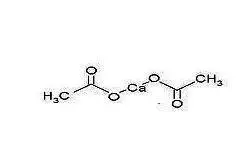
Drug Detail:Phoslo (Calcium acetate [ kal-see-um-as-e-tate ])
Drug Class: Minerals and electrolytes Phosphate binders
Highlights of Prescribing Information
(calcium acetate)
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PhosLo safely and effectively. see full prescribing information for PhosLo.
PhosLo (Calcium Acetate) CAPSULE for ORAL use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1990
Indications and Usage for Phoslo
- PhosLo® is a phosphate binder indicated for the reduction of serum phosphorus in patients with end stage renal disease. ( 1)
Phoslo Dosage and Administration
- Starting dose is 2 gelcaps with each meal. ( 2)
- Titrate the dose every 2-3 weeks until acceptable serum phosphorus level is reached. Most patients require 3-4 gelcaps with each meal. ( 2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Capsule: 667 mg calcium acetate gelcap. ( 3)
Contraindications
- Hypercalcemia. ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Treat mild hypercalcemia by reducing or interrupting PhosLo® and Vitamin D. Severe hypercalcemia may require hemodialysis and discontinuation of PhosLo®. ( 5.1)
- Hypercalcemia may aggravate digitalis toxicity. ( 5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common (>10%) adverse reactions are hypercalcemia, nausea, and vomiting. ( 6.1).
- In clinical studies, patients have occasionally experienced nausea during calcium acetate therapy. (
6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Medical Care North America at 1-800-323-5188 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- PhosLo® may decrease the bioavailability of tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones. ( 7)
- When clinically significant drug interactions are expected, administer the drug at least one hour before or at least three hours after PhosLo®, or consider monitoring blood levels of the drug. ( 7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2013
Related/similar drugs
calcium acetate, aluminum hydroxide, Phoslyra, AmphojelFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Phoslo
PhosLo® is a phosphate binder indicated to reduce serum phosphorus in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD).
2. Phoslo Dosage and Administration
The recommended initial dose of PhosLo® for the adult dialysis patient is 2 gelcaps with each meal. Increase the dose gradually to lower serum phosphorus levels to the target range, as long as hypercalcemia does not develop. Most patients require 3-4 gelcaps with each meal.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypercalcemia
Patients with end stage renal disease may develop hypercalcemia when treated with calcium, including calcium acetate (PhosLo®). Avoid the use of calcium supplements, including calcium-based nonprescription antacids, concurrently with PhosLo®.
An overdose of PhosLo may lead to progressive hypercalcemia, which may require emergency measures. Therefore, early in the treatment phase during the dosage adjustment period, monitor serum calcium levels twice weekly. Should hypercalcemia develop, reduce the PhosLo® dosage or discontinue the treatment, depending on the severity of hypercalcemia.
More severe hypercalcemia (Ca>12 mg/dL) is associated with confusion, delirium, stupor and coma. Severe hypercalcemia can be treated by acute hemodialysis and discontinuing PhosLo® therapy.
Mild hypercalcemia (10.5 to 11.9 mg/dL) may be asymptomatic or manifest as constipation, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Mild hypercalcemia is usually controlled by reducing the PhosLo® dose or temporarily discontinuing therapy. Decreasing or discontinuing Vitamin D therapy is recommended as well.
Chronic hypercalcemia may lead to vascular calcification and other soft-tissue calcification. Radiographic evaluation of suspected anatomical regions may be helpful in early detection of soft tissue calcification. The long term effect of PhosLo® on the progression of vascular or soft tissue calcification has not been determined.
Hypercalcemia (>11 mg/dL) was reported in 16% of patients in a 3-month study of a solid dose formulation of calcium acetate; all cases resolved upon lowering the dose or discontinuing treatment.
Maintain the serum calcium-phosphorus (Ca x P) product below 55 mg 2/dL 2.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Hypercalcemia is discussed elsewhere [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical studies, calcium acetate has been generally well tolerated.
PhosLo® was studied in a 3-month, open-label, non-randomized study of 98 enrolled ESRD hemodialysis patients and in a two week double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study with 69 enrolled ESRD hemodialysis patients. Adverse reactions (>2% on treatment) from these trials are presented in Table 1.
| Preferred Term | Total adverse reactions reported for calcium acetate
n = 167 n (%) | 3-mo, open-label study of calcium acetate
n = 98 n (%) | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study of calcium acetate
n = 69 |
|
| Calcium acetate
n (%) | Placebo
n (%) |
|||
| Nausea | 6 (3.6) | 6 (6.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Vomiting | 4 (2.4) | 4 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Hypercalcemia | 21 (12.6) | 16 (16.3) | 5 (7.2) | 0 (0.0) |
Mild hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic or manifest itself as constipation, anorexia, neusea, and vomiting. More severe hypercalcemia is associated with confusion, delirium, stupor, and coma. Decreasing dialysate calcium concentration could reduce the incidence and severity of PhosLo®-induced hypercalcemia. Isolated cases of pruritus have been reported, which may represent allergic reactions.
7. Drug Interactions
The drug interaction of PhosLo® is characterized by the potential of calcium to bind to drugs with anionic functions (e.g., carboxyl and hydroxyl groups). PhosLo® may decrease the bioavailability of tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones via this mechanism.
There are no empirical data on avoiding drug interactions between calcium acetate or PhosLo® and most concomitant drugs. When administering an oral medication with PhosLo® where a reduction in the bioavailability of that medication would have a clinically significant effect on its safety or efficacy, administer the drug one hour before or three hours after PhosLo® or calcium acetate. Monitor blood levels of the concomitant drugs that have a narrow therapeutic range. Patients taking anti-arrhythmic medications for the control of arrhythmias and anti-seizure medications for the control of seizure disorders were excluded from the clinical trials with all forms of calcium acetate.
| PHOSLO
calcium acetate capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Fresenius Medical Care North America (958291411) |