Drug Detail:Ponvory (Ponesimod)
Drug Class: Selective immunosuppressants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
PONVORY ®(ponesimod) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.11) | 08/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Ponvory
PONVORY is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. ( 1)
Ponvory Dosage and Administration
- Assessments are required prior to initiating PONVORY ( 2.1)
- Titration is required for treatment initiation ( 2.2)
- The recommended maintenance dosage is 20 mg taken orally once daily ( 2.2)
- First-dose monitoring is recommended for patients with sinus bradycardia, first- or second-degree [Mobitz type I] atrioventricular (AV) block, or a history of myocardial infarction or heart failure ( 2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 6 mg, 7 mg, 8 mg, 9 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- In the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure ( 4)
- Presence of Mobitz type II second-degree, third-degree AV block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Infections: PONVORY may increase the risk of infections. Obtain a complete blood count (CBC) before initiating treatment. Monitor for infection during treatment and for 1–2 weeks after discontinuation. Do not start PONVORY in patients with active infection. ( 5.1)
- Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays: PONVORY may result in a transient decrease in heart rate; titration is required for treatment initiation. Check an electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess for preexisting cardiac conduction abnormalities before starting PONVORY. Consider cardiology consultation for conduction abnormalities or concomitant use with other drugs that decrease heart rate. ( 5.2, 7.2, 7.3)
- Respiratory Effects: May cause a decline in pulmonary function. Assess pulmonary function (e.g., spirometry) if clinically indicated. ( 5.3)
- Liver Injury: Discontinue if significant liver injury is confirmed. Obtain liver function tests before initiating PONVORY. ( 5.4)
- Increased Blood Pressure (BP): Monitor BP during treatment. ( 5.5)
- Cutaneous Malignancies:Periodic skin examination is recommended. ( 5.6)
- Fetal Risk: Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during and for 1 week after stopping PONVORY. ( 5.7)
- Macular Edema: An ophthalmic evaluation is recommended before starting treatment and if there is any change in vision while taking PONVORY. Diabetes mellitus and uveitis increase the risk. ( 5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 10%) are upper respiratory tract infection, hepatic transaminase elevation, and hypertension. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orwww.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Vaccines: Avoid live attenuatedvaccines during and for up to 1–2 weeks after treatment with PONVORY. ( 7.4)
- Strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 Inducers: Coadministration with PONVORY is not recommended. ( 7.5)
Use In Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment: PONVORY is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B and C). ( 8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2023
Related/similar drugs
Kesimpta, Betaseron, Copaxone, Aubagio, Gilenya, Tecfidera, AvonexFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Ponvory
PONVORY is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.
2. Ponvory Dosage and Administration
2.1 Assessments Prior to First Dose of PONVORY
Before initiation of treatment with PONVORY, assess the following:
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Treatment Initiation
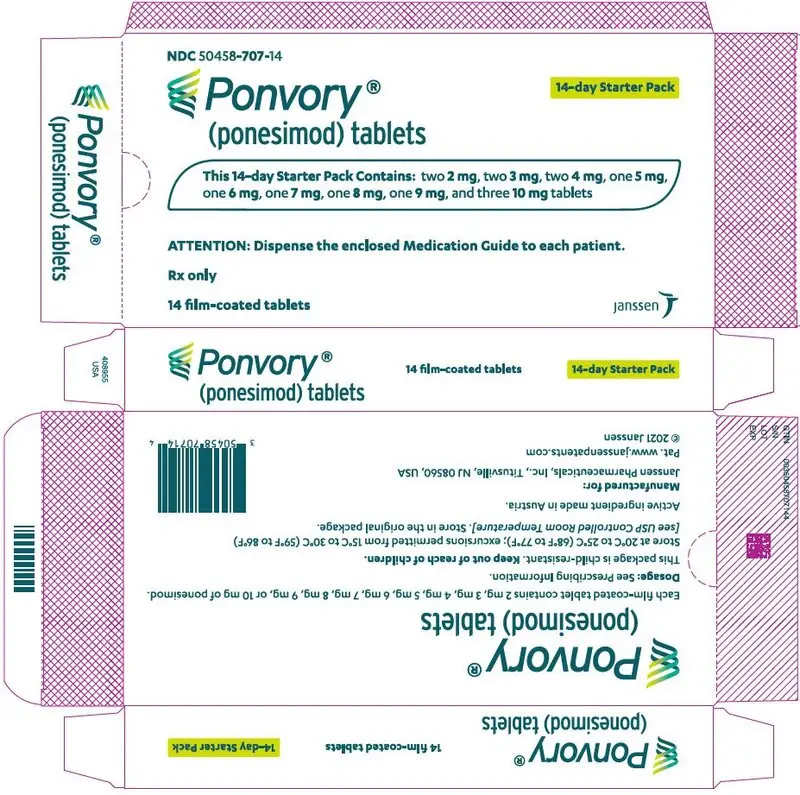
A starter pack must be used for patients initiating treatment with PONVORY [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.1)] . Initiate PONVORY treatment with a 14-day titration; start with one 2 mg tablet orally once daily and progress with the titration schedule as shown in Table 1 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
| Titration Day | Daily Dose |
|---|---|
| Days 1 and 2 | 2 mg |
| Days 3 and 4 | 3 mg |
| Days 5 and 6 | 4 mg |
| Day 7 | 5 mg |
| Day 8 | 6 mg |
| Day 9 | 7 mg |
| Day 10 | 8 mg |
| Day 11 | 9 mg |
| Days 12, 13, and 14 | 10 mg |
| Maintenance | Daily Dose |
|---|---|
| Day 15 and thereafter | 20 mg |
If dose titration is interrupted, missed dose instructions must be followed [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
2.3 First Dose Monitoring in Patients with Certain Preexisting Cardiac Conditions
Because initiation of PONVORY treatment results in a decrease in heart rate (HR), first-dose 4-hour monitoring is recommended for patients with sinus bradycardia [HR less than 55 beats per minute (bpm)], first- or second-degree [Mobitz type I] AV block, or a history of myocardial infarction or heart failure occurring more than 6 months prior to treatment initiation and in stable condition [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] .
2.4 Reinitiation of PONVORY After Treatment Interruption
Interruption during treatment, especially during titration, is not recommended; however:
- If
fewer than 4consecutive doses are missed:
- during titration: resume treatment with the first missed titration dose and resume the titration schedule at that dose and titration day.
- during maintenance: resume treatment with the maintenance dosage.
- If
4 or moreconsecutive doses are missed during titration or maintenance:
- treatment should be reinitiated with Day 1 of the titration regimen (new starter pack).
If treatment needs to be reinitiated with Day 1 of the titration regimen (new starter pack), complete first-dose monitoring in patients for whom it is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
PONVORY is available as round, biconvex, film-coated tablets for oral use. PONVORY contains ponesimod in the following dosage strengths (see Table 2):
| Tablet Strength | Tablet Color | Tablet Size | Tablet Debossing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | White | 5.0 mm | "2" on one side and an arch on the other side. |
| 3 mg | Red | 5.0 mm | "3" on one side and an arch on the other side. |
| 4 mg | Purple | 5.0 mm | "4" on one side and an arch on the other side. |
| 5 mg | Green | 8.6 mm | "5" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 6 mg | White | 8.6 mm | " 6" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 7 mg | Red | 8.6 mm | "7" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 8 mg | Purple | 8.6 mm | "8" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 9 mg | Brown | 8.6 mm | " 9" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 10 mg | Orange | 8.6 mm | "10" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
| 20 mg | Yellow | 8.6 mm | "20" on one side and an arch and an "A" on the other side. |
4. Contraindications
PONVORY is contraindicated in patients who:
- In the last 6 months, have experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III or IV heart failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Have presence of Mobitz type II second-degree, third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless patient has a functioning pacemaker [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Infections
Vaccinations
Patients without a healthcare professional confirmed history of chickenpox or without documentation of a full course of vaccination against VZV should be tested for antibodies to VZV before initiating PONVORY treatment. A full course of vaccination for antibody-negative patients with varicella vaccine is recommended prior to commencing treatment with PONVORY, following which initiation of treatment with PONVORY should be postponed for 4 weeks to allow the full effect of vaccination to occur.
No clinical data are available on the efficacy and safety of vaccinations in patients taking PONVORY. Vaccinations may be less effective if administered during PONVORY treatment.
If live attenuatedvaccine immunizations are required, administer at least 1 month prior to initiation of PONVORY. Avoid the use of live attenuatedvaccines during and for 1 to 2 weeks after treatment with PONVORY.
5.2 Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays
Since initiation of PONVORY treatment results in a transient decrease in heart rate and atrioventricular (AV) conduction delays, an up-titration scheme must be used to reach the maintenance dosage of PONVORY (20 mg) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] .
Study 1 did not include patients who had:
- A resting heart rate (HR) less than 50 beats per minute (bpm) on baseline electrocardiogram
- Myocardial infarction or unstable ischemic heart disease in the last 6 months
- Cardiac failure (New York Heart Association class III–IV) or presence of any severe cardiac disease
- Cardiac conduction or rhythm disorders (including sino-atrial heart block, symptomatic bradycardia, atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmia, cardiac arrest) either in history or observed at screening
- Mobitz Type II second degree AV block or higher-grade AV block observed at screening
- QTcF interval greater than 470 ms (females) and greater than 450 ms (males) observed at screening
- History of syncope associated with cardiac disorders
- Uncontrolled systemic arterial hypertension
5.3 Respiratory Effects
Dose-dependent reductions in forced expiratory volume over 1 second (FEV 1) and reductions in diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DL CO) were observed in PONVORY-treated patients mostly occurring in the first month after treatment initiation. In Study 1, the reduction from baseline in percent predicted FEV 1at 2 years was 8.3% in PONVORY-treated patients compared to 4.4% in patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg. In Study 1, 7 patients discontinued PONVORY because of pulmonary adverse events. There is insufficient information to determine the reversibility of the decrease in FEV 1or FVC after treatment discontinuation. PONVORY should be used with caution in patients with severe respiratory disease (i.e., pulmonary fibrosis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Spirometric evaluation of respiratory function should be performed during therapy with PONVORY if clinically indicated.
5.4 Liver Injury
Elevations of transaminases may occur in PONVORY-treated patients.
Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels, if not recently available (i.e., within last 6 months) before initiation of PONVORY.
In Study 1, elevations of ALT to 5-fold the upper limit of normal (ULN) or greater occurred in 4.6% of patients treated with PONVORY compared to 2.5% of patients who received teriflunomide 14 mg. Elevation of ALT to 3-fold the ULN or greater occurred in 17.3% of patients treated with PONVORY and 8.3% of patients treated with teriflunomide 14 mg. The median time to an elevation of 3-fold the ULN was 3 months. The majority (89%) of patients with ALT increases 3-fold or greater the ULN continued treatment with PONVORY with values returning to less than three times the ULN within approximately 2–4 weeks.
In Study 1, the discontinuation rate because of elevations in hepatic enzymes was 2.3% of patients treated with PONVORY and 1.9% of patients who received teriflunomide 14 mg.
Patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction, such as unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, rash with eosinophilia, or jaundice and/or dark urine during treatment, should have hepatic enzymes checked. PONVORY should be discontinued if significant liver injury is confirmed.
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A). PONVORY is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B and C, respectively) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
5.5 Increased Blood Pressure
In Study 1, PONVORY-treated patients had an average increase of 2.9 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure and 2.8 mm Hg in diastolic blood pressure compared to 2.8 mm Hg and 3.1 mm Hg in patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg, respectively. An increase in blood pressure with PONVORY was first detected after approximately 1 month of treatment initiation and persisted with continued treatment. Hypertensive events were reported as an adverse reaction in 10.1% of PONVORY-treated patients and in 9.0% of patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg. One patient treated with PONVORY experienced a hypertensive crisis but had evidence of longstanding hypertensive heart disease. Blood pressure should be monitored during treatment with PONVORY and managed appropriately.
5.6 Cutaneous Malignancies
Cases of basal cell carcinoma and other skin malignancies have been reported in patients treated with S1P receptor modulators, including PONVORY. In Study 1, the incidence of basal cell carcinoma was 0.4% in PONVORY-treated patients compared to 0.2% in patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg. Cases of other cutaneous malignancies, including melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma, have also been reported in patients treated with PONVORY and in patients treated with other S1P modulators.
Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer. Providers and patients are advised to monitor for suspicious skin lesions. If a suspicious skin lesion is observed, it should be promptly evaluated. As usual for patients with increased risk for skin cancer, exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using a sunscreen with a high protection factor. Concomitant phototherapy with UV-B radiation or PUVA-photochemotherapy is not recommended in patients taking PONVORY.
5.7 Fetal Risk
Based on animal studies, PONVORY may cause fetal harm [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] . Because it takes approximately 1 week to eliminate PONVORY from the body, women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to avoid pregnancy during and for 1 week after stopping PONVORY treatment.
5.8 Macular Edema
S1P receptor modulators, including PONVORY, have been associated with an increased risk of macular edema. In Study 1, macular edema was reported in 1.1% of PONVORY-treated patients compared to none of the patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg.
An ophthalmic evaluation of the fundus, including the macula, is recommended in all patients before starting treatment and again at any time if a patient reports any change in vision while on PONVORY therapy.
Continuation of PONVORY therapy in patients with macular edema has not been evaluated. A decision on whether PONVORY should be discontinued should take into account the potential benefits and risks for the individual patient.
5.9 Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Rare cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) have been reported in patients receiving a sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator. Such events have not been reported for PONVORY-treated patients in the development program. However, should a PONVORY-treated patient develop any unexpected neurological or psychiatric symptoms/signs (e.g., cognitive deficits, behavioral changes, cortical visual disturbances, or any other neurological cortical symptoms/signs), any symptom/sign suggestive of an increase of intracranial pressure, or accelerated neurological deterioration, the physician should promptly schedule a complete physical and neurological examination and should consider an MRI. Symptoms of PRES are usually reversible but may evolve into ischemic stroke or cerebral hemorrhage. Delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to permanent neurological sequelae. If PRES is suspected, PONVORY should be discontinued.
5.10 Unintended Additive Immunosuppressive Effects From Prior Treatment With Immunosuppressive or Immune-Modulating Therapies
When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, the half-life and mode of action of these drugs must be considered in order to avoid unintended additive effects on the immune system while at the same time minimizing risk of disease reactivation, when initiating PONVORY.
Initiating treatment with PONVORY after treatment with alemtuzumab is not recommended.
5.11 Severe Increase in Disability After Stopping PONVORY
Severe exacerbation of disease, including disease rebound, has been rarely reported after discontinuation of a S1P receptor modulator. The possibility of severe exacerbation of disease should be considered after stopping PONVORY treatment. Patients should be observed for a severe increase in disability upon PONVORY discontinuation and appropriate treatment should be instituted, as required.
After stopping PONVORY in the setting of PML, monitor for development of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (PML-IRIS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
5.12 Immune System Effects After Stopping PONVORY
After stopping PONVORY therapy, ponesimod remains in the blood for up to 1 week. Starting other therapies during this interval will result in concomitant exposure to ponesimod. Lymphocyte counts returned to the normal range in 90% of patients within 1 week of stopping PONVORY therapy in modeling studies [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] . However, residual pharmacodynamics effects, such as lowering effects on peripheral lymphocyte count, may persist for 1 to 2 weeks after the last dose. Use of immunosuppressants within this period may lead to an additive effect on the immune system, and therefore caution should be applied 1 to 2 weeks after the last dose of PONVORY [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Respiratory Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Liver Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Increased Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Cutaneous Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Fetal Risk [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Macular Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Unintended Additive Immunosuppressive Effects From Prior Treatment With Immunosuppressive or Immune-Modulating Therapies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Severe Increase in Disability After Stopping PONVORY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Immune System Effects After Stopping PONVORY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
A total of 1438 MS patients have received PONVORY at doses of at least 2 mg daily. These patients were included in Study 1 (2-year active-controlled versus teriflunomide 14 mg) [see Clinical Studies (14)] and in a Phase 2 (6-month placebo-controlled) study in patients with MS and the uncontrolled extension studies.
In Study 1, 82% of PONVORY-treated patients completed 2 years of study treatment, compared to 82.2% of patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg. Adverse events led to discontinuation of treatment in 8.7% of PONVORY-treated patients, compared to 6% of patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg. The most common adverse reactions (incidence at least 10%) in PONVORY-treated patients in Study 1 were upper respiratory tract infection, hepatic transaminase elevation, and hypertension. Table 3 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of PONVORY-treated patients and at a higher rate than in patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg.
| Adverse Reaction | PONVORY | Teriflunomide 14 mg |
|---|---|---|
| N=565
(%) | N=566
(%) |
|
|
||
| Upper respiratory infection * | 37 | 34 |
| Hepatic transaminase elevation † | 23 | 12 |
| Hypertension ‡ | 10 | 9 |
| Urinary tract infection | 6 | 5 |
| Dyspnea | 5 | 1 |
| Dizziness | 5 | 3 |
| Cough | 4 | 2 |
| Pain in extremity | 4 | 3 |
| Somnolence | 3 | 2 |
| Pyrexia | 2 | 1 |
| C-reactive protein increased | 2 | 1 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 2 | 1 |
| Vertigo | 2 | 1 |
In Study 1, the following adverse reactions occurred in less than 2% of PONVORY-treated patients, but at a rate at least 1% higher than in patients receiving teriflunomide 14 mg: viral infection, herpes zoster, hyperkalemia, lymphopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and macular edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Adverse reactions in patients treated with PONVORY in an additional 6-month placebo-controlled study were generally similar to those in Study 1. The following additional adverse reactions occurred in at least 2% of PONVORY 20 mg-treated patients and at a higher rate than in patients receiving placebo (but did not meet the reporting rate criteria for inclusion in Study 1): rhinitis, fatigue, chest discomfort, peripheral edema, joint swelling, blood cholesterol increased, migraine, insomnia, depression, dyspepsia, dry mouth, bradycardia, back pain, and sinusitis.
Additionally, in uncontrolled extension trials, the adverse reaction of pneumonia was reported.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Anti-Neoplastic, Immune-Modulating, or Immunosuppressive Therapies
PONVORY has not been studied in combination with anti-neoplastic, immune-modulating, or immunosuppressive therapies. Caution should be used during concomitant administration because of the risk of additive immune effects during such therapy and in the weeks following administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, the half-life and mode of action of these drugs must be considered in order to avoid unintended additive effects on the immune system [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Because of the characteristics and duration of alemtuzumab immune suppressive effects, initiating treatment with PONVORY after alemtuzumab is not recommended.
PONVORY can generally be started immediately after discontinuation of beta interferon or glatiramer acetate.
7.2 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs, QT Prolonging Drugs, Drugs that may Decrease Heart Rate
PONVORY has not been studied in patients taking QT prolonging drugs.
Class Ia (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) anti-arrhythmic drugs have been associated with cases of Torsades de Pointes in patients with bradycardia. If treatment with PONVORY is considered, advice from a cardiologist should be sought.
Because of the potential additive effects on heart rate, treatment with PONVORY should generally not be initiated in patients who are concurrently treated with QT prolonging drugs with known arrhythmogenic properties, heart rate lowering calcium channel blockers (e.g., verapamil, diltiazem), or other drugs that may decrease heart rate (e.g., digoxin) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)and Drug Interactions (7.3)] . If treatment with PONVORY is considered, advice from a cardiologist should be sought.
7.3 Beta-Blockers
Caution should be applied when PONVORY is initiated in patients receiving treatment with a beta-blocker because of the additive effects on lowering heart rate; temporary interruption of the beta-blocker treatment may be needed prior to initiation of PONVORY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] . Beta-blocker treatment can be initiated in patients receiving stable doses of PONVORY.
7.4 Vaccination
During, and for up to 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuation of, treatment with PONVORY, vaccinations may be less effective. The use of live attenuatedvaccines may carry the risk of infection and should therefore be avoided during PONVORY treatment and for 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuation of treatment with PONVORY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
7.5 Strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 Inducers
In vitroassessments and limited clinical data indicated that concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine) may decrease the systemic exposure of ponesimod. It is unclear whether this decrease in ponesimod systemic exposure would be considered of clinical relevance. Coadministration of PONVORY with strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 inducers is not recommended.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of PONVORY did not include patients 65 years of age and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Use of PONVORY in elderly patients should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
PONVORY is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B and C, respectively), as the risk of adverse reactions may be greater [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
11. Ponvory Description
PONVORY (ponesimod) is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator.
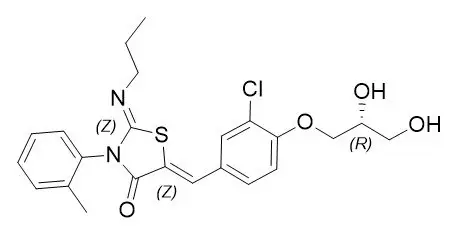
The chemical name for ponesimod is (2 Z,5 Z)-5-[3-chloro-4-[(2 R)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy]benzylidene]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(propylimino)-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one. It has one chiral center with absolute configuration of (R). Its molecular formula is C 23H 25ClN 2O 4S and its molecular weight is 460.97 g/mol. Ponesimod has the following structural formula:
Ponesimod is a white to light yellowish powder that is practically insoluble or insoluble in water.
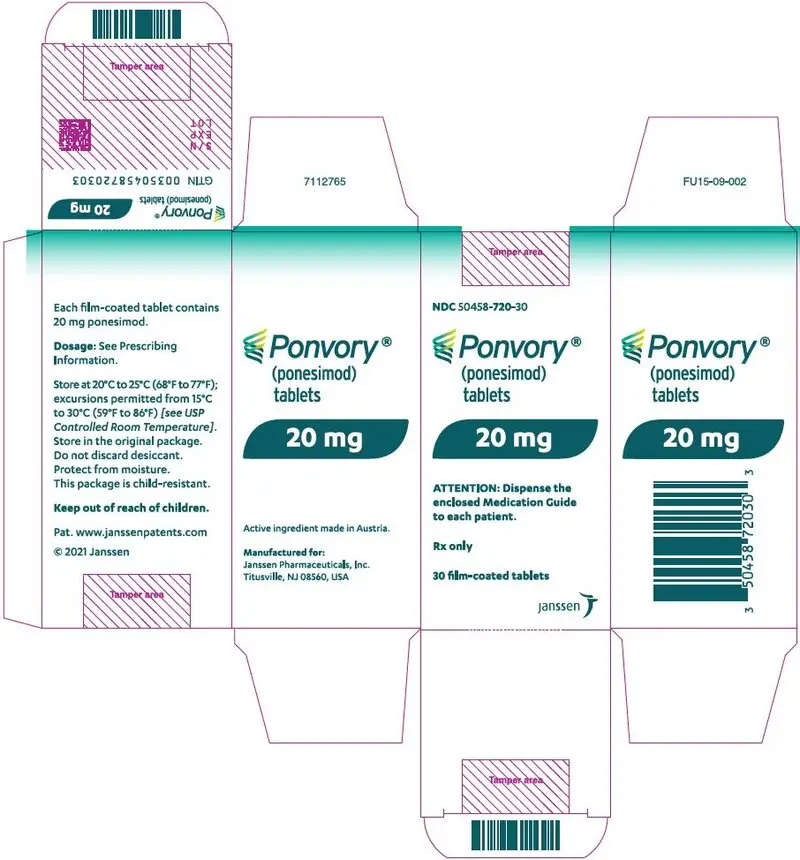
PONVORY ®(ponesimod) is provided as 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 6 mg, 7 mg, 8 mg, 9 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration.
Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, silica colloidal anhydrous, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
Each tablet coating contains ferrosoferric oxide (included in 4 mg, 5 mg, 8 mg, and 9 mg film-coated tablets), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2910, iron oxide red (included in 3 mg, 4 mg, 7 mg, 8 mg, 9 mg, and 10 mg film-coated tablets), iron oxide yellow (included in 3 mg, 5 mg, 7 mg, 9 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg film-coated tablets), lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
12. Ponvory - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ponesimod is a sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 modulator that binds with high affinity to S1P receptor 1.
Ponesimod blocks the capacity of lymphocytes to egress from lymph nodes, reducing the number of lymphocytes in peripheral blood. The mechanism by which ponesimod exerts therapeutic effects in multiple sclerosis is unknown, but may involve reduction of lymphocyte migration into the central nervous system.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following ponesimod oral dosing, C maxand AUC increased approximately dose-proportionally in the dose-range studied (1–75 mg). Steady-state levels are approximately 2.0- to 2.6-fold greater than with a single dose, and are achieved following 3 days of administration of the maintenance dose of ponesimod.
The pharmacokinetics of ponesimod are similar in healthy subjects and patients with multiple sclerosis, with 25% inter-subject variability across studies.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Increases in lung weight and histopathology (alveolar histiocytosis, edema) were observed in oral toxicity studies in mice, rats, and dogs. At the higher doses tested in short-term studies, alveolar histiocytosis was associated with lung edema, emphysema, or hyalinosis, and with bronchioloalveolar hyperplasia after cessation of dosing in rats and alveolar histiocytosis and hyalinosis in dogs. Effects tended to be absent or less severe after chronic treatment. These findings are considered secondary to increased vascular permeability caused by S1P 1receptor modulation. The NOAELs for lung findings in the 4-week oral toxicity studies in rats and dogs were associated with plasma exposures (AUC) similar or lower than that expected in humans at the recommended human dose (RHD) of 20 mg/day.
In dogs, coronary arterial lesions (thickening of the vessel wall, hyperplasia/hypertrophy of smooth muscles cells of the tunica media, subendocardial fibrosis) involving the papillary muscle of the left ventricle were observed in oral toxicity studies of 13 to 52 weeks in duration. At the NOAEL (2 mg/kg/day) for these findings, plasma exposures (AUC) were approximately 2 times that expected in humans at the RHD.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of PONVORY was demonstrated in Study 1, a randomized, double-blind, parallel group, active-controlled superiority study in patients with relapsing forms of MS (NCT02425644). Patients were treated for 108 weeks. This study included patients who had an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of 0 to 5.5 at baseline, had experienced at least one relapse within the year prior, or two relapses within the prior 2 years, or who had at least one gadolinium-enhancing (Gd-enhancing) lesion on a brain MRI within the prior 6 months or at baseline. Patients with primary progressive MS were excluded.
Patients were randomized to receive either once daily PONVORY, beginning with a 14-day dose titration [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] or teriflunomide 14 mg. Neurological evaluations were performed at baseline, every 3 months during the study, and at the time of a suspected relapse. Brain MRI scans were performed at baseline and at Weeks 60 and 108.
The primary endpoint was the annualized relapse rate (ARR) over the study period. Additional outcome measures included: 1) the number of new Gd-enhancing T1 lesions from baseline to Week 108, 2) the number of new or enlarging T2 lesions (without double-counting of lesions) from baseline to Week 108, and 3) the time to 3-month and 6-month confirmed disability progression. A confirmed disability progression was defined as an increase of at least 1.5 in EDSS for patients with a baseline EDSS score of 0, an increase of at least 1.0 in EDSS for patients with a baseline EDSS score of 1.0 to 5.0, or an increase of at least 0.5 in EDSS for patients with a baseline EDSS score at least 5.5, which was confirmed after 3 months and 6 months.
A total of 1133 patients were randomized to either PONVORY (N=567) or teriflunomide 14 mg (N=566); 86.4% of PONVORY-treated patients and 87.5% of teriflunomide 14 mg-treated patients completed the study as per protocol. At baseline, the mean age of patients was 37 years, 97% were White, and 65% were female. The mean disease duration was 7.6 years, the mean number of relapses in the previous year was 1.3, and the mean EDSS score was 2.6; 57% of patients had not received any prior non-steroid treatments for MS. At baseline, 42.6% of patients had one or more Gd-enhancing T1 lesions (mean 2.0) on their baseline MRI scan.
The ARR was statistically significantly lower in patients treated with PONVORY than in patients who received teriflunomide 14 mg. The number of Gd-enhancing T1 lesions and the number of new or enlarging T2 lesions were statistically significantly lower in patients treated with PONVORY than in patients who received teriflunomide 14 mg.
There was no statistically significant difference in the 3-month and 6-month confirmed disability progression outcomes between PONVORY- and teriflunomide 14 mg-treated patients over 108 weeks.
The efficacy results for Study 1 are presented in Table 4.
| Endpoints | PONVORY 20 mg
N=567 | Teriflunomide 14 mg
N=566 |
|---|---|---|
| All analyses are based on the full analysis set (FAS), which includes all randomized patients. N refers to the number of patients included in the FAS, per treatment group. | ||
|
||
| Clinical Endpoints | ||
| Annualized Relapse Rate * | 0.202 | 0.290 |
| Relative reduction | 30.5% (p=0.0003) | |
| Percentage of patients without relapse † | 70.7% | 60.6% |
| Proportion of Patients with 3-month Confirmed Disability Progression ‡ | 10.8% | 13.2% |
| Hazard Ratio § | 0.83 (p=0.29) ¶ | |
| MRI Endpoints†,# | ||
| Mean number of new or enlarging T2 hyperintense lesions per year | 1.40 | 3.16 |
| Relative reduction | 55.7% (p <.0001) | |
| Mean number of T1 Gd-enhancing lesions per MRI | 0.18 | 0.43 |
| Relative reduction | 58.5% (p <.0001) | |
A similar effect of PONVORY on the ARR and secondary MRI outcomes compared to teriflunomide 14 mg was observed in exploratory subgroups defined by age, gender, prior non-steroid therapy for MS, and baseline disease activity.
16. How is Ponvory supplied
16.1 How Supplied
PONVORY ®(ponesimod) tablet is available as round, biconvex, film-coated tablets supplied in the following dosage strengths and package configurations.
| PONVORY
ponesimod tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PONVORY
ponesimod kit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon France | 543127229 | manufacture(50458-720, 50458-707) , analysis(50458-720, 50458-707) , pack(50458-720, 50458-707) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACM Pharma | 384719527 | analysis(50458-720, 50458-707) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Konapharma AG | 482314432 | manufacture(50458-720, 50458-707) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Austria GmbH & Co KG | 300398976 | api manufacture(50458-720, 50458-707) , analysis(50458-720, 50458-707) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jetpharma SA | 481885861 | particle size reduction(50458-720, 50458-707) | |