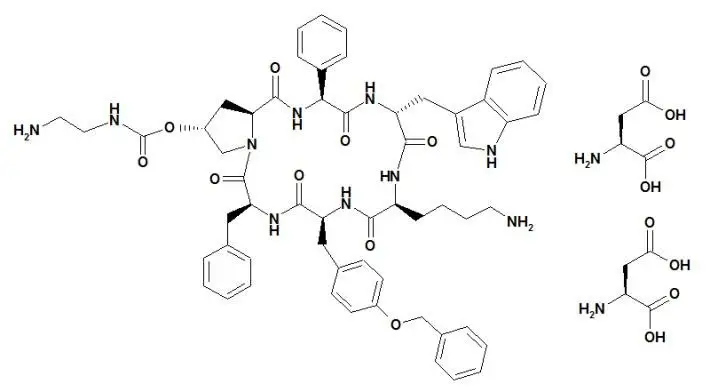
Drug Detail:Signifor (Pasireotide [ pas-i-ree-oh-tide ])
Drug Class: Somatostatin and somatostatin analogs
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SIGNIFOR ®(pasireotide) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
Recent Major Changes
|
Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) |
1/2020 |
|
Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5) |
4/2019 |
Indications and Usage for Signifor Injection
SIGNIFOR is a somatostatin analog indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Cushing's disease for whom pituitary surgery is not an option or has not been curative ( 1)
Signifor Injection Dosage and Administration
- Recommended initial dosage is either 0.6 mg or 0.9 mg by subcutaneous injection twice a day; recommended dosage range is 0.3 mg to 0.9 mg twice a day ( 2.1)
- Titrate dosage based on treatment response [clinically meaningful reduction in 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) and/or improvements in signs and symptoms of disease] and tolerability ( 2.1)
- Testing Prior to Dosing: fasting plasma glucose (FPG), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), liver tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), gallbladder ultrasound, and serum potassium and magnesium levels ( 2.2)
-
Patients With Hepatic Impairment:
- Child-Pugh B:Recommended initial dosage is 0.3 mg twice a day and maximum dosage is 0.6 mg twice a day ( 2.3, 8.6)
- Child-Pugh C: Avoid use in these patients ( 2.3, 8.6)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 0.3 mg/mL, 0.6 mg/mL, and 0.9 mg/mL in a single-dose ampule ( 3)
Contraindications
None ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypocortisolism: Decreases in circulating levels of cortisol may occur resulting in biochemical and/or clinical hypocortisolism. SIGNIFOR dose reduction or interruption and/or adding a low-dose short-term glucocorticoid may be necessary ( 5.1)
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes (occurs with initiation): Intensive glucose monitoring is recommended and may require initiation or adjustment of anti-diabetic treatment per standard of care ( 5.2)
- Bradycardia and QT Prolongation: Use with caution in at-risk patients; ECG testing prior to dosing and on treatment ( 5.3, 7.1)
- Liver Test Elevations: Evaluate liver tests prior to and during treatment ( 5.4)
- Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis: Monitor periodically. Discontinue if complications of cholelithiasis are suspected ( 5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 20% of patients are diarrhea, nausea, hyperglycemia, cholelithiasis, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, and diabetes mellitus ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Recordati Rare Diseases at 1-888-575-8344 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that Prolong QT: Use with caution in patients who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation ( 5.3, 7.1)
- Cyclosporine: Consider additional monitoring ( 7.2)
- Bromocriptine: Consider bromocriptine dose reduction ( 7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy ( 8.3)
- Safety and effectiveness of SIGNIFOR in children under 18 years have not been established ( 8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2020
Full Prescribing Information
2. Signifor Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage Range
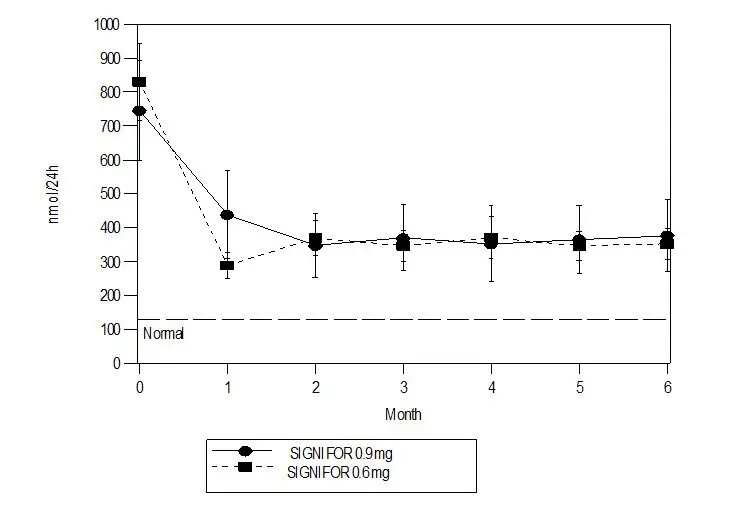
The recommended dosage range of SIGNIFOR is 0.3 mg to 0.9 mg by subcutaneous injection twice a day. The recommended initial dose is either 0.6 mg or 0.9 mg twice a day. Titrate dose based on response and tolerability.
Patients should be evaluated for a treatment response [clinically meaningful reduction in 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) levels and/or improvement in signs or symptoms of the disease] and should continue receiving therapy with SIGNIFOR as long as benefit is derived [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Maximum UFC reduction is typically seen by two months of treatment [see Clinical Studies (14)]. For patients who are started on 0.6 mg twice a day, a dosage increase to 0.9 mg twice a day may be considered based on the response to the treatment, as long as the 0.6 mg dosage is well tolerated by the patient.
Management of suspected adverse reactions may require temporary dose reduction of SIGNIFOR. Dose reduction by 0.3 mg decrements per injection is suggested.
2.2 Recommendations Prior to Initiation of SIGNIFOR
Prior to the start of SIGNIFOR, patients should have baseline levels of the following:
- fasting plasma glucose (FPG) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- liver tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- serum potassium and magnesium levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Patients should also have a baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) and gallbladder ultrasound [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)].
Treatment of patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus should be intensively optimized with anti-diabetic therapy prior to starting SIGNIFOR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.3 Dosage in Patients With Hepatic Impairment
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B), the recommended initial dosage is 0.3 mg twice a day and the maximum dosage is 0.6 mg twice a day. Avoid the use of SIGNIFOR in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 0.3 mg/mL, 0.6 mg/mL, and 0.9 mg/mL in a single-dose, 1 mL colorless glass ampule.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypocortisolism
Treatment with SIGNIFOR leads to suppression of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion in Cushing's disease. Suppression of ACTH may lead to a decrease in circulating levels of cortisol and potentially hypocortisolism.
Monitor and instruct patients on the signs and symptoms associated with hypocortisolism (e.g., weakness, fatigue, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, hyponatremia, or hypoglycemia). If hypocortisolism occurs, consider temporary dose reduction or interruption of treatment with SIGNIFOR, as well as temporary, exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy.
5.2 Hyperglycemia and Diabetes
Blood glucose elevations have been seen in healthy volunteers and patients treated with SIGNIFOR. In the clinical study [see Clinical Studies (14)], patients developed pre-diabetes and diabetes. Nearly all patients in the study, including those with normal glucose status at baseline, pre-diabetes, and diabetes, developed worsening glycemia in the first two weeks of treatment. Cushing's disease patients with poor glycemic control (HbA1c > 8%) may be at a higher risk of developing severe hyperglycemia and associated complications, e.g., ketoacidosis.
Assess the patient's glycemic status prior to starting treatment with SIGNIFOR. In patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, optimize anti-diabetic therapy prior to SIGNIFOR initiation. Glycemic monitoring should be done every week for the first two to three months and periodically thereafter, as well as over the first two to four weeks after any dose increase. If hyperglycemia develops, initiate or adjust anti-diabetic treatment per standard of care. If uncontrolled hyperglycemia persists despite appropriate treatment, reduce the dose or discontinue SIGNIFOR and perform glycemic monitoring according to clinical practice. Patients who were initiated on anti-diabetic treatment as a result of SIGNIFOR require closer monitoring after discontinuation of SIGNIFOR, especially if the anti-diabetic therapy has a risk of causing hypoglycemia.
5.3 Bradycardia and QT Prolongation
Bradycardia
Bradycardia has been reported with the use of SIGNIFOR [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Patients with cardiac disease and/or risk factors for bradycardia, such as history of clinically significant bradycardia, high-grade heart block, or concomitant use of drugs associated with bradycardia, should be carefully monitored. Dose adjustments of beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or correction of electrolyte disturbances may be necessary.
QT Prolongation
SIGNIFOR is associated with QT prolongation. In two thorough QT studies with SIGNIFOR, QT prolongation occurred at therapeutic and supra-therapeutic doses. SIGNIFOR should be used with caution in patients who are at significant risk of developing prolongation of QTc, such as those:
- with congenital long QT prolongation.
- with uncontrolled or significant cardiac disease, including recent myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, unstable angina, or clinically significant bradycardia.
- on anti-arrhythmic therapy or other substances that are known to lead to QT prolongation.
- with hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia.
A baseline ECG is recommended prior to initiating therapy with SIGNIFOR and monitoring for an effect on the QTc interval is advisable. Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia must be corrected prior to SIGNIFOR administration and should be monitored periodically during therapy.
5.4 Liver Test Elevations
In the Phase III trial, 5% of patients had an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). In the entire clinical development program of SIGNIFOR, there were 4 cases of concurrent elevations in ALT greater than 3 x ULN and bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN: one patient with Cushing's disease and 3 healthy volunteers [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In these cases, total bilirubin elevations were seen either concomitantly or preceding the transaminase elevation.
Monitoring of liver tests should be done after 1- to 2 weeks on treatment, then monthly for 3 months, and every 6 months thereafter. If ALT is normal at baseline and elevations of ALT of 3-5 times the ULN are observed on treatment, repeat the test within a week or within 48 hours if exceeding 5 times ULN. If ALT is abnormal at baseline and elevations of ALT of 3 to 5 times the baseline values are observed on treatment, repeat the test within a week or sooner if exceeding 5 times ULN. Tests should be done in a laboratory that can provide same-day results. If the values are confirmed or rising, interrupt SIGNIFOR treatment and investigate for probable cause of the findings, which may or may not be SIGNIFOR-related. Serial measures of ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin, should be done weekly, or more frequently, if any value exceeds 5 times the baseline value in case of abnormal baselines, or 5 times the ULN in case of normal baselines. If resolution of abnormalities to normal or near normal occurs, resuming treatment with SIGNIFOR may be done cautiously, with close observation, and only if some other likely cause has been found.
5.5 Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis has been frequently reported in clinical studies with SIGNIFOR [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. There have been postmarketing reports of cholelithiasis (gallstones) resulting in complications, including cholecystitis or cholangitis and requiring cholecystectomy in patients taking SIGNIFOR. Ultrasonic examination of the gallbladder before, and periodically during SIGNIFOR therapy is recommended. If complications of cholelithiasis are suspected, discontinue SIGNIFOR and treat appropriately.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Clinically significant adverse reactions that appear in other sections of the labeling include:
- Hypocortisolism
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Bradycardia and QT prolongation
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Liver Test Elevations
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Pituitary Hormone Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on SIGNIFOR
Drugs That Prolong QT
Coadministration of drugs that prolong the QT interval with SIGNIFOR may have additive effects on the prolongation of the QT interval. Caution is required when coadministering SIGNIFOR with drugs that may prolong the QT interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.2 Effects of SIGNIFOR on Other Drugs
Cyclosporine
Concomitant administration of cyclosporine with pasireotide may decrease the relative bioavailability of cyclosporine and, therefore, dose adjustment of cyclosporine to maintain therapeutic levels may be necessary.
Bromocriptine
Coadministration of somatostatin analogues with bromocriptine may increase the blood levels of bromocriptine. Dose reduction of bromocriptine may be necessary.
Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of SIGNIFOR in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Studies show that pasireotide administered subcutaneously passes into the milk of lactating rats; however, due to species-specific differences in lactation physiology, animal data may not reliably predict drug levels in human milk (see Data). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for SIGNIFOR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from SIGNIFOR or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Available data in animals have shown excretion of pasireotide in milk. After a single 1 mg/kg [ 14C]-pasireotide subcutaneous dose to lactating rats, the transfer of radioactivity into milk was observed. The overall milk:plasma (M/P) exposure ratio of total radioactivity was 0.28, based on AUC 0-∞values.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as the therapeutic benefits of a reduction or normalization of serum cortisol levels in female patients with Cushing's disease treated with pasireotide may lead to improved fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of SIGNIFOR have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Dose adjustment is not required in patients with mild impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh A), but is required for patients with moderately impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid the use of SIGNIFOR in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C).
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
A life-time carcinogenicity study was conducted in rats and transgenic mice. Rats were given daily subcutaneous doses of pasireotide at 0.01, 0.05, 0.3 mg/kg/day for 104 weeks. There were no drug-related tumors in rats at exposures up to 7-fold higher than the maximum recommended clinical exposure at the 1.8 mg/day dose. Mice were given subcutaneous doses of pasireotide at 0.5, 1.0, 2.5 mg/kg/day for 26 weeks and did not identify any carcinogenic potential.
Mutagenesis
Pasireotide was not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro assays (Ames mutation test in Salmonellaand Escherichia coliand mutation test in human peripheral lymphocytes). Pasireotide was not genotoxic in an in vivorat bone marrow nucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Subcutaneous dosing at 0.1 mg/kg/day before mating and continuing into gestation in rats at exposures less than the human clinical exposure based on body surface area comparisons across species resulted in statistically significant increased implantation loss and decreased viable fetuses, corpora lutea, and implantation sites. Abnormal cycles or acyclicity were observed at 1 mg/kg/day (5-fold higher than the maximum therapeutic exposure based on surface area, comparisons across species).
How is Signifor Injection supplied
SIGNIFOR is supplied as a single dose, colorless glass ampule packaged in a box of 60 ampules, arranged in 10 packs of 6 ampules each. The following packaging configurations are available.
0.3 mg/1 mL pasireotide (as diaspartate)
Box of 60 ampules NDC# 55292-131-60
0.6 mg/1 mL pasireotide (as diaspartate)
Box of 60 ampules NDC# 55292-132-60
0.9 mg/1 mL pasireotide (as diaspartate)
Box of 60 ampules NDC# 55292-133-60
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F), protect from light.
Patient Counseling Information
See FDA approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Counsel patients on the following possible significant adverse reactions:
- Hypocortisolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hyperglycemia and Diabetes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Bradycardia and QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Liver Test elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs or symptoms of gallstones (cholelithiasis) or complications of gallstones (e.g., cholecystitis or cholangitis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Pituitary Hormone Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Pregnancy: Inform female patients that treatment with SIGNIFOR may result in unintended pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Instruct the patientson the proper use of SIGNIFOR, including instructions to:
- Carefully review the Medication Guide.
- Do not reuse unused portions of SIGNIFOR ampules and properly dispose of the ampules after use.
- Avoid multiple injections at or near the same site within short periods of time.
For instructions on the use of SIGNIFOR glass ampules, refer to the Medication Guide that follows.

Distributed by:
Recordati Rare Diseases Inc., Lebanon, NJ 08833 U.S.A
RRD-LIAM-D2020-00
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: March 2020 |
| Medication Guide
SIGNIFOR®[sig-na-for] (pasireotide) Injection |
|
|
Read this Medication Guide before you start using SIGNIFOR and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about SIGNIFOR? SIGNIFOR can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
|
What is SIGNIFOR? SIGNIFOR is a prescription medicine used to treat Cushing's disease in adults who cannot have surgery or have failed surgery. It is not known if SIGNIFOR is safe and effective in children. |
|
|
What should I tell my doctor before using SIGNIFOR? Before you take SIGNIFOR, tell your doctor if you:
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking SIGNIFOR with certain other medicines can affect each other and cause side effects. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
Ask your doctor for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
|
How should I use SIGNIFOR?
If you take too much SIGNIFOR, tell your doctor right away. |
|
|
What are the possible side effects of SIGNIFOR? SIGNIFOR may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of SIGNIFOR include:
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of SIGNIFOR. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1–800–FDA–1088. |
|
|
How should I store SIGNIFOR?
Keep SIGNIFOR and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of SIGNIFOR. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SIGNIFOR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SIGNIFOR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about SIGNIFOR. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about SIGNIFOR that is written for health professionals. For more information go to www.SIGNIFOR.com or call 1-888-575-8344. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in SIGNIFOR? Active ingredient:Pasireotide Inactive ingredients:Mannitol, sodium hydroxide, tartaric acid, and water for injection. |
|
RRD-LIAM-D2020-00
Instructions for Use
SIGNIFOR®[sig-na-for]
(pasireotide)
Injection
Supplies you will need to give your SIGNIFOR injection:
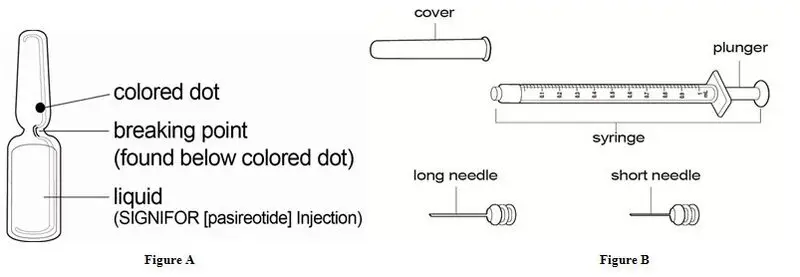
- 1 SIGNIFOR ampule (See Figure A)
- 1 sterile syringe (See Figure B)
- 1 long sterile needle (See Figure B)
- This needle is used to draw up your SIGNIFOR from the ampule. You should only use this needle if your doctor or nurse tells you to.
- 1 short sterile needle (See Figure B)
- Alcohol wipes
- 1 cotton ball or gauze
- A sharps disposal container or other closeable, puncture resistant disposal container
Getting started:
Step 1:Wash your hands well with soap and water and dry them.
Step 2:Take 1 SIGNIFOR ampule out of the box.
Step 3:Look at the SIGNIFOR ampule. Check that the ampule is not cracked or broken and that the liquid medicine in the ampule is clear and colorless.
Do notuse SIGNIFOR if the ampule is cracked or broken or if the liquid looks cloudy or contains particles. Take the whole box back to the pharmacy and get a new one.
Ampules should be opened just prior to administration and any unused portion discarded.
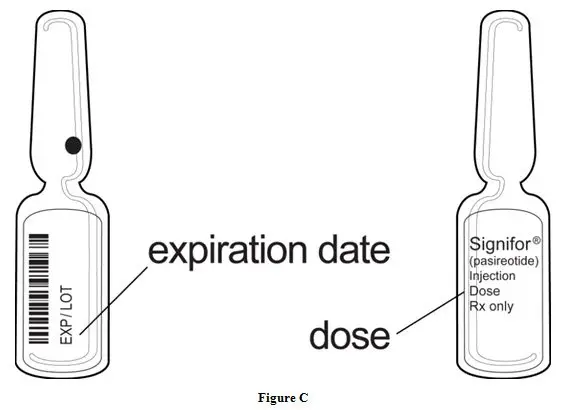
Step 4:Check the dose and expiration date printed on the ampule (See Figure C).
Preparing your SIGNIFOR dose:
| Step 5:Hold the SIGNIFOR ampule at the bottom with 1 hand. With your other hand, tap the top of the SIGNIFOR ampule with your finger to make sure there is no liquid in the top of the ampule when you open it (See Figure D). |  Figure D |
Step 6:Hold the ampule with 1 hand. With your other hand, hold the top of the ampule and
pull it sideways until the top snaps off at the line marked on the ampule neck (See Figure E).
| 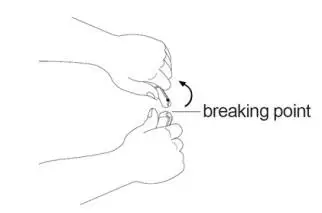 Figure E |
Step 7:Open the sterile needle package. Place the needle on the top of the syringe. Push down on the needle and twist it clockwise until it is tight (See Figure F).
|
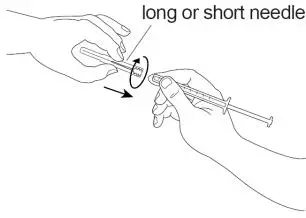 Figure F |
| Step 8:Pull the needle cover straight off the sterile needle (See Figure G). | 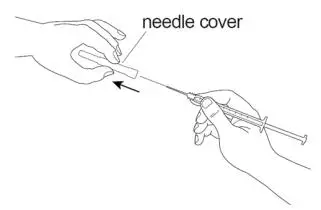 Figure G |
Step 9:Put the needle into the ampule making sure you do not touch the outside of the ampule and pull up on the plunger to draw up all of the SIGNIFOR liquid into the syringe (See Figure H).
|
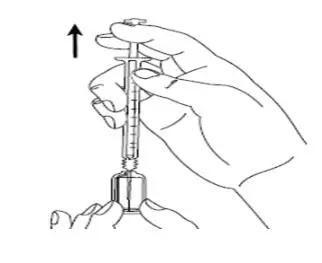 Figure H |
| Step 10:Hold the syringe upright in 1 hand between 2 fingers with your thumb at the bottom of the plunger. With your other hand, tap the syringe with your finger to get rid of air bubbles (See Figure I). |
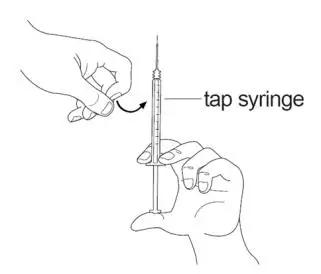 Figure I |
Step 11:Push up on the plunger until you see a drop of liquid on the tip of the needle (See Figure J).
| 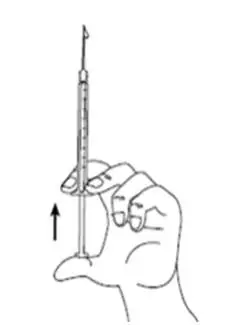 Figure J |
Injecting your SIGNIFOR dose:
| Step 12:Choose your injection site and wipe the site with an alcohol wipe (See Figure K). Let the site dry. | 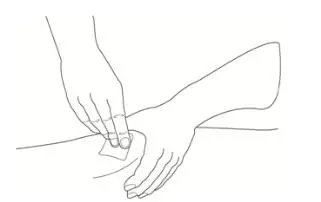 Figure K |
Step 13:With 1 hand, gently pinch the skin at the injection site you have chosen and wiped with an alcohol wipe. With your other hand, pick up the syringe and hold it like a pencil. Insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45 degree angle using a quick dart like motion (See Figure L).
|
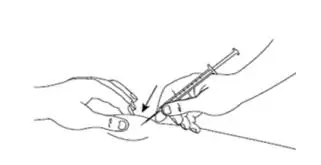 Figure L |
| Step 14:Gently press the plunger all the way down, until the syringe is empty (See Figure M). |
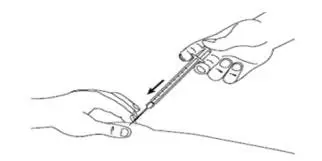 Figure M |
| Step 15:When the syringe is empty, slowly let go of the skin and gently pull the needle out of the skin (See Figure N). |
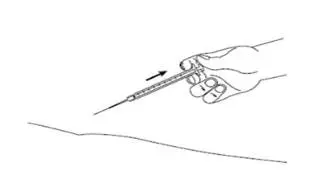 Figure N |
Step 16:Place a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site and press for about 5 seconds.
Do notmassage the injection site.
|
After injecting your SIGNIFOR dose:
- Put your used needles and syringes in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: March 2020

Distributed by:
Recordati Rare Diseases Inc., Lebanon, NJ 08833 U.S.A
RRD-LIAM-D2020-00
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label –0.3 mg/mL
Rx Only NDC 55292-131-60
Signifor®
(pasireotide) Injection
0.3 mg/mL
For subcutaneous use only
Dispense with enclosed Medication Guide.
60 ampules (10 packs of 6 ampules)
| SIGNIFOR
pasireotide injection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIGNIFOR
pasireotide injection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIGNIFOR
pasireotide injection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Recordati Rare Diseases, Inc. (181699406) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delpharm DIjon | 266919024 | manufacture(55292-131, 55292-132, 55292-133) | |