique.
- After dilution, administer immediately into a running infusion of either 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, respectively.
- Administer over a period of 1-2 hours.
- Do not infuse other drugs through the same intravenous line during administration of ONCASPAR.
- The diluted solution should be used immediately. If immediate use is not possible, the diluted solution should be stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 48 hours. Protect infusion bags from direct sunlight.
ONCASPAR does not contain a preservative. Use only one dose per vial; discard unused product.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 3,750 International Units/5 mL (750 International Units/mL) clear, colorless solution in a single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
ONCASPAR is contraindicated in patients with a:
- History of serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to ONCASPAR or to any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- History of serious thrombosis with prior L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- History of pancreatitis, including pancreatitis related to prior L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- History of serious hemorrhagic events with prior L-asparaginase therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Severe hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Anaphylaxis and Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and serious hypersensitivity reactions can occur in patients receiving ONCASPAR. The risk of serious hypersensitivity reactions is higher in patients with known hypersensitivity to (E.) coli derived L-asparaginase formulations. Other hypersensitivity reactions can include angioedema, lip swelling, eye swelling, erythema, blood pressure decreased, bronchospasm, dyspnea, pruritus, and rash [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedicate patients 30-60 minutes prior to administration of ONCASPAR. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Observe patients for 1 hour after administration of ONCASPAR in a setting with resuscitation equipment and other agents necessary to treat anaphylaxis (for example, epinephrine, oxygen, intravenous steroids, antihistamines) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients with serious hypersensitivity reactions.
5.2 Thrombosis
Serious thrombotic events, including sagittal sinus thrombosis can occur in patients receiving ONCASPAR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients with serious thrombotic events [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis can occur in patients receiving ONCASPAR. Hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis with fatal outcomes have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of pancreatitis, which, if left untreated, could be fatal. Assess serum amylase and/or lipase levels to confirm early signs of pancreatic inflammation. Discontinue ONCASPAR in patients where pancreatitis is suspected. If pancreatitis is confirmed, do not resume ONCASPAR [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Glucose Intolerance
Glucose intolerance can occur in patients receiving ONCASPAR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In some cases, glucose intolerance is irreversible. Monitor serum glucose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Hemorrhage
Increased prothrombin time, increased partial thromboplastin time, and hypofibrinogenemia can occur in patients receiving ONCASPAR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Evaluate patients with signs and symptoms of hemorrhage with coagulation parameters including PT, PTT, fibrinogen. Consider appropriate replacement therapy in patients with severe or symptomatic coagulopathy. Discontinue ONCASPAR for severe or life-threatening hemorrhage [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity and abnormal liver function, including elevations of transaminase, elevations of bilirubin (direct and indirect), reduced serum albumin, and reduced plasma fibrinogen can occur. Evaluate bilirubin and transaminases at least weekly during cycles of treatment that include ONCASPAR through at least 6 weeks after the last dose of ONCASPAR. In the event of serious liver toxicity, discontinue treatment with ONCASPAR and provide supportive care [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Anaphylaxis and serious hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Glucose intolerance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The most common grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions (>5%) included: hypoalbuminemia, elevated transaminase, febrile neutropenia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, bilirubin increased, pancreatitis, abnormal clotting studies, embolic and thrombotic events, hypersensitivity, sepsis, and infections.
First-Line Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Study CCG-1962 was a randomized (1:1), active controlled study that enrolled 118 patients, with a median age of 4.7 years (1.1-9.9 years), of whom 54% were males and 65% White, 14% Hispanic, 8% Black, 8% Asian, and 6% other race. Of the 59 patients in Study 1 who were randomized to ONCASPAR, 48 patients (81%) received all 3 planned doses of ONCASPAR, 6 (10%) received 2 doses, 4 (7%) received 1 dose, and 1 patient (2%) did not receive the assigned treatment.
In Study CCG-1962, detailed safety information was collected for pre-specified adverse reactions identified as asparaginase induced adverse reactions and for grade 3 and 4 nonhematologic adverse reactions according to the Children's Cancer Group (CCG) Toxicity and Complication Criteria. The per-patient incidence, by treatment arm, for these selected adverse reactions occurring at a severity of grade 3 or 4 are presented in Table 2:
| ONCASPAR (n=58) | Native E. coli L-Asparaginase (n=59) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Infection | 3 (5%) | 3 (5%) |
| Abnormal Liver Tests | 3 (5%) | 5 (8%) |
| Elevated Transaminases* | 2 (3%) | 4 (7%) |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 1 (2%) | 1 (2%) |
| Hyperglycemia | 3 (5%) | 2 (3%) |
| Central Nervous System Thrombosis | 2 (3%) | 2 (3%) |
| Coagulopathy† | 1 (2%) | 3 (5%) |
| Pancreatitis | 1 (2%) | 1 (2%) |
| Allergic Reactions to Asparaginase | 1 (2%) | 0 |
The safety of ONCASPAR was investigated in Study DFCI 11-001, an open label, randomized, active-controlled multicenter clinical trial that included 119 children and adolescents with newly diagnosed ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma treated with ONCASPAR in combination with the Dana Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) ALL Consortium backbone therapy. The median age on enrollment was 4 years (range, 1-18 years). The majority of patients were male (60%) and white (75%). Most patients were considered standard risk ALL (59%) and had B-cell lineage ALL (87%).
The median number of doses of ONCASPAR during the study was 16 doses (one dose during induction therapy then administered every two weeks during post induction therapy). The median duration of exposure to ONCASPAR was 8 months. Table 3 summarizes the incidence of selected Grades ≥3 adverse reactions that occurred in 2 or more patients receiving ONCASPAR. Because not all grade 1 and 2 adverse reactions were collected prospectively, only grade 3 and 4 adverse reactions are presented in Table 3.
| Adverse Reaction* | ONCASPAR 2500 IU/m2 N=119 Grade ≥3† n (%) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Elevated transaminase* | 79 (66) |
| Febrile neutropenia | 48 (40) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 36 (30) |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 33 (28) |
| Bilirubin increased* | 30 (25) |
| Hyperglycemia | 29 (24) |
| Pancreatitis* | 29 (24) |
| Abnormal clotting studies* | 25 (21) |
| Embolic and thrombotic events* | 10 (8) |
| Hypersensitivity* | 8 (7) |
| Pneumonia* | 8 (7) |
| Sepsis* | 7 (6) |
| Diarrhea* | 6 (5) |
| Hemorrhages* | 5 (4) |
| Fungal Infection* | 3 (3) |
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions include the following: bronchospasm, hypotension, laryngeal edema, local erythema or swelling, systemic rash, and urticaria.
Among 58 ONCASPAR-treated patients enrolled in Study CCG-1962, clinical allergic reactions were reported in 2 patients (3%). One patient experienced a grade 1 allergic reaction and the other grade 3 hives; both occurred during the first delayed intensification phase of the study (see Table 4).
Among 62 patients with relapsed ALL and prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 35 patients (56%) had a history of clinical allergic reactions to native Escherichia (E.) coli L-asparaginase, and 27 patients (44%) had a history of clinical allergic reactions to both native E. coli and native Erwinia L-asparaginase. Twenty (32%) of these 62 patients experienced clinical allergic reactions to ONCASPAR (see Table 4).
Among 112 patients with relapsed ALL with no prior hypersensitivity reactions to asparaginase, 11 patients (10%) experienced clinical allergic reactions to ONCASPAR (see Table 4).
| Patient Status | Toxicity Grade, n (%) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Previously Hypersensitive Patients (n=62) | 7 (11) | 8 (13) | 4 (6) | 1 (2) | 20 (32) |
| Non-Hypersensitive Patients (n=112) | 5 (4) | 4 (4) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 11 (10) |
| First Line (n=58) | 1 (2) | 0 | 1 (2) | 0 | 2 (3) |
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other asparaginase products may be misleading.
In Study CCG-1962, ONCASPAR treated patients were assessed for evidence of binding antibodies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The incidence of protocol-specified "high-titer" antibody formation was 2% in Induction (n=48), 10% in Delayed Intensification 1 (n=50), and 11% in Delayed Intensification 2 (n=44). In study CCG-1962, there is insufficient information to determine whether the development of antibodies is associated with an increased risk of clinical allergic reactions or altered pharmacokinetics (i.e., loss of asparaginase activity).
In Study DFCI 11-001, of the 100 evaluable patients treated with ONCASPAR, 19 (19%) patients developed anti-drug antibodies (ADA) during treatment; 18 of these 19 patients were positive for anti-PEG antibodies. The presence of ADA correlated with the occurrence of hypersensitivity reactions. There is insufficient information to determine whether the development of antibodies is associated with altered pharmacokinetics (i.e., loss of asparaginase activity).
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ONCASPAR. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Coagulopathy.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Hepatic impairment, pancreatic cyst, pancreatitis.
Immune system disorders: Anaphylactic shock, hypersensitivity reaction.
Investigations: Blood cholesterol increased.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hyperglycemia, hyperammonemia.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Osteonecrosis.
Vascular disorders: Hemorrhage including central nervous system hemorrhage, thrombosis including
superior sagittal sinus thrombosis.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
ONCASPAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ONCASPAR in the treatment of ALL have been established in pediatric patients. Use of ONCASPAR in these age groups is supported by evidence of efficacy as first-line treatment from one adequate and well-controlled trial, and evidence of efficacy for treatment of patients with hypersensitivity to asparaginase from four adequate and well-controlled trials [see Clinical Studies (14.1)], and safety data from 7 total trials. The pediatric patients treated with ONCASPAR 2,500 International Units/m2 on these trials included 26 infants (1 month to <2 years old), 165 children (2 years to <12 years old), and 39 adolescents (12 to 17 years old).
10. Overdosage
Three patients received 10,000 International Units/m2 of ONCASPAR as an intravenous infusion. One patient experienced a slight increase in liver enzymes. A second patient developed a rash 10 minutes after the start of the infusion, which was controlled with the administration of an antihistamine and by slowing down the infusion rate. A third patient did not experience any adverse reactions.
There is no specific antidote for ONCASPAR overdosage. In case of overdose, monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions, and appropriately manage with symptomatic and supportive treatment.
11. Oncaspar Description
Pegaspargase is a conjugate of monomethoxypolyethylene glycol (mPEG) and L-asparaginase (L-asparagine amidohydrolase), an asparagine specific enzyme. L-asparaginase is a tetrameric enzyme that is produced endogenously by E. coli and consists of identical 34.5 kDa subunits. Approximately 69 to 82 molecules of mPEG are linked to L-asparaginase; the molecular weight of each mPEG molecule is about 5 kDa. ONCASPAR activity is expressed in International Units.
ONCASPAR (pegaspargase) injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, preservative-free, isotonic sterile solution in phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.3, for intramuscular use or for dilution prior to intravenous infusion. Each vial of ONCASPAR contains 3,750 International Units of pegaspargase in 5 mL of solution. Each milliliter contains 750 International Units of pegaspargase, dibasic sodium phosphate, USP (5.58 mg), monobasic sodium phosphate, USP (1.20 mg), and Sodium Chloride, USP (8.50 mg) in Water for Injection, USP.
12. Oncaspar - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
L-asparaginase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of the amino acid L-asparagine into aspartic acid and ammonia. The pharmacological effect of ONCASPAR is thought to be based on the killing of leukemic cells due to depletion of plasma asparagine. Leukemic cells with low expression of asparagine synthetase have a reduced ability to synthesize asparagine, and therefore depend on an exogenous source of asparagine for survival.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
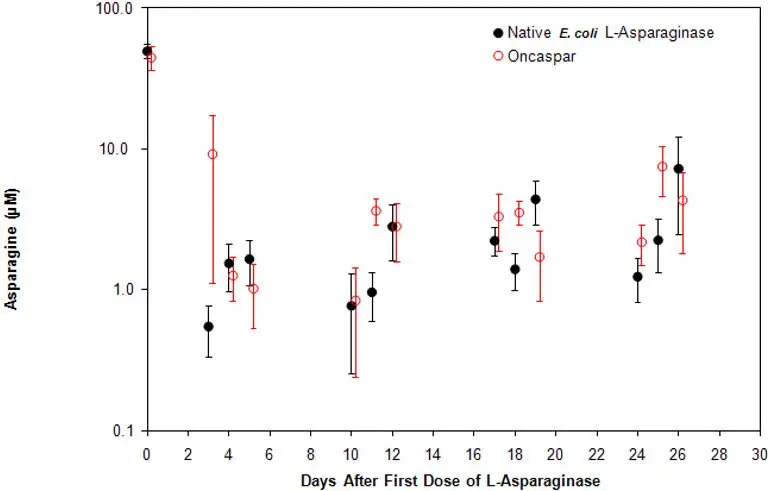
Pharmacodynamic activity was assessed through serial measurements of asparagine in sera and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
In Study CCG-1962, pharmacodynamics were assessed in 57 newly diagnosed pediatric patients with standard-risk ALL who received three intramuscular doses of ONCASPAR (2,500 International Units/m2), one each during induction and two delayed intensification treatment phases [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
In Study AALL07P4, the pharmacodynamic response of pegaspargase was assessed in 47 evaluable patients with newly diagnosed high risk B-precursor ALL. Asparagine concentrations in plasma (N=42) were maintained below the assay limit of quantification for at least 11 days following a single dose of ONCASPAR 2,500 International Units/m2 during the induction phase. CSF asparagine concentration was decreased from a mean pretreatment concentration of 0.6 µg/mL (N=20) to 0.2 µg/mL on Day 4 (N=41) and remained decreased at 0.2 µg/mL (N=39) 25 days after the administration of a single dose of ONCASPAR in the induction phase.
14. Clinical Studies
14.2 Patients with ALL Hypersensitive to Asparaginase
The safety and effectiveness of ONCASPAR was evaluated in 4 open label studies enrolling a total of 42 patients with multiply relapsed, acute leukemia [39 (93%) with ALL] with a history of prior clinical allergic reaction to asparaginase. Hypersensitivity to asparaginase was defined by a history of systemic rash, urticaria, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, hypotension, or local erythema, urticaria, or swelling, greater than 2 centimeters, for at least 10 minutes following administration of any form of native E. coli L-asparaginase. All patients received ONCASPAR at a dose of 2,000 or 2,500 International Units/m2 administered intramuscularly or intravenously every 14 days. Patients received ONCASPAR as a single agent or in combination with multi-agent chemotherapy. The re-induction response rate was 50% (95% confidence interval: 35%, 65%), based upon 36% complete remissions and 14% partial remissions. These results were similar to the overall response rates reported for patients with ALL receiving second-line, native E. coli L-asparaginase-containing re-induction chemotherapy. Anti-tumor activity was also observed with single-agent ONCASPAR. Three responses (1 complete remission and 2 partial remissions) were observed in 9 adult and pediatric patients with relapsed ALL and hypersensitivity to native E. coli L-asparaginase.
16. How is Oncaspar supplied
ONCASPAR (pegaspargase) injection is supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution in Type I single-dose vial containing 3,750 International Units of pegaspargase per 5 mL (750 International Units per mL) solution (NDC 72694-954-01).
| ONCASPAR
pegaspargase injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC (116608503) |