Drug Detail:Oxtellar xr (Oxcarbazepine)
Drug Class: Dibenzazepine anticonvulsants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
OXTELLAR XR (oxcarbazepine) extended-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
Recent Major Changes
| Indications ( 1) | 12/2018 |
| Dosage and Administration ( 2.2, 2.5, 2.6) | 12/2018 |
| Contraindications ( 4) | 12/2018 |
| Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.6, 5.7, 5.10) | 12/2018 |
Indications and Usage for Oxtellar XR
Oxtellar XR® is indicated for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 6 years of age and older ( 1)
Oxtellar XR Dosage and Administration
- Adult Patients: The recommended initial dosage is 600 mg once per day. Increase the dosage in weekly increments of 600 mg once per day, based on clinical response and tolerability, to a recommended maintenance dosage of 1200 mg to 2400 mg once per day. ( 2.2)
- In adult patients with a creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, initiate at one-half the usual starting dosage and increase slowly ( 2.3)
- Pediatric Patients: The recommended dosage is based on body weight and is administered orally once per day. Increase the dosage in weekly intervals based on clinical response and tolerability, to the recommended dosage ( 2.2).
- Geriatric Patients: Start at lower dosage (300 mg or 450 mg/day) and increase slowly ( 2.4)
- In conversion of oxcarbazepine immediate-release to Oxtellar XR ®, higher dosages of Oxtellar XR ®may be necessary ( 2.7, 12.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release tablets:150 mg, 300 mg and 600 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to oxcarbazepine, any of the components of Oxtellar XR, or to eslicarbazepine acetate ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hyponatremia:Monitor sodium as recommended. ( 5.1)
- Cross Hypersensitivity Reaction to Carbamazepine:Discontinue immediately if hypersensitivity occurs ( 5.3)
- Serious Dermatological Reactions:Discontinue if observed ( 5.4)
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation:Monitor for symptoms ( 5.5)
- Withdrawal ofOxtellar XR ®:Withdrawal gradually ( 5.6)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic symptoms (DRESS)/Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity:Discontinue if suspected ( 5.7)
- Hematologic Reactions:Discontinue if suspected ( 5.8)
- Risk of Seizure Aggravation:Discontinue if occurs ( 5.10)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most commonly observed (≥5% and more frequent than placebo) adverse reactions in adults were dizziness, somnolence, headache, balance disorder, tremor, vomiting, diplopia, asthenia, and fatigue ( 6.1).
Adverse reactions in pediatric patients are similar to those seen in adult patients.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Supernus, Inc. at (1-866-398-0833) or contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, and Phenobarbital:Coadministration decreased blood levels of an active metabolite of Oxtellar XR ®: Greater dosage of Oxtellar XR ®may be required ( 2.5, 7.2).
- Oral Contraceptives: Advise patients that Oxtellar XR ®may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Additional non-hormonal forms of contraception are recommended. ( 7.3)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy:May cause fetal harm. ( 5.9, 8.1).
- Severe Hepatic Impairment:Not recommended ( 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2018
Related/similar drugs
gabapentin, clonazepam, pregabalin, lamotrigine, diazepam, Lyrica, topiramateFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Oxtellar XR
Oxtellar XR ®is indicated for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 6 years of age and older.
2. Oxtellar XR Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Administer Oxtellar XR ®as a single daily dose taken on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or at least 2 hours after meals) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . If Oxtellar XR ®is taken with food, adverse reactions are more likely to occur because of increased peak levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Swallow Oxtellar XR ®tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew the tablets. For ease of swallowing in pediatric patients or patients with difficulty swallowing, achieve daily dosages with multiples of appropriate lower strength tablets (e.g., 150 mg tablets).
2.3 Dosage Modifications in Adult Patients with Renal Impairment
In adult patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute), initiate Oxtellar XR ®at one-half the usual starting dosage (300 mg/day). Subsequent dosage increases can be made at weekly intervals in increments of 300 mg to 450 mg/day to achieve the desired clinical response [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications in Geriatric Patients
In geriatric patients, consider starting at a lower dosage (300 mg or 450 mg/day). Subsequent dosage increases can be made at weekly intervals in increments of 300 mg to 450 mg/day to achieve the desired clinical effect [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
2.5 Dosage Modification with Concomitant Use of Strong CYP3A4 Enzyme Inducers or UGT Enzyme Inducers
Strong CYP3A4 inducers, including enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin, and UGT inducers (e.g., rifampin) decrease exposure to 10-monohydroxy derivative (MHD), the active metabolite [see Drug Interactions (7.2)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Dosage adjustment of Oxtellar XR may be required after initiation, dosage modification, or discontinuation of such inducers. Dosage increases of Oxtellar XR may be necessary with concomitant use. Consider initiating at 900 mg once daily for adults and 12 to 15 mg/kg orally once daily (not to exceed 900 mg per day in the first week) in pediatric patients.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release tablets:
- 150 mg: yellow modified-oval shaped with "150" printed on one side
- 300 mg: brown modified-oval shaped with "300" printed on one side
- 600 mg: brownish red modified-oval shaped with "600" printed on one side
4. Contraindications
Oxtellar XR ®is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to oxcarbazepine, to any of the components of Oxtellar XR, or to eslicarbazepine acetate. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hyponatremia
Clinically significant hyponatremia (sodium <125 mmol/L) may develop during Oxtellar XR use. Serum sodium levels less than 125 mmol/L have occurred in immediate-release oxcarbazepine-treated patients generally in the first three months of treatment. However, clinically significant hyponatremia may develop more than a year after initiating therapy. Clinically significant hyponatremia (sodium <125 mmol/L) may develop during Oxtellar XR ®use. Serum sodium levels less than 125 mmol/L have occurred in immediate-release oxcarbazepine-treated patients generally in the first three months of treatment. However, clinically significant hyponatremia may develop more than a year after initiating therapy.
Most immediate-release oxcarbazepine-treated patients who developed hyponatremia were asymptomatic in clinical trials. However, some of these patients had their dosage reduced, discontinued, or had their fluid intake restricted for hyponatremia. Serum sodium levels returned toward normal when the dosage was reduced or discontinued, or when the patient was treated conservatively (e.g., fluid restriction). Cases of symptomatic hyponatremia and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) have been reported during post-marketing use of immediate-release oxcarbazepine.
Among treated patients in a controlled trial of adjunctive therapy with Oxtellar XR in 366 adults with complex partial seizures, 1 patient receiving 2400 mg experienced a severe reduction in serum sodium (117 mEq/L) requiring discontinuation from treatment, while 2 other patients receiving 1200 mg experienced serum sodium concentrations low enough (125 and 126 mEq/L) to require discontinuation from treatment. The overall incidence of clinically significant hyponatremia in patients treated with Oxtellar XR was 1.2%, although slight shifts in serum sodium concentrations from Normal to Low (<135 mEq/L) were observed for the 2400 mg (6.5%) and 1200 mg (9.8%) groups compared to placebo (1.7%). Among treated patients in a controlled trial of adjunctive therapy with Oxtellar XR ®in 366 adults with complex partial seizures, 1 patient receiving 2400 mg experienced a severe reduction in serum sodium (117 mEq/L) requiring discontinuation from treatment, while 2 other patients receiving 1200 mg experienced serum sodium concentrations low enough (125 and 126 mEq/L) to require discontinuation from treatment. The overall incidence of clinically significant hyponatremia in patients treated with Oxtellar XR ®was 1.2%, although slight shifts in serum sodium concentrations from Normal to Low (<135 mEq/L) were observed for the 2400 mg (6.5%) and 1200 mg (9.8%) groups compared to placebo (1.7%).
Measure serum sodium concentrations if patients develop symptoms of hyponatremia (e.g., nausea, malaise, headache, lethargy, confusion, obtunded consciousness, or increase in seizure frequency or severity). Consider measurement of serum sodium concentrations during treatment with Oxtellar XR , particularly if the patient receives concomitant medications known to decrease serum sodium levels (for example, drugs associated with inappropriate ADH secretion). Measure serum sodium concentrations if patients develop symptoms of hyponatremia (e.g., nausea, malaise, headache, lethargy, confusion, obtunded consciousness, or increase in seizure frequency or severity). Consider measurement of serum sodium concentrations during treatment with Oxtellar XR ®, particularly if the patient receives concomitant medications known to decrease serum sodium levels (for example, drugs associated with inappropriate ADH secretion).
5.2 Anaphylactic Reactions and Angioedema
Rare cases of anaphylaxis and angioedema involving the larynx, glottis, lips and eyelids have been reported in patients after taking the first or subsequent doses of immediate-release oxcarbazepine. Angioedema associated with laryngeal edema can be fatal. If a patient develops any of these reactions after treatment with Oxtellar XR ®, discontinue the drug and initiate an alternative treatment. Do not rechallenge these patients with Oxtellar XR ®.
5.3 Cross Hypersensitivity Reaction to Carbamazepine
Approximately 25% to 30% of patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to carbamazepine will experience hypersensitivity reactions with Oxtellar XR ®. For this reason, patients should be specifically questioned about any prior experience with carbamazepine, and patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to carbamazepine should ordinarily be treated with Oxtellar XR ®only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. Discontinue Oxtellar XR ®immediately if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity develop [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.7)].
5.4 Serious Dermatological Reactions
Serious dermatological reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have occurred in both children and adults treated with immediate-release oxcarbazepine use. The median time of onset for reported cases was 19 days. Such serious skin reactions may be life threatening, and some patients have required hospitalization with very rare reports of fatal outcome. Recurrence of the serious skin reactions following rechallenge with immediate-release oxcarbazepine has also been reported.
The reporting rate of TEN and SJS associated with immediate-release oxcarbazepine use, which is generally accepted to be an underestimate due to underreporting, exceeds the background incidence rate estimates by a factor of 3- to 10-fold. Estimates of the background incidence rate for these serious skin reactions in the general population range between 0.5 to 6 cases per million-person years. Therefore, if a patient develops a skin reaction while taking Oxtellar XR ®, consider discontinuing Oxtellar XR ®use and prescribing another AED.
5.5 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including Oxtellar XR ®, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Monitor patients treated with any AED for any indication for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5-100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Table 2 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
| Indication | Placebo Patients with Events per 1000 Patients | Drug Patients with Events per 1000 Patients | Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence in Placebo Patients | Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events per 1000 Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | 1.0 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
| Psychiatric | 5.7 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| Other | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
| Total | 2.4 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing Oxtellar XR ®or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during Oxtellar XR ®treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
5.6 Withdrawal of AEDs
As with most AEDs, Oxtellar XR ®should be withdrawn gradually because of the risk of increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus. But if withdrawal is needed because of a serious adverse event, rapid discontinuation can be considered.
5.7 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as multi-organ hypersensitivity, has occurred with immediate-release oxcarbazepine. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling, in associated with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematologic abnormalities, myocaraditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. This disorder is variable in its expression, and other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestatios of hypersensitivity (e.g., fever, lymphadenopathy) may be present even though rash is not evident. Oxtellar XR ®should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established.
5.8 Hematologic Reactions
Rare reports of pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and leukopenia have been seen in patients treated with immediate-release oxcarbazepine during post-marketing experience. Discontinuation of Oxtellar XR ®should be considered if any evidence of these hematologic reactions develops.
5.9 Risk of Seizures in the Pregnant Patient
Due to physiological changes during pregnancy, plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of oxcarbazepine, the 10-monohydroxy derivative (MHD), may gradually decrease throughout pregnancy. Monitor patients carefully during pregnancy and through the postpartum period because MHD concentrations may increase after delivery.
5.10 Risk of Seizure Aggravation
Exacerbation of or new onset primary generalized seizures has been reported with immediate-release oxcarbazepine. The risk of aggravation of primary generalized seizures is seen especially in children but may also occur in adults. In case of seizure aggravation, Oxtellar XR ®should be discontinued.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described in other sections of the labeling:
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions and Angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cross Hypersensitivity Reaction to Carbamazepine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Serious Dermatological Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Withdrawal of AEDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multi-Organ Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hematologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Risk of Seizures in the Pregnant Patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety data presented below are from 384 patients with partial-onset seizures who received Oxtellar XR ®(366 adults and 18 pediatric patients) with concomitant AEDs.
In addition, safety data presented below are from a total of 2288 patients with seizure disorders treated with immediate-release oxcarbazepine; 1832 were adults and 456 were pediatric patients.
6.2 Postmarketing and Other Experience
The following adverse reactions have been observed in named patient programs or post-marketing experience with immediate-release oxcarbazepine or Oxtellar XR ®. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole:multi-organ hypersensitivity disorders characterized by features such as rash, fever, lymphadenopathy, abnormal liver function tests, eosinophilia, and arthralgia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Cardiovascular System:atrioventricular block
Digestive System:pancreatitis and/or lipase and/or amylase increase
Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems:aplastic anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
Immune System Disorders: anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: hypothyroidism and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue dDsorders:erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)], Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP)
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders: There have been reports of decreased bone mineral density, osteoporosis and fractures in patients on long-term therapy with immediate-release oxcarbazepine.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Oxtellar XR on Other Drugs
It is recommended that the plasma levels of phenytoin be monitored during the period of Oxtellar XR titration and dosage modification [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A decrease in the dosage of phenytoin may be required.
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on Oxtellar XR
If Oxtellar XR and strong CYP3A4 inducers or UGT inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin and phenobarbital) are administered concurrently, it is recommended that the plasma levels of MHD be monitored during the period of Oxtellar XR titration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dosage adjustment of Oxtellar XR may be required after initiation, dosage modification, or discontinuation of such inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Oxtellar XR ®in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older for the treatment of partial-onset seizures is supported by:
1) An adequate and well-controlled safety and efficacy study of Oxtellar XR ®in adults that included pharmacokinetic sampling [see Clinical Studies (14.1)],
2) A pharmacokinetic study of Oxtellar XR ®in pediatric patients, which included patients 6 to less than 17 years of age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)],
3) Safety and efficacy studies with the immediate-release formulation in adults and pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Oxtellar XR ®is not approved for pediatric patients less than 6 years of age because the size of the tablets are inappropriate for younger children.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Following administration of single (300 mg) and multiple (600 mg/day) doses of immediate-release oxcarbazepine to elderly volunteers (60-82 years of age), the maximum plasma concentrations and AUC values of MHD were 30%-60% higher than in younger volunteers (18-32 years of age). Comparisons of creatinine clearance in young and elderly volunteers indicate that the difference was due to age-related reductions in creatinine clearance. Consider starting at a lower dosage and lower titration [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . Close monitoring of sodium levels is required in elderly patients at risk for hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
There is a linear correlation between creatinine clearance and the renal clearance of MHD [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
The pharmacokinetics of Oxtellar XR ®has not been evaluated in patients with renal impairment. In patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) given immediate-release oxcarbazepine, the elimination half-life of MHD was prolonged with a corresponding two-fold increase in AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In these patients initiate Oxtellar XR ®at a lower starting dosage and increase, if necessary, at a slower than usual rate until the desired clinical response is achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
In patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis, it is recommended that immediate-release oxcarbazepine be used instead of Oxtellar XR ®.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
11. Oxtellar XR Description
Oxtellar XR ®is an antiepileptic drug (AED). Oxtellar XR ®extended-release tablets contain oxcarbazepine for once-a-day oral administration. Oxcarbazepine is 10,11-Dihydro-10-oxo-5H-dibenz[b,f]-azepine-5-carboxamide, and its structural formula is
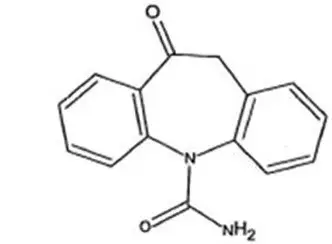
Oxcarbazepine is off-white to yellow crystalline powder.
Oxcarbazepine is sparingly soluble in chloroform (30-100 g/L). In aqueous media over pH range 1 to 8, oxcarbazepine is practically insoluble and its solubility is 40 mg/L (0.04 g/L) at pH 7.0, 25°C. The molecular formula is C 15H 12N 2O 2and its molecular weight is 252.27.
Oxtellar XR ®tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, yellow iron oxide (150 mg, 300 mg tablets only), red iron oxide (300 mg, 600 mg tablets only), black iron oxide (300 mg tablet only), magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide. Each tablet is printed on one side with edible black ink.
10. Overdosage
10.1 Human Overdose Experience
Isolated cases of overdose with immediate-release oxcarbazepine have been reported. The maximum dose taken was approximately 48,000 mg. All patients recovered with symptomatic treatment. Nausea, vomiting, somnolence, aggression, agitation, hypotension, and tremor each occurred in more than one patient. Coma, confusional state, convulsion, dyscoordination, depressed level of consciousness, diplopia, dizziness, dyskinesia, dyspnea, QT prolongation, headache, miosis, nystagmus, overdose, decreased urine output, and blurred vision also occurred.
12. Oxtellar XR - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The pharmacological activity of Oxtellar XR ®is primarily exerted through the 10-monohydroxy metabolite (MHD) of oxcarbazepine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The precise mechanism by which oxcarbazepine and MHD exert their antiseizure effect is unknown; however, in vitro electrophysiological studies indicate that they produce blockade of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, resulting in stabilization of hyperexcited neural membranes, inhibition of repetitive neuronal firing, and diminution of propagation of synaptic impulses. These actions are thought to be important in the prevention of seizure spread in the intact brain. In addition, increased potassium conductance and modulation of high-voltage activated calcium channels may contribute to the anticonvulsant effects of the drug. No significant interactions of oxcarbazepine or MHD with brain neurotransmitter or modulator receptor sites have been demonstrated.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Oxcarbazepine and its active metabolite (MHD) exhibit anticonvulsant properties in animal seizure models. They protected rodents against electrically induced tonic extension seizures and, to a lesser degree, chemically induced clonic seizures, and abolished or reduced the frequency of chronically recurring focal seizures in Rhesus monkeys with aluminum implants. No development of tolerance (i.e., attenuation of anticonvulsive activity) was observed in the maximal electroshock test when mice and rats were treated daily for five days and four weeks, respectively, with oxcarbazepine or MHD.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, oxcarbazepine is absorbed and extensively metabolized to its pharmacologically active 10-monohydroxy metabolite (MHD), which is responsible for most antiepileptic activity.
In clinical studies of Oxtellar XR ®, the elimination half-life of oxcarbazepine was between 7 and 11 hours; the elimination half-life of MHD is between 9 and 11 hours.
In a mass balance study in humans, only 2% of total radioactivity in plasma after administration of immediate-release oxcarbazepine was due to unchanged oxcarbazepine, with approximately 70% present as MHD, and the remainder attributable to minor metabolites.
14. Clinical Studies
Oxtellar XR ®has been evaluated as adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in adults. The use of Oxtellar XR ®for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is based on adequate and well-controlled studies of Oxtellar XR ®in adults, along with clinical trials of immediate-release oxcarbazepine in pediatric patients, and on pharmacokinetic evaluations of the use of Oxtellar XR ®in pediatric patients.
14.1 Oxtellar XR ®Primary Trial
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, three-arm, parallel-group study (Study 1) in male and female adults with refractory partial-onset seizures (18 to 65 years of age, inclusive) was performed to examine the safety and efficacy of Oxtellar XR ®.
Patients had at least three partial-onset seizures per 28 days during an 8 week Baseline Period. Subjects were receiving treatment with at least one to three antiepileptic drugs and were on stable treatment for a minimum of 4 weeks. Subjects with a diagnosis other than partial-onset seizures were excluded.
The study included an 8 week Baseline Period, followed by a Treatment Period, which included a 4 week Titration Phase followed by a 12 week Maintenance Phase. The primary endpoint of the study was median percentage change from baseline in seizure frequency per 28 days during the treatment period relative to the baseline period. The criterion for statistical significance was p<0.05. A total of 366 patients were enrolled at 88 sites in North America and Eastern Europe. Subjects were randomized to one of three treatment groups and took Oxtellar XR ®(1200 or 2400 mg/day) or placebo.
Table 6 presents the primary efficacy results by treatment group.
| Median seizure frequency during 8-week baseline period (per 28 days) | Median seizure frequency during 16-week treatment period (per 28 days) | Median percent change in seizure frequency | Seizure frequency percent change effect size | P value vs placebo * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Placebo
(N=121) | 7.0 | 5.0 | -28.7 % | ||
| Oxtellar XR
®
1200mg/day (N=122) | 6.0 | 4.3 | -38.2 % | 9.5% | 0.078 |
| Oxtellar XR
®
2400mg/day (N=123) | 6.0 | 3.7 | -42.9 % | 14.2% | 0.003 |
Although the 1200 mg/day-placebo contrast did not reach statistical significance, concentration-response analyses reveal that the 1200 mg/day dosage is an effective dosage.
14.2 Immediate-Release Oxcarbazepine Adjunctive Therapy Trials
The effectiveness of immediate-release oxcarbazepine as an adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in adults was demonstrated at dosages of 600mg/day, 1200mg/day, and 2400mg/day (divided twice daily) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. All dosages resulted in a statistically significant reduction in seizure frequency when compared to placebo (p<0.05).
The effectiveness of immediate-release oxcarbazepine in dosages of 30-46 mg/kg/day, depending on baseline weight, as an adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients, including patients 6 to less than 17 years of age, was studied in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Oxcarbazepine in the single weight-based dosage group resulted in a statistically significant reduction in seizure frequency when compared to placebo (p<0.05).
16. How is Oxtellar XR supplied
16.1 Dosage Form Supplied
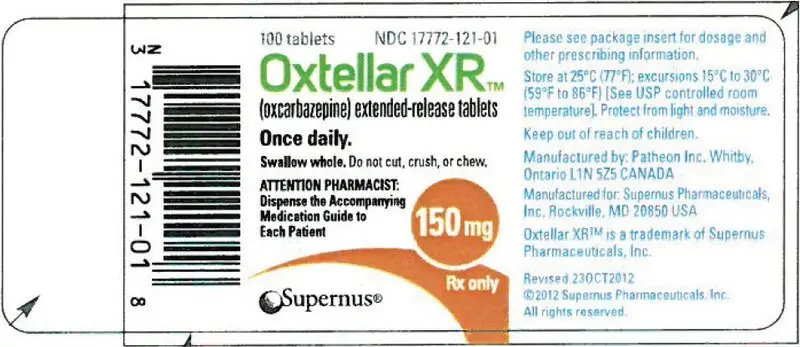
150 mg (yellow modified-oval shaped tablet printed "150" on one side with edible black ink).
| Bottles of 100 tablets | NDC 17772-121-01 |
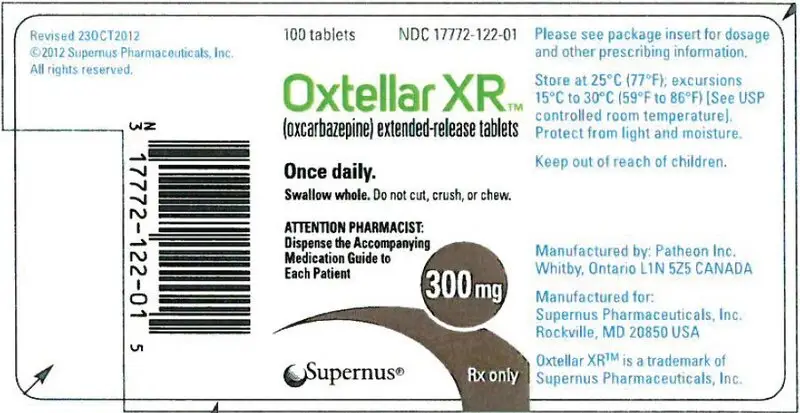
300 mg (brown modified-oval shaped tablet printed "300" on one side with edible black ink).
| Bottles of 100 tablets | NDC 17772-122-01 |
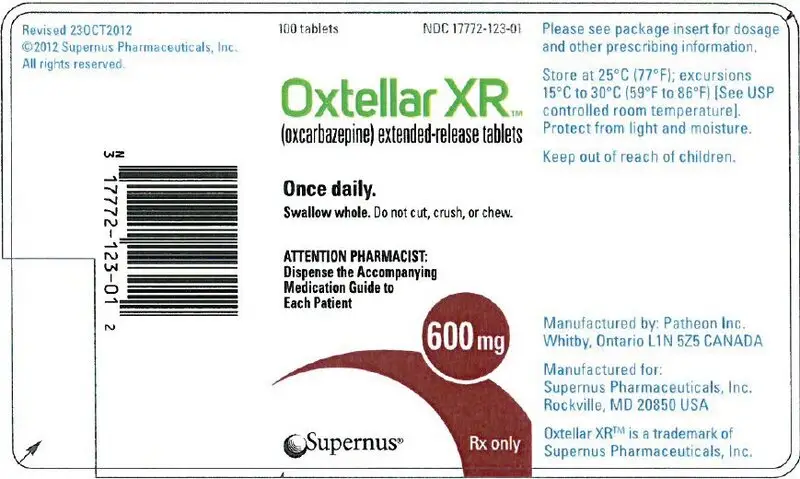
600 mg (brownish red modified-oval shaped tablet printed "600" on one side with edible black ink).
| Bottles of 100 tablets | NDC 17772-123-01 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg Tablet Bottle Label
100 tablets
NDC 17772-121-01
Oxtellar XR
™
(oxcarbazepine) extended-release tablets
Once daily.
Swallow whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew.
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense the Accompanying
Medication Guide to
Each Patient
150 mg
Rx only
Supernus ®
| OXTELLAR XR
oxcarbazepine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OXTELLAR XR
oxcarbazepine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OXTELLAR XR
oxcarbazepine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (363066452) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jubilant Pharmova Limited | 650351666 | api manufacture(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , pack(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , label(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Element Materials Technology Canada Inc. | 243681538 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curia Indiana, LLC | 020593403 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Chemical Laboratories | 071344167 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| R.D. Laboratories | 603223066 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon, Inc. (Patheon TRO) | 240769596 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Pharma Solutions | 014167995 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Laboratories, Inc. | 208526590 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon, Inc. (Patheon WRO) | 205475333 | manufacture(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , label(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , pack(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon, Inc. | 053217022 | pack(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) , label(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 363066452 | analysis(17772-121, 17772-122, 17772-123) | |