Drug Detail:Pediapred (Prednisolone [ pred-nis-oh-lone ])
Drug Class: Glucocorticoids
Pediapred Oral Solution Description
PEDIAPRED® (prednisolone sodium phosphate) Oral Solution is a dye free, colorless to light straw colored, raspberry flavored solution. Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) of PEDIAPRED® contains 6.7 mg prednisolone sodium phosphate (5 mg prednisolone base) in a palatable, aqueous vehicle. PEDIAPRED® also contains dibasic sodium phosphate, edetate disodium, methylparaben, purified water, sodium biphosphate, sorbitol, natural and artificial raspberry flavor. Prednisolone sodium phosphate occurs as white or slightly yellow, friable granules or powder. It is freely soluble in water; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol and in chloroform; and very slightly soluble in acetone and in dioxane. The chemical name of prednisolone sodium phosphate is: pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11,17-dihydroxy-21-(phosphonooxy)-,disodium salt,(11β)-. The empirical formula is C21H27Na2O8P; the molecular weight is 484.39. Its chemical structure is:
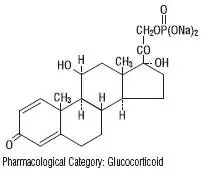
Pharmacological Category: Glucocorticoid
Pediapred Oral Solution - Clinical Pharmacology
Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Their synthetic analogs are primarily used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems. Prednisolone is a synthetic adrenocortical steroid drug with predominantly glucocorticoid properties. Some of these properties reproduce the physiological actions of endogenous glucocorticosteroids, but others do not necessarily reflect any of the adrenal hormones’ normal functions; they are seen only after administration of large therapeutic doses of the drug. The pharmacological effects of prednisolone which are due to its glucocorticoid properties include: promotion of gluconeogenesis; increased deposition of glycogen in the liver; inhibition of the utilization of glucose; anti-insulin activity; increased catabolism of protein; increased lipolysis; stimulation of fat synthesis and storage; increased glomerular filtration rate and resulting increase in urinary excretion of urate (creatinine excretion remains unchanged); and increased calcium excretion.
Depressed production of eosinophils and lymphocytes occurs, but erythropoiesis and production of polymorphonuclear leukocytes are stimulated. Inflammatory processes (edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilatation, migration of leukocytes and phagocytosis) and the later stages of wound healing (capillary proliferation, deposition of collagen, cicatrization) are inhibited.
Prednisolone can stimulate secretion of various components of gastric juice. Suppression of the production of corticotropin may lead to suppression of endogenous corticosteroids. Prednisolone has slight mineralocorticoid activity, whereby entry of sodium into cells and loss of intracellular potassium is stimulated. This is particularly evident in the kidney, where rapid ion exchange leads to sodium retention and hypertension.
Prednisolone is rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. PEDIAPRED® Oral Solution produces a 14% higher peak plasma level of prednisolone which occurs 20% faster than that seen with tablets. Prednisolone is 70-90% protein bound in the plasma and it is eliminated from the plasma with a half-life of 2 to 4 hours. It is metabolized mainly in the liver and excreted in the urine as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates.
The systemic availability, metabolism and elimination of prednisolone after administration of single weight-based doses (0.8 mg/kg) of intravenous (IV) prednisolone and oral prednisone were reported in a small study of 19 young (23 to 34 years) and 12 elderly (65 to 89 years) subjects. Results showed that the systemic availability of total and unbound prednisolone, as well as interconversion between prednisolone and prednisone were independent of age. The mean unbound fraction of prednisolone was higher, and the steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of unbound prednisolone was reduced in elderly patients. Plasma prednisolone concentrations were higher in elderly subjects, and the higher AUCs of total and unbound prednisolone were most likely reflective of an impaired metabolic clearance, evidenced by reduced fractional urinary clearance of 6β-hydroxyprednisolone. Despite these findings of higher total and unbound prednisolone concentrations, elderly subjects had higher AUCs of cortisol, suggesting that the elderly population is less sensitive to suppression of endogenous cortisol or their capacity for hepatic inactivation of cortisol is diminished.
Related/similar drugs
Kesimpta, Betaseron, prednisone, albuterol, doxycycline, fluticasone, dexamethasoneIndications and Usage for Pediapred Oral Solution
PEDIAPRED® is indicated in the following conditions:
For the treatment of acute leukemia and aggressive lymphomas in adults and children.
Precautions
The lowest possible dose of corticosteroid should be used to control the condition under treatment, and when reduction in dosage is possible, the reduction should be gradual.
Since complications of treatment with glucocorticoids are dependent on the size of the dose and the duration of treatment, a risk/benefit decision must be made in each individual case as to dose and duration of treatment and as to whether daily or intermittent therapy should be used.
There is an enhanced effect of corticosteroids in patients with hypothyroidism and in those with cirrhosis.
Kaposi’s sarcoma has been reported to occur in patients receiving corticosteroid therapy, most often for chronic conditions. Discontinuation of corticosteroids may result in clinical improvement.
Cardio-renal
As sodium retention with resultant edema and potassium loss may occur in patients receiving corticosteroids, these agents should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, congestive heart failure, or renal insufficiency.
Drug-induced secondary adrenocortical insufficiency may be minimized by gradual reduction of dosage. This type of relative insufficiency may persist for months after discontinuation of therapy; therefore, in any situation of stress occurring during that period, hormone therapy should be reinstituted. Since mineralocorticoid secretion may be impaired, salt and/or a mineralocorticoid should be administered concurrently.
Steroids should be used with caution in nonspecific ulcerative colitis, if there is a probability of impending perforation, abscess or other pyogenic infection; diverticulitis; fresh intestinal anastomoses; active or latent peptic ulcer.
Signs of peritoneal irritation following gastrointestinal perforation in patients receiving corticosteroids may be minimal or absent.
Corticosteroids decrease bone formation and increase bone resorption both through their effect on calcium regulation (i.e., decreasing absorption and increasing excretion) and inhibition of osteoblast function. This, together with a decrease in the protein matrix of the bone secondary to an increase in protein catabolism, and reduced sex hormone production, may lead to inhibition of bone growth in children and adolescents and the development of osteoporosis at any age. Special consideration should be given to patients at increased risk of osteoporosis (i.e., postmenopausal women) before initiating corticosteroid therapy.
Although controlled clinical trials have shown corticosteroids to be effective in speeding the resolution of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, they do not show that they affect the ultimate outcome or natural history of the disease. The studies do show that relatively high doses of corticosteroids are necessary to demonstrate a significant effect. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Intraocular pressure may become elevated in some individuals. If steroid therapy is continued for more than 6 weeks, intraocular pressure should be monitored.
Patients should be warned not to discontinue the use of PEDIAPRED® (prednisolone sodium phosphate) Oral Solution abruptly or without medical supervision, to advise any medical attendants that they are taking PEDIAPRED® and to seek medical advice at once should they develop fever or other signs of infection.
Persons who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chicken pox or measles. Patients should also be advised that if they are exposed, medical advice should be sought without delay.
Drugs such as barbiturates, phenytoin, ephedrine, and rifampin, which induce hepatic microsomal drug metabolizing enzyme activity may enhance metabolism of prednisolone and require that the dosage of PEDIAPRED® be increased.
Increased activity of both cyclosporin and corticosteroids may occur when the two are used concurrently. Convulsions have been reported with this concurrent use.
Estrogens may decrease the hepatic metabolism of certain corticosteroids thereby increasing their effect.
Ketoconazole has been reported to decrease the metabolism of certain corticosteroids by up to 60% leading to an increased risk of corticosteroid side effects.
Coadministration of corticosteroids and warfarin usually results in inhibition of response to warfarin, although there have been some conflicting reports. Therefore, coagulation indices should be monitored frequently to maintain the desired anticoagulant effect.
Concomitant use of aspirin (or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents) and corticosteroids increases the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Aspirin should be used cautiously in conjunction with corticosteroids in hypoprothrombinemia. The clearance of salicylates may be increased with concurrent use of corticosteroids.
When corticosteroids are administered concomitantly with potassium-depleting agents (i.e., diuretics, amphotericin-B), patients should be observed closely for development of hypokalemia. Patients on digitalis glycosides may be at increased risk of arrhythmias due to hypokalemia.
Concomitant use of anticholinesterase agents and corticosteroids may produce severe weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis. If possible, anticholinesterase agents should be withdrawn at least 24 hours before initiating corticosteroid therapy.
Due to inhibition of antibody response, patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy may exhibit a diminished response to toxoids and live or inactivated vaccines. Corticosteroids may also potentiate the replication of some organisms contained in live attenuated vaccines. If possible, routine administration of vaccines or toxoids should be deferred until corticosteroid therapy is discontinued.
Because corticosteroids may increase blood glucose concentrations, dosage adjustments of antidiabetic agents may be required.
Corticosteroids may suppress reactions to skin tests.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Cardiovascular: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in premature infants.
Metabolic: Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
Ophthalmic: Exophthalmos; glaucoma; increased intraocular pressure; posterior subcapsular cataracts.
Other: Increased appetite; malaise; nausea; weight gain.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Royal Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-510-3401 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Pediapred Oral Solution Dosage and Administration
The initial dosage of PEDIAPRED® may vary from 5 mL to 60 mL (5 to 60 mg prednisolone base) per day depending on the specific disease entity being treated. In situations of less severity, lower doses will generally suffice while in selected patients higher initial doses may be required. The initial dosage should be maintained or adjusted until a satisfactory response is noted. If after a reasonable period of time, there is a lack of satisfactory clinical response, PEDIAPRED® should be discontinued and the patient placed on other appropriate therapy. IT SHOULD BE EMPHASIZED THAT DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE UNDER TREATMENT AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT. After a favorable response is noted, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial drug dosage in small decrements at appropriate time intervals until the lowest dosage which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached. It should be kept in mind that constant monitoring is needed in regard to drug dosage. Included in the situations which may make dosage adjustments necessary are changes in clinical status secondary to remissions or exacerbations in the disease process, the patient’s individual drug responsiveness, and the effect of patient exposure to stressful situations not directly related to the disease entity under treatment; in this latter situation it may be necessary to increase the dosage of PEDIAPRED® for a period of time consistent with the patient’s condition. If after long term therapy the drug is to be stopped, it is recommended that it be withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly.
In the treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, daily doses of 200 mg of prednisolone for a week followed by 80 mg every other day or 4 to 8 mg dexamethasone every other day for one month have been shown to be effective.
In pediatric patients, the initial dose of PEDIAPRED® may vary depending on the specific disease entity being treated. The range of initial doses is 0.14 to 2 mg/kg/day in three or four divided doses (4 to 60 mg/m2bsa/day).
The standard regimen used to treat nephrotic syndrome in pediatric patients is 60 mg/m2/day given in three divided doses for 4 weeks, followed by 4 weeks of single dose alternate-day therapy at 40 mg/m2/day.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) recommended dosing for systemic prednisone, prednisolone or methylprednisolone in children whose asthma is uncontrolled by inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators is 1-2 mg/kg/day in single or divided doses. It is further recommended that short course, or “burst” therapy, be continued until a child achieves a peak expiratory flow rate of 80% of his or her personal best or symptoms resolve. This usually requires 3 to 10 days of treatment, although it can take longer. There is no evidence that tapering the dose after improvement will prevent a relapse.
For the purpose of comparison, 5 mL of prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution (33.6 mg prednisolone sodium phosphate) is equivalent to the following milligram dosage of the various glucocorticoids:
| Cortisone, 25 | Triamcinolone, 4 | Hydrocortisone, 20 | Paramethasone, 2 |
| Prednisolone, 5 | Betamethasone, 0.75 | Prednisone, 5 | Dexamethasone, 0.75 |
| Methylprednisolone, 4 |
These dose relationships apply only to oral or intravenous administration of these compounds. When these substances or their derivatives are injected intramuscularly or into joint spaces, their relative properties may be greatly altered.
| PEDIAPRED
prednisolone sodium phosphate solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Royal Pharmaceuticals (078374385) |
| Registrant - Seton Pharmaceuticals (828898002) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIKART, INC. | 030034847 | MANUFACTURE(68791-104) | |





