Drug Detail:Protamine (monograph) (Medically reviewed)
Drug Class:
WARNING
Protamine sulfate can cause severe hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, catastrophic pulmonary vasoconstriction, and pulmonary hypertension. Risk factors include high dose or overdose, rapid administration (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION), repeated doses, previous administration of protamine, and current or previous use of protamine-containing drugs (NPH insulin, protamine zinc insulin, and certain beta-blockers). Allergy to fish, previous vasectomy, and severe left ventricular dysfunction and abnormal preoperative pulmonary hemodynamics also may be risk factors. In patients with any of these risk factors, the risk to benefit of administration of protamine sulfate should be carefully considered. Vasopressors and resuscitation equipment should be immediately available in case of a severe reaction to protamine. Protamine sulfate should not be given when bleeding occurs without prior heparin use.
Protamine Sulfate Injection Description
Protamines are simple proteins of low molecular weight that are rich in arginine and strongly basic. They occur in the sperm of salmon and certain other species of fish.
Protamine sulfate occurs as fine white or off-white amorphous or crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water. The pH is between 6.0 and 7.0. The cationic hydrogenated protamine at a pH of 6.8 to 7.1 reacts with anionic heparin at a pH of 5.0 to 7.5 to form an inactive complex.
Protamine Sulfate Injection, USP is a sterile, isotonic solution of protamine sulfate. It acts as a heparin antagonist. It is also a weak anticoagulant.
Each mL contains: Protamine sulfate 10 mg; sodium chloride 9 mg; Water for Injection q.s. Sulfuric acid and/or dibasic sodium phosphate (heptahydrate) may have been added for pH adjustment.
The preparation is preservative free.
Protamine sulfate is administered intravenously.
Protamine Sulfate Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
When administered alone, protamine has an anticoagulant effect. However, when it is given in the presence of heparin (which is strongly acidic), a stable salt is formed and the anticoagulant activity of both drugs is lost.
Protamine sulfate has a rapid onset of action. Neutralization of heparin occurs within five minutes after intravenous administration of an appropriate dose of protamine sulfate. Although the metabolic fate of the heparin-protamine complex has not been elucidated, it has been postulated that protamine sulfate in the heparin-protamine complex may be partially metabolized or may be attacked by fibrinolysin, thus freeing heparin.
Related/similar drugs
protamineIndications and Usage for Protamine Sulfate Injection
Protamine Sulfate Injection, USP is indicated in the treatment of heparin overdosage.
Contraindications
Protamine sulfate is contraindicated in patients who have shown previous intolerance to the drug.
Warnings
Hyperheparinemia or bleeding has been reported in experimental animals and in some patients 30 minutes to 18 hours after cardiac surgery (under cardiopulmonary bypass) in spite of complete neutralization of heparin by adequate doses of protamine sulfate at the end of the operation. It is important to keep the patient under close observation after cardiac surgery. Additional doses of protamine sulfate should be administered if indicated by coagulation studies, such as the heparin titration test with protamine and the determination of plasma thrombin time.
Too-rapid administration of protamine sulfate can cause severe hypotensive and anaphylactoid reactions (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and WARNINGS). Facilities to treat shock should be available.
Precautions
General
Because of the anticoagulant effect of protamine, it is unwise to give more than 50 mg over a short period unless a larger dose is clearly needed .
Patients with a history of allergy to fish may develop hypersensitivity reactions to protamine, although to date no relationship has been established between allergic reactions to protamine and fish allergy.
Previous exposure to protamine can induce a humoral immune response and predispose susceptible individuals to the development of untoward reactions from the subsequent use of this drug. Patients exposed to protamine through the use of protamine-containing insulin or during heparin neutralization may experience life-threatening reactions and fatal anaphylaxis upon receiving large doses of protamine intravenously. Severe reactions to intravenous protamine can occur in the absence of local or systemic allergic reactions to subcutaneous injection of protamine-containing insulin. Reports of the presence of antiprotamine antibodies in the sera of infertile or vasectomized men suggest that some of these individuals may react to the use of protamine sulfate.
Fatal anaphylaxis has been reported in one patient with no prior history of allergies.
Drug Interactions
Protamine sulfate has been shown to be incompatible with certain antibiotics, including several of the cephalosporins and penicillins (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies have not been performed to determine potential for carcinogenicity, mutagenicity or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with protamine sulfate. It is also not known whether protamine sulfate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Protamine sulfate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The intravenous administration of protamine sulfate may cause a sudden fall in blood pressure and bradycardia. Other reactions include transitory flushing and feeling of warmth, dyspnea, nausea, vomiting and lassitude. Back pain has been reported in conscious patients undergoing such procedures as cardiac catheterization.
Severe adverse reactions have been reported including: (1) Anaphylaxis that resulted in severe respiratory distress, circulation collapse and capillary leak (see PRECAUTIONS). Fatal anaphylaxis has been reported in one patient with no prior history of allergies; (2) Anaphylactoid reactions with circulatory collapse, capillary leak, and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema; acute pulmonary hypertension.
Complement activation by the heparin-protamine complexes, release of lysosomal enzymes from neutrophils, and prostaglandin and thomboxane generation have been associated with the development of anaphylactoid reactions.
Severe and potentially irreversible circulatory collapse associated with myocardial failure and reduced cardiac output can also occur. The mechanism(s) of this reaction and the role played by concurrent factors are unclear.
High-protein, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema associated with the use of protamine has been reported in patients on cardiopulmonary bypass who are undergoing cardiovascular surgery. The etiologic role of protamine in the pathogenesis of this condition is uncertain, and multiple factors have been present in most cases. The condition has been reported in association with administration of certain blood products, other drugs, cardiopulmonary bypass alone, and other etiologic factors. It is difficult to treat, and it can be life-threatening. Because fatal anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported after the administration of protamine sulfate, the drug should be given only when resuscitation techniques and treatment of anaphylactic and anaphylactoid shock are readily available.
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms
Overdose of protamine sulfate may cause bleeding. Protamine has a weak anticoagulant effect due to an interaction with platelets and with many proteins including fibrinogen. This effect should be distinguished from the rebound anticoagulation that may occur 30 minutes to 18 hours following the reversal of heparin with protamine.
Rapid administration of protamine is more likely to result in bradycardia, dyspnea, a sensation of warmth, flushing, and severe hypotension. Hypertension has also occurred.
The median lethal dose of protamine sulfate is 50 mg/kg in mice. Serum concentrations of protamine sulfate are not clinically useful. Information is not available on the amount of drug in a single dose that is associated with overdosage or is likely to be life-threatening.
Treatment
To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is your certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference (PDR). In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs and unusual drug kinetics in your patient.
Replace blood loss with blood transfusions or fresh frozen plasma.
If the patient is hypotensive, consider fluids, epinephrine, dobutamine or dopamine.
Protamine Sulfate Injection Dosage and Administration
Each mg of protamine sulfate, calculated on the dried basis, neutralizes not less than 100 USP Heparin Units.
Protamine sulfate injection should be given by very slow intravenous injection over a 10-minute period in doses not to exceed 50 mg (see WARNINGS).
Protamine sulfate is intended for injection without further dilution; however, if further dilution is desired, D5-W or normal saline may be used. Diluted solutions should not be stored since they contain no preservative.
Protamine sulfate should not be mixed with other drugs without knowledge of their compatibility, because protamine sulfate has been shown to be incompatible with certain antibiotics, including several of the cephalosporins and penicillins.
Because heparin disappears rapidly from the circulation, the dose of protamine sulfate required also decreases rapidly with the time elapsed following intravenous injection of heparin. For example, if the protamine sulfate is administered 30 minutes after the heparin, one-half the usual dose may be sufficient.
The dosage of protamine sulfate should be guided by blood coagulation studies (see WARNINGS).
Parenteral drug products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
How is Protamine Sulfate Injection supplied
| Product Code | Unit of Sale | Strength | Each |
| 22905 | NDC 63323-229-05 Unit of 25 | 50 mg per 5 mL (10 mg per mL) | NDC 63323-229-01 5 mL Single Dose Flip-top Vial |
| 22930 | NDC 63323-229-30 Individually Packaged | 250 mg per 25 mL (10 mg per mL) | NDC 63323-229-30 25 mL Single Dose Flip-top Vial |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not permit to freeze.
CAUTION: The total dose of protamine sulfate contained in product No. 22925 and 22930 (250 mg in 25 mL) is 5 times greater than in product No. 22905 (50 mg in 5 mL).
The large size 25 mL vials are designed for antiheparin treatment only when large doses of heparin have been given during surgery and are to be neutralized by large doses of protamine sulfate after surgical procedures.
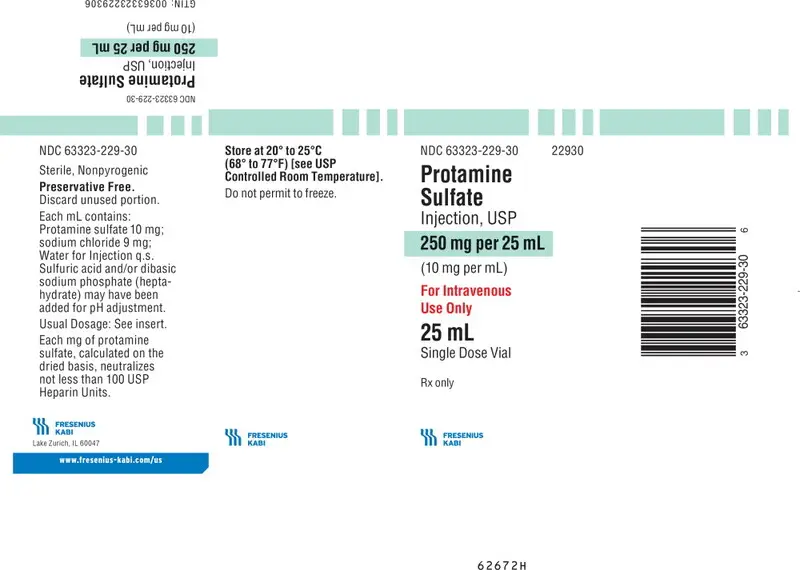
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Protamine 25 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-229-30 22930
Protamine
Sulfate
Injection, USP
250 mg per 25 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous
Use Only
25 mL
Single Dose Vial
Rx only
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Protamine 25 mL Single Dose Vial Carton Panel
NDC 63323-229-30 22930
Protamine
Sulfate
Injection, USP
250 mg per 25 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous
Use Only
25 mL
Single Dose Vial
Rx only
| PROTAMINE SULFATE
protamine sulfate injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC | 023648251 | manufacture(63323-229) , analysis(63323-229) | |