Drug Detail:Rapivab (Peramivir [ per-am-i-vir ])
Drug Class: Neuraminidase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
RAPIVAB® (peramivir) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
Indications and Usage for Rapivab
RAPIVAB is an influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in patients 6 months and older who have been symptomatic for no more than two days. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- Efficacy based on clinical trials in which the predominant influenza virus type was influenza A; a limited number of subjects infected with influenza B virus were enrolled. (1)
- Consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use. (1)
- Efficacy could not be established in patients with serious influenza requiring hospitalization. (1)
Rapivab Dosage and Administration
- Administer RAPIVAB as a single dose within 2 days of onset of influenza symptoms (2.1)
- Administer RAPIVAB by intravenous infusion for a minimum of 15 minutes (2.1)
Recommended Dosage Single Dose Adults and adolescents (13 years and older) 600 mg Pediatric patients (6 months to 12 years of age) 12 mg/kg
(up to 600 mg)Recommended Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Altered Creatinine Clearance Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) ≥50 30-49 10-29 a Up to maximum dose of 600 mg. Adults and adolescents
(13 years and older)600 mg 200 mg 100 mg Pediatric patientsa
(2 to 12 years of age)12 mg/kg 4 mg/kg 2 mg/kg - No recommendation for dosage adjustment can be made for pediatric patients 6 months to less than 2 years of age with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min (2.2)
- Hemodialysis: Administer after dialysis (2.2)
- RAPIVAB must be diluted prior to administration (2.3)
- See the Full Prescribing Information for drug compatibility information (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 200 mg in 20 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-use vial (3)
Contraindications
Patients with known serious hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis to peramivir or any component of RAPIVAB (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cases of anaphylaxis and serious skin/hypersensitivity reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme have occurred with RAPIVAB. Discontinue RAPIVAB and initiate appropriate treatment if anaphylaxis or serious skin reaction occurs or is suspected. (5.1)
- Neuropsychiatric events: Patients with influenza may be at an increased risk of hallucinations, delirium and abnormal behavior early in their illness. Monitor for signs of abnormal behavior. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction (incidence >2%) is diarrhea. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-833-633-2279 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV), intranasal: Avoid use of LAIV within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after administration of RAPIVAB, unless medically indicated (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 11/2022
Related/similar drugs
amantadine, Tamiflu, oseltamivir, Vicks DayQuil Severe Cold & Flu, Dologesic, Coricidin HBP Cold & FluFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Rapivab
RAPIVAB is indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in patients 6 months and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 2 days.
2. Rapivab Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Acute Uncomplicated Influenza
Administer RAPIVAB within 2 days of onset of symptoms of influenza.
2.2 Dosing in Patients with Renal Impairment
Significantly increased drug exposures were observed when RAPIVAB was administered to adult subjects with renal dysfunction [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, the RAPIVAB dosage should be reduced for patients with baseline creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min using the recommendations in Table 1 and Table 2. No dosage adjustment is required for single administration of RAPIVAB in patients with creatinine clearance of 50 mL/min or higher [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In patients with chronic renal impairment maintained on hemodialysis, RAPIVAB should be administered after dialysis at a dose adjusted based on renal function (Table 1 and Table 2) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Creatinine Clearancea (mL/min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥50 | 30 to 49 | 10 to 29 | |
| a Calculated using the Cockcroft and Gault equation. | |||
| Recommended Dose (mg) | 600 mg | 200 mg | 100 mg |
| Creatinine Clearancea (mL/min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥50 | 30 to 49 | 10 to 29 | |
| a Calculated using the Cockcroft and Gault equation. | |||
| b Up to maximum dose of 600 mg. | |||
| Recommended Dose (mg/kg)b | 12 mg/kg | 4 mg/kg | 2 mg/kg |
No data are available to inform a recommendation for dosage adjustment with RAPIVAB in pediatric patients 6 months to less than 2 years of age with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Preparation of RAPIVAB for Intravenous Infusion
Use aseptic technique during the preparation of RAPIVAB to prevent inadvertent microbial contamination. There is no preservative or bacteriostatic agent present in the solution.
Follow the steps below to prepare a diluted solution of RAPIVAB:
- (a)
- Do not use if seal over bottle opening is broken or missing.
- (b)
- Visually inspect RAPIVAB for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
- (c)
- Dilute an appropriate dose of RAPIVAB 10 mg/mL solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)] in 0.9% or 0.45% sodium chloride, 5% dextrose, or lactated Ringer's. The maximum infusion volume is provided in Table 3. The final concentration of diluted RAPIVAB for administration should be between 1 mg/mL and 6 mg/mL.
Table 3. Maximum Infusion Volume by Age and Weight Age Weight (kg) Maximum Infusion Volumea (mL) aInfusion volume is the total volume of RAPIVAB 10 mg/mL solution and diluent. The final concentration of diluted RAPIVAB for administration should be between 1 mg/mL and 6 mg/mL. Infants 6 months to 1 year of age Any 25 mL Adults and pediatric patients 1 year and older 5 kg to less than 10 kg 25 mL 10 kg to less than 15 kg 50 mL 15 kg to less than 20 kg 75 mL At least 20 kg 100 mL - (d)
- Administer the diluted solution via intravenous infusion for 15 to 30 minutes.
- (e)
- Discard any unused diluted solution of RAPIVAB after 24 hours.
Once a diluted solution of RAPIVAB has been prepared, administer immediately or store under refrigerated conditions (2° to 8°C or 36° to 46°F) for up to 24 hours. If refrigerated, allow the diluted solution of RAPIVAB to reach room temperature then administer immediately.
2.4 Drug Compatibility
RAPIVAB injection is compatible with 0.9% or 0.45% sodium chloride, 5% dextrose, or lactated Ringer's. Do not mix or co-infuse RAPIVAB with other intravenous medications.
RAPIVAB injection is compatible with materials commonly used for administration such as polyvinylchloride (PVC) bags and PVC-free bags, polypropylene syringes, and polyethylene tubing.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Each vial of RAPIVAB injection contains 200 mg per 20 mL (10 mg per mL) as a clear, colorless solution [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
4. Contraindications
RAPIVAB is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis to peramivir or any component of the product. Severe allergic reactions have included anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reactions
Rare cases of serious skin reactions, including erythema multiforme, have been reported with RAPIVAB in clinical studies and in postmarketing experience. Cases of anaphylaxis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported in postmarketing experience with RAPIVAB. Discontinue RAPIVAB and institute appropriate treatment if anaphylaxis or a serious skin reaction occurs or is suspected. The use of RAPIVAB is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis to RAPIVAB [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Neuropsychiatric Events
Influenza can be associated with a variety of neurologic and behavioral symptoms that can include events such as hallucinations, delirium, and abnormal behavior, in some cases resulting in fatal outcomes. These events may occur in the setting of encephalitis or encephalopathy but can occur in uncomplicated influenza as well.
There have been postmarketing reports of delirium and abnormal behavior leading to injury in patients with influenza who were receiving neuraminidase inhibitors, including RAPIVAB. Because these events were reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made, but they appear to be uncommon. These events were reported primarily among pediatric patients and often had an abrupt onset and rapid resolution. The contribution of RAPIVAB to these events has not been established. Patients with influenza should be closely monitored for signs of abnormal behavior.
5.3 Risk of Bacterial Infections
There is no evidence for efficacy of RAPIVAB in any illness caused by agents other than influenza viruses. Serious bacterial infections may begin with influenza-like symptoms or may coexist with or occur as complications during the course of influenza. RAPIVAB has not been shown to prevent such complications.
Prescribers should be alert to the potential for secondary bacterial infections and treat with antibiotics as appropriate.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious skin and hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neuropsychiatric events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of RAPIVAB. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Psychiatric: Abnormal behavior, hallucination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7. Drug Interactions
This section describes clinically relevant drug interactions with RAPIVAB. Drug-drug interaction studies are described elsewhere in the labeling [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.1 Influenza Vaccines
Inactivated influenza vaccine can be administered at any time relative to use of RAPIVAB. For live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV), antiviral drugs may inhibit viral replication and thus may reduce vaccine efficacy. The concurrent use of RAPIVAB with LAIV intranasal has not been evaluated. Because of the potential for interference between these two products, avoid use of LAIV within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after administration of RAPIVAB unless medically indicated.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
A pharmacokinetic study was performed in lactating rats administered a single intravenous dose of peramivir (10 mg/kg) on Lactation/Postpartum Days 11 to 13. The maximum concentration of peramivir in milk was reached at 0.75 hours post-dose. The milk to plasma AUC ratio of peramivir was approximately 0.5.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RAPIVAB for the treatment of influenza has been established in pediatric patients 6 months to 17 years of age. Use of RAPIVAB for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials of RAPIVAB in adults with additional data from Study 305, a randomized, active-controlled trial of 130 adolescent and pediatric subjects with acute uncomplicated influenza who received open-label treatment with a single dose of RAPIVAB or 5 days of treatment with oseltamivir administered within 48 hours of onset of symptoms of influenza [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Study 305 included:
- 13 to 17 years of age: 21 subjects treated with RAPIVAB 600 mg
- 6 months to 12 years of age: 86 subjects treated with RAPIVAB 12 mg/kg (up to a maximum dose of 600 mg)
Safety and effectiveness of RAPIVAB in pediatric patients less than 6 months of age have not been established. No data are available for RAPIVAB use in pediatric patients 6 months to less than 2 years with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min to inform a recommendation for dosage adjustment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of RAPIVAB did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in exposures between the elderly and younger subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Patients with Impaired Renal Function
A reduced dose of RAPIVAB is recommended for patients 2 years and older with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dose adjustment is not required for a single administration of RAPIVAB for patients with creatinine clearance ≥50 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In patients with chronic renal impairment maintained on hemodialysis, RAPIVAB should be administered after dialysis at a dose adjusted based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No data are available for RAPIVAB use in pediatric patients 6 months to less than 2 years with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min to inform a recommendation for dosage adjustment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
There is no human experience of acute overdosage with RAPIVAB. Treatment of overdosage with RAPIVAB should consist of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. There is no specific antidote for overdose with RAPIVAB.
RAPIVAB is cleared by renal excretion and can be cleared by hemodialysis.
11. Rapivab Description
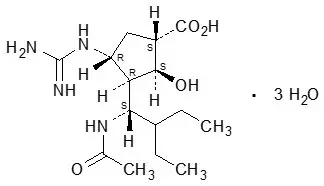
RAPIVAB (peramivir) is an inhibitor of influenza virus neuraminidase. The chemical name is (1S,2S,3R,4R)-3-[(1S)-1-(acetylamino)-2-ethylbutyl]-4-(carbamimidoylamino)-2-hydroxycyclopentanecarboxylic acid, trihydrate. The chemical formula is C15H28N4O4 ∙ 3H2O, representing a molecular weight of 382.45. The molecular structure is as follows:
RAPIVAB injection is a clear, colorless, sterile, isotonic solution (200 mg per 20 mL) in glass vials fitted with rubber stoppers and royal blue flip-off seals. Each mL contains 10 mg peramivir (on an anhydrous basis) in 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The pH may have been adjusted with sodium hydroxide, USP and/or hydrochloric acid, USP. The pH is 5.5 to 8.5.
12. Rapivab - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Peramivir is an antiviral drug with activity against influenza virus [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Cardiac Electrophysiology
At twice the maximum recommended dose, RAPIVAB did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of RAPIVAB was evaluated in Phase 1 trials in adults. The pharmacokinetic parameters following intravenous administration of RAPIVAB (0.17 to 2 times the recommended dose) showed a linear relationship between dose and exposure parameters (Cmax and AUC).
Following intravenous administration of a single dose of RAPIVAB 600 mg over 30 minutes, a maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of 46,800 ng/mL (46.8 µg/mL) was reached at the end of infusion. AUC0-∞ values were 102,700 ng∙hr/mL.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Peramivir caused renal tubular necrosis and abnormal renal function in rabbits. Toxicities included tubular dilatation and necrosis with protein casts in cortical areas, dilated tubules with mineralization in corticomedullary junction areas, and multifocal tubular regeneration. The rabbit appeared to be the sensitive species for peramivir renal toxicity, which was noted at exposures approximately 2- to 4-fold those in humans at the clinically recommended dose.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Acute Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults
Study 621 was a randomized, multicenter, blinded study conducted in Japan that evaluated a single intravenous administration of RAPIVAB 300 mg, RAPIVAB 600 mg, or placebo administered over 30 minutes in subjects 20 to 65 years of age with acute uncomplicated influenza. Subjects were eligible if they had fever ≥38°C (axillary) and a positive rapid antigen test for influenza virus, accompanied by at least 2 symptoms (cough, nasal symptoms, sore throat, myalgia, chills/sweats, malaise, fatigue, or headache). In addition, all subjects enrolled were allowed to take fever-reducing medications.
Study treatment was started within 48 hours of onset of symptoms. Subjects participating in the study were required to self-assess their influenza symptoms as "none", "mild", "moderate", or "severe" twice daily. The primary endpoint, time to alleviation of symptoms, was defined as the number of hours from initiation of study drug until the start of the 24-hour period in which all 7 symptoms of influenza (cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, headache, feverishness, myalgia, and fatigue) were either absent or present at a level no greater than mild for at least 21.5 hours.
The overall efficacy population, consisting of subjects with confirmed influenza and administered study drug, totaled 297 subjects. Among the 98 subjects enrolled in the RAPIVAB 600 mg dose group, the mean age was 34 years; 55% were male; 34% were smokers; 99% were infected with influenza A virus and 1% were infected with influenza B virus. The majority of subjects (53%) had influenza illness lasting <24 hours at the time of presentation.
Overall, subjects receiving RAPIVAB 600 mg experienced alleviation of their combined influenza symptoms a median of 21 hours sooner than those receiving placebo. The median time to recovery to normal temperature (<37°C) in the 600 mg group was approximately 12 hours sooner compared to placebo.
Insufficient numbers of subjects infected with influenza B virus were enrolled to determine efficacy of RAPIVAB in this influenza type.
14.2 Acute Uncomplicated Influenza in Pediatric Subjects
Study 305 was a randomized, multicenter, open-label, active-controlled trial to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of a single intravenous dose of RAPIVAB administered for a minimum of 15 minutes in subjects 6 months to 17 years of age with acute uncomplicated influenza who had fever ≥37.8°C (oral) with at least one respiratory symptom (cough or rhinitis) or a positive influenza rapid antigen test. Study treatment was started within 48 hours of onset of symptoms. Subjects were randomized to receive RAPIVAB 600 mg (13 to 17 years of age), RAPIVAB 12 mg/kg up to a maximum dose of 600 mg (6 months to 12 years of age), or oral oseltamivir taken twice daily for 5 days. In addition, all enrolled subjects were allowed to take fever-reducing medications.
The overall efficacy population, consisting of subjects with confirmed influenza who were administered study drug, totaled 97 subjects. Among the 81 subjects treated with RAPIVAB, the median age was 7.5 years; 52% were male; 60% were infected with influenza A virus, 33% were infected with influenza B virus, and 6% were co-infected with influenza A and B viruses.
The primary endpoint was the safety of peramivir compared to oseltamivir as measured by adverse events, laboratory analysis, vital signs, and physical exams. Secondary endpoints included efficacy outcomes such as time to resolution of influenza symptoms and time to resolution of fever; however, the study was not powered to detect statistically significant differences in these secondary endpoints. Subjects receiving RAPIVAB experienced a median time to alleviation of their combined influenza symptoms of 79 hours (interquartile range: 31 to 126 hours) compared to 100 hours (interquartile range: 57 to 145 hours) in subjects receiving oseltamivir. The median time to recovery to normal temperature (<37°C) was 40 hours (interquartile range: 21 to 68 hours) and 35 hours (interquartile range: 16 to 42 hours) in subjects receiving RAPIVAB and oseltamivir, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
14.3 Serious Influenza Requiring Hospitalization
The efficacy of RAPIVAB could not be established in patients with serious influenza requiring hospitalization [see Indications and Usage (1)].
A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial (Study 301) was conducted in 398 subjects with serious influenza requiring hospitalization. Subjects were randomized to receive RAPIVAB 600 mg daily for 5 days plus standard of care versus standard of care plus placebo within 72 hours of start of symptoms. The primary endpoint was time to clinical resolution defined as the time in hours from initiation of study treatment until resolution of at least 4 of 5 signs (temperature, oxygen saturation, respiration rate, heart rate, or systolic blood pressure), maintained for at least 24 hours. RAPIVAB plus standard of care did not improve median time to clinical resolution compared with standard of care alone.
16. How is Rapivab supplied
RAPIVAB injection is a clear, colorless sterile, isotonic solution. Each single-use vial contains 200 mg per 20 mL (10 mg/mL) of peramivir in a clear glass vial (NDC # 72769-181-01). RAPIVAB injection is supplied in cartons containing 3 single-use vials (NDC # 72769-181-03).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients of the following:
- There is a risk of severe allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis) or serious skin reactions with RAPIVAB use. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if an allergic-like reaction occurs or is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- There is a risk of neuropsychiatric events in patients with influenza. Patients should contact their physician if they experience signs of abnormal behavior after receiving RAPIVAB [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
| RAPIVAB
peramivir solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (618194609) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcami Carolinas Corporation | 117877975 | ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cilag Ag | 483237103 | API MANUFACTURE(72769-181) , ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories Inc. | 069777290 | ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galbraith Laboratories Inc. | 042456145 | ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jubilant HollisterStier LLC | 069263643 | MANUFACTURE(72769-181) , PACK(72769-181) , LABEL(72769-181) , ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Manufacturing Services LLC | 079415560 | MANUFACTURE(72769-181) , PACK(72769-181) , LABEL(72769-181) , ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siegfried USA, LLC | 001213784 | API MANUFACTURE(72769-181) , ANALYSIS(72769-181) | |





