Drug Detail:Prevymis (Letermovir (oral/injection) [ le-term-oh-vir ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antivirals
Highlights of Prescribing Information
PREVYMIS® (letermovir) tablets, for oral use
PREVYMIS® (letermovir) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, CMV Prophylaxis in Kidney Transplant Recipients (1.2) | 06/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration, Recommended Dosage for Adult Patients (2.2) | 08/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Prevymis
PREVYMIS is a CMV DNA terminase complex inhibitor indicated for:
- Prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). (1.1)
- Prophylaxis of CMV disease in adult kidney transplant recipients at high risk (Donor CMV seropositive/Recipient CMV seronegative [D+/R-]). (1.2)
Prevymis Dosage and Administration
- HSCT: 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an intravenous (IV) infusion over 1 hour through 100 days post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through 200 days post-HSCT. (2.1, 2.2)
- Kidney Transplant: 480 mg administered once daily orally or as an IV infusion over 1 hour through 200 days post-transplant. (2.1, 2.2)
- PREVYMIS injection must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter. (2.1, 2.7)
- Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended. (2.3)
- Dosage Adjustment: If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily. (2.4)
- Do not use PREVYMIS injection with IV bags and infusion set materials containing the plasticizer diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). (2.7, 2.9)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablet: 240 mg; 480 mg (3)
- Injection: 240 mg/12 mL (20 mg/mL) or 480 mg/24 mL (20 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial (3)
Contraindications
PREVYMIS is contraindicated with:
- Pimozide. (4)
- Ergot Alkaloids. (4)
- Pitavastatin and simvastatin when co-administered with cyclosporine. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Adverse Reactions or Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Drug Interactions: The concomitant use of PREVYMIS with certain drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to adverse reactions (PREVYMIS or concomitant drugs) or reduced therapeutic effect of PREVYMIS or the concomitant drug. Consult the full prescribing information for contraindications and dosage recommendations for concomitant drugs. (4, 5.1, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- HSCT Patients: Most common adverse events (occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency at least 2% greater than placebo) are nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, cough, headache, fatigue, and abdominal pain. (6.1)
- Kidney Transplant Patients: Most common adverse event (occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency greater than valganciclovir) is diarrhea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .
Drug Interactions
- Dosage Adjustment: If PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily. (2.4)
- Co-administration of PREVYMIS may alter the plasma concentrations of other drugs and other drugs may alter the plasma concentrations of PREVYMIS. Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug interactions. (2.4, 4, 5.1, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 12.3)
Use In Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment: Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min using PREVYMIS injection. (8.6)
- Hepatic Impairment: PREVYMIS is not recommended for patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2023
Related/similar drugs
valacyclovir, valganciclovir, Valcyte, letermovirFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Prevymis
2. Prevymis Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosing and Administration Information
PREVYMIS Tablets
- Administer with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole.
PREVYMIS Injection
- PREVYMIS injection must be administered through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter.
- Administer by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour.
- Do not administer as an intravenous bolus injection.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Adult Patients
The recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily.
Dosage of PREVYMIS should be adjusted when co-administered with cyclosporine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
PREVYMIS injection, which contains hydroxypropyl betadex, should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy. Patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. PREVYMIS tablet and injection may be used interchangeably at the discretion of the physician, and no dosage adjustment is necessary when switching formulations.
HSCT
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 28 post-HSCT (before or after engraftment) and continue through Day 100 post-HSCT. In patients at risk for late CMV infection and disease, PREVYMIS may be continued through Day 200 post-HSCT [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Kidney Transplant
Initiate PREVYMIS between Day 0 and Day 7 post-transplant and continue through Day 200 post-transplant.
2.3 Patient Monitoring
Following the completion of PREVYMIS prophylaxis, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2.4 Dosage Adjustment When Co-administered with Cyclosporine
If oral or intravenous PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the dosage of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2, 7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- If cyclosporine is initiated after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be decreased to 240 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine is discontinued after starting PREVYMIS, the next dose of PREVYMIS should be increased to 480 mg once daily.
- If cyclosporine dosing is interrupted due to high cyclosporine levels, no dose adjustment of PREVYMIS is needed.
2.5 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
- For patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) greater than 10 mL/min, no dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- There are insufficient data in patients with CLcr 10 mL/min or less or in patients on dialysis to make PREVYMIS dosing recommendations.
- In patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min receiving PREVYMIS injection, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropyl betadex, may occur. Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in these patients.
2.6 Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required for patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. PREVYMIS is not recommended for patients with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
2.7 Preparation and Administration of Intravenous Solution
PREVYMIS injection is supplied in 30 mL single-dose vials containing either 240 mg/12 mL per vial (20 mg/mL) or 480 mg/24 mL per vial (20 mg/mL). The preparation and administration instructions are the same for either dose.
PREVYMIS vials are for single use only. Discard any unused portion.
4. Contraindications
- PREVYMIS is contraindicated in patients receiving pimozide or ergot alkaloids:
- Pimozide: Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in patients receiving pimozide may result in increased concentrations of pimozide due to inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) by letermovir, which may lead to QT prolongation and torsades de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
- Ergot alkaloids: Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in patients receiving ergot alkaloids may result in increased concentrations of ergot alkaloids (ergotamine and dihydroergotamine) due to inhibition of CYP3A by letermovir, which may lead to ergotism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
- PREVYMIS is contraindicated with pitavastatin and simvastatin when co-administered with cyclosporine. Concomitant administration of PREVYMIS in combination with cyclosporine may result in significantly increased pitavastatin or simvastatin concentrations, which may lead to myopathy or rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Adverse Reactions or Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of PREVYMIS and certain drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to adverse reactions (PREVYMIS or concomitant drugs) or reduced therapeutic effect of PREVYMIS or the concomitant drug [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2, 7.3)].
See Table 4 for steps to prevent or manage these possible or known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during PREVYMIS therapy; review concomitant medications during PREVYMIS therapy; and monitor for adverse reactions associated with PREVYMIS and concomitant medications.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Common Adverse Events
The rate of adverse events occurring in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency at least 2% greater than placebo are outlined in Table 1.
| Adverse Events | PREVYMIS (N=373) | Placebo (N=192) |
|---|---|---|
| nausea | 27% | 23% |
| diarrhea | 26% | 24% |
| vomiting | 19% | 14% |
| peripheral edema | 14% | 9% |
| cough | 14% | 10% |
| headache | 14% | 9% |
| fatigue | 13% | 11% |
| abdominal pain | 12% | 9% |
Overall, similar proportions of subjects in each group discontinued study medication due to an adverse event (13% of PREVYMIS subjects vs. 12% of placebo subjects). The most frequently reported adverse event that led to study drug discontinuation was nausea, occurring in 2% of PREVYMIS subjects and 1% of placebo subjects. Hypersensitivity reaction, with associated moderate dyspnea, occurred in one subject following the first infusion of IV PREVYMIS after switching from oral PREVYMIS, leading to treatment discontinuation.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities reported during treatment or within 2 weeks of stopping treatment are presented in the table below.
| PREVYMIS N=373 | Placebo N=192 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Absolute neutrophil count (cells/μL) | ||
| < 500 | 19% | 19% |
| 500 – < 750 | 4% | 7% |
| 750 – < 1000 | 8% | 9% |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||
| < 6.5 | 2% | 1% |
| 6.5 – < 8.0 | 14% | 15% |
| 8.0 – < 9.5 | 41% | 43% |
| Platelets (cells/μL) | ||
| < 25000 | 27% | 21% |
| 25000 – < 50000 | 17% | 18% |
| 50000 – < 100000 | 20% | 30% |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | ||
| > 2.5 | 2% | 3% |
| > 1.5 – 2.5 | 17% | 20% |
The median time to engraftment (defined as absolute neutrophil count ≥ 500/mm3 on 3 consecutive days after transplantation) was 19 days in the PREVYMIS group and 18 days in the placebo group.
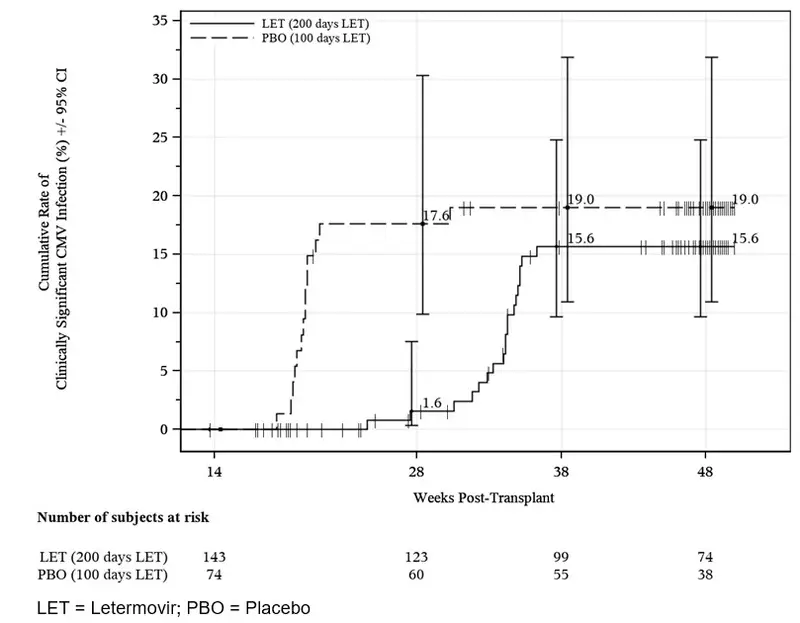
Prophylaxis From Week 14 (~100 days) Through Week 28 (~200 days) Post-HSCT
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (P040) in which 218 subjects who completed PREVYMIS prophylaxis through ~100 days post-HSCT were randomized to treatment with PREVYMIS (N=144) or placebo (N=74) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT. Adverse events were those reported while subjects were on study drug or within two weeks of study drug completion/discontinuation.
The most commonly reported adverse events in P040 were similar to those reported in P001. Study drug was discontinued due to an adverse event in 5% of PREVYMIS subjects and 1% of placebo subjects. The cardiac adverse event rate was 4% in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups.
The rates of hematologic laboratory abnormalities were comparable in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups. Serum creatinine abnormalities > 1.5 mg/dL occurred in 15% of PREVYMIS and 8% of placebo subjects.
Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients [D+/R-]
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in a Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled trial (P002) in which 589 subjects were treated with PREVYMIS (N=292) or valganciclovir (N=297) through Week 28 post-transplant. Adverse events were those reported while subjects were on study medication or within two weeks of study medication completion/discontinuation. In these subjects, diarrhea was reported in at least 10% of subjects in the PREVYMIS group and at a frequency greater than valganciclovir (PREVYMIS, 32%; valganciclovir, 29%). Study drug was discontinued due to an adverse event in 4% of PREVYMIS subjects and 14% of valganciclovir subjects. The most frequently reported adverse events that led to study drug discontinuation were neutropenia (PREVYMIS, 1%; valganciclovir, 2%) and leukopenia (PREVYMIS, 1%; valganciclovir, 5%).
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected laboratory abnormalities reported through Week 28 post-transplant are presented in the table below.
| PREVYMIS N=292 | Valganciclovir N=297 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Absolute neutrophil count (cells/μL) | ||
| < 500 | 2% | 7% |
| 500 – < 750 | 1% | 4% |
| 750 – < 1000 | 1% | 8% |
| Total < 1000 | 5% | 18% |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||
| < 6.5 | 2% | 0% |
| 6.5 – < 8.0 | 4% | 5% |
| 8.0 – < 9.5 | 29% | 32% |
| Total < 9.5 | 34% | 37% |
| Platelets (cells/μL) | ||
| < 50000 | 0% | 0% |
| 50000 – < 100000 | 1% | 3% |
| Total < 100000 | 1% | 3% |
| Leukocytes (cells/μL) | ||
| < 1000 | 1% | 2% |
| 1000 – < 2000 | 5% | 19% |
| 2000 – < 2500 | 4% | 14% |
| Total < 2500 | 10% | 35% |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | ||
| > 2.5 | 24% | 22% |
| > 1.5 – 2.5 | 49% | 52% |
| Total > 1.5 | 73% | 73% |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect PREVYMIS
Letermovir is a substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1/3 (OATP1B1/3) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporters and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1/3 (UGT1A1/3) enzymes. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are inhibitors of OATP1B1/3 transporters may result in increases in letermovir plasma concentrations (Table 4).
Co-administration of PREVYMIS with inducers of transporters (e.g. P-gp) and/or enzymes (e.g. UGTs) is not recommended due to the potential for a decrease in letermovir plasma concentrations (see Table 4).
7.2 Potential for PREVYMIS to Affect Other Drugs
Co-administration of PREVYMIS with midazolam results in increased midazolam plasma concentrations, indicating that letermovir is a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are CYP3A substrates may result in clinically relevant increases in the plasma concentrations of co-administered CYP3A substrates (Table 4) [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Letermovir is an inhibitor of OATP1B1/3 transporters. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1/3 transporters may result in a clinically relevant increase in plasma concentrations of co-administered OATP1B1/3 substrates (Table 4).
The magnitude of CYP3A- and OATP1B1/3-mediated drug interactions on co-administered drugs may be different when PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine. See the prescribing information for cyclosporine for information on drug interactions with cyclosporine.
7.3 Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
If dose adjustments of concomitant medications are made due to treatment with PREVYMIS, doses should be readjusted after treatment with PREVYMIS is completed.
Table 4 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with PREVYMIS or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with PREVYMIS [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Concomitant Drug Class and/or Clearance Pathway: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Anti-arrhythmic Agents | ||
| amiodarone | ↑ amiodarone | Close clinical monitoring for adverse events related to amiodarone is recommended during co-administration. Frequently monitor amiodarone concentrations when amiodarone is co-administered with PREVYMIS. |
| Antibiotics | ||
| nafcillin | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and nafcillin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Anticoagulants | ||
| warfarin | ↓ warfarin | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with warfarin, frequently monitor International Normalized Ratio (INR) ‡. |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| carbamazepine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and carbamazepine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| phenobarbital | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and phenobarbital is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| phenytoin | ↓ letermovir ↓ phenytoin | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and phenytoin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Antidiabetic Agents | ||
| Examples: glyburide, repaglinide, rosiglitazone | ↑ glyburide ↑ repaglinide ↑ rosiglitazone | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with glyburide, repaglinide, or rosiglitazone, frequently monitor glucose concentrations‡. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of repaglinide is not recommended. |
| Antifungals | ||
| voriconazole§ | ↓ voriconazole | If concomitant administration of voriconazole is necessary, closely monitor for reduced effectiveness of voriconazole‡. |
| Antimycobacterials | ||
| rifabutin | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and rifabutin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| rifampin§ | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and rifampin is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Antipsychotics | ||
| pimozide | ↑ pimozide | Co-administration is contraindicated due to risk of QT prolongation and torsades de pointes [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| thioridazine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and thioridazine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Endothelin Antagonists | ||
| bosentan | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and bosentan is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| Ergot Alkaloids | ||
| ergotamine, dihydroergotamine | ↑ ergotamine, dihydroergotamine | Co-administration is contraindicated due to risk of ergotism [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Herbal Products | ||
| St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and St. John's wort is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| HIV Medications | ||
| efavirenz | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and efavirenz is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| etravirine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and etravirine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| nevirapine | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and nevirapine is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | ||
| atorvastatin§ | ↑ atorvastatin | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with atorvastatin, do not exceed an atorvastatin dosage of 20 mg daily‡. Closely monitor patients for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of atorvastatin is not recommended. |
| pitavastatin, simvastatin | ↑ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and pitavastatin or simvastatin is not recommended. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of either pitavastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated due to significantly increased pitavastatin or simvastatin concentrations and risk of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin | ↑ HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with these statins, a statin dosage reduction may be necessary‡. Closely monitor patients for myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, use of lovastatin is not recommended. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, refer to the statin prescribing information for specific statin dosing recommendations. |
| Immunosuppressants | ||
| cyclosporine§ | ↑ cyclosporine ↑ letermovir | Decrease the dosage of PREVYMIS to 240 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Frequently monitor cyclosporine whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of cyclosporine accordingly‡. |
| sirolimus§ | ↑ sirolimus | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with sirolimus, frequently monitor sirolimus whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of sirolimus accordingly§. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine and sirolimus, refer to the sirolimus prescribing information for specific sirolimus dosing recommendations‡. |
| tacrolimus§ | ↑ tacrolimus | Frequently monitor tacrolimus whole blood concentrations during treatment and after discontinuation of PREVYMIS and adjust the dose of tacrolimus accordingly‡. |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | ||
| omeprazole | ↓ omeprazole | Clinical monitoring and dose adjustment may be needed. |
| pantoprazole | ↓ pantoprazole | Clinical monitoring and dose adjustment may be needed. |
| Wakefulness-Promoting Agents | ||
| modafinil | ↓ letermovir | Co-administration of PREVYMIS and modafinil is not recommended due to potential for loss of efficacy of PREVYMIS. |
| CYP3A Substrates | ||
| Examples: alfentanil, fentanyl, midazolam, and quinidine | ↑ CYP3A substrate | When PREVYMIS is co-administered with a CYP3A substrate, refer to the prescribing information for dosing of the CYP3A substrate with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor‡. When PREVYMIS is co-administered with cyclosporine, the combined effect on CYP3A substrates may be similar to a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Refer to the prescribing information for dosing of the CYP3A substrate with a strong CYP3A inhibitor‡. CYP3A substrates pimozide and ergot alkaloids are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. |
7.4 Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with PREVYMIS
No clinically significant interactions were observed in clinical drug-drug interaction studies of letermovir and acyclovir, digoxin, mycophenolate mofetil, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, ethinyl estradiol, and levonorgestrel.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of PREVYMIS in patients below 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 373 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P001, 56 (15%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Of 144 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P040, 32 (22%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Of the 292 subjects treated with PREVYMIS in Trial P002, 48 (16%) subjects were 65 years of age or older. Safety and efficacy were similar across older and younger subjects in each trial. No dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
For patients with CLcr greater than 10 mL/min (by Cockcroft-Gault equation), no dosage adjustment of PREVYMIS is required based on renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The safety of PREVYMIS in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr less than 10 mL/min), including patients on dialysis, is unknown.
In patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min receiving PREVYMIS injection, accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropyl betadex, could occur. Closely monitor serum creatinine levels in these patients.
10. Overdosage
There is no specific antidote for overdose with PREVYMIS. In case of overdose, it is recommended that the patient be monitored for adverse reactions and appropriate symptomatic treatment be instituted.
It is unknown whether dialysis will result in meaningful removal of PREVYMIS from systemic circulation.
11. Prevymis Description
PREVYMIS contains letermovir, an inhibitor of the CMV DNA terminase complex, and is administered orally or by intravenous infusion.
PREVYMIS is available as 240 mg and 480 mg tablets. PREVYMIS tablets contain either 240 mg or 480 mg of letermovir and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone 25, and film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose 2910, iron oxide red (only for 480 mg tablets), iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Carnauba wax is added as a polishing agent.
PREVYMIS is also available as 240 mg and 480 mg injection for intravenous infusion. PREVYMIS injection is a clear, preservative-free sterile solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles in single-dose vials of either 240 mg or 480 mg per vial. Each 1 mL of solution contains 20 mg letermovir, hydroxypropyl betadex (150 mg), sodium chloride (3.1 mg), sodium hydroxide (1.2 mg), and Water for Injection, USP. The amount of sodium hydroxide may be adjusted to achieve a pH of approximately 7.5.
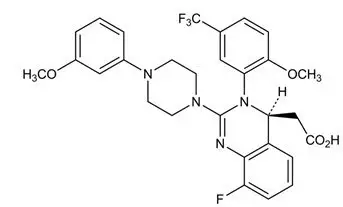
Letermovir has a molecular formula of C29H28F4N4O4 and a molecular weight of 572.55. The chemical name for letermovir is (4S)-2-{8-Fluoro-2-[4-(3- methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-[2-methoxy-5- (trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetic acid. Letermovir is very slightly soluble in water.
The chemical structure of letermovir is:
12. Prevymis - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of letermovir are displayed in Table 5.
|
|
| Pharmacokinetics in HSCT Recipients | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state median (90% prediction interval) AUC (ng∙hr/mL) of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily, no cyclosporine | 34,400 (16,900, 73,700) |
| 480 mg IV once daily, no cyclosporine | 100,000 (65,300, 148,000) |
| 240 mg oral once daily, with cyclosporine | 60,800 (28,700, 122,000) |
| 240 mg IV once daily, with cyclosporine | 70,300 (46,200, 106,000) |
| Pharmacokinetics in Kidney Transplant Recipients | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state median (90% prediction interval) AUC (ng∙hr/mL) of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily, no cyclosporine | 62,700 (17,500, 139,000) |
| 240 mg oral once daily, with cyclosporine | 71,900 (42,400, 125,000) |
| Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Subjects | |
| Treatment Regimen | Steady-state geometric mean AUC and Cmax of PREVYMIS |
| 480 mg oral once daily | Cmax: 13,000 ng/mL |
| AUC: 71,500 ng∙hr/mL | |
| Dose proportionality | Greater than proportional following single and multiple oral or IV doses of PREVYMIS 240 mg and 480 mg |
| Accumulation ratio† | Cmax: 1.03 AUC: 1.22 |
| Time to steady-state | 9-10 days |
| Absorption | |
| Bioavailability | Healthy subjects administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 94% at an oral dose range of 240 mg to 480 mg HSCT recipients administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 35% with 480 mg oral once daily HSCT recipients administered PREVYMIS with cyclosporine: 85% with 240 mg oral once daily Kidney transplant recipients administered PREVYMIS without cyclosporine: 56%‡ with 480 mg oral once daily |
| Median Tmax (hr) | 1.5 to 3.0 hr |
| Effect of food (relative to fasting)§ | AUC: 99.63% [84.27% - 117.80%] Cmax: 129.82% [104.35% -161.50%] |
| Distribution | |
| Mean steady-state volume of distribution | 45.5 L following IV administration in HSCT recipients |
| % In vitro bound to human plasma proteins | 99% across the concentration range of 0.2 to 50 mg/L |
| In vitro blood-to plasma ratio | 0.56 across the concentration range of 0.1 to 10 mg/L |
| Metabolism | |
| In vitro metabolism | UGT1A1/1A3 (minor) |
| Drug-related component in plasma | 97% unchanged parent No major metabolites detected in plasma |
| Elimination | |
| Route of elimination | Hepatic uptake (OATP1B1/3) |
| Mean terminal t1/2 (hr) | 12 hrs after dosing of PREVYMIS 480 mg IV once daily |
| % of dose excreted in feces¶ | 93% |
| % of dose excreted in urine¶ | <2% |
| % of unchanged drug excreted in feces¶ | 70% |
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interaction studies were performed in healthy subjects with PREVYMIS and drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions (see Table 6 and Table 7).
In vitro results indicate that letermovir is a substrate of drug metabolizing enzymes CYP3A, CYP2D6, UGT1A1, and UGT1A3, and transporters OATP1B1/3 and P-gp. Oxidative metabolism is considered to be a minor elimination pathway based on in vivo human data. Inhibitors of OATP1B1/3 may result in increases in letermovir plasma concentrations. Changes in letermovir plasma concentrations due to inhibition of P-gp/BCRP by itraconazole were not clinically relevant. Changes in letermovir plasma concentrations due to inhibition of UGTs are not anticipated to be clinically relevant.
Based on in vitro studies, the metabolism of letermovir is not mediated by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C18, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, CYP4A11, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A7, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, UGT1A10, UGT2B4, UGT2B7, UGT2B15, or UGT2B17. The transport of letermovir is not mediated by OATP2B1, OCT1, OAT1, BCRP, or MRP2 in vitro.
Letermovir is a time-dependent inhibitor and inducer of CYP3A in vitro. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with midazolam resulted in increased exposure of midazolam, indicating that the net effect of letermovir on CYP3A is moderate inhibition (see Table 7). Based on these results, co-administration of PREVYMIS with CYP3A substrates may increase the plasma concentrations of the CYP3A substrates [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3), and Table 4]. Letermovir is a reversible inhibitor of CYP2C8 in vitro. When co-administered with PREVYMIS, plasma concentrations of CYP2C8 substrates are predicted to be increased [see Table 4 in Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Co-administration of PREVYMIS reduced the exposure of voriconazole, most likely due to the induction of voriconazole elimination pathways, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrates may decrease the plasma concentrations of the CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrates [see Table 4 in Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Letermovir is an inducer of CYP2B6 in vitro; the clinical relevance is unknown.
Letermovir inhibited efflux transporters P-gp, breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), bile salt export pump (BSEP), multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2), OAT3, and hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1/3 in vitro. Co-administration of PREVYMIS with substrates of OATP1B1/3 transporters (e.g. atorvastatin, a known substrate of CYP3A, OATP1B1/3, and potentially BCRP) may result in a clinically relevant increase in plasma concentrations of OATP1B1/3 substrates [see Table 4 in Drug Interactions (7.3)]. There were no clinically relevant changes in plasma concentrations of digoxin, a P-gp substrate, or acyclovir, an OAT3 substrate, following co-administration with PREVYMIS in clinical studies (see Table 7). The effect of letermovir on BCRP, BSEP, and MRP2 substrates was not evaluated in clinical studies; the clinical relevance is unknown.
Based on in vitro results letermovir is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, or UGT2B7 and is not an inducer of CYP1A2. Letermovir is not an inhibitor of OATP2B1, OCT1, OCT2, or OAT1 in vitro.
| Co-administered Drug | Regimen of Co-administered Drug | Letermovir Regimen | Geometric Mean Ratio [90% CI] of Letermovir PK with/without Co-administered Drug (No Effect=1.00) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | C24hr* | |||
| Abbreviations: PO= oral | |||||
|
|||||
| Antifungals | |||||
| fluconazole | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.11 (1.01, 1.23) | 1.06 (0.93, 1.21) | 1.28 (1.15, 1.43) |
| itraconazole | 200 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.33 (1.17, 1.51) | 1.21 (1.05, 1.39) | 1.90 (1.58, 2.28) |
| Antimycobacterials | |||||
| rifampin | 600 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 2.03 (1.84, 2.26) | 1.59 (1.46, 1.74) | 2.01 (1.59, 2.54) |
| 600 mg single dose IV | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.58 (1.38, 1.81) | 1.37 (1.16, 1.61) | 0.78 (0.65, 0.93) |
|
| 600 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.81 (0.67, 0.98) | 1.01 (0.79, 1.28) | 0.14 (0.11, 0.19) |
|
| 600 mg once daily PO (24 hours after rifampin)† | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.15 (0.13, 0.17) | 0.27 (0.22, 0.31) | 0.09 (0.06, 0.12) |
|
| Immunosuppressants | |||||
| cyclosporine | 200 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 2.11 (1.97, 2.26) | 1.48 (1.33, 1.65) | 2.06 (1.81, 2.35) |
| mycophenolate mofetil | 1 g single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.18 (1.04, 1.32) | 1.11 (0.92, 1.34) | 1.39 (1.12, 1.74) |
| tacrolimus | 5 mg single dose PO | 80 mg twice daily PO | 1.02 (0.97, 1.07) | 0.92 (0.84, 1.00) | 1.02 (0.93, 1.12) |
| Co-administered Drug | Regimen of Co-administered Drug | Letermovir Regimen | Geometric Mean Ratio [90% CI] of Co-administered Drug PK with/without Letermovir (No Effect=1.00) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | C24hr* | |||
| Abbreviations: PO=oral | |||||
|
|||||
| CYP3A Substrates | |||||
| midazolam | 1 mg single dose IV | 240 mg once daily PO | 1.47 (1.37, 1.58) | 1.05 (0.94, 1.17) | 2.74 (2.16, 3.49) |
| 2 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 2.25 (2.04, 2.48) | 1.72 (1.55, 1.92) | Not available | |
| P-gp Substrates | |||||
| digoxin | 0.5 mg single dose PO | 240 mg twice daily PO | 0.88 (0.80, 0.96) | 0.75 (0.63, 0.89) | 0.90 (0.84, 0.96) |
| Immunosuppressants | |||||
| cyclosporine | 50 mg single dose PO | 240 mg once daily PO | 1.66 (1.51, 1.82) | 1.08 (0.97, 1.19) | 2.19 (1.80, 2.66) |
| mycophenolate mofetil | 1 g single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.08 (0.97, 1.20) | 0.96 (0.82, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.86, 1.27) |
| tacrolimus | 5 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 2.42 (2.04, 2.88) | 1.57 (1.32, 1.86) | 2.53 (2.12, 3.03) |
| sirolimus | 2 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 3.40 (3.01, 3.85) | 2.76 (2.48, 3.06) | 3.15 (2.80, 3.55) |
| Antifungals and Antivirals | |||||
| acyclovir | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.02 (0.87, 1.2) | 0.82 (0.71, 0.93) | 1.13 (0.94, 1.36) |
| fluconazole | 400 mg single dose PO | 480 mg single dose PO | 1.03 (0.99, 1.08) | 0.95 (0.92, 0.99) | 1.04 (1.00, 1.08) |
| itraconazole | 200 mg once daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.76 (0.71, 0.81) | 0.84 (0.76, 0.92) | 0.67 (0.61, 0.73) |
| posaconazole | 300 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.98 (0.82, 1.17) | 1.11 (0.95, 1.29) | 1.10 (0.94, 1.30) |
| voriconazole | 200 mg twice daily PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 0.56 (0.51, 0.62) | 0.61 (0.53, 0.71) | 0.49 (0.42, 0.57) |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | |||||
| atorvastatin | 20 mg single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 3.29 (2.84, 3.82) | 2.17 (1.76, 2.67) | 3.62 (2.87, 4.55) |
| Oral Contraceptives | |||||
| ethinyl estradiol (EE) /levonorgestrel (LNG) | 0.03 mg EE single dose PO | 480 mg once daily PO | 1.42 (1.32, 1.52) | 0.89 (0.83, 0.96) | 1.57 (1.45, 1.70) |
| 0.15 mg LNG single dose PO | 1.36 (1.30, 1.43) | 0.95 (0.86, 1.04) | 1.38 (1.32, 1.46) |
||
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Testicular toxicity in rats observed at ≥180 mg/kg/day (greater than or equal to 3 times the human exposure at the RHD) was characterized by decreased testis weight, bilateral seminiferous tubular degeneration, decreased sperm count and motility, and resultant decreased male fertility. Male reproductive system toxicities were not observed in either a monkey testicular toxicity study up to 240 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times higher than human exposure at the RHD), or a general toxicology study in mice up to 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times higher than human exposure at the RHD).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Overview of Clinical Studies
An overview of the trials contributing to the assessment of efficacy and safety of PREVYMIS in HSCT and kidney transplant recipients is provided in Table 8.
| Trial (NCT Number) | Population | Trial Arms (N)* | Duration of Prophylaxis Post-Transplant | Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
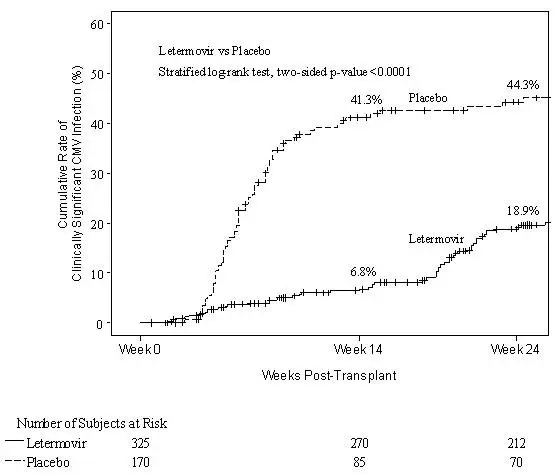
| P001 (NCT02137772) | Adult allogeneic HSCT recipients [R+] | PREVYMIS (373) Placebo (192) | Through Week 14 | Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 24 post-HSCT |
| P040 (NCT03930615) | Adult allogeneic HSCT recipients [R+] at risk for late CMV infection and disease | PREVYMIS (144) Placebo (74) | Extension of prophylaxis from Week 14 through Week 28 | Clinically significant CMV infection through Week 28 post-HSCT |
| P002 (NCT03443869) | Adult kidney transplant recipients [D+/R-] | PREVYMIS (292) Valganciclovir (297) | Through Week 28 | CMV disease through Week 52 post-kidney transplant |
14.2 Adult CMV-seropositive Recipients [R+] of an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (Trial P001 and Trial P040)
Prophylaxis Through Week 14 (~100 days) Post-HSCT (Trial P001)
To evaluate PREVYMIS prophylaxis as a preventive strategy for CMV infection or disease in transplant recipients at high risk for CMV reactivation, the efficacy of PREVYMIS was assessed in a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 Trial (P001, NCT02137772) in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). Subjects were randomized (2:1) to receive either PREVYMIS at a dose of 480 mg once daily adjusted to 240 mg when co-administered with cyclosporine, or placebo. Randomization was stratified by investigational site and risk level for CMV reactivation at the time of study entry. Study drug was initiated after HSCT (at any time from Day 0 to Day 28 post-HSCT) and continued through Week 14 post-HSCT. Study drug was administered either orally or intravenously; the dose of PREVYMIS was the same regardless of the route of administration. Subjects received CMV DNA monitoring weekly until post-HSCT Week 14 and then bi-weekly until post-HSCT Week 24, with initiation of standard-of-care CMV pre-emptive therapy if CMV viremia was considered clinically significant. Subjects had continued follow-up through Week 48 post-HSCT.
Among the 565 treated subjects, 70 subjects were found to have CMV viremia prior to study drug initiation and were therefore excluded from the efficacy analyses. The efficacy population consisted of 325 subjects who received PREVYMIS (including 91 subjects who received at least one IV dose) and 170 who received placebo (including 41 subjects who received at least one IV dose). The IV formulation of PREVYMIS was used at investigators' discretion in subjects who were unable to take oral therapy (e.g., unable to tolerate oral intake). The median time to starting study drug was 8 days after transplantation. Thirty-four percent (34%) of subjects were engrafted at baseline. The median age was 55 years (range: 18 to 76 years). 57% were male; 84% were White; 9% were Asian; 2% were Black or African American; and 5% were other (American Indian or Alaska Native, multiple, and missing). 7% were Hispanic or Latino; 89% not Hispanic or Latino; and 4% other (not reported, unknown, and missing).
At baseline, 30% of all subjects had one or more of the following factors associated with increased risk for CMV reactivation (high risk stratum): Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)-related donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following three HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B or –DR; haploidentical donor; unrelated donor with at least one mismatch at one of the following four HLA-gene loci: HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1; use of umbilical cord blood as stem cell source; use of ex vivo T-cell-depleted grafts; Grade 2 or greater Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD) requiring systemic corticosteroids. The remaining 70% of subjects did not meet any of these high risk stratum criteria and were therefore included in the low risk stratum. Additionally, 48% of subjects received a myeloablative regimen, 51% were receiving cyclosporine, and 43% were receiving tacrolimus. The most common primary reasons for transplant were acute myeloid leukemia (38%), myelodysplastic syndrome (16%), and lymphoma (12%).
14.3 Adult CMV-seronegative Recipients of a Kidney Transplant from a CMV-seropositive Donor [D+/R-] (Trial P002)
To evaluate PREVYMIS prophylaxis as a preventive strategy for CMV disease in kidney transplant recipients, the efficacy of PREVYMIS was assessed in a multicenter, double-blind, active comparator-controlled non-inferiority Phase 3 trial (P002, NCT03443869) in adult kidney transplant recipients at high risk [D+/R-]. Subjects were randomized (1:1) to receive either PREVYMIS or valganciclovir. PREVYMIS was administered at a dose of 480 mg once daily (adjusted to 240 mg when co-administered with cyclosporine). PREVYMIS was given concomitantly with acyclovir. Valganciclovir was given concomitantly with a placebo to acyclovir. Randomization was stratified by the use or nonuse of highly cytolytic, anti-lymphocyte immunotherapy during induction. Study drug was initiated between Day 0 and Day 7 post-kidney transplant and continued through Week 28 (~200 days) post-transplant. Study drug was administered either orally or IV; the dose of PREVYMIS was the same regardless of the route of administration. Three subjects received IV PREVYMIS for a mean duration of 1.7 days. Subjects were monitored through Week 52 post-transplant.
Among the 589 treated subjects, 292 subjects received PREVYMIS and 297 received valganciclovir. The median age was 51 years (range: 18 to 82 years); 72% were male; 84% were White; 9% were Black; 3% were multiple; 2% were Asian; 1% Alaskan native or American Indian; 17% were Hispanic or Latino; and 60% received a kidney from a deceased donor. The most common primary reasons for transplant were congenital cystic kidney disease (17%), hypertension (16%), and diabetes/diabetic nephropathy (14%).
CMV Disease
The primary efficacy endpoint of Trial P002 was the incidence of CMV disease (CMV end-organ disease or CMV syndrome, confirmed by an independent adjudication committee) through Week 52 post-transplant. The Observed Failure (OF) approach was used, where subjects who discontinued prematurely from the study for any reason or were missing data at the timepoint were not counted as failures. The number of subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 52 was 32 (11%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 28 (9%) in the valganciclovir arm. The number of subjects with a missing outcome in the Week 52 visit window was 24 (8%) in the PREVYMIS arm and 25 (8%) in the valganciclovir arm.
Efficacy results from Trial P002 are shown in Table 11.
| Parameter |
PREVYMIS (N=289) |
Valganciclovir (N=297) |
|---|---|---|
| Note: Approach to handling missing values: Observed failure (OF) approach. With OF approach, subjects who discontinued from the study before Week 52 or had a missing outcome in the Week 52 visit window were not counted as failures. | ||
|
||
| CMV Disease* Through Week 52 | 10% | 12% |
| CMV Syndrome† | 8% | 11% |
| CMV End-organ Disease | 2% | <1% |
| Stratum-adjusted Treatment Difference‡
(PREVYMIS – Valganciclovir) | -1.4 (-6.5, 3.8)§ | |
Efficacy was comparable across all subgroups, including the use/nonuse of highly cytolytic, anti-lymphocyte immunotherapy during induction.
In an exploratory analysis of the incidence of CMV disease through Week 28 post-transplant, the difference (PREVYMIS – Valganciclovir) was -1.7% with 95% CI of (-3.4, 0.1). No subjects in the PREVYMIS group experienced CMV disease through Week 28 post-transplant (end of treatment period) compared with 5 subjects in the valganciclovir group.
16. How is Prevymis supplied
| PREVYMIS
letermovir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PREVYMIS
letermovir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PREVYMIS
letermovir injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| PREVYMIS
letermovir injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC (118446553) |