Drug Detail:Rozerem (Ramelteon [ ram-el-tee-on ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous anxiolytics, sedatives and hypnotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ROZEREM (ramelteon) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2005
Indications and Usage for Rozerem
ROZEREM is indicated for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset. (1)
Rozerem Dosage and Administration
- Adult dose: 8 mg taken within 30 minutes of going to bed. (2.1)
- Should not be taken with or immediately after a high-fat meal. (2.1)
- Total daily dose should not exceed 8 mg. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
8 mg tablets. (3)
Contraindications
- History of angioedema while taking ROZEREM. (4)
- Fluvoxamine (strong CYP1A2 inhibitor): Increases AUC for ramelteon and should not be used in combination. (7.1)
Warnings and Precautions
- Severe anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions: Angioedema and anaphylaxis have been reported. Do not rechallenge if such reactions occur. (5.1)
- Need to evaluate for comorbid diagnoses: Reevaluate if insomnia persists after 7 to 10 days of treatment. (5.2)
- Abnormal thinking, behavioral changes, complex behaviors: May include "sleep-driving" and hallucinations. Immediately evaluate any new onset behavioral changes. (5.3)
- Depression: Worsening of depression or suicidal thinking may occur. (5.3)
- CNS effects: Potential impairment of activities requiring complete mental alertness such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle, after ingesting the drug. (5.4)
- Reproductive effects: Include decreased testosterone and increased prolactin levels. Effect on reproductive axis in developing humans is unknown. (5.5)
- Patients with severe sleep apnea: ROZEREM is not recommended for use in this population. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥3% and more common than with placebo) are: somnolence, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, and exacerbated insomnia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. at 1-877-TAKEDA-7 (1-877-825-3327) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Rifampin (strong CYP enzyme inducer): Decreases exposure to and effects of ramelteon. (7.1)
- Ketoconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor): Increases AUC for ramelteon; administer with caution. (7.1)
- Fluconazole (strong CYP2C9 inhibitor): Increases systemic exposure of ramelteon; administer with caution. (7.1)
- Donepezil: Increases systemic exposure of ramelteon; patients should be closely monitored when ramelteon is coadministered with donepezil. (7.1)
- Doxepin: Increases systemic exposure of ramelteon; patients should be closely monitored when ramelteon is coadministered with doxepin. (7.1)
- Alcohol: Causes additive psychomotor impairment; should not be used in combination. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness not established. (8.4)
- Geriatric use: No overall differences in safety and efficacy between elderly and younger adult subjects. (8.5)
- Hepatic impairment: Is not recommended in patients with severe impairment; use with caution in moderate impairment. (8.8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Rozerem
ROZEREM is indicated for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep onset.
The clinical trials performed in support of efficacy were up to six months in duration. The final formal assessments of sleep latency were performed after two days of treatment during the crossover study (elderly only), at five weeks in the six week studies (adults and elderly), and at the end of the six month study (adults and elderly) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Rozerem Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Adults
The recommended dose of ROZEREM is 8 mg taken within 30 minutes of going to bed. It is recommended that ROZEREM not be taken with or immediately after a high-fat meal.
The total ROZEREM dose should not exceed 8 mg per day.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ROZEREM is available in an 8 mg strength tablet for oral administration.
ROZEREM 8 mg tablets are round, pale orange-yellow, film-coated, with "TAK" and "RAM-8" printed on one side.
4. Contraindications
Patients who develop angioedema after treatment with ROZEREM should not be rechallenged with the drug.
Patients should not take ROZEREM in conjunction with fluvoxamine [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Anaphylactic and Anaphylactoid Reactions
Rare cases of angioedema involving the tongue, glottis or larynx have been reported in patients after taking the first or subsequent doses of ROZEREM. Some patients have had additional symptoms such as dyspnea, throat closing, or nausea and vomiting that suggest anaphylaxis. Some patients have required medical therapy in the emergency department. If angioedema involves the tongue, glottis or larynx, airway obstruction may occur and be fatal. Patients who develop angioedema after treatment with ROZEREM should not be rechallenged with the drug.
5.2 Need to Evaluate for Comorbid Diagnoses
Since sleep disturbances may be the presenting manifestation of a physical and/or psychiatric disorder, symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after a careful evaluation of the patient. The failure of insomnia to remit after 7 to 10 days of treatment may indicate the presence of a primary psychiatric and/or medical illness that should be evaluated. Worsening of insomnia, or the emergence of new cognitive or behavioral abnormalities, may be the result of an unrecognized underlying psychiatric or physical disorder and requires further evaluation of the patient. Exacerbation of insomnia and emergence of cognitive and behavioral abnormalities were seen with ROZEREM during the clinical development program.
5.3 Abnormal Thinking and Behavioral Changes
A variety of cognitive and behavior changes have been reported to occur in association with the use of hypnotics. In primarily depressed patients, worsening of depression (including suicidal ideation and completed suicides) has been reported in association with the use of hypnotics.
Hallucinations, as well as behavioral changes such as bizarre behavior, agitation and mania have been reported with ROZEREM use. Amnesia, anxiety and other neuro-psychiatric symptoms may also occur unpredictably.
Complex behaviors such as "sleep-driving" (i.e., driving while not fully awake after ingestion of a hypnotic) and other complex behaviors (e.g., preparing and eating food, making phone calls, or having sex), with amnesia for the event, have been reported in association with hypnotic use. The use of alcohol and other CNS depressants may increase the risk of such behaviors. These events can occur in hypnotic-naive as well as in hypnotic-experienced persons. Complex behaviors have been reported with the use of ROZEREM. Discontinuation of ROZEREM should be strongly considered for patients who report any complex sleep behavior.
5.4 CNS Effects
Patients should avoid engaging in hazardous activities that require concentration (such as operating a motor vehicle or heavy machinery) after taking ROZEREM.
After taking ROZEREM, patients should confine their activities to those necessary to prepare for bed.
Patients should be advised not to consume alcohol in combination with ROZEREM as alcohol and ROZEREM may have additive effects when used in conjunction.
5.5 Reproductive Effects
ROZEREM has been associated with an effect on reproductive hormones in adults, e.g., decreased testosterone levels and increased prolactin levels. It is not known what effect chronic or even chronic intermittent use of ROZEREM may have on the reproductive axis in developing humans [see Clinical Trials (14.3)].
5.6 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
ROZEREM has not been studied in subjects with severe sleep apnea and is not recommended for use in this population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
ROZEREM should not be used by patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections:
- Severe anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Abnormal thinking, behavior changes, and complex behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- CNS effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.2 Effect of Alcohol on ROZEREM
Alcohol by itself impairs performance and can cause sleepiness. Since the intended effect of ROZEREM is to promote sleep, patients should be cautioned not to consume alcohol when using ROZEREM [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. Use of the products in combination may have an additive effect.
7.3 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
ROZEREM is not known to interfere with commonly used clinical laboratory tests. In addition, in vitro data indicate that ramelteon does not cause false-positive results for benzodiazepines, opiates, barbiturates, cocaine, cannabinoids, or amphetamines in two standard urine drug screening methods in vitro.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to ROZEREM through breastmilk should be monitored for somnolence and feeding problems. A lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk during treatment and for 25 hours (approximately 5 elimination half-lives) after ROZEREM administration in order to minimize drug exposure to a breastfed infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ROZEREM in pediatric patients have not been established. Further study is needed prior to determining that this product may be used safely in prepubescent and pubescent patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 654 subjects in double-blind, placebo-controlled, efficacy trials who received ROZEREM were at least 65 years of age; of these, 199 were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between elderly and younger adult subjects.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in elderly subjects with insomnia (n=33) evaluated the effect of a single dose of ROZEREM on balance, mobility, and memory functions after middle of the night awakening. There is no information on the effect of multiple dosing. Night time dosing of ROZEREM 8 mg did not impair middle of the night balance, mobility, or memory functions relative to placebo. The effects on night balance in the elderly cannot be definitively known from this study.
8.6 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The respiratory depressant effect of ROZEREM was evaluated in a crossover design study of subjects (n=26) with mild to moderate COPD after administering a single 16 mg dose or placebo, and in a separate study (n=25), the effects of ROZEREM on respiratory parameters were evaluated after administering an 8 mg dose or placebo in a crossover design to patients with moderate to severe COPD, defined as patients who had forced expiratory volume at one second (FEV1)/forced vital capacity ratio of <70%, and a FEV1 <80% of predicted with <12% reversibility to albuterol. Treatment with a single dose of ROZEREM has no demonstrable respiratory depressant effects in subjects with mild to severe COPD, as measured by arterial O2 saturation (SaO2). There is no available information on the respiratory effects of multiple doses of ROZEREM in patients with COPD. The respiratory depressant effects in patients with COPD cannot be definitively known from this study.
8.7 Sleep Apnea
The effects of ROZEREM were evaluated after administering a 16 mg dose or placebo in a crossover design to subjects (n=26) with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. Treatment with ROZEREM 16 mg for one night showed no difference compared with placebo on the Apnea/Hypopnea Index (the primary outcome variable), apnea index, hypopnea index, central apnea index, mixed apnea index, and obstructive apnea index. Treatment with a single dose of ROZEREM does not exacerbate mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. There is no available information on the respiratory effects of multiple doses of ROZEREM in patients with sleep apnea. The effects on exacerbation in patients with mild to moderate sleep apnea cannot be definitively known from this study.
ROZEREM has not been studied in subjects with severe obstructive sleep apnea; use of ROZEREM is not recommended in such patients.
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
Exposure to ROZEREM was increased by four-fold in subjects with mild hepatic impairment and by more than ten-fold in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment. ROZEREM should be used with caution in patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]. ROZEREM is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
ROZEREM is not a controlled substance.
Discontinuation of ramelteon in animals or in humans after chronic administration did not produce withdrawal signs. Ramelteon does not appear to produce physical dependence.
10. Overdosage
General symptomatic and supportive measures should be used, along with immediate gastric lavage where appropriate. Intravenous fluids should be administered as needed. As in all cases of drug overdose, respiration, pulse, blood pressure, and other appropriate vital signs should be monitored, and general supportive measures employed.
Hemodialysis does not effectively reduce exposure to ROZEREM. Therefore, the use of dialysis in the treatment of overdosage is not appropriate.
11. Rozerem Description
ROZEREM (ramelteon) is an orally active hypnotic chemically designated as (S)-N-[2-(1,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2H-indeno-[5,4-b]furan-8-yl)ethyl]propionamide and containing one chiral center. The compound is produced as the (S)-enantiomer, with an empirical formula of C16H21NO2, molecular weight of 259.34, and the following chemical structure:
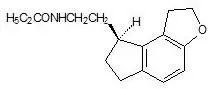
Ramelteon is freely soluble in organic solvents, such as methanol, ethanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide; soluble in 1-octanol and acetonitrile; and very slightly soluble in water and in aqueous buffers from pH 3 to pH 11.
Each ROZEREM tablet includes the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, copovidone, titanium dioxide, yellow ferric oxide, polyethylene glycol 8000, and ink containing shellac and synthetic iron oxide black.
12. Rozerem - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ramelteon is a melatonin receptor agonist with both high affinity for melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors and relative selectivity over the MT3 receptor.
The activity of ramelteon at the MT1 and MT2 receptors is believed to contribute to its sleep-promoting properties, as these receptors, acted upon by endogenous melatonin, are thought to be involved in the maintenance of the circadian rhythm underlying the normal sleep-wake cycle.
Ramelteon has no appreciable affinity for the GABA receptor complex or for receptors that bind neuropeptides, cytokines, serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline, acetylcholine, and opiates. Ramelteon also does not interfere with the activity of a number of selected enzymes in a standard panel.
The major metabolite of ramelteon, M-II, is pharmacologically active and has approximately one tenth and one fifth the binding affinity of the parent molecule for the human MT1 and MT2 receptors, respectively. However, M-II circulates at higher concentrations than the parent producing 20- to 100-fold greater mean systemic exposure when compared to ramelteon. Similar to ramelteon, M-II does not interfere with the activity of a number of endogenous enzymes.
All other known metabolites of ramelteon are inactive.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of ROZEREM has been evaluated in healthy subjects as well as in subjects with hepatic or renal impairment. When administered orally to humans in doses ranging from 4 to 64 mg, ramelteon undergoes rapid, high first-pass metabolism, and exhibits linear pharmacokinetics. Maximal serum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) data show substantial intersubject variability, consistent with the high first-pass effect; the coefficient of variation for these values is approximately 100%. Several metabolites have been identified in human serum and urine.
12.4 Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Age
In a group of 24 elderly subjects aged 63 to 79 years administered a single ROZEREM 16 mg dose, the mean Cmax and AUC0-inf values were 11.6 ng/mL (SD, 13.8) and 18.7 ng∙hr/mL (SD, 19.4), respectively. The elimination half-life was 2.6 hours (SD, 1.1). Compared with younger adults, the total exposure (AUC0-inf) and Cmax of ramelteon were 97 and 86% higher, respectively, in elderly subjects. The AUC0-inf and Cmax of M-II were increased by 30 and 13%, respectively, in elderly subjects.
Gender
There are no clinically meaningful gender-related differences in the pharmacokinetics of ROZEREM or its metabolites.
Hepatic Impairment
Exposure to ROZEREM was increased almost four-fold in subjects with mild hepatic impairment after seven days of dosing with 16 mg/day; exposure was further increased (more than ten-fold) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment. Exposure to M-II was only marginally increased in mildly and moderately impaired subjects relative to healthy matched controls. The pharmacokinetics of ROZEREM have not been evaluated in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). ROZEREM should be used with caution in patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of ROZEREM were studied after administering a 16 mg dose to subjects with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment based on predose creatinine clearance (53 to 95, 35 to 49, or 15 to 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, respectively), and in subjects who required chronic hemodialysis. Wide intersubject variability was seen in ROZEREM exposure parameters. However, no effects on Cmax or AUC0-t of parent drug or M-II were seen in any of the treatment groups; the incidence of adverse events was similar across groups. These results are consistent with the negligible renal clearance of ramelteon, which is principally eliminated via hepatic metabolism. No adjustment of ROZEREM dosage is required in patients with renal impairment, including patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of ≤30 mL/min/1.73 m2) and patients who require chronic hemodialysis.
12.5 Drug-Drug Interactions
ROZEREM has a highly variable intersubject pharmacokinetic profile (approximately 100% coefficient of variation in Cmax and AUC). As noted above, CYP1A2 is the major isozyme involved in the metabolism of ROZEREM; the CYP2C subfamily and CYP3A4 isozymes are also involved to a minor degree.
14. Clinical Studies
14.2 Studies Pertinent to Safety Concerns for Sleep-Promoting Drugs
Residual Pharmacological Effect in Insomnia Trials
In order to evaluate potential next-day residual effects, the following scales were used: a Memory Recall Test, a Word List Memory Test, a Visual Analog Mood and Feeling Scale, the Digit-Symbol Substitution Test, and a post-sleep questionnaire to assess alertness and ability to concentrate. There was no evidence of next-day residual effect seen after two nights of ramelteon use during the crossover studies.
In a 35 night, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in adults with chronic insomnia, measures of residual effects were performed at three time points. Overall, the magnitudes of any observed differences were small. At Week 1, patients who received 8 mg of ROZEREM had a mean VAS score (46 mm on a 100 mm scale) indicating more fatigue in comparison to patients who received placebo (42 mm). At Week 3, patients who received 8 mg of ROZEREM had a lower mean score for immediate recall (7.5 out of 16 words) compared to patients who received placebo (8.2 words); and the patients treated with ROZEREM had a mean VAS score indicating more sluggishness (27 mm on a 100 mm VAS) in comparison to the placebo-treated patients (22 mm). Patients who received ROZEREM did not have next-morning residual effects that were different from placebo at Week 5.
14.3 Studies to Evaluate Effects on Endocrine Function
Two controlled studies evaluated the effects of ROZEREM on endocrine function.
In the first trial, ROZEREM 16 mg once daily or placebo was administered to 99 healthy volunteer subjects for four weeks. This study evaluated the thyroid axis, adrenal axis and reproductive axis. No clinically significant endocrinopathies were demonstrated in this study. However, the study was limited in its ability to detect such abnormalities due to its limited duration.
In the second trial, ROZEREM 16 mg once daily or placebo was administered to 122 subjects with chronic insomnia for six months. This study evaluated the thyroid axis, adrenal axis and reproductive axis. There were no significant abnormalities seen in either the thyroid or the adrenal axes. Abnormalities were, however, noted within the reproductive axis. Overall, the mean serum prolactin level change from baseline was 4.9 mcg/L (34% increase) for women in the ROZEREM group compared with -0.6 mcg/L (4% decrease) for women in the placebo group (p=0.003). No differences between active- and placebo-treated groups occurred among men. Thirty two percent of all patients who were treated with ramelteon in this study (women and men) had prolactin levels that increased from normal baseline levels compared to 19% of patients who were treated with placebo. Subject-reported menstrual patterns were similar between the two treatment groups.
In a 12 month, open-label study in adult and elderly patients, there were two patients who were noted to have abnormal morning cortisol levels, and subsequent abnormal ACTH stimulation tests. A 29 year old female patient was diagnosed with a prolactinoma. The relationship of these events to ROZEREM therapy is not clear.
16. How is Rozerem supplied
ROZEREM is available as round, pale orange-yellow, film-coated, 8 mg tablets, with "TAK" and "RAM-8" printed on one side, in the following quantities:
| NDC 64764-805-30 | Bottles of 30 |
| NDC 64764-805-10 | Bottles of 100 |
| NDC 64764-805-50 | Bottles of 500 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Severe Anaphylactic and Anaphylactoid Reactions
Inform patients that severe anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have occurred with ramelteon. Describe the relevant signs/symptoms and advise seeking immediate medical attention if any such things occur.
Sleep-Driving and other Complex Behaviors
There have been reports of people getting out of bed after taking a sleep medication and driving their cars while not fully awake, often with no memory of the event. If a patient experiences such an episode, it should be reported to his or her doctor immediately, since "sleep-driving" can be dangerous. This behavior is more likely to occur when sleep medications are taken with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants. Other complex behaviors (e.g., preparing and eating food, making phone calls, or having sex) have been reported in patients who are not fully awake after taking a sleep medication. As with sleep-driving, patients usually do not remember these events.
Endocrine Effects
Patients should consult their healthcare providers if they experience one of the following: cessation of menses or galactorrhea in females, decreased libido, or problems with fertility. Describe the relevant signs/symptoms and advise seeking medical attention if any such things occur.
Administration Instructions
- Patients should be advised to take ROZEREM within 30 minutes prior to going to bed and should confine their activities to those necessary to prepare for bed.
- Patients should be advised that they should not take ROZEREM with or immediately after a high-fat meal.
- Do not break the tablet; it should be swallowed whole.
MEDICATION GUIDE
ROZEREM (rō-Zair-em)
(ramelteon)
Read the Medication Guide that comes with ROZEREM before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about ROZEREM?
ROZEREM may cause severe allergic reactions. Symptoms include swelling of the tongue or throat, trouble breathing, and nausea and vomiting. Get emergency medical help if you get these symptoms after taking ROZEREM.
After taking ROZEREM, you may get up out of bed while not being fully awake and do an activity that you do not know you are doing. The next morning, you may not remember that you did anything during the night. You have a higher chance for doing these activities if you drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy with ROZEREM. Activities may include:
- driving a car ("sleep-driving")
- making and eating food
- talking on the phone
- having sex
- sleep-walking
Call your doctor right away if you find out that you have done any of the above activities after taking ROZEREM.
Important:
- 1.
-
Take ROZEREM exactly as prescribed
- Do not take more ROZEREM than prescribed.
- Take ROZEREM within 30 minutes of going to bed, not sooner.
- 2.
-
Do not take ROZEREM if you:
- drink alcohol
- take other medicines that can make you sleepy. Talk to your doctor about all of your medicines. Your doctor will tell you if you can take ROZEREM with your other medicines
- cannot get a full night's sleep
WHAT IS ROZEREM?
ROZEREM is a hypnotic (sleep) medicine. ROZEREM is used in adults for the treatment of the symptom of trouble falling asleep from insomnia.
ROZEREM is not for children.
Who should not take ROZEREM?
Do not take ROZEREM if you are allergic to anything in it. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ROZEREM.
Do not take ROZEREM if you are currently taking Luvox (fluvoxamine).
ROZEREM may not be right for you. Before starting ROZEREM, tell your doctor about all of your health conditions, including if you:
- have a history of depression, mental illness, or suicidal thoughts
- have liver disease
- have a lung disease or breathing problems
- are pregnant, or planning to become pregnant
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. ROZEREM may cause somnolence in a breastfed infant. You may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breastmilk during treatment and for 25 hours after administration of ROZEREM.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Medicines can interact with each other, sometimes causing serious side effects.
Do not take ROZEREM with:
- other medicines that can make you sleepy
- Luvox (fluvoxamine)
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take ROZEREM?
- Take ROZEREM exactly as prescribed. Do not take more ROZEREM than prescribed for you.
- Do not break the tablets. They should be swallowed whole.
- Take ROZEREM within 30 minutes of going to bed. After taking ROZEREM only do activities to get ready for bed.
- Do not take ROZEREM with or right after a meal.
- Do not take ROZEREM unless you are able to get a full night's sleep before you must be active again.
- Call your doctor if your insomnia worsens or is not better within 7 to 10 days. This may mean that there is another condition causing your sleep problems.
- If you take too much ROZEREM or overdose, call your doctor or poison control center right away, or get emergency treatment.
What are the possible side effects of ROZEREM?
Possible serious side effects of ROZEREM include:
- severe allergic reactions. Symptoms include swelling of the tongue or throat, trouble breathing, and nausea and vomiting. Get emergency medical help if you get these symptoms after taking ROZEREM.
- getting out of bed while not being fully awake and do an activity that you do not know you are doing. (See "What is the most important information I should know about ROZEREM?")
- abnormal thoughts and behavior. Symptoms include worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or actions, nightmares, and hallucinations.
-
hormone effects. ROZEREM can decrease testosterone levels and increase prolactin levels in the blood. Symptoms of low testosterone or high prolactin levels are:
- decreased interest in sex
- problems getting pregnant
- irregular menstrual periods or no menstrual periods
- leakage of milk from the nipples of a person who is not breastfeeding
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the above side effects or any other side effects that worry you while using ROZEREM. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
The most common side effects of ROZEREM are:
- drowsiness
- tiredness
- dizziness
- You may still feel drowsy the next day after taking ROZEREM. Do not drive or do other dangerous activities after taking ROZEREM until you feel fully awake.
These are not all the side effects of ROZEREM. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I Store ROZEREM?
- Store ROZEREM tablets at room temperature, 59° to 86° F (15° to 30°C). Keep the container tightly closed and protected from moisture and humidity.
- Keep ROZEREM and all medicines out of reach of children.
General Information about ROZEREM
- Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide.
- Do not use ROZEREM for a condition for which it was not prescribed.
- Do not share ROZEREM with other people, even if you think they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about ROZEREM. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about ROZEREM that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information about ROZEREM, please call Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. at 1-877-TAKEDA-7 (1-877-825-3327) or visit www.rozerem.com.
What are the ingredients in ROZEREM?
Active Ingredient: ramelteon
Inactive Ingredients: lactose monohydrate, starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, copovidone, titanium dioxide, yellow ferric oxide, polyethylene glycol 8000, and ink containing shellac and synthetic iron oxide black.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
ROZEREM is a trademark of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
All other trademark names are the property of their respective owners.
©2005-2021 Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
ROZ014 R11 Dec 2018
| ROZEREM
ramelteon tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. (039997266) |





