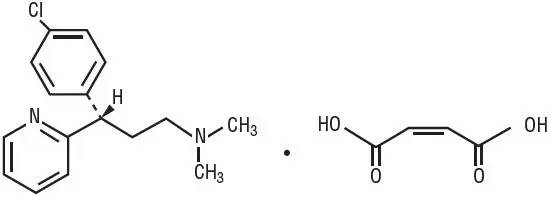
Overdosage
Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Stimulation is particularly likely in children. Atropine-like signs and symptoms—dry mouth, fixed, dilated pupils, flushing, and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur.
If vomiting has not occurred spontaneously the patient should be induced to vomit. This is best done by having the patient drink a glass of water or milk after which the patient should be made to gag. Precautions against aspiration must be taken, especially in infants and children.
Saline cathartics, such as milk of magnesia, draw water into the bowel by osmosis and therefore, are valuable for their action in rapid dilution of bowel content.
Stimulants should not be used.
Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension.