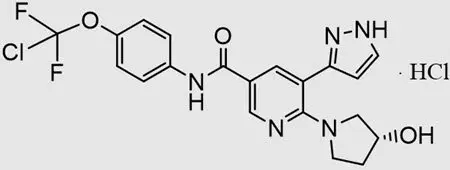
Drug Detail:Scemblix (Asciminib)
Drug Class: BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SCEMBLIX® (asciminib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Indications and Usage for Scemblix
SCEMBLIX is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase (CP), previously treated with two or more tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). (1)
- Ph+ CML in CP with the T315I mutation. (1)
Scemblix Dosage and Administration
- Recommended Dosage in Ph+ CML in CP: 80 mg orally once daily or 40 mg twice daily. (2.1)
- Recommended Dosage in Ph+ CML in CP with the T315I Mutation: 200 mg orally twice daily. (2.2)
- Avoid food for at least 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking SCEMBLIX. (2.5)
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not break, crush, or chew the tablets. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Film-coated tablets: 20 mg and 40 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Myelosuppression: Severe thrombocytopenia and neutropenia events may occur. Monitor complete blood counts regularly during therapy and manage by treatment interruption or dose reduction. (2.4, 5.1)
- Pancreatic Toxicity: Monitor serum lipase and amylase. Interrupt, then resume at reduced dose or discontinue SCEMBLIX based on severity. Evaluate for pancreatitis when lipase elevation is accompanied by abdominal symptoms. (2.4, 5.2)
- Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure and manage hypertension as clinically indicated. Interrupt, dose reduce, or stop SCEMBLIX if hypertension is not medically controlled. (2.4, 5.3)
- Hypersensitivity: May cause hypersensitivity reactions. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms and initiate appropriate treatment as clinically indicated. (5.4)
- Cardiovascular Toxicity: Cardiovascular toxicity may occur. Monitor patients with history of cardiovascular risk factors for cardiovascular signs and symptoms. Initiate appropriate treatment as clinically indicated. (5.5)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) are upper respiratory tract infections, musculoskeletal pain, headache, fatigue, nausea, rash, and diarrhea. (6.1)
Most common laboratory abnormalities (≥ 20%) are platelet count decreased, triglycerides increased, neutrophil count decreased, hemoglobin decreased, creatine kinase increased, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased, lipase increased, amylase increased, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased, uric acid increased, and lymphocyte count decreased. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Closely monitor for adverse reactions during concomitant use of SCEMBLIX at 200 mg twice daily. (7.1)
- Itraconazole Oral Solution Containing Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: Avoid concomitant use of SCEMBLIX at all recommended doses. (7.1)
- Certain Substrates of CYP3A4: Closely monitor for adverse reactions during concomitant use of SCEMBLIX at 80 mg total daily dose. Avoid use of SCEMBLIX at 200 mg twice daily. (7.2)
-
Substrates of CYP2C9: Avoid concomitant use of SCEMBLIX at all recommended doses.
- 80 mg total daily dose: If unavoidable, reduce the CYP2C9 substrate dosage as necessary. (7.2)
- 200 mg twice daily: If unavoidable, consider alternative therapy with non-CYP2C9 substrate. (7.2)
- Certain P-gp Substrates: Closely monitor for adverse reactions during concomitant use of SCEMBLIX at all recommended doses. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Scemblix
SCEMBLIX is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase (CP), previously treated with two or more tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
- Ph+ CML in CP with the T315I mutation.
2. Scemblix Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP, Previously Treated with Two or More TKIs
The recommended dose of SCEMBLIX is 80 mg taken orally once daily at approximately the same time each day or 40 mg twice daily at approximately 12-hour intervals. The recommended dose of SCEMBLIX is taken orally without food. Avoid food consumption for at least 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking SCEMBLIX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Continue treatment with SCEMBLIX as long as clinical benefit is observed or until unacceptable toxicity occurs.
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation
The recommended dose of SCEMBLIX is 200 mg taken orally twice daily at approximately 12-hour intervals. The recommended dose of SCEMBLIX is taken orally without food. Avoid food consumption for at least 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking SCEMBLIX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
2.3 Missed Dose
Once Daily Dosage Regimen: If a SCEMBLIX dose is missed by more than approximately 12 hours, skip the dose and take the next dose as scheduled.
Twice Daily Dosage Regimens: If a SCEMBLIX dose is missed by more than approximately 6 hours, skip the dose and take the next dose as scheduled.
2.4 Dosage Modifications
Dosage Modifications for Patients with Ph+ CML-CP, Previously Treated with Two or More TKIs
For the management of adverse reactions, reduce the SCEMBLIX dose as described in Table 1.
Dosage Modifications for Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation
For the management of adverse reactions, reduce the SCEMBLIX dose as described in Table 1.
| Dosage Reduction | Dosage for Patients with CP-CML, Previously Treated with Two or More TKIs | Dosage for Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation |
| First |
| 160 mg twice daily |
| Subsequent Reduction | Permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX in patients unable to tolerate 40 mg once daily OR 20 mg twice daily. | Permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX in patients unable to tolerate 160 mg twice daily. |
The recommended dosage modifications for the management of selected adverse reactions are shown in Table 2.
| Abbreviations: ANC, absolute neutrophil count; PLT, platelets; ULN, upper limit of normal. 1Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.03. |
|
| Adverse Reaction | Dosage Modification |
| Thrombocytopenia and/or neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| ANC less than 1.0 x 109/L and/or PLT less than 50 x 109/L |
Withhold SCEMBLIX until resolved to ANC greater than or equal to 1 x 109/L and/or PLT greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L.
If resolved:
|
| Asymptomatic amylase and/or lipase elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |
| Elevation greater than 2.0 x ULN |
Withhold SCEMBLIX until resolved to less than 1.5 x ULN. If resolved:
|
| Non-hematologic adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4, 5.5)] | |
| Grade 31 or higher |
Withhold SCEMBLIX until recovery to Grade 1 or less. If resolved:
|
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- 20 mg film-coated tablets: pale yellow, unscored, round, biconvex, with beveled edges, film-coated tablet debossed with “20” on one side and the “Novartis” logo on the other side.
- 40 mg film-coated tablets: violet white, unscored, round, biconvex, with beveled edges, film-coated tablet debossed with “40” on one side and the “Novartis” logo on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myelosuppression
Thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia have occurred in patients receiving SCEMBLIX. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 98 of 356 (28%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia reported in 24 (7%) and 42 (12%) of patients, respectively. Among the patients with Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia, median time to first occurrence of events was 6 weeks (range, 0.1 to 64 weeks). Of the 98 patients with thrombocytopenia, 7 (2%) patients permanently discontinued SCEMBLIX, while SCEMBLIX was temporarily withheld in 45 (13%) patients due to the adverse reaction.
Neutropenia occurred in 69 (19%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 and 4 neutropenia reported in 26 (7%) and 30 (8%) patients, respectively. Among the patients with Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, median time to first occurrence of events was 6 weeks (range, 0.1 to 180 weeks). Of the 69 patients with neutropenia, 4 (1.1%) patients permanently discontinued SCEMBLIX, while SCEMBLIX was temporarily withheld in 34 (10%) patients due to the adverse reaction.
Anemia occurred in 46 (13%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 anemia occurring in 19 (5%) patients. Among the patients with Grade 3 or 4 anemia, median time to first occurrence of events was 30 weeks (range, 0.4 to 207 weeks). Of the 46 patients with anemia, SCEMBLIX was temporarily withheld in 2 (0.6%) patients due to the adverse reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Perform complete blood counts every two weeks for the first 3 months of treatment and monthly thereafter or as clinically indicated. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of myelosuppression.
Based on the severity of thrombocytopenia and/or neutropenia, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Pancreatic Toxicity
Pancreatitis occurred in 9 of 356 (2.5%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 pancreatitis occurring in 4 (1.1%) patients. All cases of pancreatitis occurred in the Phase I study (X2101). Of the 9 patients with pancreatitis, two (0.6%) patients permanently discontinued SCEMBLIX, while SCEMBLIX was temporarily withheld in 4 (1.1%) patients due to the adverse reaction. Asymptomatic elevation of serum lipase and amylase occurred in 76 of 356 (21%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 and Grade 4 pancreatic enzyme elevations occurring in 36 (10%) and 8 (2.2%) patients, respectively. Of the 76 patients with pancreatic enzymes elevated, SCEMBLIX was permanently discontinued in 8 (2.2%) patients due to the adverse reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Assess serum lipase and amylase levels monthly during treatment with SCEMBLIX, or as clinically indicated. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pancreatic toxicity. Perform more frequent monitoring in patients with a history of pancreatitis. If lipase and amylase elevation are accompanied by abdominal symptoms, temporarily withhold SCEMBLIX and consider appropriate diagnostic tests to exclude pancreatitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Based on the severity of lipase and amylase elevation, reduce dose, temporarily withhold, or permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Hypertension
Hypertension occurred in 68 of 356 (19%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 or 4 hypertension reported in 32 (9%) and 1 (0.3%) patients, respectively. Among the patients with Grade 3 or 4 hypertension, median time to first occurrence was 14 weeks (range, 0.1 to 156 weeks). Of the 68 patients with hypertension, SCEMBLIX was temporarily withheld in 3 (0.8%) patients due to the adverse reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor and manage hypertension using standard antihypertensive therapy during treatment with SCEMBLIX as clinically indicated; for Grade 3 or higher hypertension, temporarily withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX depending on persistence of hypertension [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity occurred in 115 of 356 (32%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 or 4 hypersensitivity reported in 6 (1.7%) patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Reactions included rash, edema, and bronchospasm. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity and initiate appropriate treatment as clinically indicated; for Grade 3 or higher hypersensitivity, temporarily withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX depending on persistence of hypersensitivity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.5 Cardiovascular Toxicity
Cardiovascular toxicity (including ischemic cardiac and CNS conditions, arterial thrombotic and embolic conditions) and cardiac failure occurred in 46 (13%) and in 9 (2.5%) of 356 patients receiving SCEMBLIX, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Grade 3 cardiovascular toxicity was reported in 12 (3.4%) patients, while Grade 3 cardiac failure was observed in 5 (1.4%) patients. Grade 4 cardiovascular toxicity occurred in 2 (0.6%) patients, with fatalities occurring in 3 (0.8%) patients. Permanent discontinuation of SCEMBLIX occurred in 3 (0.8%) patients due to cardiovascular toxicity and in 1 (0.3%) patient due to cardiac failure, respectively. Cardiovascular toxicity occurred in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions or risk factors, and/or prior exposure to multiple TKIs.
Arrhythmia, including QTc prolongation, occurred in 24 of 356 (7%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 arrhythmia reported in 8 (2%) patients. QTc prolongation occurred in 3 of 356 (0.8%) patients receiving SCEMBLIX, with Grade 3 QTc prolongation reported in 1 (0.3%) patient [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients with history of cardiovascular risk factors for cardiovascular signs and symptoms. Initiate appropriate treatment as clinically indicated; for Grade 3 or higher cardiovascular toxicity, temporarily withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue SCEMBLIX depending on persistence of cardiovascular toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, SCEMBLIX can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of asciminib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal mortality and malformations at maternal exposures (AUC) equivalent to or less than those in patients at the recommended doses. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus if SCEMBLIX is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking SCEMBLIX. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with SCEMBLIX. Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment with SCEMBLIX and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions can occur with SCEMBLIX and are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Pancreatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cardiovascular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to SCEMBLIX at 10 mg to 200 mg orally twice daily (between 0.25 to 5 times the recommended dosage for the 80 mg daily dosage and between 0.05 times and up to the recommended dosage for the 200 mg twice daily dosage) in 356 patients enrolled in one of two clinical trials, including patients with Ph+ CML in CP receiving SCEMBLIX as monotherapy: study CABL001A2301 (ASCEMBL) and study CABL001X2101 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Among the 356 patients receiving SCEMBLIX, the median duration of exposure to SCEMBLIX was 116 weeks (range, 0.1 to 342 weeks).
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP, Previously Treated with Two or More TKIs
The clinical trial randomized and treated 232 patients with Ph+ CML-CP, previously treated with two or more TKIs to receive SCEMBLIX 40 mg twice daily or bosutinib 500 mg once daily (ASCEMBL) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The safety population (received at least 1 dose of SCEMBLIX) included 156 patients with Ph+ CML-CP, previously treated with two or more TKIs. Among patients who received SCEMBLIX, 83% were exposed for 24 weeks or longer and 56% were exposed for 96 weeks or longer.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients who received SCEMBLIX. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 1% included cardiac failure congestive (1.9%), pyrexia (1.9%), urinary tract infection (1.9%), headache (1.3%), and thrombocytopenia (1.3%). Two patients (1.3%) had a fatal adverse reaction, one each for mesenteric artery thrombosis and ischemic stroke.
Permanent discontinuation of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of SCEMBLIX in > 2% of patients included thrombocytopenia (3.2%) and neutropenia (2.6%).
Dosage interruptions of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 41% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included thrombocytopenia (19%) and neutropenia (18%).
Dose reductions of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 6% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 1% of patients included thrombocytopenia (4.5%) and neutropenia (1.3%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions in patients who received SCEMBLIX were upper respiratory tract infections, musculoskeletal pain, headache, and fatigue.
The most common select laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline in ≥ 20% of patients who received SCEMBLIX were platelet count decreased, triglycerides increased, neutrophil count decreased, hemoglobin decreased, creatine kinase increased, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased, uric acid increased, and lymphocyte count decreased.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in ASCEMBL.
| Abbreviations: Ph+ CML in CP, Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase (CP); TKIs, tyrosine kinase inhibitors. aUpper respiratory tract infection includes: nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, and pharyngotonsillitis. bMusculoskeletal pain includes: pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, bone pain, spinal pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal pain, and musculoskeletal chest pain. cHeadache includes: headache and post-traumatic headache. dFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia. eRash includes: rash, rash maculopapular, dermatitis acneiform, rash pustular, eczema, dermatitis, skin exfoliation, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, rash morbilliform, drug eruption, erythema multiform, and rash erythematous. fHypertension includes: hypertension and hypertensive crisis. gDiarrhea includes: diarrhea and colitis. hAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, abdominal tenderness, and epigastric discomfort. |
||||
| SCEMBLIX N = 156 | Bosutinib N = 76 |
|||
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infectiona | 26 | 0.6 | 12 | 1.3 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal painb | 24 | 2.6 | 17 | 1.3 |
| Arthralgia | 13 | 0.6 | 3.9 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Headachec | 21 | 1.9 | 16 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||||
| Fatigued | 20 | 0.6 | 11 | 1.3 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rashe | 18 | 0.6 | 30 | 8 |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hypertensionf | 14 | 7 | 5 | 3.9 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrheag | 13 | 0 | 72 | 11 |
| Nausea | 12 | 0.6 | 46 | 0 |
| Abdominal painh | 14 | 0 | 24 | 2.6 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients treated with SCEMBLIX in ASCEMBL included: cough, dyspnea, pleural effusion, dizziness, neuropathy peripheral, edema, pyrexia, vomiting, constipation, dyslipidemia, decreased appetite, pruritus, urticaria, lower respiratory tract infection, influenza, urinary tract infection, pneumonia, hemorrhage, arrhythmia (including electrocardiogram QT prolonged), palpitations, cardiac failure congestive, vision blurred, dry eye, hypothyroidism, and febrile neutropenia.
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in ASCEMBL.
| 1The denominator used to calculate the rate for SCEMBLIX and bosutinib varied from 152 to 156 and 75 to 76, respectively, based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. CTCAE version 4.03. |
||||
| SCEMBLIX1 | Bosutinib1 | |||
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % |
| Hematologic parameters | ||||
| Platelet count decreased | 46 | 24 | 36 | 12 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 43 | 22 | 33 | 15 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 37 | 2 | 54 | 5 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 20 | 3.3 | 34 | 2.6 |
| Biochemical parameters | ||||
| Triglycerides increased | 44 | 5 | 30 | 2.6 |
| Creatine kinase increased | 30 | 2.6 | 24 | 5 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased | 26 | 0.6 | 50 | 16 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased | 21 | 1.9 | 46 | 7 |
| Uric acid increased | 21 | 6 | 18 | 2.6 |
| Phosphate decreased | 18 | 6 | 20 | 7 |
| Corrected calcium decreased | 16 | 0.6 | 22 | 0 |
| Lipase increased | 15 | 4.5 | 18 | 7 |
| Creatinine increased | 15 | 0 | 26 | 0 |
| Amylase increased | 13 | 1.3 | 13 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) increased | 13 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Bilirubin increased | 12 | 0 | 3.9 | 0 |
| Cholesterol increased | 12 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| Potassium decreased | 11 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I Mutation
The single-arm clinical trial enrolled patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I mutation [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The safety population (received at least 1 dose of SCEMBLIX) included 48 patients with Ph+ CML-CP with the T315I mutation who received 200 mg of SCEMBLIX twice daily. Among these patients, 83% were exposed for 24 weeks or longer, and 75% were exposed for 48 weeks or longer.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 23% of patients who received SCEMBLIX. Serious adverse reactions in > 1% included abdominal pain (4.2%), vomiting (4.2%), pneumonia (4.2%), musculoskeletal pain (2.1%), headache (2.1%), hemorrhage (2.1%), constipation (2.1%), arrhythmia (2.1%), and pleural effusion (2.1%).
Permanent discontinuation of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 10% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of SCEMBLIX in > 2% of patients included pancreatic enzymes increased (2.1%).
Dosage interruptions of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 31% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pancreatic enzymes increased (17%) and thrombocytopenia (8%).
Dose reductions of SCEMBLIX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 23% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 1% of patients included pancreatic enzymes increased (10%), abdominal pain (4.2%), anemia (2.1%), blood bilirubin increased (2.1%), dizziness (2.1%), fatigue (2.1%), hepatic enzymes increased (2.1%), musculoskeletal pain (2.1%), nausea (2.1%), neutropenia (2.1%), pruritus (2.1%), and thrombocytopenia (2.1%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions in patients who received SCEMBLIX were musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, nausea, rash, and diarrhea.
The most common select laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline in ≥ 20% of patients who received SCEMBLIX were alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased, lipase increased, triglycerides increased, hemoglobin decreased, neutrophil count decreased, lymphocyte count decreased, phosphate decreased, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased, amylase increased, platelet count decreased, and bilirubin increased.
Table 5 summarizes adverse reactions in study X2101.
| aMusculoskeletal pain includes: pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, non-cardiac chest pain, bone pain, arthritis, and musculoskeletal chest pain. bFatigue includes: fatigue and asthenia. cAbdominal pain includes: abdominal pain and hepatic pain. dRash includes: rash, rash maculopapular, dermatitis acneiform, eczema, rash papular, skin exfoliation, and dyshidrotic eczema. eHeadache includes: headache and migraine. fCough includes: cough and productive cough. gHemorrhage includes: epistaxis, ear hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, post procedural hemorrhage, skin hemorrhage, and vaginal hemorrhage. hHypertension includes: hypertension and hypertensive crisis. iUpper respiratory tract infection includes: upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, rhinitis, and pharyngitis. |
||
| SCEMBLIX 200 mg twice daily N = 48 |
||
| Adverse Reaction | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal paina | 42 | 4.2 |
| Arthralgia | 17 | 0 |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||
| Fatigueb | 31 | 2.1 |
| Edema | 10 | 4.2 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 27 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 21 | 2.1 |
| Vomiting | 19 | 6 |
| Abdominal painc | 17 | 8 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rashd | 27 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 13 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headachee | 19 | 2.1 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Coughf | 15 | 0 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hemorrhageg | 15 | 2.1 |
| Hypertensionh | 13 | 8 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infectioni | 13 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients treated with SCEMBLIX in X2101 included: constipation, pancreatitis, pyrexia, dizziness, neuropathy peripheral, pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, dyspnea, pleural effusion, dry eye, vision blurred, arrhythmia, palpitations, cardiac failure congestive, decreased appetite, dyslipidemia, hypersensitivity, and urticaria.
Table 6 summarizes laboratory abnormalities in X2101.
| 1The denominator used to calculate the rate was 48 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. CTCAE version 4.03. |
||
| SCEMBLIX1
200 mg twice daily |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality | All Grades % | Grade 3-4 % |
| Hematologic parameters | ||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 44 | 4.2 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 44 | 15 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 42 | 4.2 |
| Platelet count decreased | 25 | 15 |
| Biochemical parameters | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased | 48 | 6 |
| Potassium increased | 48 | 2.1 |
| Triglycerides increased | 46 | 2.1 |
| Lipase increased | 46 | 21 |
| Phosphate decreased | 40 | 6 |
| Uric acid increased | 40 | 4.2 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased | 35 | 2.1 |
| Calcium corrected decreased | 33 | 0 |
| Creatinine increased | 31 | 0 |
| Amylase increased | 29 | 10 |
| Bilirubin increased | 23 | 0 |
| Cholesterol increased | 15 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) increased | 13 | 0 |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on SCEMBLIX
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Asciminib is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use of SCEMBLIX with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor increases both the asciminib Cmax and AUC, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Closely monitor for adverse reactions in patients treated with SCEMBLIX at 200 mg twice daily with concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Itraconazole Oral Solution Containing Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
Concomitant use of SCEMBLIX with itraconazole oral solution containing hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin decreases asciminib Cmax and AUC, which may reduce SCEMBLIX efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of SCEMBLIX at all recommended doses with itraconazole oral solution containing hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin.
7.2 Effect of SCEMBLIX on Other Drugs
Certain CYP3A4 Substrates
Asciminib is a CYP3A4 inhibitor. Concomitant use of SCEMBLIX increases the Cmax and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Closely monitor for adverse reactions in patients treated with SCEMBLIX at 80 mg total daily dose with concomitant use of certain CYP3A4 substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. Avoid coadministration of SCEMBLIX at 200 mg twice daily with certain CYP3A4 substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
CYP2C9 Substrates
Asciminib is a CYP2C9 inhibitor. Concomitant use of SCEMBLIX increases the Cmax and AUC of CYP2C9 substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Avoid coadministration of SCEMBLIX at 80 mg total daily dose with certain CYP2C9 substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce the CYP2C9 substrate dosage as recommended in its prescribing information.
Avoid coadministration of SCEMBLIX at 200 mg twice daily with sensitive CYP2C9 substrates and certain CYP2C9 substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. If coadministration is unavoidable, consider alternative therapy with a non-CYP2C9 substrate.
Certain P-gp Substrates
Asciminib is a P-gp inhibitor. Concomitant use of SCEMBLIX increases the plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Closely monitor for adverse reactions in patients treated with SCEMBLIX at all recommended doses with concomitant use of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, SCEMBLIX can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on SCEMBLIX use in pregnant women to evaluate a drug associated risk.
Animal reproduction studies in pregnant rats and rabbits demonstrated that oral administration of asciminib during organogenesis induced structural abnormalities, embryo-fetal mortality, and alterations to growth (see Data).
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies, pregnant animals received oral doses of asciminib at 25, 150, and 600 mg/kg/day in rats and at 15, 50, and 300 mg/kg/day in rabbits during the period of organogenesis.
In rats, maternal toxicity at the asciminib dose of 600 mg/kg/day resulted in the early termination of the dose group; a complete embryo-fetal examination was not conducted for this group. Adverse embryo-fetal findings were observed at 25 and 150 mg/kg; these doses did not cause maternal toxicities. Increases in fetal weights at 25 and 150 mg/kg/day were observed, which may be related to increased ossification (i.e., increased rate of development). Malformations were evident at 150 mg/kg and included cleft palate, anasarca (edema), and cardiac abnormalities. Additional fetal findings included urinary tract and skeletal variations, observed primarily at 150 mg/kg/day. At the dose of 25 mg/kg/day, the area under the curve (AUC) exposures were equivalent to or below those achieved in patients at the 40 mg twice daily or 80 mg once daily doses, respectively. At the dose of 25 mg/kg/day, the AUC exposures were below those achieved in patients at the 200 mg twice daily dose.
In rabbits, maternal toxicities at the asciminib dose of 300 mg/kg/day resulted in the early termination of the dose group; a complete embryo-fetal examination was not conducted for this group. Adverse embryo-fetal findings were observed at 50 mg/kg; this dose did not cause maternal toxicities. Findings at the 50 mg/kg dose included increases in early resorptions and post-implantation loss, decreases in the number of live fetuses, and cardiac malformations. At the dose of 50 mg/kg/day, the AUC exposures were 4-fold those achieved in patients at the 40 mg twice daily or 80 mg once daily doses. At the dose of 50 mg/kg/day, the AUC exposures were below those achieved in patients at the 200 mg twice daily dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of asciminib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or milk production.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with SCEMBLIX and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on findings from animal studies, SCEMBLIX can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with SCEMBLIX.
Contraception
Females
Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment with SCEMBLIX and for 1 week after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings in animals, SCEMBLIX may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. The reversibility of the effect on fertility is unknown.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of SCEMBLIX in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the ASCEMBL study, 44 of the 233 (19%) patients were 65 years of age or older and 6 (2.6%) were 75 years of age or older.
In the X2101 study, 16 of the 48 (33%) patients with the T315I mutation were 65 years of age or older and 4 (8%) were 75 years of age or older.
Overall, no differences in safety or efficacy of SCEMBLIX were observed between patients 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients. There is an insufficient number of patients 75 years of age or older to assess whether there are differences in safety or efficacy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild to severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] 15 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2) and not requiring dialysis receiving SCEMBLIX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild [total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 times ULN and any AST] to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 times ULN and any AST) receiving SCEMBLIX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| SCEMBLIX
asciminib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SCEMBLIX
asciminib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |