Drug Detail:Oxbryta (Voxelotor [ vox-el-oh-tor ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
OXBRYTA® (voxelotor) tablets, for oral use
OXBRYTA® (voxelotor) tablets for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 12/2021 |
| Dosage and Administration (2) | 10/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Oxbryta
OXBRYTA is a hemoglobin S polymerization inhibitor indicated for the treatment of sickle cell disease in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on increase in hemoglobin (Hb). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s). (1)
Oxbryta Dosage and Administration
OXBRYTA can be taken with or without food. (2.7)
Recommended dosage:
- Adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older: 1,500 mg orally once daily. (2.1)
- Pediatric patients 4 to less than 12 years: Dosing with OXBRYTA is based on body weight. See Table 1 for complete dosing recommendations. (2.2)
Recommended dosage for severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C):
- Adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older: 1,000 mg orally once daily. (2.3)
- Pediatric patients 4 to less than 12 years: Reduce the dose of OXBRYTA based on body weight. See Table 2 for complete dosing recommendations. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 300 mg and 500 mg (3)
- Tablets for oral suspension: 300 mg (3)
Contraindications
Prior drug hypersensitivity to voxelotor or excipients. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Observe for signs and symptoms and manage promptly. (5.1)
- Laboratory Test Interference: Perform quantification of hemoglobin species when patient is not receiving OXBRYTA. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% with a difference of >3% compared to placebo) are headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, rash, and pyrexia. (6.1)
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >10%) reported in pediatric patients 4 to <12 years are pyrexia, vomiting, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-833-GBT-4YOU (1-833-428-4968) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Sensitive CYP3A4 Substrates: Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. (7.2)
- Strong or moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers. If unavoidable, increase the dose of OXBRYTA. (2.5, 2.6, 7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Oxbryta
OXBRYTA is indicated for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on increase in hemoglobin (Hb) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
2. Oxbryta Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
The recommended dosage of OXBRYTA is 1,500 mg orally once daily.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients 4 Years to Less Than 12 Years
For pediatric patients 4 years to less than 12 years, select the appropriate product (OXBRYTA tablets or OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension) based on patient's ability to swallow tablets and patient's weight.
The recommended dosage of OXBRYTA for pediatric patients 4 years to less than 12 years is shown in Table 1.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dose (once daily) |
|---|---|
| 40 kg or greater | 1,500 mg |
| 20 kg to less than 40 kg | 900 mg |
| 10 kg to less than 20 kg | 600 mg |
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of OXBRYTA in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C) is 1,000 mg orally once daily.
No dosage adjustment of OXBRYTA is required for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients 4 Years to Less Than 12 Years with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of OXBRYTA in pediatric patients 4 years to less than 12 years with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh C) is described in Table 2.
No dosage adjustment of OXBRYTA is required for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Body Weight | Recommended Dose (once daily) |
|---|---|
| 40 kg or greater | 1,000 mg (two 500 mg tablets) or 900 mg (three 300 mg tablets for oral suspension or three 300 mg tablets) |
| 20 kg to less than 40 kg | 600 mg |
| 10 kg to less than 20 kg | 300 mg |
2.5 Recommended Dosage of OXBRYTA for Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older When Used with Concomitant Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
2.6 Recommended Dosage of OXBRYTA for Pediatric Patients 4 Years to Less Than 12 Years When Used with Concomitant Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers with OXBRYTA [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is unavoidable, see Table 3 for dosage.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dose (once daily) | |
|---|---|---|
| Concomitant Use of Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | Concomitant Use of Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| 40 kg or greater | 2,500 mg (five 500 mg tablets) or 2,400 mg (eight 300 mg tablets for oral suspension or eight 300 mg tablets) | 2,000 mg (four 500 mg tablets) or 2,100 mg (seven 300 mg tablets for oral suspension or seven 300 mg tablets) |
| 20 kg to less than 40 kg | 1,500 mg | 1,200 mg |
| 10 kg to less than 20 kg | 900 mg | 900 mg |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 300 mg light purple to purple, oval shaped, biconvex, debossed with "G 300" on one side.
Tablets: 500 mg light yellow to yellow, oval shaped, biconvex, debossed with "GBT 500" on one side.
Tablets for oral suspension: 300 mg light yellow to yellow, round shaped, debossed with "300 D" on one side.
4. Contraindications
OXBRYTA is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious drug hypersensitivity reaction to voxelotor or excipients. Clinical manifestations may include generalized rash, urticaria, mild shortness of breath, mild facial swelling, and eosinophilia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions after administration of OXBRYTA have occurred in <1% of patients treated. Clinical manifestations may include generalized rash, urticaria, mild shortness of breath, mild facial swelling, and eosinophilia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue OXBRYTA and administer appropriate medical therapy. Do not reinitiate OXBRYTA in patients who experience these symptoms with previous use.
5.2 Laboratory Test Interference
OXBRYTA administration may interfere with measurement of Hb subtypes (HbA, HbS, and HbF) by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. If precise quantitation of Hb species is required, chromatography should be performed when the patient has not received OXBRYTA therapy in the immediately preceding 10 days.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reaction is discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
The safety of OXBRYTA was evaluated in the HOPE trial based on data from 88 patients with SCD who received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg and 91 patients who received placebo orally once daily [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Seventy-four patients received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg once daily for ≥24 weeks, 65 patients for ≥48 weeks, and 63 patients completed the 72-week treatment period.
In patients who received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg once daily the median age was 24 years (range:12 to 59 years); 65% female; 66% Black or African American and 23% Arab/Middle Eastern; and 65% receiving hydroxyurea at baseline.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 3% (3/88) of patients receiving OXBRYTA 1,500 mg, which included headache, drug hypersensitivity, and pulmonary embolism occurring in 1 patient each. Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction (Grades 1-4) occurred in 5% (4/88) of patients who received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg.
Dosage modifications (dose reduction or dosing interruption) due to an adverse reaction occurred in 48% (42/88) of patients who received OXBRYTA. Most frequent adverse reactions requiring dosage modifications occurring in more than two patients who received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg included diarrhea and rash.
The safety profile observed in pediatric patients 12 to <17 years treated with OXBRYTA in the HOPE trial was similar to that seen in adult patients.
The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥10% of patients treated with OXBRYTA 1,500 mg with a difference of >3% compared to placebo are summarized in Table 4.
| Adverse Reaction* | OXBRYTA 1,500 mg (N=88) | Placebo (N=91) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Headache | 32% | 25% |
| Diarrhea | 23% | 11% |
| Abdominal Pain† | 23% | 16% |
| Nausea | 19% | 10% |
| Rash‡ | 15% | 11% |
| Pyrexia | 15% | 8% |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients included:
- Drug hypersensitivity
7. Drug Interactions
7.2 Effect of Voxelotor on Other Drugs
Voxelotor increased the systemic exposure of midazolam (a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of OXBRYTA with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. If concomitant use is unavoidable, consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate(s).
7.3 Laboratory Test Interference
OXBRYTA administration may interfere with measurement of Hb subtypes (HbA, HbS, and HbF) by HPLC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. If precise quantitation of Hb species is required, chromatography should be performed when the patient has not received OXBRYTA therapy in the immediately preceding 10 days.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of OXBRYTA for SCD have been established in pediatric patients aged 4 years and older. The safety and efficacy of OXBRYTA in pediatric patients with SCD below the age of 4 years have not been established.
Use of OXBRYTA in pediatric patients 12 to <17 years for SCD is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study in adults and pediatric patients (HOPE trial). The HOPE trial enrolled 26 pediatric patients aged 12 to <17 years, in which 12 pediatric patients received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg once daily and 14 pediatric patients received OXBRYTA 900 mg once daily [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Use of OXBRYTA in pediatric patients 4 to <12 years for SCD is supported by evidence from an open-label, Phase 2 study. The study enrolled 45 pediatric patients aged 4 to <12 years and 11 patients aged 12 to <17 years with SCD. Patients 12 to <17 years received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg once daily. Patients 4 to <12 years were administered OXBRYTA based on body weight.
OXBRYTA doses of 600 mg, 900 mg, or 1,500 mg once daily were administered to patients weighing 10 kg to <20 kg, 20 kg to <40 kg, or ≥40 kg, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy were similar across the pediatric age groups and across pediatric and adult patients [see Dosage and Administration (2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The adverse reactions observed were similar across the pediatric age groups and across pediatric and adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
11. Oxbryta Description
OXBRYTA contains voxelotor, a hemoglobin S polymerization inhibitor. The chemical name of voxelotor is 2-hydroxy-6-((2-(1-isopropyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)methoxy)benzaldehyde with a molecular formula of C19H19N3O3 and a molecular weight of 337.4.
The chemical structure of voxelotor is:
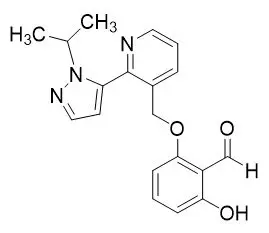
Voxelotor is a white-to-yellow-to-beige compound in crystalline Form II of its free base. It is non-hygroscopic and highly soluble in common organic solvents such as acetone and toluene and insoluble in water.
OXBRYTA film-coated tablets for oral use contain either 300 mg or 500 mg of voxelotor. Both strengths of OXBRYTA film-coated tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. In addition, the 500 mg tablet film coating contains: polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The 300 mg tablet film coating contains: black and red iron oxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Each OXBRYTA tablet for oral suspension contains 300 mg of voxelotor with the following inactive ingredients: artificial grape flavor, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide pigment, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sucralose.
12. Oxbryta - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Voxelotor is a hemoglobin S (HbS) polymerization inhibitor that binds to HbS with a 1:1 stoichiometry and exhibits preferential partitioning to red blood cells (RBCs). By increasing the affinity of Hb for oxygen, voxelotor demonstrates dose-dependent inhibition of HbS polymerization. Nonclinical studies suggest that voxelotor may inhibit RBC sickling, improve RBC deformability, and reduce whole blood viscosity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamic effect of voxelotor treatment demonstrated a dose-dependent increase in Hb oxygen affinity as determined by the change in p50 (partial pressure of oxygen at which Hb oxygen saturation of 50% is achieved) that was linearly correlated with voxelotor exposure.
The pharmacodynamic effect of voxelotor treatment also demonstrated a dose-dependent reduction in clinical measures of hemolysis (indirect bilirubin and % reticulocytes).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Voxelotor is absorbed into plasma and is then distributed predominantly into RBCs due to its preferential binding to Hb. The major route of elimination of voxelotor is by metabolism with subsequent excretion of metabolites into urine and feces. The PK are linear and voxelotor exposures increased proportionally with either single or multiple doses (Table 5) in whole blood, plasma, and RBCs. Steady-state after repeated administration is reached within 8 days and exposures of voxelotor are consistent with accumulation predicted based on single dose data in patients with SCD.
| PK Parameter | Voxelotor 1,500 mg Geometric Mean (%CV) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Plasma PK | |
| AUC0-24h (μg∙hr/mL) | 278 (28.4) |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 14 (24.5) |
| Half-life (hours) | 38.7 (30.2) |
| Whole Blood PK | |
| AUC0-24h (μg∙hr/mL) | 3,830 (33.5) |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 180 (31) |
In healthy subjects, voxelotor exposures were comparable when administered as tablet for oral suspension dispersed in water or as oral tablet swallowed whole.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Voxelotor was not carcinogenic in a 26-week study in RasH2 transgenic mice at oral doses of 30, 150, or 500 mg/kg/day.
Voxelotor was not genotoxic in the reverse mutation bacterial (Ames) test, rat Comet assay, or rat micronucleus assay.
In a fertility and early embryonic development study, voxelotor was administered orally to rats at 15, 50, and 250 mg/kg/day. Males were dosed 28 days prior to mating through cohabitation and females were dosed 14 days prior to mating through gestation Day 7. Voxelotor had no effect on fertility or reproductive function. Sperm motility was decreased and changes in sperm morphology occurred at 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 5-times the human exposure at 1,500 mg/day).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Adults and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
The efficacy and safety of OXBRYTA in SCD was evaluated in HOPE, a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial [NCT 03036813]. In this study, 274 patients were randomized to daily oral administration of OXBRYTA 1,500 mg (N=90), OXBRYTA 900 mg (N=92), or placebo (N=92). Patients were included if they had from 1 to 10 vasoocclusive crisis (VOC) events within 12 months prior to enrollment and baseline hemoglobin (Hb) ≥5.5 to ≤10.5 g/dL. Eligible patients on stable doses of hydroxyurea for at least 90 days were allowed to continue hydroxyurea therapy throughout the study. Randomization was stratified by patients already receiving hydroxyurea (yes, no), geographic region (North America, Europe, Other), and age (12 to <17 years, 18 to 65 years). The trial excluded patients who received red blood cell (RBC) transfusions within 60 days and erythropoietin within 28 days of enrollment, had renal insufficiency, uncontrolled liver disease, were pregnant, or lactating.
The majority of patients had HbSS or HbS/beta0-thalassemia genotype (90%) and were receiving background hydroxyurea therapy (65%). The median age was 24 years (range: 12 to 64 years); 46 (17%) patients were 12 to <17 years. Median baseline Hb was 8.5 g/dL (5.9 to 10.8 g/dL). One hundred and fifteen (42%) had 1 VOC event and 159 (58%) had 2 to 10 events within 12 months prior to enrollment. In the OXBRYTA 1,500 mg group, 63 (70%) patients completed the study through Week 72.
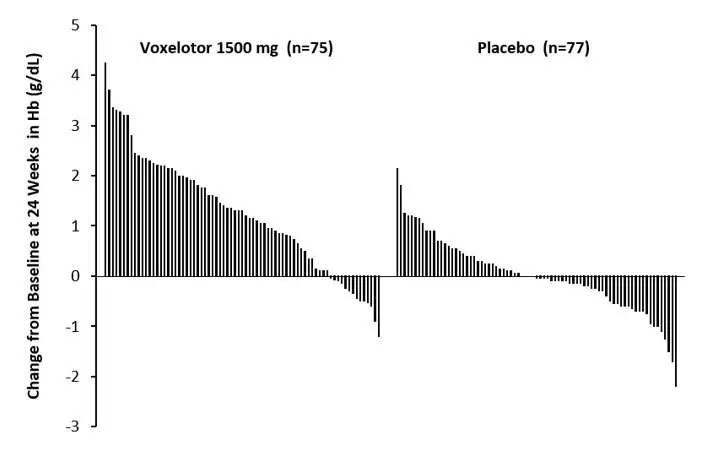
Efficacy was based on Hb response rate defined as a Hb increase of >1 g/dL from baseline to Week 24 in patients treated with OXBRYTA 1,500 mg versus placebo. The response rate for OXBRYTA 1,500 mg was 51.1% (46/90) compared to 6.5% (6/92) in the placebo group (p < 0.001). No outlier subgroups were observed. The distribution of Hb change from baseline for individual patients completing 24 weeks of treatment with OXBRYTA 1,500 mg or placebo is depicted in Figure 1.
|
| Figure 1: Subject-level Change from Baseline in Hemoglobin at Week 24 in Patients Who Completed 24 Weeks of Treatment* |
|
|
Additional efficacy evaluation included change in Hb and percent change in indirect bilirubin and percent reticulocyte count from baseline to Week 24 (Table 6).
| OXBRYTA 1,500 mg QD (N=90) | Placebo (N=92) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| QD = once daily; SE = standard error | |||
| Hemoglobin | 1.1 g/dL (0.1) | -0.1 g/dL (0.1) | < 0.001 |
| Indirect Bilirubin | -29.1% (3.5) | -2.8% (3.5) | < 0.001 |
| Percent Reticulocyte Count | -18.0% (4.7) | 6.8% (4.7) | < 0.001 |
14.2 Pediatric Patients 4 to <12 Years
The efficacy and safety of OXBRYTA in patients 4 to <12 years with SCD was evaluated in an open-label, multi-center, Phase 2 trial [NCT 02850406]. In this study, 45 patients 4 to <12 years and 11 patients 12 to <17 years received OXBRYTA. Patients 4 to <12 years received tablets for oral suspension based on body weight at baseline. OXBRYTA doses of 600 mg, 900 mg, or 1,500 mg once daily were administered to patients weighing 10 kg to <20 kg, 20 kg to <40 kg, or ≥40 kg, respectively. Patients 12 to <17 years received OXBRYTA 1,500 mg once daily.
Patients were included if their baseline hemoglobin (Hb) was ≤10.5 g/dL. Eligible patients on stable doses of hydroxyurea for at least 90 days were allowed to continue hydroxyurea therapy throughout the study. The trial excluded patients who had a VOC event within 14 days prior to enrollment, received red blood cell (RBC) transfusions within 30 days of enrollment, and had renal insufficiency or uncontrolled liver disease.
All patients had HbSS or HbS/beta0-thalassemia genotype (100%) and most were receiving background hydroxyurea therapy (80%). The median age was 8 years (range: 4 to 15 years); 45 (80%) patients were 4 to <12 years. In this age group, mean baseline Hb was 8.6 g/dL (range: 6.1 to 10.5 g/dL).
Efficacy was based on Hb response rate, which is defined as a Hb increase of >1 g/dL from baseline to Week 24. Hb response rate for OXBRYTA in patients aged 4 to <12 years who took at least one dose of OXBRYTA was 36% (16/45) (95% CI: 21.6%, 49.5%).
16. How is Oxbryta supplied
The 300 mg tablet is film-coated, light purple to purple, oval shaped, biconvex, debossed with "G 300" on one side, available in:
- Bottles of 60 tablets with one desiccant canister, a polyester coil and child-resistant closure: NDC 72786-102-02
- Bottles of 90 tablets with one desiccant canister, a polyester coil and child-resistant closure: NDC 72786-102-03
The 500 mg tablet is film-coated, light yellow to yellow, oval shaped, biconvex, debossed with "GBT 500" on one side, and available in:
- Bottles of 90 tablets with one desiccant canister, a polyester coil and child-resistant closure: NDC 72786-101-01
The 300 mg tablet for oral suspension is light yellow to yellow, round shaped, debossed with "300 D" on one side, and available in:
- Bottles of 60 tablets for oral suspension with a polyester coil and child-resistant closure: NDC 72786-111-02
- Bottles of 90 tablets for oral suspension with a polyester coil and child-resistant closure: NDC 72786-111-03
Do not eat the desiccant canister or the polyester coil.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| PATIENT INFORMATION | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXBRYTA® (ox brye ta) (voxelotor) tablets | OXBRYTA® (ox brye ta) (voxelotor) tablets for oral suspension | |||
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 10/2022 | |||
| What is OXBRYTA?
OXBRYTA is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of sickle cell disease in adults and children 4 years of age and older. It is not known if OXBRYTA is safe and effective in children with sickle cell disease below 4 years of age. |
||||
| Do not take OXBRYTA if you or your child have had an allergic reaction to voxelotor or any of the ingredients in OXBRYTA. See the end of this leaflet for a list of the ingredients in OXBRYTA. | ||||
Before taking OXBRYTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you or your child:
|
||||
How should I take OXBRYTA?
|
||||
| What should I avoid while taking OXBRYTA?
Do not take St. John's wort during treatment with OXBRYTA. |
||||
| What are the possible side effects of OXBRYTA? OXBRYTA can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
| The most common side effects of OXBRYTA include: | ||||
|
|
|||
| The most common side effects of OXBRYTA in children ages 4 to less than 12 years of age include: | ||||
|
|
|||
| These are not all the possible side effects of OXBRYTA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-833-428-4968 (1-833-GBT-4YOU). |
||||
How should I store OXBRYTA?
|
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of OXBRYTA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use OXBRYTA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give OXBRYTA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about OXBRYTA that is written for health professionals. |
||||
| What are the ingredients of OXBRYTA?
Active Ingredient: voxelotor Inactive Ingredients: OXBRYTA tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The 500 mg tablet film coating contains: polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The 300 mg tablet film coating contains: black and red iron oxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension: artificial grape flavor, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide pigment, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sucralose. Manufactured for: Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA. OXBRYTA® © 2022 Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved. For more information, call 1-833-428-4968 (1-833-GBT-4YOU) or go to www.OXBRYTA.com. |
||||
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OXBRYTA® [ox brye ta] (voxelotor) tablets for oral suspension 300 mg |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 10/2022 | |||
| This Instructions for Use contains information on how to take OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension. Read this Instructions for Use before you or your child start taking OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension for the first time and each time you or your child get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your or your child's medical condition or treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have questions about how to take or give the prescribed dose of OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension. |
||||
Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking OXBRYTA Tablets for Oral Suspension:
|
||||
| Gather supplies | ||||
You will need the following items to prepare the dose of OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension (not included with OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension):
|  |
|||
| Preparing a dose of OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension | ||||
| Step 1. | Wash and dry your hands well before preparing the dose. | |||
| Step 2. | Pour room temperature clear drink into the cup. The table below shows the amount of clear drink needed for your prescribed dose. You may add more clear drink if needed to mix the tablets. |  |
||
| Number of OXBRYTA Tablets for Oral Suspension | Amount of Clear Drink | |||
| 1 | 1 teaspoon (5 mL) | |||
| 2 | 2 teaspoons (10 mL) | |||
| 3 | 3 teaspoons (15 mL) | |||
| 4 | 4 teaspoons (20 mL) | |||
| 5 | 5 teaspoons (25 mL) | |||
| 7 | 7 teaspoons (35 mL) | |||
| 8 | 8 teaspoons (40 mL) | |||
| Step 3. | Add the prescribed number of OXBRYTA tablets for oral suspension into the cup. |  |
||
| Step 4. | Swirl the cup until the tablet(s) break apart (disperse) in the drink. Be careful not to spill the mixture.
|  |
||
| Step 5. | Wait for 1 to 5 minutes. |  |
||
| Giving the dose | ||||
| Step 6. | Swirl the cup again. Take or give all of the prepared medicine right away.
|  |
||
| Step 7. | Add 1 or 2 teaspoons of room temperature clear drink to the cup to make sure the full dose is taken. Swirl the cup until the remaining medicine is mixed and take or give it right away.
|  |
||
| Step 8. | Wash the teaspoon and cup with warm soap and water. | |||
Storing OXBRYTA
|
||||
| Disposing of OXBRYTA
When all the tablets in the bottle have been taken, throw away the bottle. Safely dispose of (throw away) OXBRYTA that is out of date or no longer needed using your local household waste guidelines. Manufactured for: Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA. OXBRYTA® © 2022 Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved. For more information, call 1-833-428-4968 (1-833-GBT-4YOU) or go to www.OXBRYTA.com. |
||||
| OXBRYTA
voxelotor tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OXBRYTA
voxelotor tablet, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| OXBRYTA
voxelotor tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Global Blood Therapeutics Inc. (028636495) |