Drug Detail:Risperdal (Risperidone (oral) [ ris-per-i-done ])
Drug Class: Atypical antipsychotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
RISPERDAL® (risperidone) tablets, for oral use
RISPERDAL® (risperidone) oral solution
RISPERDAL® M-TAB® (risperidone) orally disintegrating tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 1993
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. RISPERDAL® is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.6) | 3/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Risperdal
RISPERDAL® is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for:
- Treatment of schizophrenia (1.1)
- As monotherapy or adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate, for the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes associated with Bipolar I Disorder (1.2)
- Treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder (1.3)
Risperdal Dosage and Administration
- Recommended daily dosage:
| Initial Dose | Target Dose | Effective Dose Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia: adults (2.1) | 2 mg | 4 to 8 mg | 4 to 16 mg |
| Schizophrenia: adolescents (2.1) | 0.5 mg | 3 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Bipolar mania: adults (2.2) | 2 to 3 mg | 1 to 6 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Bipolar mania: in children and adolescents (2.2) | 0.5 mg | 1 to 2.5 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Irritability associated with autistic disorder (2.3) | 0.25 mg (Weight < 20 kg) 0.5 mg (Weight ≥20 kg) | 0.5 mg (<20 kg) 1 mg (≥20 kg) | 0.5 to 3 mg |
- Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment in Adults: Use a lower starting dose of 0.5 mg twice daily. May increase to dosages above 1.5 mg twice daily at intervals of at least one week. (2.4)
- Oral Solution: Can be administered directly from calibrated oral dosing syringe or mixed with beverage (water, coffee, orange juice, or low-fat milk). (2.6)
- M-TAB Orally Disintegrating Tablets: Open the blister only when ready to administer, and immediately place tablet on the tongue. Can be swallowed with or without liquid. (2.7)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg (3)
- Oral solution: 1 mg per mL (3)
- Orally disintegrating tablets: 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to risperidone, paliperidone, or to any excipients in RISPERDAL®. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cerebrovascular events, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis: RISPERDAL® is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.2)
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Manage with immediate discontinuation of RISPERDAL® and close monitoring. (5.3)
- Tardive dyskinesia: Consider discontinuing RISPERDAL® if clinically indicated. (5.4)
- Metabolic Changes: Atypical antipsychotic drugs have been associated with metabolic changes that may increase cardiovascular/ cerebrovascular risk. These metabolic changes include hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and weight gain. (5.5)
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus: Monitor patients for symptoms of hyperglycemia including polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and weakness. Monitor glucose regularly in patients with diabetes or at risk for diabetes. (5.5)
- Dyslipidemia: Undesirable alterations have been observed in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. (5.5)
- Weight Gain: Significant weight gain has been reported. Monitor weight gain. (5.5)
- Hyperprolactinemia: Prolactin elevations occur and persist during chronic administration. (5.6)
- Orthostatic hypotension: For patients at risk, consider a lower starting dose and slower titration. (5.7)
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: Perform complete blood counts in patients with a history of clinically significant low white blood cell count (WBC). Consider discontinuing RISPERDAL® if a clinically significant decline in WBC occurs in the absence of other causative factors. (5.9)
- Potential for cognitive and motor impairment: Use caution when operating machinery. (5.10)
- Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold. (5.11)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions in clinical trials (≥5% and twice placebo) were parkinsonism, akathisia, dystonia, tremor, sedation, dizziness, anxiety, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, upper abdominal pain, stomach discomfort, dyspepsia, diarrhea, salivary hypersecretion, constipation, dry mouth, increased appetite, increased weight, fatigue, rash, nasal congestion, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and pharyngolaryngeal pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers decrease plasma concentrations of risperidone. Increase the RISPERDAL® dose up to double the patient's usual dose. Titrate slowly. (7.1)
- Fluoxetine, paroxetine, and other CYP 2D6 enzyme inhibitors increase plasma concentrations of risperidone. Reduce the initial dose. Do not exceed a final dose of 8 mg per day of RISPERDAL®. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in neonates with third trimester exposure. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. RISPERDAL® is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
1. Indications and Usage for Risperdal
1.1 Schizophrenia
RISPERDAL® (risperidone) is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia. Efficacy was established in 4 short-term trials in adults, 2 short-term trials in adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years), and one long-term maintenance trial in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
1.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder
RISPERDAL® is indicated for the treatment of irritability associated with autistic disorder, including symptoms of aggression towards others, deliberate self-injuriousness, temper tantrums, and quickly changing moods. Efficacy was established in 3 short-term trials in children and adolescents (ages 5 to 17 years) [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
2. Risperdal Dosage and Administration
| Initial Dose | Titration (Increments) | Target Dose | Effective Dose Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia: adults (2.1) | 2 mg | 1 to 2 mg | 4 to 8 mg | 4 to 16 mg |
| Schizophrenia: adolescents (2.2) | 0.5 mg | 0.5 to 1 mg | 3 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Bipolar mania: adults (2.2) | 2 to 3 mg | 1 mg | 1 to 6 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Bipolar mania: children and adolescents (2.2) | 0.5 mg | 0.5 to 1 mg | 1 to 2.5 mg | 1 to 6 mg |
| Irritability in autistic disorder (2.3) | 0.25 mg Can increase to 0.5 mg by Day 4: (body weight less than 20 kg) 0.5 mg Can increase to 1 mg by Day 4: (body weight greater than or equal to 20 kg) | After Day 4, at intervals of > 2 weeks: 0.25 mg (body weight less than 20 kg) 0.5 mg (body weight greater than or equal to 20 kg) | 0.5 mg: (body weight less than 20 kg) 1 mg: (body weight greater than or equal to 20 kg) | 0.5 to 3 mg |
Severe Renal and Hepatic Impairment in Adults: use a lower starting dose of 0.5 mg twice daily. May increase to dosages above 1.5 mg twice daily at intervals of one week or longer.
2.3 Irritability Associated with Autistic Disorder – Pediatrics (Children and Adolescents)
The dosage of RISPERDAL® should be individualized according to the response and tolerability of the patient. The total daily dose of RISPERDAL® can be administered once daily, or half the total daily dose can be administered twice daily.
For patients with body weight less than 20 kg, initiate dosing at 0.25 mg per day. For patients with body weight greater than or equal to 20 kg, initiate dosing at 0.5 mg per day. After a minimum of four days, the dose may be increased to the recommended dose of 0.5 mg per day for patients less than 20 kg and 1.0 mg per day for patients greater than or equal to 20 kg. Maintain this dose for a minimum of 14 days. In patients not achieving sufficient clinical response, the dose may be increased at intervals of 2 weeks or greater, in increments of 0.25 mg per day for patients less than 20 kg, or increments of 0.5 mg per day for patients greater than or equal to 20 kg. The effective dose range is 0.5 mg to 3 mg per day. No dosing data are available for children who weigh less than 15 kg.
Once sufficient clinical response has been achieved and maintained, consider gradually lowering the dose to achieve the optimal balance of efficacy and safety. The physician who elects to use RISPERDAL® for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term risks and benefits of the drug for the individual patient.
Patients experiencing persistent somnolence may benefit from a once-daily dose administered at bedtime or administering half the daily dose twice daily, or a reduction of the dose.
2.4 Dosing in Patients with Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment
For patients with severe renal impairment (Clcr< 30 mL/min) or hepatic impairment (10–15 points on Child Pugh System), the initial starting dose is 0.5 mg twice daily. The dose may be increased in increments of 0.5 mg or less, administered twice daily. For doses above 1.5 mg twice daily, increase in intervals of one week or greater [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 and 8.7)].
2.5 Dose Adjustments for Specific Drug Interactions
When RISPERDAL® is co-administered with enzyme inducers (e.g., carbamazepine), the dose of RISPERDAL® should be increased up to double the patient's usual dose. It may be necessary to decrease the RISPERDAL® dose when enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine are discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Similar effect may be expected with co-administration of RISPERDAL® with other enzyme inducers (e.g., phenytoin, rifampin, and phenobarbital).
When fluoxetine or paroxetine is co-administered with RISPERDAL®, the dose of RISPERDAL® should be reduced. The RISPERDAL® dose should not exceed 8 mg per day in adults when co-administered with these drugs. When initiating therapy, RISPERDAL® should be titrated slowly. It may be necessary to increase the RISPERDAL® dose when enzyme inhibitors such as fluoxetine or paroxetine are discontinued [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.6 Administration of RISPERDAL® Oral Solution
RISPERDAL® Oral Solution can be administered directly from the calibrated oral dosing syringe, or can be mixed with a beverage prior to administration. RISPERDAL® Oral Solution is compatible in the following beverages: water, coffee, orange juice, and low-fat milk; it is NOT compatible with either cola or tea.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
RISPERDAL® Tablets are available in the following strengths and colors: 0.5 mg (red-brown), 1 mg (white), 2 mg (orange), 3 mg (yellow), and 4 mg (green). All are capsule shaped, and imprinted with "JANSSEN" on one side and either "Ris 0.5", "R1", "R2", "R3", or "R4" on the other side according to their respective strengths.
RISPERDAL® Oral Solution is available in a 1 mg/mL strength.
RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets are available in the following strengths, colors, and shapes: 0.5 mg (light coral, round), 1 mg (light coral, square), 2 mg (coral, square), 3 mg (coral, round), and 4 mg (coral, round). All are biconvex and etched on one side with "R0.5", "R1", "R2", "R3", or "R4" according to their respective strengths.
4. Contraindications
RISPERDAL® is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to either risperidone or paliperidone, or to any of the excipients in the RISPERDAL® formulation. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema, have been reported in patients treated with risperidone and in patients treated with paliperidone. Paliperidone is a metabolite of risperidone.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear.
In two of four placebo-controlled trials in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis, a higher incidence of mortality was observed in patients treated with furosemide plus RISPERDAL® when compared to patients treated with RISPERDAL® alone or with placebo plus furosemide. No pathological mechanism has been identified to explain this finding, and no consistent pattern for cause of death was observed.
RISPERDAL® (risperidone) is not approved for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning].
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Cerebrovascular adverse reactions (e.g., stroke, transient ischemic attack), including fatalities, were reported in patients (mean age 85 years; range 73–97) in trials of risperidone in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis. In placebo-controlled trials, there was a significantly higher incidence of cerebrovascular adverse events in patients treated with risperidone compared to patients treated with placebo. RISPERDAL® is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex, has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status including delirium, and autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and acute renal failure.
If NMS is suspected, immediately discontinue RISPERDAL® and provide symptomatic treatment and monitoring.
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive dyskinesia, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to predict which patients will develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
The risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible increase with the duration of treatment and the cumulative dose. The syndrome can develop after relatively brief treatment periods, even at low doses. It may also occur after discontinuation of treatment.
Tardive dyskinesia may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is discontinued. Antipsychotic treatment, itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome, possibly masking the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, RISPERDAL® should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients: (1) who suffer from a chronic illness that is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and (2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, use the lowest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response. Periodically reassess the need for continued treatment.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on RISPERDAL®, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment with RISPERDAL® despite the presence of the syndrome.
5.5 Metabolic Changes
Atypical antipsychotic drugs have been associated with metabolic changes that may increase cardiovascular/cerebrovascular risk. These metabolic changes include hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain. While all of the drugs in the class have been shown to produce some metabolic changes, each drug has its own specific risk profile.
5.6 Hyperprolactinemia
As with other drugs that antagonize dopamine D2 receptors, RISPERDAL® elevates prolactin levels and the elevation persists during chronic administration. RISPERDAL® is associated with higher levels of prolactin elevation than other antipsychotic agents.
Hyperprolactinemia may suppress hypothalamic GnRH, resulting in reduced pituitary gonadotropin secretion. This, in turn, may inhibit reproductive function by impairing gonadal steroidogenesis in both female and male patients. Galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence have been reported in patients receiving prolactin-elevating compounds. Long-standing hyperprolactinemia when associated with hypogonadism may lead to decreased bone density in both female and male subjects.
Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if the prescription of these drugs is contemplated in a patient with previously detected breast cancer. An increase in pituitary gland, mammary gland, and pancreatic islet cell neoplasia (mammary adenocarcinomas, pituitary and pancreatic adenomas) was observed in the risperidone carcinogenicity studies conducted in mice and rats [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic studies conducted to date have shown an association between chronic administration of this class of drugs and tumorigenesis in humans; the available evidence is considered too limited to be conclusive at this time.
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension
RISPERDAL® may induce orthostatic hypotension associated with dizziness, tachycardia, and in some patients, syncope, especially during the initial dose-titration period, probably reflecting its alpha-adrenergic antagonistic properties. Syncope was reported in 0.2% (6/2607) of RISPERDAL®-treated patients in Phase 2 and 3 studies in adults with schizophrenia. The risk of orthostatic hypotension and syncope may be minimized by limiting the initial dose to 2 mg total (either once daily or 1 mg twice daily) in normal adults and 0.5 mg twice daily in the elderly and patients with renal or hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4)]. Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in patients for whom this is of concern. A dose reduction should be considered if hypotension occurs. RISPERDAL® should be used with particular caution in patients with known cardiovascular disease (history of myocardial infarction or ischemia, heart failure, or conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, and conditions which would predispose patients to hypotension, e.g., dehydration and hypovolemia, and in the elderly and patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered if hypotension occurs. Clinically significant hypotension has been observed with concomitant use of RISPERDAL® and antihypertensive medication.
5.8 Falls
Somnolence, postural hypotension, motor and sensory instability have been reported with the use of antipsychotics, including RISPERDAL®, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other fall-related injuries. For patients, particularly the elderly, with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, assess the risk of falls when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently for patients on long-term antipsychotic therapy.
5.10 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Somnolence was a commonly reported adverse reaction associated with RISPERDAL® treatment, especially when ascertained by direct questioning of patients. This adverse reaction is dose-related, and in a study utilizing a checklist to detect adverse events, 41% of the high-dose patients (RISPERDAL® 16 mg/day) reported somnolence compared to 16% of placebo patients. Direct questioning is more sensitive for detecting adverse events than spontaneous reporting, by which 8% of RISPERDAL® 16 mg/day patients and 1% of placebo patients reported somnolence as an adverse reaction. Since RISPERDAL® has the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or motor skills, patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that RISPERDAL® therapy does not affect them adversely.
5.11 Seizures
During premarketing testing in adult patients with schizophrenia, seizures occurred in 0.3% (9/2607) of RISPERDAL®-treated patients, two in association with hyponatremia. RISPERDAL® should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures.
5.12 Dysphagia
Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration have been associated with antipsychotic drug use. Aspiration pneumonia is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with advanced Alzheimer's dementia. RISPERDAL® and other antipsychotic drugs should be used cautiously in patients at risk for aspiration pneumonia. [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5.13 Priapism
Priapism has been reported during postmarketing surveillance. Severe priapism may require surgical intervention.
5.14 Body Temperature Regulation
Disruption of body temperature regulation has been attributed to antipsychotic agents. Both hyperthermia and hypothermia have been reported in association with oral RISPERDAL® use. Caution is advised when prescribing for patients who will be exposed to temperature extremes.
5.15 Patients with Phenylketonuria
Inform patients that RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain phenylalanine. Phenylalanine is a component of aspartame. Each 4 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablet contains 0.84 mg phenylalanine; each 3 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablet contains 0.63 mg phenylalanine; each 2 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablet contains 0.42 mg phenylalanine; each 1 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablet contains 0.28 mg phenylalanine; and each 0.5 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablet contains 0.14 mg phenylalanine.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cerebrovascular adverse events, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Tardive dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Metabolic Changes (Hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus, Dyslipidemia, and Weight Gain) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hyperprolactinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Orthostatic hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Potential for cognitive and motor impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Disruption of body temperature regulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Patients with Phenylketonuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
The most common adverse reactions in clinical trials (>5% and twice placebo) were parkinsonism, akathisia, dystonia, tremor, sedation, dizziness, anxiety, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, upper abdominal pain, stomach discomfort, dyspepsia, diarrhea, salivary hypersecretion, constipation, dry mouth, increased appetite, increased weight, fatigue, rash, nasal congestion, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and pharyngolaryngeal pain.
The most common adverse reactions that were associated with discontinuation from clinical trials (causing discontinuation in >1% of adults and/or >2% of pediatrics) were nausea, somnolence, sedation, vomiting, dizziness, and akathisia [see Adverse Reactions, Discontinuations Due to Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The data described in this section are derived from a clinical trial database consisting of 9803 adult and pediatric patients exposed to one or more doses of RISPERDAL® for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, autistic disorder, and other psychiatric disorders in pediatrics and elderly patients with dementia. Of these 9803 patients, 2687 were patients who received RISPERDAL® while participating in double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. The conditions and duration of treatment with RISPERDAL® varied greatly and included (in overlapping categories) double-blind, fixed- and flexible-dose, placebo- or active-controlled studies and open-label phases of studies, inpatients and outpatients, and short-term (up to 12 weeks) and longer-term (up to 3 years) exposures. Safety was assessed by collecting adverse events and performing physical examinations, vital signs, body weights, laboratory analyses, and ECGs.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of risperidone. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions include: alopecia, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, cardiopulmonary arrest, catatonia, diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with impaired glucose metabolism, dysgeusia, hypoglycemia, hypothermia, ileus, inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, intestinal obstruction, jaundice, mania, pancreatitis, pituitary adenoma, precocious puberty, pulmonary embolism, QT prolongation, sleep apnea syndrome, somnambulism, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), sudden death, thrombocytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, urinary retention, and water intoxication.
Postmarketing cases of extrapyramidal symptoms (dystonia and dyskinesia) have been reported in patients concomitantly taking methylphenidate and risperidone when there was an increase or decrease in dosage, initiation, or discontinuation of either or both medications.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Pharmacokinetic-related Interactions
The dose of RISPERDAL® should be adjusted when used in combination with CYP2D6 enzyme inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, and paroxetine) and enzyme inducers (e.g., carbamazepine) [see Table 18 and Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Dose adjustment is not recommended for RISPERDAL® when co-administered with ranitidine, cimetidine, amitriptyline, or erythromycin [see Table 18].
| Coadministered Drug | Dosing Schedule | Effect on Active Moiety (Risperidone + 9-Hydroxy-Risperidone (Ratio*) | Risperidone Dose Recommendation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Risperidone | AUC | Cmax | ||
|
|||||
| Enzyme (CYP2D6) Inhibitors | |||||
| Fluoxetine | 20 mg/day | 2 or 3 mg twice daily | 1.4 | 1.5 | Re-evaluate dosing. Do not exceed 8 mg/day |
| Paroxetine | 10 mg/day | 4 mg/day | 1.3 | - | Re-evaluate dosing. Do not exceed 8 mg/day |
| 20 mg/day | 4 mg/day | 1.6 | - | ||
| 40 mg/day | 4 mg/day | 1.8 | - | ||
| Enzyme (CYP3A/PgP inducers) Inducers | |||||
| Carbamazepine | 573 ± 168 mg/day | 3 mg twice daily | 0.51 | 0.55 | Titrate dose upwards. Do not exceed twice the patient's usual dose |
| Enzyme (CYP3A) Inhibitors | |||||
| Ranitidine | 150 mg twice daily | 1 mg single dose | 1.2 | 1.4 | Dose adjustment not needed |
| Cimetidine | 400 mg twice daily | 1 mg single dose | 1.1 | 1.3 | Dose adjustment not needed |
| Erythromycin | 500 mg four times daily | 1 mg single dose | 1.1 | 0.94 | Dose adjustment not needed |
| Other Drugs | |||||
| Amitriptyline | 50 mg twice daily | 3 mg twice daily | 1.2 | 1.1 | Dose adjustment not needed |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of RISPERDAL® in the treatment of schizophrenia did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether or not they respond differently than younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, a lower starting dose is recommended for an elderly patient, reflecting a decreased pharmacokinetic clearance in the elderly, as well as a greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.5)]. While elderly patients exhibit a greater tendency to orthostatic hypotension, its risk in the elderly may be minimized by limiting the initial dose to 0.5 mg twice daily followed by careful titration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in patients for whom this is of concern.
This drug is substantially excreted by the kidneys, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
In patients with moderate to severe (Clcr 59 to 15 mL/min) renal disease, clearance of the sum of risperidone and its active metabolite decreased by 60%, compared to young healthy subjects. RISPERDAL® doses should be reduced in patients with renal disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
While the pharmacokinetics of risperidone in subjects with liver disease were comparable to those in young healthy subjects, the mean free fraction of risperidone in plasma was increased by about 35% because of the diminished concentration of both albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. RISPERDAL® doses should be reduced in patients with liver disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
8.8 Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Lewy Body Dementia
Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies can experience increased sensitivity to RISPERDAL®. Manifestations can include confusion, obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and clinical features consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.2 Abuse
RISPERDAL® has not been systematically studied in animals or humans for its potential for abuse. While the clinical trials did not reveal any tendency for any drug-seeking behavior, these observations were not systematic and it is not possible to predict on the basis of this limited experience the extent to which a CNS-active drug will be misused, diverted, and/or abused once marketed. Consequently, patients should be evaluated carefully for a history of drug abuse, and such patients should be observed closely for signs of RISPERDAL® misuse or abuse (e.g., development of tolerance, increases in dose, drug-seeking behavior).
10. Overdosage
10.1 Human Experience
Premarketing experience included eight reports of acute RISPERDAL® overdosage with estimated doses ranging from 20 to 300 mg and no fatalities. In general, reported signs and symptoms were those resulting from an exaggeration of the drug's known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness and sedation, tachycardia and hypotension, and extrapyramidal symptoms. One case, involving an estimated overdose of 240 mg, was associated with hyponatremia, hypokalemia, prolonged QT, and widened QRS. Another case, involving an estimated overdose of 36 mg, was associated with a seizure.
Postmarketing experience includes reports of acute RISPERDAL® overdosage, with estimated doses of up to 360 mg. In general, the most frequently reported signs and symptoms are those resulting from an exaggeration of the drug's known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness, sedation, tachycardia, hypotension, and extrapyramidal symptoms. Other adverse reactions reported since market introduction related to RISPERDAL® overdose include prolonged QT interval and convulsions. Torsade de pointes has been reported in association with combined overdose of RISPERDAL® and paroxetine.
10.2 Management of Overdosage
For the most up to date information on the management of RISPERDAL® overdosage, contact a certified poison control center (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org). Provide supportive care including close medical supervision and monitoring. Treatment should consist of general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug. Consider the possibility of multiple drug overdosage. Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. Use supportive and symptomatic measures. There is no specific antidote to RISPERDAL®.
11. Risperdal Description
RISPERDAL® contains risperidone, an atypical antipsychotic belonging to the chemical class of benzisoxazole derivatives. The chemical designation is 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one. Its molecular formula is C23H27FN4O2 and its molecular weight is 410.49. The structural formula is:
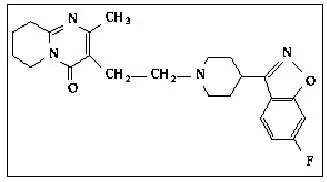
Risperidone is a white to slightly beige powder. It is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, and soluble in methanol and 0.1 N HCl.
RISPERDAL® Tablets are for oral administration and available in 0.5 mg (red-brown), 1 mg (white), 2 mg (orange), 3 mg (yellow), and 4 mg (green) strengths. RISPERDAL® tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, propylene glycol, sodium lauryl sulfate, and starch (corn). The 0.5 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg tablets also contain talc and titanium dioxide. The 0.5 mg tablets contain red iron oxide; the 2 mg tablets contain FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake; the 3 mg and 4 mg tablets contain D&C Yellow No. 10; the 4 mg tablets contain FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake.
RISPERDAL® is also available as a 1 mg/mL oral solution. RISPERDAL® Oral Solution contains the following inactive ingredients: tartaric acid, benzoic acid, sodium hydroxide, and purified water.
RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets are available in 0.5 mg (light coral), 1 mg (light coral), 2 mg (coral), 3 mg (coral), and 4 mg (coral) strengths. RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: Amberlite® resin, gelatin, mannitol, glycine, simethicone, carbomer, sodium hydroxide, aspartame, red ferric oxide, and peppermint oil. In addition, the 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets contain xanthan gum.
12. Risperdal - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of risperidone in schizophrenia is unclear. The drug's therapeutic activity in schizophrenia could be mediated through a combination of dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2) receptor antagonism. The clinical effect from risperidone results from the combined concentrations of risperidone and its major metabolite, 9-hydroxyrisperidone (paliperidone) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Antagonism at receptors other than D2 and 5HT2 may explain some of the other effects of risperidone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Risperidone is a monoaminergic antagonist with high affinity (Ki of 0.12 to 7.3 nM) for the serotonin Type 2 (5HT2), dopamine Type 2 (D2), α1 and α2 adrenergic, and H1 histaminergic receptors. Risperidone showed low to moderate affinity (Ki of 47 to 253 nM) for the serotonin 5HT1C, 5HT1D, and 5HT1A receptors, weak affinity (Ki of 620 to 800 nM) for the dopamine D1 and haloperidol-sensitive sigma site, and no affinity (when tested at concentrations >10-5 M) for cholinergic muscarinic or β1 and β2 adrenergic receptors.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
14. Clinical Studies
14.3 Bipolar Mania – Adjunctive Therapy with Lithium or Valproate
The efficacy of RISPERDAL® with concomitant lithium or valproate in the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes was established in one controlled trial in adult patients who met the DSM-IV criteria for Bipolar I Disorder. This trial included patients with or without psychotic features and with or without a rapid-cycling course.
- (1)
- In this 3-week placebo-controlled combination trial, 148 in- or outpatients on lithium or valproate therapy with inadequately controlled manic or mixed symptoms were randomized to receive RISPERDAL®, placebo, or an active comparator, in combination with their original therapy. RISPERDAL®, in a dose range of 1–6 mg/day, once daily, starting at 2 mg/day (mean modal dose of 3.8 mg/day), combined with lithium or valproate (in a therapeutic range of 0.6 mEq/L to 1.4 mEq/L or 50 mcg/mL to 120 mcg/mL, respectively) was superior to lithium or valproate alone in the reduction of YMRS total score.
- (2)
- In a second 3-week placebo-controlled combination trial, 142 in- or outpatients on lithium, valproate, or carbamazepine therapy with inadequately controlled manic or mixed symptoms were randomized to receive RISPERDAL® or placebo, in combination with their original therapy. RISPERDAL®, in a dose range of 1–6 mg/day, once daily, starting at 2 mg/day (mean modal dose of 3.7 mg/day), combined with lithium, valproate, or carbamazepine (in therapeutic ranges of 0.6 mEq/L to 1.4 mEq/L for lithium, 50 mcg/mL to 125 mcg/mL for valproate, or 4–12 mcg/mL for carbamazepine, respectively) was not superior to lithium, valproate, or carbamazepine alone in the reduction of YMRS total score. A possible explanation for the failure of this trial was induction of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone clearance by carbamazepine, leading to subtherapeutic levels of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone.
16. How is Risperdal supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
RISPERDAL® Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature 15°–25°C (59°–77°F). Protect from light and moisture.
RISPERDAL® 1 mg/mL Oral Solution should be stored at controlled room temperature 15°–25°C (59°–77°F). Protect from light and freezing.
RISPERDAL® M-TAB® Orally Disintegrating Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature 15°–25°C (59°–77°F).
Keep out of reach of children.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients using RISPERDAL oral solution to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use) for RISPERDAL oral solution.
Physicians are advised to discuss the following issues with patients for whom they prescribe RISPERDAL®.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
RISPERDAL® (RISS-per-dal)
(risperidone)
Oral Solution
Read these Instructions for Use before you start using RISPERDAL Oral Solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Important information you need to know before taking RISPERDAL Oral Solution:
- Take RISPERDAL Oral Solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Each 1 mL contains 1 mg of RISPERDAL Oral Solution.
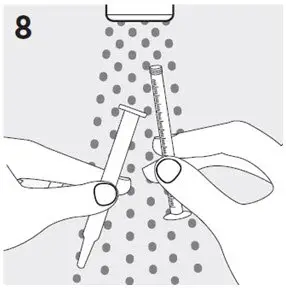
- Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist to show you how to measure your prescribed dose using the oral dosing syringe.
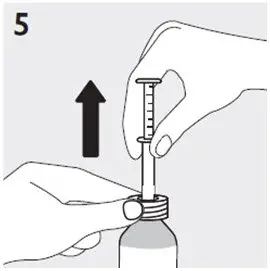
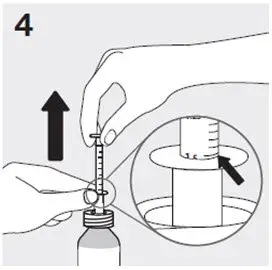
- Always use the oral dosing syringe that comes with RISPERDAL Oral Solution. Contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you lose or damage the oral dosing syringe, or if your carton does not come with one.
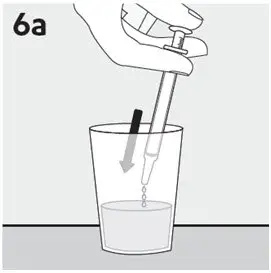
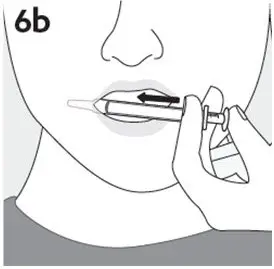
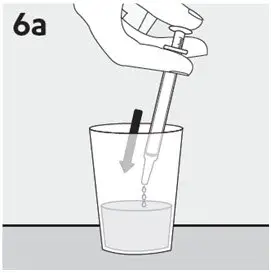
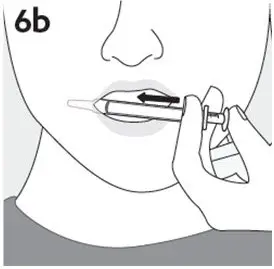
- RISPERDAL Oral Solution can be taken directly from the oral dosing syringe or mixed with water, coffee, orange juice, or low-fat milk. Do not mix RISPERDAL Oral Solution with cola or tea.
Each RISPERDAL Oral Solution carton contains:
| 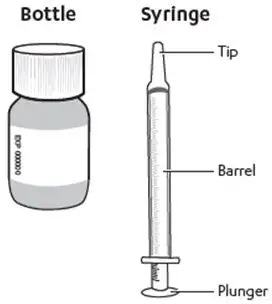 |
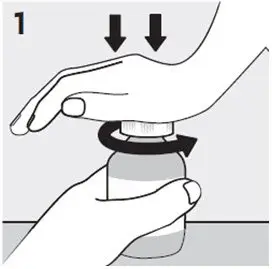
Gather and check supplies:
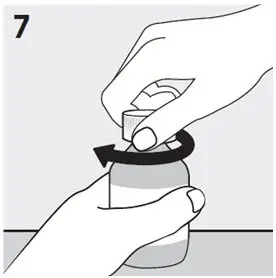
- Gather the RISPERDAL Oral Solution bottle and oral dosing syringe.
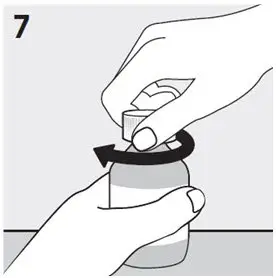
- Check the expiration date on the bottle. Do not use the bottle of RISPERDAL Oral Solution if the expiration date has passed.
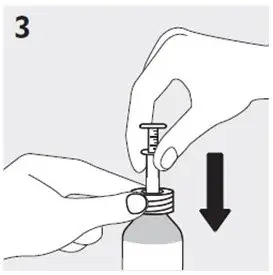
- Check your dose in mLs as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Find this mL marking on the plunger of the oral dosing syringe. If your dose is more than 3 mL, you will need to divide your dose. Follow the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider or pharmacist on how to divide your dose.
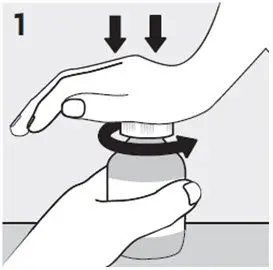
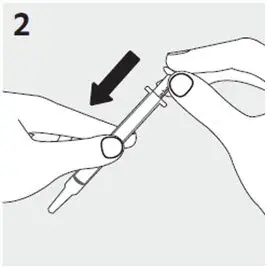
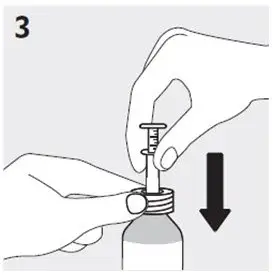
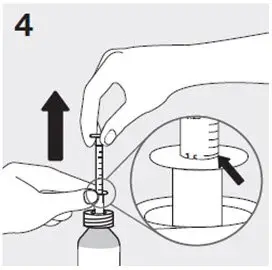
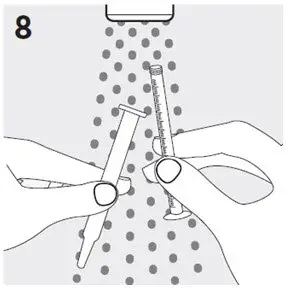
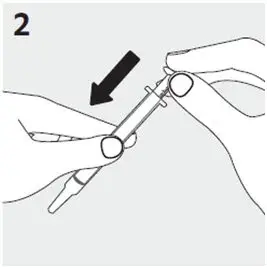
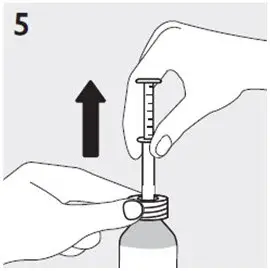
Preparing a dose of RISPERDAL Oral Solution:
Storing RISPERDAL Oral Solution:
- Store RISPERDAL Oral Solution at room temperature between 59°F to 77°F (15°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze RISPERDAL Oral Solution. Protect from light.
- Keep RISPERDAL Oral Solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by:
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Beerse, Belgium
Manufactured for:
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Titusville, NJ, 08560
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 3/2022
INSTRUCCIONES DE USO
RISPERDAL® (RISS-per-dal)
(risperidona)
Solución oral
Lea estas Instrucciones de uso antes de comenzar a usar RISPERDAL Solución oral y cada vez que renueve su receta. Es posible que este material contenga información nueva. Esta información no reemplaza la consulta con su proveedor de atención médica acerca de su enfermedad o tratamiento.
Información importante que debe saber antes de tomar RISPERDAL Solución oral:
- Tome RISPERDAL Solución oral exactamente como se lo indica su proveedor de atención médica.
- Cada 1 ml contiene 1 mg de RISPERDAL Solución oral.
- Pídale a su proveedor de atención médica o farmacéutico que le muestre cómo medir la dosis recetada con la jeringa de dosificación oral.
- Utilice siempre la jeringa de dosificación oral que viene con RISPERDAL Solución oral. Comuníquese con su proveedor de atención médica o farmacéutico si pierde o daña la jeringa de dosificación oral, o si su caja no viene con una.
- RISPERDAL Solución oral se puede tomar directamente de la jeringa de dosificación oral o se puede mezclar con agua, café, jugo de naranja o leche con bajo contenido de grasa. No mezcle RISPERDAL Solución oral con refrescos de cola o té.
Cada caja de RISPERDAL Solución oral contiene lo siguiente:
| 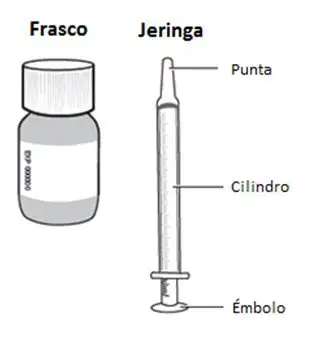 |
Reúna y verifique los suministros:
- Reúna el frasco de RISPERDAL Solución oral y la jeringa de dosificación oral.
- Consulte la fecha de caducidad en el frasco. No utilice el frasco de RISPERDAL Solución oral si ha pasado la fecha de caducidad.
- Verifique su dosis en ml según lo prescrito por su proveedor de atención médica. Busque esta marca de ml en el émbolo de la jeringa de dosificación oral. Si su dosis supera los 3 ml, deberá dividir la dosis. Siga las instrucciones que le dé su proveedor de atención médica o farmacéutico sobre cómo dividir su dosis.
Preparación de una dosis de RISPERDAL Solución oral:
Almacenamiento de RISPERDAL Solución oral
- Almacene RISPERDAL Solución oral a temperatura ambiente entre 59 °F y 77 °F (de 15 °C a 25 °C).
- No congelar RISPERDAL Solución oral. Proteger de la luz.
- Mantenga RISPERDAL Solución oral y todos los medicamentos fuera del alcance de los niños.
Fabricado por:
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Beerse, Bélgica
Fabricado para:
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Titusville, NJ, 08560
Estas Instrucciones de uso han sido aprobadas por la Administración de Alimentos y Medicamentos (FDA) de los EE. UU.
Revisado: 3/2022
| RISPERDAL
risperidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL
risperidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL
risperidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL
risperidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL
risperidone tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL M-TAB
risperidone tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL M-TAB
risperidone tablet, orally disintegrating |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL M-TAB
risperidone tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL M-TAB
risperidone tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL M-TAB
risperidone tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| RISPERDAL
risperidone solution |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Ortho LLC | 805887986 | MANUFACTURE(50458-302, 50458-300, 50458-320, 50458-330, 50458-350, 50458-395, 50458-315, 50458-325, 50458-335, 50458-355) , ANALYSIS(50458-302, 50458-300, 50458-320, 50458-330, 50458-350, 50458-395, 50458-315, 50458-325, 50458-335, 50458-355) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica, N.V | 370005019 | MANUFACTURE(50458-305) , ANALYSIS(50458-305) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutical Sciences Unlimited Company | 985639841 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-302, 50458-300, 50458-320, 50458-330, 50458-350, 50458-395, 50458-315, 50458-325, 50458-335, 50458-355, 50458-305) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica, N.V. | 400345889 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-305) | |