Drug Detail:Ortikos (Budesonide (oral) [ bue-des-oh-nide ])
Drug Class: Glucocorticoids
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ORTIKOS® (budesonide) delayed-release capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
Indications and Usage for Ortikos
ORTIKOS is a corticosteroid indicated for:
- Treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon, in patients 8 years and older. (1.1)
- Maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon for up to 3 months in adults. (1.2)
Ortikos Dosage and Administration
Administration Instructions (2.1):
- Take once daily in the morning.
- Swallow whole. Do not chew or crush.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit juice for the duration of therapy.
Recommended Dosage:
Mild to moderate active Crohn's disease (2.2):
- Adults: 9 mg once daily for up to 8 weeks; repeat 8 week treatment courses for recurring episodes of active disease.
- Pediatric patients 8 to 17 years who weigh more than 25 kg: 9 mg once daily for up to 8 weeks, followed by 6 mg once daily in the morning for 2 weeks.
Maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease (2.3):
- Adults: 6 mg once daily for up to 3 months; taper to complete cessation after 3 months. Continued treatment for more than 3 months has not been shown to provide substantial clinical benefit.
- When switching from oral prednisolone, begin tapering prednisolone concomitantly with initiating ORTIKOS.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Delayed-Release Capsules: 6 mg and 9 mg (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to budesonide or any of the ingredients in ORTIKOS. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypercorticism and Adrenal Axis Suppression: Follow general warnings concerning corticosteroids and pediatrics and patients with hepatic impairment may be at increased risk. (5.1, 8.4)
- Symptoms of Steroid Withdrawal in Patients Transferred from Other Systemic Corticosteroids: Taper slowly from corticosteroids with high systemic effects; monitor for withdrawal symptoms and unmasking of allergies (rhinitis, eczema). (5.2)
- Increased Risk of Infection, including Serious and Fatal Chicken Pox and Measles: Monitor patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infection, untreated fungal, bacterial, systemic viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex. (5.3)
- Other Corticosteroid Effects: Monitor patients with concomitant conditions where corticosteroids may have unwanted effects (e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus). (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) in adults are: headache, respiratory infection, nausea, back pain, dyspepsia, dizziness, abdominal pain, flatulence, vomiting, fatigue, and pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, grapefruit juice): Can increase systemic budesonide concentrations: avoid use. (2.1, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2022
Related/similar drugs
Entyvio, Cimzia, prednisone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, budesonide, HumiraFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Ortikos
2. Ortikos Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration Instructions
- Take ORTIKOS once daily in the morning.
- Swallow ORTIKOS whole. Do not chew or crush.
- Avoid consumption of grapefruit juice for the duration of therapy with ORTIKOS [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.2 Treatment of Mild to Moderate Active Crohn's Disease
The recommended dosage of ORTIKOS is:
Adults: 9 mg orally once daily for up to 8 weeks. Repeated 8 week courses of ORTIKOS can be given for recurring episodes of active disease.
Pediatric patients 8 to 17 years who weigh more than 25 kg: 9 mg orally once daily for up to 8 weeks, followed by 6 mg once daily for 2 weeks.
2.3 Maintenance of Clinical Remission of Mild to Moderate Crohn's Disease
The recommended dosage in adults, following an 8 week course(s) of treatment for active disease and once the patient's symptoms are controlled (CDAI less than 150), is ORTIKOS 6 mg orally once daily for maintenance of clinical remission up to 3 months. If symptom control is still maintained at 3 months an attempt to taper to complete cessation is recommended. Continued treatment with ORTIKOS 6 mg for more than 3 months has not been shown to provide substantial clinical benefit.
Patients with mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or ascending colon have been switched from oral prednisolone to ORTIKOS with no reported episodes of adrenal insufficiency. Since prednisolone should not be stopped abruptly, tapering should begin concomitantly with initiating ORTIKOS treatment.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Delayed-Release Capsules:
- 6 mg: hard gelatin capsules with light grey colored cap and pink colored body imprinted with "061" on cap and body in black ink containing white to off-white pellets.
- 9 mg: hard gelatin capsules with pink colored cap and pink colored body imprinted with "062" on cap and body in black ink containing white to off-white pellets.
4. Contraindications
ORTIKOS is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to budesonide or any of the ingredients of the capsules. Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis have occurred [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypercorticism and Adrenal Axis Suppression
When corticosteroids are used chronically, systemic effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression may occur. Corticosteroids can reduce the response of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to stress. In situations where patients are subject to surgery or other stress situations, supplementation with a systemic corticosteroid is recommended. Since ORTIKOS contains a corticosteroid, general warnings concerning corticosteroids should be followed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), (5.3), (5.4)].
Pediatric patients with Crohn's disease have a slightly higher systemic exposure of budesonide and increased cortisol suppression than adults with Crohn's disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B and C respectively) could be at an increased risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression due to an increased systemic exposure of oral budesonide. Avoid use of ORTIKOS in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.2 Symptoms of Steroid Withdrawal in Patients Transferred from Other Systemic Corticosteroids
Monitor patients who are transferred from corticosteroid treatment with high systemic effects to corticosteroids with lower systemic availability, such as budesonide, since symptoms attributed to withdrawal of steroid therapy, including those of acute adrenal axis suppression or benign intracranial hypertension, may develop. Adrenocortical function monitoring may be required in these patients and the dose of corticosteroid treatment with high systemic effects should be reduced cautiously.
Replacement of systemic corticosteroids with budesonide may unmask allergies (e.g., rhinitis and eczema), which were previously controlled by the systemic drug.
5.3 Increased Risk of Infection
Patients who are on drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infection than healthy individuals. Chicken pox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible patients or patients on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids. In patients who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure.
How the dose, route and duration of corticosteroid administration affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If exposed, therapy with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), as appropriate, may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See prescribing information for VZIG and IG). If chicken pox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
Corticosteroids should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infection, untreated fungal, bacterial, systemic viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Symptoms of steroid withdrawal in those patients transferred from other systemic corticosteroids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased risk of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Other corticosteroid effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ORTIKOS has been established from adequate and well-controlled studies of another oral budesonide product [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Below is a display of the adverse reactions of budesonide in these adequate and well-controlled studies.
Adults
The data described below reflect exposure to budesonide in 520 patients with Crohn's disease, including 520 exposed to 9 mg per day (total daily dose) for 8 weeks and 145 exposed to 6 mg per day for one year in placebo controlled clinical trials. Of the 520 patients, 38% were males and the age range was 17 to 74 years.
Treatment of Mild to Moderate Active Crohn's Disease
The safety of budesonide was evaluated in 651 adult patients in five clinical trials of 8 weeks duration in patients with active mild to moderate Crohn's disease. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in greater than or equal to 5% of the patients, are listed in Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Budesonide 9 mg n=520 | Placebo n=107 | Prednisolone†
40 mg n=145 | Comparator‡
n=88 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Number (%) | Number (%) | Number (%) |
|
|
||||
| Headache | 107(21) | 19(18) | 31(21) | 11(13) |
| Respiratory Infection | 55 (11) | 7(7) | 20(14) | 5(6) |
| Nausea | 57(11) | 10(9) | 18(12) | 7(8) |
| Back Pain | 36(7) | 10(9) | 17(12) | 5(6) |
| Dyspepsia | 31(6) | 4(4) | 17(12) | 3(3) |
| Dizziness | 38(7) | 5(5) | 18(12) | 5(6) |
| Abdominal Pain | 32(6) | 18(17) | 6(4) | 10(11) |
| Flatulence | 30(6) | 6(6) | 12(8) | 5(6) |
| Vomiting | 29(6) | 6(6) | 6(4) | 6(7) |
| Fatigue | 25(5) | 8(7) | 11(8) | 0(0) |
| Pain | 24(5) | 8(7) | 17(12) | 2(2) |
The incidence of signs and symptoms of hypercorticism reported by active questioning of patients in 4 of the 5 short-term clinical trials are displayed in Table 2.
| Signs/Symptom | Budesonide 9 mg n=427 | Placebo n=107 | Prednisolone* 40 mg n=145 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Number (%) | Number (%) | |
|
|||
| Total | 145 (34%) | 29 (27%) | 69 (48%) |
| Acne | 63(15) | 14(13) | 33(23)† |
| Bruising Easily | 63(15) | 12(11) | 13(9) |
| Moon Face | 46(11) | 4(4) | 53(37)† |
| Swollen Ankles | 32(7) | 6(6) | 13(9) |
| Hirsutism‡ | 22(5) | 2(2) | 5(3) |
| Buffalo Hump | 6(1) | 2(2) | 5(3) |
| Skin Striae | 4(1) | 2(2) | 0(0) |
Maintenance of Clinical Remission of Mild to Moderate Crohn's Disease
The safety of budesonide was evaluated in 233 adult patients in four long-term clinical trials (52 weeks) of maintenance of clinical remission in patients with mild to moderate Crohn's disease. A total of 145 patients were treated with budesonide 6 mg once daily.
The adverse reaction profile of budesonide 6 mg once daily in maintenance of Crohn's disease was similar to that of short-term treatment with budesonide 9 mg once daily in active Crohn's disease. In the long-term clinical trials, the following adverse reactions occurred in greater than or equal to 5% and are not listed in Table 1: diarrhea (10%); sinusitis (8%); infection viral (6%); and arthralgia (5%).
Signs/symptoms of hypercorticism reported by active questioning of patients in the long-term maintenance clinical trials are displayed in Table 3.
| Signs/Symptom | Budesonide 6 mg n=145 | Placebo n=143 |
|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Number (%) | |
| Bruising Easily | 15(10) | 5(4) |
| Acne | 14(10) | 3(2) |
| Moon Face | 6(4) | 0 |
| Hirsutism | 5(3) | 1(1) |
| Swollen Ankles | 3(2) | 3(2) |
| Buffalo Hump | 1(1) | 0 |
| Skin Striae | 0 | 0 |
The incidence of signs/symptoms of hypercorticism as described above in long-term maintenance clinical trials was similar to that seen in the short-term treatment clinical trials.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of another oral formulation of budesonide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactic reactions
Nervous System Disorders: Benign intracranial hypertension
Psychiatric Disorders: Mood swings
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Budesonide is a substrate for CYP3A4. Avoid use with CYP3A4 inhibitors. Concomitant oral administration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (ketoconazole) caused an eight-fold increase of the systemic exposure to oral budesonide. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, indinavir, saquinavir, erythromycin, and cyclosporine) can increase systemic budesonide concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
One published study reports that budesonide is present in human milk following maternal inhalation of budesonide which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.3% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.4 and 0.5. Budesonide plasma concentrations were not detected and no adverse events were noted in the breastfed infants following maternal use of inhaled budesonide. The recommended daily dose of ORTIKOS is higher (up to 9 mg daily) compared with inhaled budesonide (up to 800 mcg daily) given to mothers in the above described study. The maximum budesonide plasma concentration following a 9 mg daily dose (in both single-and repeated-dose pharmacokinetic studies) of oral budesonide is approximately 5 nmol/L to 10 nmol/L which is up to 10 times higher than the 1 nmol/L to 2 nmol/L for a 800 mcg daily dose of inhaled budesonide at steady state in the above inhalation study. Assuming the coefficient of extrapolation between the inhaled and oral doses is constant across all dose levels, at therapeutic doses of ORTIKOS, budesonide exposure to the nursing child may be up to 10 times higher than that by budesonide inhalation.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ORTIKOS have been established in pediatric patients 8 to 17 years of age who weigh more than 25 kg for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon. Use of ORTIKOS in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well controlled studies of oral budesonide in adults, with additional data from 2 clinical studies in 149 pediatric patients treated up to 8 weeks and one pharmacokinetic study in 8 pediatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The observed safety profile of oral budesonide in pediatric patients is consistent with its known safety profile in adults and no new safety concerns were identified [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of ORTIKOS have not been established in pediatric patients less than 8 years of age for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon.
The safety and effectiveness of ORTIKOS have not been established in pediatric patients for the maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease. An open-label study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of oral budesonide as maintenance treatment in pediatric patients aged 5 to 17 years was conducted, and did not establish the safety and efficacy of maintenance of clinical remission.
Systemic corticosteroids, including ORTIKOS, may cause a reduction of growth velocity in pediatric patients. Pediatric patients with Crohn's disease have a 17% higher mean systemic exposure and cortisol suppression than adults with Crohn's disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of oral budesonide did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Of the 651 patients treated with oral budesonide in clinical studies, 17 (3%) were greater than or equal to 65 years of age and none were greater than 74 years of age. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B and C, respectively) could be at an increased risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression due to an increased systemic exposure to budesonide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Avoid use of ORTIKOS in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A).
10. Overdosage
Reports of acute toxicity and/or death following overdosage of glucocorticoids are rare. Treatment consists of immediate gastric lavage or emesis followed by supportive and symptomatic therapy.
If corticosteroids are used at excessive doses for prolonged periods, systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression may occur. For chronic overdosage in the case of severe disease requiring continuous steroid therapy, the dosage may be reduced temporarily.
Single oral doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg were lethal in female and male mice, respectively. The signs of acute toxicity were decreased motor activity, piloerection and generalized edema.
11. Ortikos Description
Budesonide, the active ingredient in ORTIKOS, is a synthetic corticosteroid. Budesonide is designated chemically as (RS)-11β, 16α, 17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of two epimers (22R and 22S). The molecular formula of budesonide is C25H34O6 and its molecular weight is 430.5. Its structural formula is:
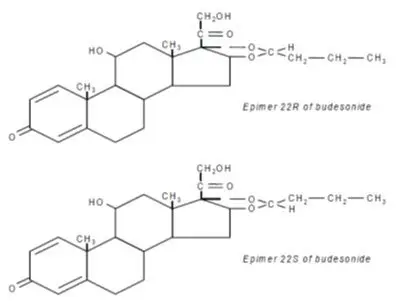
Budesonide is a white to off-white powder that is practically insoluble in water and heptane, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in chloroform. Its partition coefficient between octanol and water at pH 5 is 1.6 × 103 ionic strength 0.01.
Ortikos is formulated as hard gelatin capsules filled with enteric-coated pellets that dissolve at pH greater than 5.5
Each delayed-release capsule for oral administration contains 6 mg or 9 mg of budesonide, USP (micronized) with the following inactive ingredients: acetyl tributyl citrate, corn starch, ethylcellulose aqueous dispersion, methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer dispersion, polysorbate 80, simethicone emulsion, sucrose, talc, and triethyl citrate.
Capsule shell contains gelatin, iron oxide black (for 6 mg), iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, sodium lauryl sulphate and titanium dioxide.
The imprinting ink contains black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide and shellac.
12. Ortikos - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Budesonide is an anti-inflammatory corticosteroid and has a high glucocorticoid effect and a weak mineralocorticoid effect, and the affinity of budesonide to glucocorticoid receptors, which reflects the intrinsic potency of the drug, is about 200-fold that of cortisol and 15-fold that of prednisolone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Treatment with glucocorticoids, including ORTIKOS is associated with a suppression of endogenous cortisol concentrations and an impairment of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function. There was a positive correlation between the percent (%) reduction of AUC0-24 of plasma cortisol and systemic exposure to budesonide both in pediatric and adult patients.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Drug Interaction Studies
Budesonide is metabolized via CYP3A4. Potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 can increase the plasma concentrations of budesonide several-fold. Conversely, induction of CYP3A4 potentially could result in the lowering of budesonide plasma concentrations.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with budesonide were conducted in rats and mice. In a two-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of gliomas in male rats at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). In addition, there were increased incidences of primary hepatocellular tumors in male rats at 25 mcg/kg (approximately 0.023 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) and above. No tumorigenicity was seen in female rats at oral doses up to 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). In an additional two-year study in male Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused no gliomas at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). However, it caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular tumors at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). The concurrent reference corticosteroids (prednisolone and triamcinolone acetonide) showed similar findings. In a 91-week study in mice, budesonide caused no treatment-related carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 200 mcg/kg (approximately 0.1 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis).
Budesonide was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma cell forward gene mutation (TK+/-) test, the human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test, the Drosophila melanogaster sex-linked recessive lethality test, the rat hepatocyte UDS test and the mouse micronucleus test.
In rats, budesonide had no effect on fertility at subcutaneous doses up to 80 mcg/kg (approximately 0.07 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). However, it caused a decrease in prenatal viability and viability in pups at birth and during lactation, along with a decrease in maternal body-weight gain, at subcutaneous doses of 20 mcg/kg (approximately 0.02 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) and above. No such effects were noted at 5 mcg/kg (approximately 0.005 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis).
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of ORTIKOS have been established based on adequate and well-controlled adult studies of another oral budesonide product in patients with Crohn's Disease. Below is a display of the results of these adequate and well-controlled studies of budesonide in these conditions.
14.1 Treatment of Mild to Moderate Active Crohn's Disease
Adults
The efficacy of oral budesonide were evaluated in 994 patients with mild to moderate active Crohn's disease of the ileum and/or ascending colon in 5 randomized and double-blind studies of 8 weeks duration. The study patients ranged in age from 17 to 85 (mean 35), 40% were male and 97% were white. The Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI) was the main clinical assessment used for determining efficacy in these 5 studies.1 The CDAI is a validated index based on subjective aspects rated by the patient (frequency of liquid or very soft stools, abdominal pain rating and general well-being) and objective observations (number of extraintestinal symptoms, need for antidiarrheal drugs, presence of abdominal mass, body weight and hematocrit). Clinical improvement, defined as a CDAI score of less than or equal to 150 assessed after 8 weeks of treatment, was the primary efficacy variable in these 5 comparative efficacy studies of oral budesonide. Safety assessments in these studies included monitoring of adverse reactions. A checklist of potential symptoms of hypercorticism was used.
One study (Study 1) compared the efficacy of budesonide 9 mg daily in the morning to a comparator. At baseline, the median CDAI was 272. Budesonide 9 mg daily resulted in a significantly higher clinical improvement rate at Week 8 than the comparator. See Table 5.
| Clinical Study | Budesonide | Comparator* | Placebo | Prednisolone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 mg Daily | 4.5 mg Twice Daily | ||||
|
|||||
| 1 | 62/91 (69%)† | 37/83 (45%) | |||
| 2 | 31/61 (51%)‡ | 13/64 (20%) | |||
| 3 | 38/79 (48%) | 41/78 (53%) | 13/40 (33%) | ||
| 4 | 35/58 (60%) | 25/60 (42%) | 35/58 (60%) | ||
| 5 | 45/86 (52%) | 56/85 (65%) | |||
Two placebo-controlled clinical trials (Studies 2 and 3) were conducted. Study 2 involved 258 patients and tested the effects of graded doses of budesonide (1.5 mg twice daily, 4.5 mg twice daily, or 7.5 mg twice daily) versus placebo. At baseline, the median CDAI was 290. The 1.5 mg twice daily arm (data not shown) could not be differentiated from placebo. The 4.5 mg twice daily arm was statistically different from placebo (Table 5), while no additional benefit was seen when the daily budesonide dose was increased to 15 mg per day (data not shown). Study 3 was a 3-armed parallel group study. The groups were treated with budesonide 9 mg once daily, budesonide 4.5 mg twice daily and placebo for 8 weeks, followed by a 2-week double-blind taper phase. The median CDAI at baseline was 263. Neither 9 mg daily nor 4.5 mg twice daily budesonide dose levels were statistically different from placebo (Table 5). The recommended dosage of budesonide for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon in adults is 9 mg once daily in the morning for up to 8 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Two clinical trials (Studies 4 and 5) compared oral budesonide with oral prednisolone (initial dose 40 mg per day). Study 4 was a 3-armed parallel group study. The groups were treated with budesonide 9 mg once daily, budesonide 4.5 mg twice daily and prednisolone 40 mg (tapered dose) for 8 weeks, followed by a 4-week double blind taper phase. At baseline, the median CDAI was 277. Equal clinical improvement rates (60%) were seen in the budesonide 9 mg daily and the prednisolone groups in Study 4. In Study 5, 13% fewer patients in the budesonide group experienced clinical improvement than in the prednisolone group (no statistical difference) (Table 5).
The proportion of patients with normal plasma cortisol values (greater than 150 nmol/L) was significantly higher in the budesonide groups in both trials (60% to 66%) than in the prednisolone groups (26% to 28%) at Week 8.
15. References
- Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F: Development of a Crohn's Disease Activity Index, National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology 1976; 70(3): 439-444.
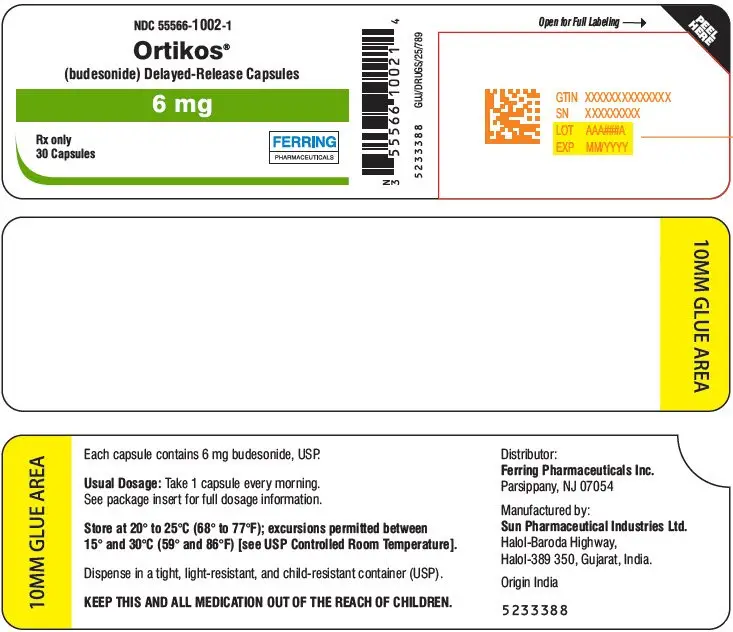
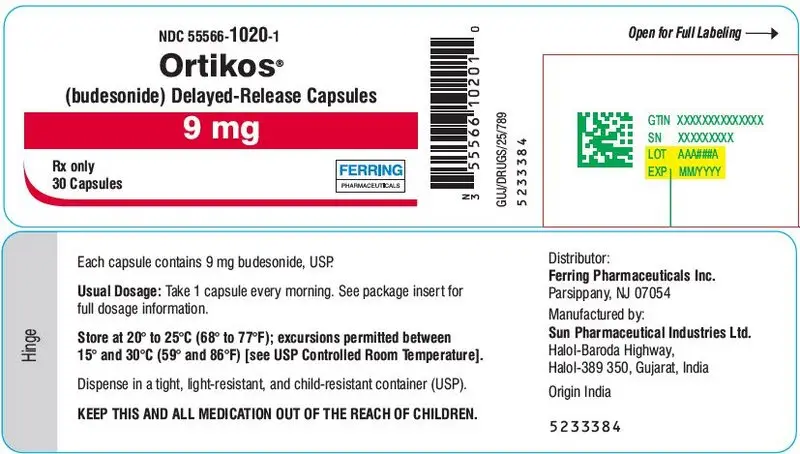
16. How is Ortikos supplied
- ORTIKOS 6 mg are hard gelatin capsules with light grey colored cap and pink colored body imprinted with "061" on cap and body in black ink containing white to off-white pellets.
| Bottles of 30 with Child Resistant Cap | NDC 55566-1002-1 |
- ORTIKOS 9 mg are hard gelatin capsules with pink colored cap and pink colored body imprinted with "062" on cap and body in black ink containing white to off-white pellets.
| Bottles of 30 with Child Resistant Cap | NDC 55566-1020-1 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise Patients to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued: June 2022 | ||
| Patient Information | |||
| ORTIKOS® (or-TEE-kos) (budesonide) delayed-release capsules, for oral use |
|||
| Read this Patient Information before you start taking ORTIKOS and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. | |||
| What is ORTIKOS? | |||
ORTIKOS is a prescription corticosteroid medicine used to treat mild to moderate Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine (ileum) and part of the large intestine (ascending colon):
|
|||
| It is not known if ORTIKOS is safe and effective in children under 8 years of age, or in children 8 to 17 years of age who weigh 55 pounds (25 kg) or less, for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine and part of the large intestine. | |||
| It is not known if ORTIKOS is safe and effective in children to help keep symptoms of mild to moderate Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine and part of the large intestine from coming back. | |||
Do not take ORTIKOS if:
|
|||
Before you take ORTIKOS tell your healthcare provider if you have any other medical conditions including if you:
|
|||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. ORTIKOS and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. | |||
How should I take ORTIKOS?
|
|||
What should I avoid while taking ORTIKOS?
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of ORTIKOS? ORTIKOS may cause serious side effects, including: |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
The most common side effects of ORTIKOS in adults include: |
|||
|
|
||
| The most common side effects of ORTIKOS in children 8 to 17 years of age, who weigh more than 55 pounds (25 kg), are similar to the most common side effects in adults. | |||
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | |||
| These are not all the possible side effects of ORTIKOS. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | |||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||
How should I store ORTIKOS?
|
|||
| Keep ORTIKOS and all medicines out of reach of children. | |||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ORTIKOS. | |||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ORTIKOS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ORTIKOS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ORTIKOS that is written for health professionals. | |||
| What are the ingredients in ORTIKOS?
Active ingredient: budesonide Inactive ingredients: acetyl tributyl citrate, corn starch, ethylcellulose aqueous dispersion, methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer dispersion, polysorbate 80, simethicone emulsion, sucrose, talc, and triethyl citrate. Capsule shell contains gelatin, iron oxide black (for 6 mg), iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, sodium lauryl sulphate and titanium dioxide. The imprinting ink contains, black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide and shellac. Distributor: Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. Parsippany, NJ 07054 Manufactured by: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. Halol-Baroda Highway, Halol-389 350, Gujarat, India For more information, call 1-800-818-4555. |
|||
| ORTIKOS
budesonide capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ORTIKOS
budesonide capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. (103722955) |