Drug Detail:Recarbrio (Imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam [ im-i-pen-em, sye-la-stat-in, rel-e-bak-tam ])
Drug Class: Carbapenems / beta-lactamase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
RECARBRIO™ (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Indications and Usage for Recarbrio
RECARBRIO is a combination of imipenem, a penem antibacterial, cilastatin, a renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor, and relebactam, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, indicated in patients 18 years of age and older for the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms:
- Hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP). (1.1)
- Complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis (cUTI) in patients who have limited or no alternative treatment options. (1.2)
- Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) in patients who have limited or no alternative treatment options. (1.3)
Approval of the cUTI and cIAI indications is based on limited clinical safety and efficacy data for RECARBRIO. (1.2, 1.3, 14)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of RECARBRIO and other antibacterial drugs, RECARBRIO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.3)
Recarbrio Dosage and Administration
- Administer RECARBRIO 1.25 grams (imipenem 500 mg, cilastatin 500 mg, relebactam 250 mg) by intravenous (IV) infusion over 30 minutes every 6 hours in patients 18 years of age and older with creatinine clearance (CLcr) 90 mL/min or greater. (2.1)
- Dosage adjustment in patients with renal impairment. (2.2)
| Estimated Creatinine Clearance (mL/min)* | Recommended Dose of RECARBRIO (imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam) (mg) administered by IV infusion over 30 minutes every 6 hours |
|---|---|
|
|
| 60 to 89 | 1 gram (imipenem 400 mg, cilastatin 400 mg, and relebactam 200 mg |
| 30 to 59 | 0.75 grams (imipenem 300 mg, cilastatin 300 mg, and relebactam 150 mg |
| 15 to 29 | 0.5 grams (imipenem 200 mg, cilastatin 200 mg, and relebactam 100 mg |
| End Stage Renal Disease on Hemodialysis | 0.5 grams (imipenem 200 mg, cilastatin 200 mg, and relebactam 100 mg |
- Patients with CLcr less than 15 mL/min should not receive RECARBRIO unless hemodialysis is instituted within 48 hours. (2.2)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions for constituting supplied dry powder and subsequent required dilution. (2.3, 2.4)
- See Full Prescribing Information for drug compatibilities and incompatibilities. (2.6, 2.7)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
RECARBRIO 1.25 grams for injection is supplied as sterile powder for constitution in a single-dose vial containing imipenem 500 mg (anhydrate equivalent), cilastatin 500 mg (free acid equivalent), and relebactam 250 mg (anhydrate equivalent). (3)
Contraindications
RECARBRIO is contraindicated in patients with a history of known severe hypersensitivity to any component of RECARBRIO. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta lactam drugs. Discontinue RECARBRIO immediately if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs. (5.1)
- Seizures and Central Nervous System Adverse Reactions: CNS adverse reactions such as seizures have been reported with imipenem/cilastatin, a component of RECARBRIO. If focal tremors, myoclonus, or seizures occur, evaluate patients, to determine whether RECARBRIO should be discontinued. (5.2)
- Increased Seizure Potential Due to Interaction with Valproic Acid: Concomitant use of RECARBRIO with valproic acid or divalproex sodium may reduce the serum concentration of valproic acid which may increase the risk of breakthrough seizures. Avoid concomitant use or consider alternative antibacterial drugs other than carbapenems. (5.3, 7.2)
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): Has been reported with RECARBRIO. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- HABP/VABP Patients: The most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 5% of patients treated with RECARBRIO were alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, anemia, diarrhea, hypokalemia, and hyponatremia. (6)
- cUTI and cIAI Patients: The most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam 250 mg, the components of RECARBRIO, were diarrhea, nausea, headache, vomiting, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, phlebitis/infusion site reactions, pyrexia, and hypertension. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Ganciclovir: Avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
- Valproic Acid or Divalproex Sodium: Avoid concomitant use. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Recarbrio
1.1 Hospital-acquired Bacterial Pneumonia and Ventilator-associated Bacterial Pneumonia (HABP/VABP)
RECARBRIO™ is indicated for the treatment of patients 18 years of age and older with hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia, caused by the following susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.
1.2 Complicated Urinary Tract Infections (cUTI), including Pyelonephritis
RECARBRIO is indicated in patients 18 years of age and older who have limited or no alternative treatment options, for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis, caused by the following susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Approval of this indication is based on limited clinical safety and efficacy data for RECARBRIO [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.3 Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections (cIAI)
RECARBRIO is indicated in patients 18 years of age and older who have limited or no alternative treatment options for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) caused by the following susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: Bacteroides caccae, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides stercoris, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Parabacteroides distasonis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Approval of this indication is based on limited clinical safety and efficacy data for RECARBRIO [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.4 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of RECARBRIO and other antibacterial drugs, RECARBRIO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2. Recarbrio Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of RECARBRIO is 1.25 grams (imipenem 500 mg, cilastatin 500 mg, and relebactam 250 mg) administered by intravenous (IV) infusion over 30 minutes every 6 hours in patients 18 years of age and older with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 90 mL/min or greater. A dose reduction is recommended for patients with CLcr less than 90 mL/min (Table 1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The severity and location of infection, as well as clinical response should guide the duration of therapy. The recommended duration of treatment with RECARBRIO is 4 days to 14 days.
2.2 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Renal Impairment
Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with renal impairment. Patients who have a CLcr less than 90 mL/min require dosage reduction of RECARBRIO (Table 1). For patients with fluctuating renal function, CLcr should be monitored.
| Estimated CLcr (mL/min)* | Recommended Dosage of RECARBRIO (imipenem/cilastatin and relebactam) (mg)† | Dosing Interval |
|---|---|---|
| RECARBRIO is provided as a single vial in a fixed-dose combination; the dose for each component will be adjusted equally during preparation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. | ||
|
||
| 60 to 89 | 1 gram (imipenem 400 mg, cilastatin 400 mg, and relebactam 200 mg) | Every 6 hours |
| 30 to 59 | 0.75 grams (imipenem 300 mg, cilastatin 300 mg, and relebactam 150 mg) | Every 6 hours |
| 15 to 29 | 0.5 grams (imipenem 200 mg, cilastatin 200 mg, and relebactam 100 mg) | Every 6 hours |
| End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) on Hemodialysis‡ | 0.5 grams (imipenem 200 mg, cilastatin 200 mg, and relebactam 100 mg) | Every 6 hours |
Patients with CLcr less than 15 mL/min should not receive RECARBRIO unless hemodialysis is instituted within 48 hours. There is inadequate information to recommend usage of RECARBRIO for patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.
Imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam are cleared from the circulation during hemodialysis. For patients maintained on hemodialysis, administer RECARBRIO after hemodialysis and at intervals timed from the end of that hemodialysis session.
2.3 Preparation of RECARBRIO Solution for Intravenous Administration
RECARBRIO is supplied as a dry powder in a single-dose vial that must be constituted and further diluted using aseptic technique prior to intravenous infusion. To prepare the infusion solution, contents of the vial must be constituted with the appropriate diluent as instructed below. A list of appropriate diluents is as follows:
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP + 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP + 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP + 0.225% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
RECARBRIO has low aqueous solubility. To ensure complete dissolution of RECARBRIO it is important to adhere to the following instructions:
- Step 1) For diluents available in 100 mL prefilled infusion bags, proceed to step 2. For diluents not available in 100 mL prefilled infusion bags, aseptically withdraw 100 mL of the desired diluent and transfer it to an empty infusion bag, then proceed to step 2.
- Step 2) Withdraw 20 mL (as two 10 mL aliquots) of diluent from the appropriate infusion bag and constitute the vial with one 10 mL aliquot of the diluent. The constituted suspension is for intravenous infusion only after dilution in an appropriate infusion solution.
- Step 3) After constitution, shake vial well and transfer resulting suspension into the remaining 80 mL of the infusion bag.
- Step 4) Add the second 10 mL aliquot of infusion diluent to the vial and shake well to ensure complete transfer of vial contents; repeat transfer of the resulting suspension to the infusion solution before administering. Agitate the resulting mixture until clear.
Constituted solutions of RECARBRIO range from colorless to yellow. Variations of color within this range do not affect the potency of the product.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard if discoloration or visible particles are observed.
The above instructions for preparation of RECARBRIO solution for intravenous administration must be followed for all patients, irrespective of the intended patient's renal function. The volume of this prepared RECARBRIO solution to be administered to patients is determined based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
2.4 Preparation of RECARBRIO Solution for Intravenous Administration in Patients with Renal Impairment
For patients with renal impairment, prepare a reduced dose of RECARBRIO (1 gram, 0.75 grams, or 0.5 grams) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] by preparing a 100 mL solution containing 1.25 grams (as described above in Section 2.3) then withdrawing and discarding the excess according to Table 2.
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dosage of RECARBRIO (imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam) | After preparation as instructed above, remove from the 100 mL prepared bag the volume indicated below and discard | Resulting volume that provides the indicated reduced dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 to 89 | 1 gram (imipenem 400 mg, cilastatin 400 mg, and relebactam 200 mg) | 20 mL | 80 mL |
| 30 to 59 | 0.75 grams (imipenem 300 mg, cilastatin 300 mg, and relebactam 150 mg) | 40 mL | 60 mL |
| 15 to 29 or ESRD on hemodialysis | 0.5 grams (imipenem 200 mg, cilastatin 200 mg, and relebactam 100 mg) | 60 mL | 40 mL |
2.5 Storage of Constituted Solution
RECARBRIO, as supplied in single-dose glass vials upon constitution with the appropriate diluent and following further dilution in the infusion bag, maintains satisfactory potency for at least 2 hours at room temperature (up to 30°C) or for at least 24 hours under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do not freeze solutions of RECARBRIO.
2.6 Compatible Injectable Drug Products
Compatible Drug Products
The physical compatibility of RECARBRIO with selected injectable drug products was evaluated in two commonly available diluents. Compatible drugs with the corresponding compatible diluent (i.e., 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP) are listed below. RECARBRIO should not be co-administered through the same intravenous line (or cannula), with other drug products not listed below, as no compatibility data are available. Refer to the respective prescribing information of the co-administered drug(s) to confirm compatibility of simultaneous co-administration.
List of Compatible Injectable Drugs for use with 5% Dextrose USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride USP Injection as Diluents
- dexmedetomidine
- dopamine
- epinephrine
- fentanyl
- heparin
- midazolam
- norepinephrine
- phenylephrine
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
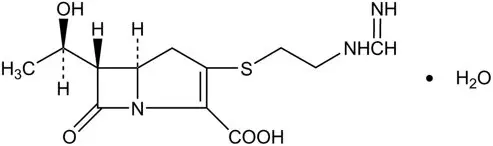
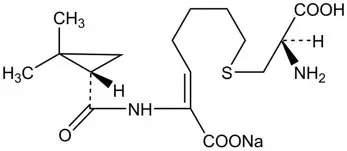
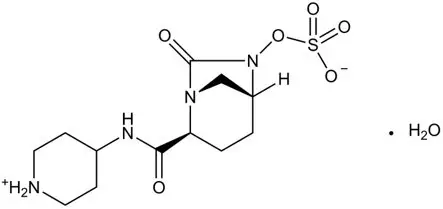
RECARBRIO (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam) for injection, 1.25 grams is supplied as a white to light yellow sterile powder for constitution in a single-dose glass vial containing imipenem 500 mg (equivalent to 530 mg imipenem monohydrate), cilastatin 500 mg (equivalent to 531 mg cilastatin sodium), and relebactam 250 mg (equivalent to 263 mg relebactam monohydrate).
4. Contraindications
RECARBRIO is contraindicated in patients with a history of known severe hypersensitivity (severe systemic allergic reaction such as anaphylaxis) to any component of RECARBRIO.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients receiving therapy with beta lactams. Before initiating therapy with RECARBRIO, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to carbapenems, penicillins, cephalosporins, other beta lactams, and other allergens. If a hypersensitivity reaction to RECARBRIO occurs, discontinue the therapy immediately.
RECARBRIO is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity to any component of RECARBRIO [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Seizures and Other Central Nervous System (CNS) Adverse Reactions
CNS adverse reactions, such as seizures, confusional states, and myoclonic activity, have been reported during treatment with imipenem/cilastatin, a component of RECARBRIO, especially when recommended dosages of imipenem were exceeded. These have been reported most commonly in patients with CNS disorders (e.g., brain lesions or history of seizures) and/or compromised renal function.
Anticonvulsant therapy should be continued in patients with known seizure disorders. If CNS adverse reactions including seizures occur, patients should undergo a neurological evaluation to determine whether RECARBRIO should be discontinued.
5.3 Increased Seizure Potential Due to Interaction with Valproic Acid
Concomitant use of RECARBRIO, with valproic acid or divalproex sodium may increase the risk of breakthrough seizures. Avoid concomitant use of RECARBRIO with valproic acid or divalproex sodium or consider alternative antibacterial drugs other than carbapenems [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.4 Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including RECARBRIO, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial drug treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail in the Warnings and Precautions section.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Seizures and Other Central Nervous System Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased Seizure Potential Due to Interaction with Valproic Acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Trial 1, adverse reactions occurred during the protocol-specified follow-up period, which was IV therapy plus 14 days following completion of therapy, in 85% (226/266) of patients receiving RECARBRIO and 87% (233/269) of patients receiving piperacillin and tazobactam. Table 3 lists the most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥4% of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg/relebactam 250 mg or piperacillin and tazobactam in Trial 1.
| Adverse Reaction | RECARBRIO*
(N=266) N (%) | Piperacillin/Tazobactam†
(N=269) N (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Anemia | 28 (10.5%) | 27 (10.0%) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Constipation | 11 (4.1%) | 3 (1.1%) |
| Diarrhea | 21 (7.9%) | 30 (11.2%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Pyrexia | 11 (4.1%) | 20 (7.4%) |
| Laboratory investigations | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 26 (9.8%) | 19 (7.1%) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 31 (11.7%) | 20 (7.4%) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Hypokalemia‡ | 21 (7.9%) | 26 (9.7%) |
| Hyponatremia§ | 17 (6.4%) | 3 (1.1%) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rash¶ | 11 (4.1%) | 5 (1.9%) |
Less Common Adverse Reactions Reported in Trial 1
The following selected adverse reaction was reported in RECARBRIO-treated subjects at a rate of less than 4%:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: thrombocytopenia
In Trials 2 and 3, adverse reactions occurred during the protocol-specified follow-up period, which was IV therapy plus 14 days following completion of therapy, in 39% (85/216) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg and 36% (77/214) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg. Table 4 lists the most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg or imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg in Trials 2 and 3.
| Adverse Reaction | Imipenem/Cilastatin and Relebactam 250 mg*
(N=216) N (%) | IMI + Placebo†
(N=214) N (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Anemia‡ | 2 (1%) | 4 (2%) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 12 (6%) | 9 (4%) |
| Nausea | 12 (6%) | 12 (6%) |
| Vomiting | 7 (3%) | 4 (2%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Phlebitis/Infusion site reactions§ | 5 (2%) | 3 (1%) |
| Pyrexia | 5 (2%) | 3 (1%) |
| Laboratory Investigations | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 7 (3%) | 4 (2%) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 6 (3%) | 3 (1%) |
| Lipase increased | 3 (1%) | 4 (2%) |
| Blood creatinine increased | 1 (<1%) | 3 (1%) |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 9 (4%) | 5 (2%) |
| Central nervous system adverse reactions¶ | 2 (1%) | 5 (2%) |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension# | 4 (2%) | 6 (3%) |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Ganciclovir
Generalized seizures have been reported in patients who received ganciclovir concomitantly with imipenem/cilastatin, a component of RECARBRIO. Ganciclovir should not be used concomitantly with RECARBRIO unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
7.2 Valproic Acid
Based on case reports in the literature concomitant use of carbapenems, including imipenem/cilastatin, components of RECARBRIO, with valproic acid or divalproex sodium may decrease valproic acid concentrations which may increase the risk of breakthrough seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Although the mechanism of this interaction is unknown, data from in vitro and animal studies suggest that carbapenems may inhibit the hydrolysis of valproic acid's glucuronide metabolite (VPA-g) back to valproic acid, thus decreasing the serum concentrations of valproic acid. Avoid concomitant use of RECARBRIO with valproic acid or divalproex sodium. Consider alternative antibacterials other than carbapenems to treat infections in patients whose seizures are well controlled on valproic acid or divalproex sodium.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of RECARBRIO in patients younger than 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 266 patients treated with RECARBRIO in Trial 1, 113 (42.5%) were 65 years of age or older, including 55 (20.7%) patients 75 years of age and older. Of the 216 patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam 250 mg in Trials 2 and 3, 67 (31.0%) were 65 years of age or older, including 25 (11.6%) patients 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
RECARBRIO is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. No dosage adjustment is required based on age. Dosage adjustment for elderly patients should be based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
In the event of overdose, discontinue RECARBRIO, treat symptomatically, and institute general supportive treatment. Imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam can be removed by hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No clinical information is available on the use of hemodialysis to treat overdosage.
11. Recarbrio Description
RECARBRIO (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam) for injection is an antibacterial combination product consisting of imipenem, a carbapenem antibacterial drug, cilastatin, a renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor, and relebactam, a diazabicyclooctane beta-lactamase inhibitor, for intravenous administration.
12. Recarbrio - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
For imipenem, the % time of dosing interval that unbound plasma concentrations of imipenem exceed the imipenem/relebactam minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) (%fT>MIC) against the infecting organism best correlates with antibacterial activity in animal and in vitro models of infection. For relebactam the ratio of the 24-hour unbound plasma relebactam AUC to imipenem/relebactam MIC (fAUC0–24hr/MIC) best predicts the activity of relebactam in animal and in vitro models of infection.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of imipenem and relebactam in patients with active bacterial infection with CLcr 90 mL/min or greater following administration of the recommended dosage are summarized in Table 5.
| PK Parameters | cUTI/cIAI Patients | HABP/VABP Patients | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0-24hr=area under the concentration time curve from 0 to 24 hours Cmax=maximum concentration CL=plasma clearance |
|||
|
|||
| Imipenem | AUC0-24hr (µM-hr) | 570.6 (253.3) | 771 (342.3) |
| Cmax (µM) | 116.1 (52.4) | 122.7 (56.8) | |
| CL (L/hr) | 14 (6.1) | 10.4 (4.5) | |
| Relebactam | AUC0-24hr (µM-hr) | 415.8 (212.6) | 692.9 (354.3) |
| Cmax (µM) | 62.1 (24.7) | 80 (33.3) | |
| CL (L/hr) | 8.7 (4.5) | 5.2 (2.7) | |
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of imipenem, cilastatin, or relebactam were observed based on age, gender, or race/ethnicity.
Patients with Renal Impairment
In a single-dose trial evaluating the effect of renal impairment on the PK of relebactam 125 mg co-infused with imipenem/cilastatin 250 mg (half the recommended dose in patients with normal renal function), mean AUC was higher in subjects with CLcr 60-89, 30-59, and 15-29 mL/min, respectively, compared to healthy subjects with CLcr 90 mL/min or greater (Table 6). In subjects with end stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis, imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam are removed by hemodialysis, with extraction coefficients of 66% to 87% for imipenem, 46% to 56% for cilastatin, and 67% to 87% for relebactam.
| Estimated CLcr (mL/min) | Imipenem | Cilastatin | Relebactam |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 to 89 | 1.1-fold | 1.2-fold | 1.2-fold |
| 30 to 59 | 1.7-fold | 2.0-fold | 2.2-fold |
| 15 to 29 | 2.6-fold | 5.5-fold | 4.7-fold |
To maintain systemic exposures similar to patients with normal renal function, dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. ESRD patients on hemodialysis should receive RECARBRIO after hemodialysis session [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Relebactam given as a single entity caused renal tubular degeneration in monkeys at AUC exposure 7-fold the human AUC exposure at the MRHD. Renal tubular degeneration was shown to be reversible after dose discontinuation. There was no evidence of nephrotoxicity at AUC exposures less than or equal to 3-fold the human AUC exposure at the MRHD.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Hospital-acquired Bacterial Pneumonia and Ventilator-associated Bacterial Pneumonia
A total of 535 hospitalized adults with HABP/VABP were randomized and received trial medications in a multinational, double-blind trial (Trial 1, NCT02493764) comparing RECARBRIO 1.25 grams (imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg/relebactam 250 mg) intravenously every 6 hours to piperacillin and tazobactam (4.5 grams) for 7 to 14 days of therapy.
The modified intent-to-treat (MITT) population, which included all randomized patients who received at least one dose of trial treatment and did not have only gram-positive cocci on Gram stain of the baseline lower respiratory tract (LRT) specimen included 531 patients; the mean age was 60 and 43% were 65 years of age or older. The majority of patients were men (69%), white (78%), and from Europe (61%). The mean APACHE II score was 15 and 47% of the population had an APACHE II score of ≥15. At randomization, 66% of patients were admitted to the ICU, 77% had been in the hospital for ≥5 days, and 48% had a creatinine clearance of <90 mL/min. Concurrent bacteremia was present at baseline in 5.8% of patients.
Table 7 presents the incidence of all-cause mortality through Day 28 and clinical response at the early follow-up (EFU) visit (7 to 14 days after the end of therapy) in the MITT population. Overall results are presented along with subgroup results by pneumonia diagnosis.
| RECARBRIO | Piperacillin/Tazobactam | Treatment Difference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/m | (%) | n/m | (%) | %* | (95% CI)* | |
| EFU = early follow up | ||||||
|
||||||
| All-Cause Mortality Through Day 28†,‡ | 42/264 | (15.9) | 57/267 | (21.3) | -5.3 | (-11.9, 1.2) |
| Non-ventilated HABP | 18/142 | (12.7) | 15/131 | (11.5) | 1.2 | (-6.8, 9.1) |
| Ventilated HABP/VABP | 24/122 | (19.7) | 42/136 | (30.9) | -11.2 | (-21.6, -0.5) |
| Clinical Response at EFU§ | 161/264 | (61.0) | 149/267 | (55.8) | 5.0 | (-3.2, 13.2) |
| Non-ventilated HABP | 95/142 | (66.9) | 87/131 | (66.4) | 0.5 | (-10.7, 11.7) |
| Ventilated HABP/VABP | 66/122 | (54.1) | 62/136 | (45.6) | 8.5 | (-3.7, 20.5) |
In the MITT population, in patients with an APACHE II score <15, Day 28 all-cause mortality rates were 17/139 (12.2%) for RECARBRIO-treated patients and 12/140 (8.6%) for piperacillin/tazobactam-treated patients, clinical cure rates were 90/139 (64.7%) and 98/140 (70%), respectively. In patients with an APACHE II score ≥15, Day 28 all-cause mortality rates were 25/125 (20%) for RECARBRIO-treated patients and 45/127 (35.4%) for piperacillin/tazobactam-treated patients, clinical cure rates were 71/125 (56.8%) and 51/127 (40.2%), respectively.
Per pathogen favorable clinical response at EFU and Day 28 all-cause mortality were assessed in a microbiological modified intention to treat (mMITT) population, which consisted of all randomized MITT subjects who had at least one baseline LRT pathogen that was susceptible to both study treatments (Table 8).
| Baseline LRT Pathogen | Day 28 All-Cause Mortality | Clinical Response at EFU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RECARBRIO n/m* (%) | Piperacillin/ Tazobactam n/m* (%) | RECARBRIO n/m† (%) | Piperacillin/ Tazobactam n/m† (%) |
|
| LRT = lower respiratory tract EFU = early follow-up |
||||
|
||||
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus- baumannii complex | 0/5‡ (0.0) | 1/10 (10.0) | 4/5‡ (80.0) | 6/10 (60.0) |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 1/7‡ (14.3) | 3/16 (18.8) | 6/7‡ (85.7) | 12/16 (75.0) |
| Escherichia coli | 5/27(18.5) | 8/33 (24.2) | 16/27 (59.3) | 19/33 (57.6) |
| Haemophilus influenzae§ | 2/13 (15.4) | 3/12 (25.0) | 9/13 (69.2) | 8/12 (66.7) |
| Klebsiella spp.¶ | 6/42 (14.3) | 8/41 (19.5) | 25/42 (59.5) | 28/41 (68.3) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 7/26 (26.9) | 5/35 (14.3) | 12/26 (46.2) | 20/35 (57.1) |
| Serratia marcescens | 2/10 (20.0) | 1/4 (25.0) | 7/10 (70.0) | 3/4 (75.0) |
14.2 Complicated Urinary Tract Infections, including Pyelonephritis and Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections
The determination of efficacy and safety of RECARBRIO was supported in part by the previous findings of the efficacy and safety of imipenem/cilastatin for the treatment of cUTI and cIAI. The contribution of relebactam to RECARBRIO was primarily established in vitro and in animal models of infection [see Microbiology (12.4)]. Imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam was studied in cUTI including pyelonephritis (Trial 2, NCT01505634) and cIAI (Trial 3, NCT01506271) in randomized, blinded, active-controlled, multicenter trials. These trials provided only limited efficacy and safety information.
16. How is Recarbrio supplied
RECARBRIO (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam) for injection, 1.25 grams is supplied as a white to light yellow sterile powder for constitution in a single-dose glass vial containing imipenem 500 mg (equivalent to 530 mg imipenem monohydrate), cilastatin 500 mg (equivalent to 531 mg cilastatin sodium), and relebactam 250 mg (equivalent to 263 mg relebactam monohydrate).
The vials are supplied as a single-dose glass vial (NDC 0006-3856-01) and in cartons containing 25 vials (NDC 0006-3856-02).
| RECARBRIO
imipenem anhydrous, cilastatin, and relebactam anhydrous injection, powder, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC (118446553) |