Drug Class: Upper respiratory combinations
Promethazine and Dextromethorphan Description
Inactive Ingredients: artificial pineapple flavor, artificial raspberry flavor, ascorbic acid, citric acid anhydrous, dehydrated alcohol, D&C Yellow No. 10, edetate disodium, FD&C Yellow No. 6, glycerin, sucrose, methylparaben, purified water, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate dihydrate and sodium propionate.
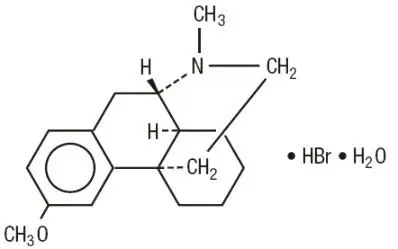
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide is a salt of the methyl ether of the dextrorotatory isomer of levorphanol, a narcotic analgesic. It is chemically designated as 3-Methoxy-17-methyl-9α, 13α, 14α-morphinan hydrobromide monohydrate. Dextromethorphan hydrobromide occurs as white crystals sparingly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. It has a molecular weight of 370.32, a molecular formula of C 18H 25NO•HBr•H 2O, and the following structural formula:
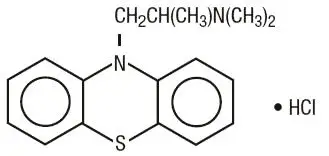
Promethazine hydrochloride occurs as a white to faint yellow, practically odorless, crystalline powder which slowly oxidizes and turns blue on prolonged exposure to air. It is soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. It has a molecular weight of 320.88, a molecular formula of C 17H 20N 2S•HCl, and the following structural formula:
Promethazine and Dextromethorphan - Clinical Pharmacology
Dextromethorphan
The drug acts centrally and elevates the threshold for coughing. It is about equal to codeine in depressing the cough reflex. In therapeutic dosage dextromethorphan does not inhibit ciliary activity.
Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and exerts its effect in 15 to 30 minutes. The duration of action after oral administration is approximately three to six hours. Dextromethorphan is metabolized primarily by liver enzymes undergoing O-demethylation, N-demethylation, and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfate. In humans, (+)-3-hydroxy-N-methyl-morphinan, (+)-3-hydroxymorphinan, and traces of unmetabolized drug were found in urine after oral administration.
Promethazine
Promethazine is an H 1 receptor blocking agent. In addition to its antihistaminic action, it provides clinically useful sedative and antiemetic effects.
Promethazine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Clinical effects are apparent within 20 minutes after oral administration and generally last four to six hours, although they may persist as long as 12 hours. Promethazine is metabolized by the liver to a variety of compounds; the sulfoxides of promethazine and N-demethylpromethazine are the predominant metabolites appearing in the urine.
Contraindications
Promethazine is contraindicated in comatose states, and in individuals known to be hypersensitive or to have had an idiosyncratic reaction to promethazine or to other phenothiazines.
Antihistamines are contraindicated for use in the treatment of lower respiratory tract symptoms, including asthma.
Warnings
WARNING
POSTMARKETING CASES OF RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, INCLUDING FATALITIES, HAVE BEEN REPORTED WITH USE OF PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS LESS THAN 2 YEARS OF AGE. A WIDE RANGE OF WEIGHT-BASED DOSES OF PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE HAVE RESULTED IN RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION IN THESE PATIENTS.
CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHEN ADMINISTERING PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE TO PEDIATRIC PATIENTS 2 YEARS OF AGE AND OLDER. IT IS RECOMMENDED THAT THE LOWEST EFFECTIVE DOSE OF PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BE USED IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS 2 YEARS OF AGE AND OLDER AND CONCOMITANT ADMINISTRATION OF OTHER DRUGS WITH RESPIRATORY DEPRESSANT EFFECTS BE AVOIDED.
Promethazine
Respiratory Depression
Promethazine may lead to potentially fatal respiratory depression.
Use of Promethazine in patients with compromised respiratory function (e.g., COPD, sleep apnea) should be avoided.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases where the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g. pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include 1) immediate discontinuation of promethazine HCl, antipsychotic drugs, if any, and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
Since recurrences of NMS have been reported with phenothiazines, the reintroduction of promethazine HCl should be carefully considered.
Use In Pediatric Patients
PROMETHAZINE PRODUCTS ARE CONTRAINDICATED FOR USE IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS LESS THAN TWO YEARS OF AGE.
CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHEN ADMINISTERING PROMETHAZINE PRODUCTS TO PEDIATRIC PATIENTS 2 YEARS OF AGE AND OLDER BECAUSE OF THE POTENTIAL FOR FATAL RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION. RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION AND APNEA, SOMETIMES ASSOCIATED WITH DEATH, ARE STRONGLY ASSOCIATED WITH PROMETHAZINE PRODUCTS AND ARE NOT DIRECTLY RELATED TO INDIVIDUALIZED WEIGHT-BASED DOSING, WHICH MIGHT OTHERWISE PERMIT SAFE ADMINISTRATION. CONCOMITANT ADMINISTRATION OF PROMETHAZINE PRODUCTS WITH OTHER RESPIRATORY DEPRESSANTS HAS AN ASSOCIATION WITH RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, AND SOMETIMES DEATH, IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS.
ANTIEMETICS ARE NOT RECOMMENDED FOR TREATMENT OF UNCOMPLICATED VOMITING IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS, AND THEIR USE SHOULD BE LIMITED TO PROLONGED VOMITING OF KNOWN ETIOLOGY. THE EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYMPTOMS WHICH CAN OCCUR SECONDARY TO PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADMINISTRATION MAY BE CONFUSED WITH THE CNS SIGNS OF UNDIAGNOSED PRIMARY DISEASE, e.g., ENCEPHALOPATHY OR REYE'S SYNDROME. THE USE OF PROMETHAZINE PRODUCTS SHOULD BE AVOIDED IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WHOSE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS MAY SUGGEST REYE'S SYNDROME OR OTHER HEPATIC DISEASES.
Excessively large dosages of antihistamines, including promethazine hydrochloride, in pediatric patients may cause sudden death (see OVERDOSAGE). Hallucinations and convulsions have occurred with therapeutic doses and overdoses of promethazine hydrochloride in pediatric patients. In pediatric patients who are acutely ill associated with dehydration, there is an increased susceptibility to dystonias with the use of promethazine HCl.
Precautions
General
Drugs having anticholinergic properties should be used with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction, and bladder-neck obstruction.
Promethazine should be used cautiously in persons with cardiovascular disease or with impairment of liver function.
Information For Patients
The concomitant use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants, including narcotic analgesics, sedatives, hypnotics, and tranquilizers, may have an additive effect and should be avoided or their dosage reduced.
Patients should be advised to report any involuntary muscle movements.
Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
Drug Interactions
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category C
Specific studies to test the action of the drug on parturition, lactation, and development of the animal neonate were not done, but a general preliminary study in rats indicated no effect on these parameters. Although antihistamines have been found to produce fetal mortality in rodents, the pharmacological effects of histamine in the rodent do not parallel those in man. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of promethazine in pregnant women.
Promethazine and dextromethorphan should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether promethazine or dextromethorphan is excreted in human milk.
Caution should be exercised when promethazine and dextromethorphan is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Promethazine hydrochloride and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup should be used with caution in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older (see WARNINGS – Use in Pediatric Patients).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Promethazine
Cardiovascular - Increased or decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia, faintness.
Dermatologic - Dermatitis, photosensitivity, urticaria.
Hematologic - Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis.
Gastrointestinal - Dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, jaundice.
Respiratory-Asthma, nasal stuffiness, respiratory depression (potentially fatal) and apnea (potentially fatal). (See WARNINGS-Promethazine; Respiratory Depression.)
Other-Angioneurotic edema. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (potentially fatal) has also been reported. (See WARNINGS-Promethazine; Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome.)
Paradoxical Reactions - Hyperexcitability and abnormal movements have been reported in patients following a single administration of promethazine HCl. Consideration should be given to the discontinuation of promethazine HCl and to the use of other drugs if these reactions occur. Respiratory depression, nightmares, delirium, and agitated behavior have also been reported in some of these patients.
Overdosage
Promethazine
Stimulation may be evident, especially in children and geriatric patients. Convulsions may rarely occur. A paradoxical reaction has been reported in children receiving single doses of 75 mg to 125 mg orally, characterized by hyperexcitability and nightmares.
Atropine-like signs and symptoms–dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils, flushing, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms, may occur.
Treatment
Severe hypotension usually responds to the administration of norepinephrine or phenylephrine. EPINEPHRINE SHOULD NOT BE USED, since its use in a patient with partial adrenergic blockage may further lower the blood pressure.
Limited experience with dialysis indicates that it is not helpful.
Promethazine and Dextromethorphan Dosage and Administration
The average effective dose is given in the following table:
| Adults
| 1 teaspoonful (5 mL) every 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 30 mL in 24 hours.
|
| Children 6 years to under 12 years
| ½ to 1 teaspoonful (2.5 to 5 mL) every 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 20 mL in 24 hours.
|
| Children 2 years to under 6 years
| ¼ to ½ teaspoonful (1.25 to 2.5 mL) every 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 10 mL in 24 hours.
|
How is Promethazine and Dextromethorphan supplied
STORAGE AND HANDLING
Keep tightly closed. Protect from light.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Manufactured For:
Wockhardt USA, LLC.
20 Waterview Blvd.,
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Manufactured By:
Halo Pharmaceutical Canada Inc.
Mirabel, QC J7J 0W8 Canada
A50-7604-16
REV. 09-22
C-11341
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 437 mL Bottle Label
NDC 64679-604-16
PROMETHAZINE
WITH
DEXTROMETHORPHAN
COUGH SYRUP
(Promethazine Hydrochloride
6.25 mg/5 mL & Dextromethorphan
Hydrobromide 15 mg/5 mL)
Alcohol 7.0%
DO NOT USE IF INNER FOIL SEAL PRINTED "SEALED FOR
YOUR PROTECTION" IS BROKEN OR MISSING.
BULK CONTAINER —
NOT FOR HOUSEHOLD USE
Rx Only
NET: 1 Pint (473 mL)

| PROMETHAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE
promethazine hydrochloride and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Wockhardt USA LLC. (170508365) |
| Registrant - Wockhardt Bio AG (483165838) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halo Pharmaceutical Canada Inc. | 250928632 | analysis(64679-604) , manufacture(64679-604) , label(64679-604) , pack(64679-604) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofie Chimie, Sisteron, France | 262600765 | analysis(64679-604) , api manufacture(64679-604) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aurobindo Pharma Limited, Andhra Pradesh, India | 918917626 | api manufacture(64679-604) , analysis(64679-604) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divis Laboratories Limited | 918598199 | api manufacture(64679-604) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neopharm Labs Inc. | 243379372 | analysis(64679-604) | |




