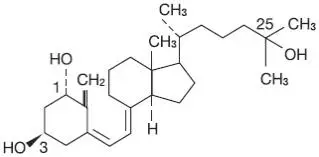
Drug Detail:Rocaltrol (Calcitriol (oral/injection) [ kal-si-trye-ol ])
Drug Class: Vitamins
Warnings
Overdosage of any form of vitamin D is dangerous (see OVERDOSAGE). Progressive hypercalcemia due to overdosage of vitamin D and its metabolites may be so severe as to require emergency attention. Chronic hypercalcemia can lead to generalized vascular calcification, nephrocalcinosis and other soft-tissue calcification. The serum calcium times phosphate (Ca x P) product should not be allowed to exceed 70 mg2/dL2. Radiographic evaluation of suspect anatomical regions may be useful in the early detection of this condition.
Rocaltrol is the most potent metabolite of vitamin D available. The administration of Rocaltrol to patients in excess of their daily requirements can cause hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hyperphosphatemia. Therefore, pharmacologic doses of vitamin D and its derivatives should be withheld during Rocaltrol treatment to avoid possible additive effects and hypercalcemia. If treatment is switched from ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) to calcitriol, it may take several months for the ergocalciferol level in the blood to return to the baseline value (see OVERDOSAGE).
Calcitriol increases inorganic phosphate levels in serum. While this is desirable in patients with hypophosphatemia, caution is called for in patients with renal failure because of the danger of ectopic calcification. A nonaluminum phosphate-binding compound and a low-phosphate diet should be used to control serum phosphorus levels in patients undergoing dialysis.
Magnesium-containing preparations (e.g., antacids) and Rocaltrol should not be used concomitantly in patients on chronic renal dialysis because such use may lead to the development of hypermagnesemia.
Studies in dogs and rats given calcitriol for up to 26 weeks have shown that small increases of calcitriol above endogenous levels can lead to abnormalities of calcium metabolism with the potential for calcification of many tissues in the body.
Precautions
General
Excessive dosage of Rocaltrol induces hypercalcemia and in some instances hypercalciuria; therefore, early in treatment during dosage adjustment, serum calcium should be determined twice weekly. In dialysis patients, a fall in serum alkaline phosphatase levels usually antedates the appearance of hypercalcemia and may be an indication of impending hypercalcemia. An abrupt increase in calcium intake as a result of changes in diet (e.g., increased consumption of dairy products) or uncontrolled intake of calcium preparations may trigger hypercalcemia.
Should hypercalcemia develop, treatment with Rocaltrol should be stopped immediately. During periods of hypercalcemia, serum calcium and phosphate levels must be determined daily. When normal levels have been attained, treatment with Rocaltrol can be continued, at a daily dose 0.25 mcg lower than that previously used. An estimate of daily dietary calcium intake should be made and the intake adjusted when indicated. Rocaltrol should be given cautiously to patients on digitalis, because hypercalcemia in such patients may precipitate cardiac arrhythmias.
Immobilized patients, e.g., those who have undergone surgery, are particularly exposed to the risk of hypercalcemia.
In patients with normal renal function, chronic hypercalcemia may be associated with an increase in serum creatinine. While this is usually reversible, it is important in such patients to pay careful attention to those factors which may lead to hypercalcemia. Rocaltrol therapy should always be started at the lowest possible dose and should not be increased without careful monitoring of the serum calcium. An estimate of daily dietary calcium intake should be made and the intake adjusted when indicated.
Patients with normal renal function taking Rocaltrol should avoid dehydration. Adequate fluid intake should be maintained.
Laboratory Tests
For dialysis patients, serum calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and alkaline phosphatase should be determined periodically. For hypoparathyroid patients, serum calcium, phosphorus, and 24-hour urinary calcium should be determined periodically. For predialysis patients, serum calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, and intact PTH (iPTH) should be determined initially. Thereafter, serum calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, and creatinine should be determined monthly for a 6-month period and then determined periodically. Intact PTH (iPTH) should be determined periodically every 3 to 4 months at the time of visits. During the titration period of treatment with Rocaltrol, serum calcium levels should be checked at least twice weekly (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Since Rocaltrol is believed to be the active hormone which exerts vitamin D activity in the body, adverse effects are, in general, similar to those encountered with excessive vitamin D intake, i.e., hypercalcemia syndrome or calcium intoxication, depending on the severity and duration of hypercalcemia (see WARNINGS). Because of the short biological half-life of calcitriol, pharmacokinetic investigations have shown normalization of elevated serum calcium within a few days of treatment withdrawal, i.e., much faster than in treatment with vitamin D3 preparations.
The early and late signs and symptoms of vitamin D intoxication associated with hypercalcemia include:
Early: weakness, headache, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, muscle pain, bone pain, metallic taste, and anorexia, abdominal pain or stomach ache.
Late: polyuria, polydipsia, anorexia, weight loss, nocturia, conjunctivitis (calcific), pancreatitis, photophobia, rhinorrhea, pruritus, hyperthermia, decreased libido, elevated BUN, albuminuria, hypercholesterolemia, elevated SGOT (AST) and SGPT (ALT), ectopic calcification, nephrocalcinosis, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, dystrophy, sensory disturbances, dehydration, apathy, arrested growth, urinary tract infections, and, rarely, overt psychosis.
In clinical studies on hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism, hypercalcemia was noted on at least one occasion in about 1 in 3 patients and hypercalciuria in about 1 in 7 patients. Elevated serum creatinine levels were observed in about 1 in 6 patients (approximately one half of whom had normal levels at baseline).
In concurrent hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia, soft-tissue calcification may occur; this can be seen radiographically (see WARNINGS).
In patients with normal renal function, chronic hypercalcemia may be associated with an increase in serum creatinine (see PRECAUTIONS: General).
Hypersensitivity reactions (pruritus, rash, urticaria, and very rarely severe erythematous skin disorders) may occur in susceptible individuals. One case of erythema multiforme and one case of allergic reaction (swelling of lips and hives all over the body) were confirmed by rechallenge.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Validus Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-866-982-5438 (1-866-9VALIDUS) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Overdosage
Administration of Rocaltrol to patients in excess of their daily requirements can cause hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hyperphosphatemia. Since calcitriol is a derivative of vitamin D, the signs and symptoms of overdose are the same as for an overdose of vitamin D (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). High intake of calcium and phosphate concomitant with Rocaltrol may lead to similar abnormalities. The serum calcium times phosphate (Ca x P) product should not be allowed to exceed 70 mg2/dL2. High levels of calcium in the dialysate bath may contribute to the hypercalcemia (see WARNINGS).
Rocaltrol Dosage and Administration
The optimal daily dose of Rocaltrol must be carefully determined for each patient. Rocaltrol can be administered orally either as a capsule (0.25 mcg or 0.50 mcg) or as an oral solution (1 mcg/mL). Rocaltrol therapy should always be started at the lowest possible dose and should not be increased without careful monitoring of serum calcium.
The effectiveness of Rocaltrol therapy is predicated on the assumption that each patient is receiving an adequate but not excessive daily intake of calcium. Patients are advised to have a dietary intake of calcium at a minimum of 600 mg daily. The U.S. RDA for calcium in adults is 800 mg to 1200 mg. To ensure that each patient receives an adequate daily intake of calcium, the physician should either prescribe a calcium supplement or instruct the patient in proper dietary measures.
Because of improved calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, some patients on Rocaltrol may be maintained on a lower calcium intake. Patients who tend to develop hypercalcemia may require only low doses of calcium or no supplementation at all.
During the titration period of treatment with Rocaltrol, serum calcium levels should be checked at least twice weekly. When the optimal dosage of Rocaltrol has been determined, serum calcium levels should be checked every month (or as given below for individual indications). Samples for serum calcium estimation should be taken without a tourniquet.
Hypoparathyroidism
The recommended initial dosage of Rocaltrol is 0.25 mcg/day given in the morning. If a satisfactory response in the biochemical parameters and clinical manifestations of the disease is not observed, the dose may be increased at 2- to 4-week intervals. During the dosage titration period, serum calcium levels should be obtained at least twice weekly and, if hypercalcemia is noted, Rocaltrol should be immediately discontinued until normocalcemia ensues (see PRECAUTIONS: General). Careful consideration should also be given to lowering the dietary calcium intake. Serum calcium, phosphorus, and 24-hour urinary calcium should be determined periodically.
Most adult patients and pediatric patients age 6 years and older have responded to dosages in the range of 0.5 mcg to 2 mcg daily. Pediatric patients in the 1- to 5-year age group with hypoparathyroidism have usually been given 0.25 mcg to 0.75 mcg daily. The number of treated patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism less than 6 years of age is too small to make dosage recommendations.
Malabsorption is occasionally noted in patients with hypoparathyroidism; hence, larger doses of Rocaltrol may be needed.
| ROCALTROL
calcitriol capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ROCALTROL
calcitriol capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| ROCALTROL
calcitriol solution |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Validus Pharmaceuticals LLC (801194619) |