Drug Detail:Poteligeo (Mogamulizumab [ moe-gam-ue-liz-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
POTELIGEO® (mogamulizumab-kpkc) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Indications and Usage for Poteligeo Injection
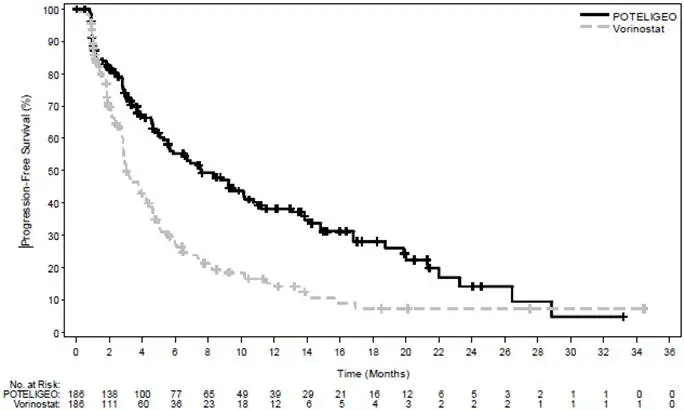
POTELIGEO is a CC chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4)-directed monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome after at least one prior systemic therapy (1).
Poteligeo Injection Dosage and Administration
1 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over at least 60 minutes on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of the first 28-day cycle and on days 1 and 15 of each subsequent cycle (2).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 20 mg/5 mL (4 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial (3).
Contraindications
None (4).
Warnings and Precautions
- Dermatologic Toxicity: Temporarily interrupt POTELIGEO for moderate or severe skin rashes. Permanently discontinue POTELIGEO for life-threatening rash (5.1).
- Infusion Reactions: Temporarily interrupt POTELIGEO for any infusion reaction. Permanently discontinue POTELIGEO for any life-threatening infusion reaction (5.2).
- Infections: Monitor and treat promptly (5.3).
- Autoimmune Complications: Interrupt or permanently discontinue POTELIGEO as appropriate (5.4).
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT after POTELIGEO: Monitor for severe acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and steroid-refractory GVHD. Transplant-related mortality has occurred (5.5).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥20% of patients) are rash, infusion related reactions, fatigue, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and upper respiratory tract infection (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kyowa Kirin, Inc. at 1-844-768-3544 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Poteligeo Injection
POTELIGEO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory mycosis fungoides (MF) or Sézary syndrome (SS) after at least one prior systemic therapy.
2. Poteligeo Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of POTELIGEO is 1 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion over at least 60 minutes. Administer on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 of the first 28-day cycle, then on days 1 and 15 of each subsequent 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Administer POTELIGEO within 2 days of the scheduled dose. If a dose is missed, administer the next dose as soon as possible and resume dosing schedule.
Do not administer POTELIGEO subcutaneously or by rapid intravenous administration.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 20 mg/5 mL (4 mg/mL) as a clear to slightly opalescent colorless solution in a single-dose vial.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Dermatologic Toxicity
Fatal and life-threatening skin adverse reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have occurred in recipients of POTELIGEO. Rash (drug eruption) is one of the most common adverse reactions associated with POTELIGEO. In Trial 1, 25% (80/319) of patients treated with POTELIGEO had an adverse reaction of drug eruption, with 18% of these cases being severe (Grade 3) and 82% of these cases being Grade 1 or 2. Of 528 patients treated with POTELIGEO in clinical trials, Grade 3 skin adverse reactions were reported in 3.6%, Grade 4 skin adverse reactions in <1%, and SJS in <1%.
The onset of drug eruption is variable, and the affected areas and appearance vary. In Trial 1, the median time to onset was 15 weeks, with 25% of cases occurring after 31 weeks. The more common presentations reported included papular or maculopapular rash, lichenoid, spongiotic or granulomatous dermatitis, and morbilliform rash. Other presentations included scaly plaques, pustular eruption, folliculitis, non-specific dermatitis, and psoriasiform dermatitis.
Monitor patients for rash throughout the treatment course. Management of dermatologic toxicity includes topical corticosteroids and interruption or permanent cessation of POTELIGEO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Consider skin biopsy to help distinguish drug eruption from disease progression.
Discontinue POTELIGEO permanently for SJS or TEN or for any life-threatening (Grade 4) reaction. For possible SJS or TEN, interrupt POTELIGEO and do not restart unless SJS or TEN is ruled out and the cutaneous reaction has resolved to Grade 1 or less.
5.2 Infusion Reactions
Fatal and life-threatening infusion reactions have been reported in patients treated with POTELIGEO. In Trial 1, infusion reactions occurred in 35% (112/319) of patients treated with POTELIGEO, with 8% of these reactions being severe (Grade 3). Most reactions (approximately 90%) occur during or shortly after the first infusion. Infusion reactions can also occur with subsequent infusions. The most commonly reported signs include chills, nausea, fever, tachycardia, rigors, headache, and vomiting.
Consider premedication (such as diphenhydramine and acetaminophen) for the first infusion of POTELIGEO in all patients. Whether premedication reduces the risk or severity of these reactions is not established. In Trial 1, infusion reactions occurred in 42% of patients without premedication and 32% of patients with premedication. Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of infusion reactions and interrupt the infusion for any grade reaction and treat promptly [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.3 Infections
Fatal and life-threatening infections have occurred in patients treated with POTELIGEO, including sepsis, pneumonia, and skin infection. In Trial 1, 18% (34/184) of patients randomized to POTELIGEO had Grade 3 or higher infection or an infection-related serious adverse reaction. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection and treat promptly.
5.4 Autoimmune Complications
Fatal and life-threatening immune-mediated complications have been reported in recipients of POTELIGEO. Grade 3 or higher immune-mediated or possibly immune-mediated reactions have included myositis, myocarditis, polymyositis, hepatitis, pneumonitis, glomerulonephritis and a variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Use of systemic immunosuppressants for immune-mediated reactions was reported in 1.9% (6/319) of recipients of POTELIGEO in Trial 1, including for a case of Grade 2 polymyalgia rheumatica. New-onset hypothyroidism (Grade 1 or 2) was reported in 1.3% of patients and managed with observation or levothyroxine. Interrupt or permanently discontinue POTELIGEO as appropriate for suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions. Consider the benefit/risk of POTELIGEO in patients with a history of autoimmune disease.
5.5 Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) after POTELIGEO
Increased risks of transplant complications have been reported in patients who receive allogeneic HSCT after POTELIGEO including severe (Grade 3 or 4) acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), steroid-refractory GVHD, and transplant-related death. Among recipients of pre-transplantation POTELIGEO, a higher risk of transplant complications has been reported if POTELIGEO is given within a shorter time frame (approximately 50 days) before HSCT. Follow patients closely for early evidence of transplant-related complications.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Dermatologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Autoimmune Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT after POTELIGEO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of incidence of antibodies to POTELIGEO with the incidences of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Among 313 patients treated with POTELIGEO and whose antibodies were tested, 44 (14.1%) tested positive for anti-mogamulizumab-kpkc antibodies. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-drug antibodies on pharmacokinetics, safety, or effectiveness of POTELIGEO. There were no positive neutralizing antibody responses.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of POTELIGEO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Infections: Hepatitis B virus reactivation
- Cardiac disorders: Stress cardiomyopathy
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
POTELIGEO is not recommended during pregnancy or in women of childbearing potential not using contraception.
8.4 Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of POTELIGEO in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric use
Of 319 patients with MF or SS who received POTELIGEO in Trial 1, 162 (51%) were ≥65 years. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients. In patients aged ≥65, Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions were reported in 45% and serious adverse reactions in 36%, whereas in patients aged <65, Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions were reported in 36% and serious adverse reactions in 29%.
11. Poteligeo Injection Description
Mogamulizumab-kpkc is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that targets CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4)-expressing cells. Mogamulizumab-kpkc is an IgG1 kappa immunoglobulin that has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 149 kDa. Mogamulizumab-kpkc is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
POTELIGEO (mogamulizumab-kpkc) injection is a sterile, ready-to-use, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent colorless solution in a single-dose vial for dilution prior to intravenous infusion. Each vial contains 20 mg of mogamulizumab-kpkc in 5 mL of solution. Each mL of solution contains 4 mg of mogamulizumab-kpkc and is formulated in: citric acid monohydrate (0.44 mg), glycine (22.5 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.2 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. May contain hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide to adjust pH to 5.5.
12. Poteligeo Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mogamulizumab-kpkc is a defucosylated, humanized IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody that binds to CCR4, a G protein-coupled receptor for CC chemokines that is involved in the trafficking of lymphocytes to various organs. Non-clinical in vitro studies demonstrate mogamulizumab-kpkc binding targets a cell for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) resulting in depletion of the target cells. CCR4 is expressed on the surface of some T-cell malignancies and is expressed on regulatory T-cells (Treg) and a subset of Th2 T-cells.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Mogamulizumab-kpkc exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamics response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mogamulizumab-kpkc pharmacokinetics (PK) was evaluated in patients with T-cell malignancies. Parameters are presented as the geometric mean [% coefficient of variation (%CV)] unless otherwise specified. Mogamulizumab-kpkc concentrations increased proportionally with dose over the dose range of 0.01 to 1.0 mg/kg (0.01 to 1 times the approved recommended dosage).
Following repeated dosing of the approved recommended dosage, steady state concentrations were reached after 8 doses (12 weeks), and the systemic accumulation was 1.6-fold. At steady state, the peak concentration (Cmax,ss) is 32 (68%) µg/mL, the trough concentration (Cmin,ss) is 11 (239%) µg/mL, and AUCss is 5,577 (125%) µg∙hr/mL.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or genotoxicity studies have been conducted with POTELIGEO.
No specific studies have been conducted to evaluate potential effects of POTELIGEO on fertility. No mogamulizumab-kpkc -related toxic effects in the male and female reproductive organs were observed in sexually mature monkeys in repeat-dose toxicology studies up to 26 weeks in duration.
16. How is Poteligeo Injection supplied
POTELIGEO (mogamulizumab-kpkc) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent colorless solution supplied in a carton containing one 20 mg/5 mL (4 mg/mL), single-dose glass vial (NDC 42747-761-01).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Inform patients of the risk of the following adverse reactions that may require additional treatment and/or withholding or discontinuation of POTELIGEO including:
- Dermatological Toxicity: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for new or worsening skin rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise patients that the rash can happen at any time while receiving POTELIGEO.
- Infusion Reactions: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Infections: Advise patients to contact their health care provider for fever or other evidence of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Autoimmune Complications: Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider of any history of autoimmune disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Complications of Allogeneic HSCT after POTELIGEO: Advise patients of potential risk of post-transplant complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Females of Reproductive Potential: Advise use of effective contraception during treatment with POTELIGEO and for 3 months following the last dose of POTELIGEO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 3/2023 | |||
| PATIENT INFORMATION POTELIGEO® (poe–te–lig'–ee–oh) (mogamulizumab-kpkc) injection, for intravenous use |
||||
| What is the most important information I should know about POTELIGEO? POTELIGEO may cause serious side effects that can be severe, life-threatening or lead to death. Call or see your healthcare provider right away if you develop any symptoms of the following problems or if these symptoms get worse:
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
Your healthcare provider will check you for these problems during treatment with POTELIGEO. Your healthcare provider may need to delay or completely stop treatment with POTELIGEO if you have severe side effects. |
||||
| What is POTELIGEO?
POTELIGEO is a prescription medicine used to treat mycosis fungoides (MF) or Sézary syndrome (SS) in adults when you have tried at least one prior medicine (taken by mouth or injection) and it did not work or the disease has come back. It is not known if POTELIGEO is safe and effective in children. |
||||
Before receiving POTELIGEO treatment, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||
How will I receive POTELIGEO?
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of POTELIGEO? POTELIGEO may cause serious side effects including:
|
||||
|
|
|||
| These are not all the possible side effects of POTELIGEO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of POTELIGEO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about POTELIGEO that is written for healthcare professionals. |
||||
| What are the ingredients in POTELIGEO?
Active ingredient: mogamulizumab-kpkc Inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate, glycine, polysorbate 80, and Water for Injection, USP. Manufactured by: Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540 U.S. License No. 2077 POTELIGEO is a registered trademark of Kyowa Kirin, Inc. For more information, call 1-844-768-3544 or go to www.POTELIGEO.com. |
||||
| POTELIGEO
mogamulizumab-kpkc injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Kyowa Kirin, Inc. (014778321) |