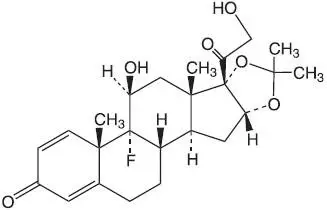
General
Oralone® may cause local adverse reactions. If irritation develops, Oralone® should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact sensitization with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant mucosal infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of Oralone® should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled. If significant regeneration or repair of oral tissues has not occurred in seven days, additional investigation into the etiology of the oral lesion is advised.
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, glucosuria, and other adverse effects known to occur with parenterally-administered steroid preparations; therefore, it may be advisable to periodically evaluate patients on prolonged therapy with corticosteroid-containing dental pastes for evidence of HPA axis suppression (see PRECAUTIONS, Laboratory Tests). If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug or to reduce the frequency of application. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of therapy.