Drug Detail:Siklos (Hydroxyurea [ hye-drox-ee-yoo-ree-a ])
Drug Class: Antimetabolites
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SIKLOS (hydroxyurea) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1967
WARNING: MYELOSUPPRESSION and MALIGNANCIES
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Myelosuppression: SIKLOS may cause severe myelosuppression. Do not give if bone marrow function is markedly depressed. Monitor blood counts at baseline and throughout treatment. Interrupt treatment and reduce dose as necessary. (5.1)
- Malignancies: Hydroxyurea is carcinogenic. Advise sun protection and monitor patients for malignancies. (5.2)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 12/2021 |
| Dosage and Administration (2) | 12/2021 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Malignancies (5.2) | 12/2021 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hemolytic Anemia (5.9) | 12/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Siklos
SIKLOS is an antimetabolite, indicated to reduce the frequency of painful crises and to reduce the need for blood transfusions in adult and pediatric patients, 2 years of age and older, with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crises. (1)
Siklos Dosage and Administration
Initial dose: 15 mg/kg in adults and 20 mg/kg in children once daily. Monitor blood counts every two weeks. (2.1)
- The dose may be increased by 5 mg/kg/day every 8 weeks, or sooner if a severe painful crisis occurs, until a maximum tolerated dose or 35 mg/kg/day is reached if blood counts are in an acceptable range. (2.1)
- Discontinue SIKLOS until hematologic recovery if blood counts are considered toxic. Resume treatment after reducing the dose by 5 mg/kg/day from the dose associated with hematological toxicity. (2.1)
- Renal impairment: Reduce the dose of SIKLOS by 50% in patients with creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/min. (2.2, 8.6, 12.3)
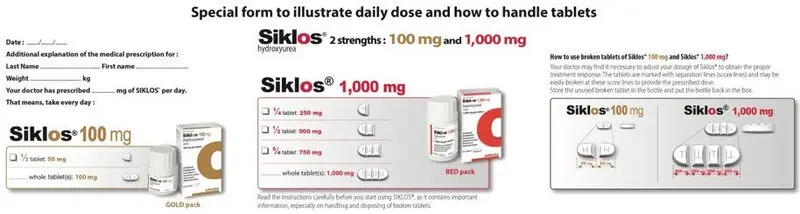
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: functionally scored 100 mg and functionally triple-scored 1,000 mg tablet (3)
Contraindications
Patients who have demonstrated a previous hypersensitivity to hydroxyurea or any other component of its formulation. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Embryo-Fetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise of potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
- Cutaneous vasculitic toxicities (incl. leg ulcers): Institute treatment and discontinue SIKLOS and/or reduce dose if this occurs. (5.4)
- Risks with concomitant use of antiretroviral drugs: Pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity, and neuropathy have occurred. Monitor for signs and symptoms patients with HIV infection using antiretroviral drugs; discontinue SIKLOS, and implement treatment. (5.5)
- Concomitant use with live virus vaccine: increased risk of severe infections. (5.6)
- Hemolytic Anemia: Monitor blood counts throughout treatment. If hemolysis persists, discontinue SIKLOS. (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions to SIKLOS (incidence > 10%) include infections and neutropenia in children and infections and headache and dry skin in adults. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the marketer Medunik at 1 844-884-5520 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise women to stop breastfeeding while taking SIKLOS. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Siklos
SIKLOS® is indicated to reduce the frequency of painful crises and to reduce the need for blood transfusions in adult and pediatric patients, 2 years of age and older, with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crises
2. Siklos Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended SIKLOS dosing is described in Table 1.
| Dosing Regimen | Dose | Dose Modification Criteria | Monitoring Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Recommended Dosing | Adults: 15 mg/kg Pediatrics: 20 mg/kg once daily based on patient's actual or ideal weight, whichever is less. | Monitor the patient's blood count every 2 weeks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. | |
| Dosing Adjustment Based on Blood Counts in an acceptable range | Increase dose 5 mg/kg/day every 8 weeks or if a painful crisis occurs. Give until mild myelosuppression (absolute neutrophil count 2,000/uL to 4,000/uL) is achieved, up to a maximum of 35 mg/kg/day. | Increase dosing only if blood counts are in an acceptable range. Increase dosing if a painful crisis occurs. Do not increase if myelosuppression occurs. | Blood Counts Acceptable Range:
- neutrophils greater than or equal to 2,000 cells/mm3 - platelets greater than or equal to 80,000/mm3 - hemoglobin greater than 5.3 g/dL - reticulocytes greater than or equal to 80,000/mm3 if the hemoglobin concentration less than 9 g/dL |
| Dosing Adjustment Based on Blood Counts in a toxic range | Discontinue treatment. | If blood counts are considered toxic, discontinue SIKLOS until hematologic recovery. | Blood Counts Toxic Range: - neutrophils less than 2,000 cells/mm3 younger patients with lower baseline counts may safely tolerate absolute neutrophil counts down to 1,250/mm3. - platelets less than 80,000/mm3 - hemoglobin less than 4.5 g/dL - reticulocytes less than 80,000/mm3 if the hemoglobin concentration less than 9 g/dL |
| Dosing After Hematologic Recovery | Reduce dose by 5 mg/kg/day. | Reduce the dose from the dose associated with hematologic toxicity. May titrate up or down every 8 weeks in 5 mg/kg/day increments. The patient should be at a stable dose with no hematologic toxicity for 24 weeks. Discontinue the treatment permanently if a patient develops hematologic toxicity twice. |
Siklos is available in 100 mg and 1,000 mg tablets. The 100 mg tablets have 1 score line and can be split into 2 parts (each 50 mg). The 1,000 mg tablets have 3 score lines and can be split into 4 parts (each 250 mg). Therefore, the two strengths can be used to deliver doses of 1,000 mg, 750 mg, 500 mg, 250 mg, 100 mg, 50 mg and combinations thereof. Calculate the rounded doses to the nearest 50 mg or 100 mg strength based on clinical judgment.
Patients must be able to follow directions regarding drug administration and their monitoring and care.
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels may be used to evaluate the efficacy of SIKLOS in clinical use. Obtain HbF levels every three to four months. Monitor for an increase in HbF of at least two-fold over the baseline value.
2.2 Dose Modifications for Renal Impairment
Reduce the dose of SIKLOS by 50% in patients with creatinine clearance of less than 60 mL/min or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Obtain the creatinine clearance using a 24-hour urine collection.
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Recommended SIKLOS Initial Dose (mg/kg daily) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Pediatrics | Adults | |
|
||
| Greater than or equal to 60 | 20 | 15 |
| Less than 60 or ESRD* | 10 | 7.5 |
Monitor the hematologic parameters closely in these patients.
4. Contraindications
SIKLOS is contraindicated in:
- -
- Patients who have demonstrated a previous hypersensitivity to hydroxyurea or any other component of its formulation [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myelosuppression
Hydroxyurea causes severe myelosuppression. Do not initiate treatment with hydroxyurea in patients if bone marrow function is markedly depressed. Bone marrow suppression may occur, and leukopenia is generally its first and most common manifestation. Thrombocytopenia and anemia occur less often, and are seldom seen without a preceding leukopenia.
Some patients, treated at the recommended initial dose of 15 mg/kg/day in adults or 20 mg/kg/day in children, have experienced severe or life-threatening myelosuppression. Due to the change in body weight requiring modification of daily dose, pediatric patients have an increased risk of myelosuppression at the time of dose adjustment.
Evaluate hematologic status prior to and every two weeks during treatment with SIKLOS. Provide supportive care and modify dose or discontinue SIKLOS as needed. Recovery from myelosuppression is usually observed within 15 days when therapy is interrupted. Resume therapy after interruption at a lower dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.2 Malignancies
Hydroxyurea is a human carcinogen. In patients receiving long-term hydroxyurea for myeloproliferative disorders (a condition for which Siklos is not approved), secondary leukemia has been reported.
Leukemia secondary to long-term hydroxyurea has also been reported in patients with sickle cell disease. Leukemia has also been reported in patients with sickle cell disease and no prior history of treatment with hydroxyurea.
Skin cancer has also been reported in patients receiving long-term hydroxyurea. Advise protection from sun exposure and monitor for the development of secondary malignancies.
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on the mechanism of action and findings in animals, SIKLOS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Hydroxyurea was embryotoxic and teratogenic in rats and rabbits at doses 0.8 times and 0.3 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after treatment with SIKLOS for at least 6 months after therapy. Advise males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after treatment with SIKLOS for at least 6 months after therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.4 Vasculitic Toxicities (Including Leg Ulcers)
Cutaneous vasculitic toxicities, including vasculitic ulcerations and gangrene, have occurred in patients with myeloproliferative disorders during therapy with hydroxyurea. These vasculitic toxicities were reported most often in patients with a history of, or currently receiving, interferon therapy. Due to potentially severe clinical outcomes for the cutaneous vasculitic ulcers reported in patients with myeloproliferative disease (a condition for which SIKLOS is not approved), treatment with SIKLOS should be discontinued and/or its dose reduced if cutaneous vasculitic ulcerations develop. Rarely, ulcers are caused by leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
Avoid use of SIKLOS in patients with wounds on the legs (leg ulcers).
5.5 Risks with Concomitant Use of Antiretroviral Drugs
Pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity, and peripheral neuropathy have occurred when hydroxyurea was administered concomitantly with antiretroviral drugs, including didanosine and stavudine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.6 Risks with Concomitant Use of Live Virus Vaccine
Avoid use of live virus vaccine in patients taking SIKLOS. Concomitant use of hydroxyurea with a live virus vaccine may potentiate the replication of the vaccine virus and/or may increase the adverse reactions of the vaccine virus and result in severe infections [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Patient's antibody response to vaccines may be decreased. Consider consultation with a specialist.
5.7 Macrocytosis
SIKLOS may cause macrocytosis, which is self-limiting, and is often seen early in the course of treatment. The morphologic change resembles pernicious anemia, but is not related to vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency. This may mask the diagnosis of pernicious anemia. Prophylactic administration of folic acid is recommended.
5.8 Test Interference
Interference with Uric Acid, Urea, or Lactic Acid Assays is possible, rendering falsely elevated results of these in patients treated with hydroxyurea [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
5.9 Hemolytic Anemia
Cases of hemolytic anemia in patients treated with hydroxyurea for myeloproliferative diseases have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients who develop acute jaundice or hematuria in the presence of persistent or worsening of anemia should have laboratory tests evaluated for hemolysis (e.g., measurement of serum lactate dehydrogenase, haptoglobin, reticulocyte, unconjugated bilirubin levels, urinalysis, and direct and indirect antiglobulin [Coombs] tests). In the setting of confirmed diagnosis of hemolytic anemia not related to the disease and in the absence of other causes, discontinue SIKLOS.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Vasculitic toxicities (including Leg Ulcers) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Risks with concomitant use of antiretroviral drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Risk with concomitant use of live virus vaccine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Macrocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hemolytic Anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of SIKLOS has been assessed in 405 pediatric patients with sickle cell disease from 2-18 years of age and 1077 adults in the European Sickle Cell Disease prospective Cohort study ESCORT-HU.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions in ESCORT-HU were infections and myelosuppression, with mild to moderate neutropenia as the most common manifestation.
Other adverse reactions include skin and subcutaneous disorders (skin depigmentation/melanonychia, skin rash, alopecia), gastrointestinal disorders, vitamin D deficiency and headache.
At least one serious adverse reaction was reported in 33% of the 405 pediatric patients and 32% of the 1077 adults with sickle cell disease in ESCORT-HU. The most frequent serious adverse reactions were infections (18%), and blood and lymphatic system disorders (9%) in children, including serious neutropenia (3.2%), thrombocytopenia (3%) and anemia (3%). Other reported serious adverse reactions were gastrointestinal disorders (3.2 %), fever (2.5 %) and nervous system disorders (4%), including headache (2.7%). Among adults, the most frequent serious adverse reactions were infections (12.9%), respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders (5.8%), blood and lymphatic disorders (4.8%), nervous system disorders (3.6%), and general disorders and administration site disorders (3.1%).
| Global Safety Set (N=405) | Total | Severity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| n: number of patients with an adverse reaction | ||||||||
| At least one adverse reaction | 261 | 64 | ||||||
| Infections | 161 | 40 | 120 | 30 | 88 | 22 | 18 | 4.4 |
| Other Infections | 92 | 23 | 66 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 3 | 0.7 |
| Bacterial | 65 | 16 | 24 | 6 | 37 | 9 | 10 | 2.5 |
| Viral | 40 | 10 | 23 | 6 | 14 | 3.5 | 3 | 0.7 |
| Parvovirus B19 | 15 | 4 | 7 | 1.7 | 5 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | 85 | 21 | 51 | 13 | 59 | 15 | 14 | 3.5 |
| Neutropenia | 51 | 13 | 26 | 6 | 31 | 8 | 4 | 1 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 30 | 7 | 16 | 4 | 15 | 3.7 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Anemia | 17 | 4.2 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 1.7 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 53 | 13 | 29 | 7 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 1 |
| Other Gastrointestinal Disorders | 30 | 7 | 13 | 3.2 | 15 | 3.7 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Constipation | 10 | 2.5 | 5 | 1.2 | 5 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea | 10 | 2.5 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Metabolic and nutrition disorders | 44 | 11 | 24 | 6 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Deficiency of vitamin D | 25 | 6 | 19 | 4.7 | 7 | 1.7 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Other Metabolic and nutrition disorders | 8 | 2 | 3 | 0.7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Weight gain | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.2 | 7 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 |
| Nervous system disorders | 45 | 11 | 19 | 4.7 | 19 | 4.7 | 8 | 2 |
| Headache | 30 | 7 | 15 | 3.7 | 7 | 1.7 | 4 | 1 |
| Other Nervous system disorders | 11 | 2.7 | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| General disorders | 41 | 10 | 22 | 5 | 17 | 4.2 | 4 | 1 |
| Fever | 31 | 8 | 20 | 4.9 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 38 | 9 | 29 | 7 | 14 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Skin reactions | 15 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 1.7 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Other Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 13 | 3.2 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Other Not SCD-related reactions | 23 | 6 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Other Not SCD-related reactions | 23 | 6 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Respiratory thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 11 | 3 | 6 | 1.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Renal and urinary disorders | 8 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Global adult safety set (N=1077) | Total | Severity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| At least one adverse reaction | 897 | 84 | 586 | 54 | 617 | 57 | 345 | 32 |
| Infections | 465 | 43 | 171 | 16 | 240 | 22 | 101 | 9 |
| Viral infection | 47 | 4.4 | 17 | 1.6 | 21 | 1.9 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Bacterial infection | 45 | 4.2 | 9 | 0.8 | 27 | 2.5 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Bronchitis | 41 | 3.8 | 10 | 0.9 | 19 | 1.8 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Influenza | 40 | 3.7 | 8 | 0.7 | 15 | 1.4 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Urinary tract infection | 40 | 3.7 | 19 | 1.8 | 11 | 1.0 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 40 | 3.7 | 21 | 1.9 | 13 | 1.2 | 1 | 0.1 |
| Nervous system disorders | 313 | 29 | 131 | 12 | 125 | 12 | 54 | 5 |
| Headache | 211 | 20 | 84 | 8 | 74 | 7 | 27 | 2.5 |
| Dizziness | 100 | 9 | 43 | 4.0 | 32 | 3.0 | 9 | 0.8 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 300 | 28 | 111 | 10 | 113 | 10 | 24 | 2.2 |
| Asthenia | 100 | 9 | 30 | 2.8 | 18 | 1.7 | 10 | 0.9 |
| Pyrexia | 91 | 8 | 27 | 2.5 | 39 | 3.6 | 4 | 0.4 |
| Fatigue | 51 | 4.7 | 22 | 2.0 | 17 | 1.6 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Edema peripheral | 33 | 3.1 | 9 | 0.8 | 13 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 297 | 28 | 160 | 15 | 123 | 11 | 23 | 2.1 |
| Dry skin | 128 | 12 | 67 | 6.2 | 36 | 3.3 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Skin ulcer | 80 | 7 | 19 | 1.8 | 44 | 4.1 | 11 | 1.0 |
| Alopecia | 49 | 4.5 | 31 | 2.9 | 13 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | 267 | 25 | 116 | 11 | 110 | 10 | 25 | 2.3 |
| Nausea | 69 | 6 | 28 | 2.6 | 26 | 2.4 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 52 | 4.8 | 15 | 1.4 | 22 | 2.0 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Diarrhea | 37 | 3.4 | 10 | 0.9 | 13 | 1.2 | ||
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 256 | 24 | 70 | 7 | 103 | 10 | 48 | 4.5 |
| Cough | 59 | 5.5 | 23 | 2.1 | 21 | 1.9 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Lung disorder | 51 | 4.7 | 4 | 0.4 | 28 | 2.6 | 16 | 1.5 |
| Dyspnea | 44 | 4.1 | 12 | 1.1 | 14 | 1.3 | 4 | 0.4 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | 250 | 23 | 74 | 7 | 121 | 11.2 | 61 | 6 |
| Anemia | 103 | 10 | 11 | 1.0 | 51 | 4.7 | 37 | 3.4 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 70 | 7 | 29 | 2.7 | 30 | 2.8 | 13 | 1.2 |
| Neutropenia | 50 | 4.6 | 24 | 2.2 | 18 | 1.7 | 7 | 0.6 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | 247 | 23 | 93 | 9 | 101 | 9 | 25 | 2.3 |
| Arthralgia | 95 | 9 | 26 | 2.4 | 31 | 2.9 | 7 | 0.6 |
| Back pain | 48 | 4.5 | 11 | 1.0 | 18 | 1.7 | 6 | 0.6 |
| Pain in extremity | 33 | 3.1 | 14 | 1.3 | 10 | 0.9 | ||
| Investigations | 198 | 18 | 40 | 3.7 | 47 | 4.4 | 10 | 0.9 |
| Weight increased | 43 | 4.0 | 15 | 1.4 | 22 | 2.0 | 4 | 0.4 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of SIKLOS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: macrocytosis, hemolytic anemia in patients who are treated with hydroxyurea for myeloproliferative disorders.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting, gastrointestinal ulcer, severe hypomagnesemia
- Hepatobiliary disorders: elevation of hepatic enzymes
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: skin reactions (oral, ungula and cutaneous pigmentation), oral mucositis, rash, melanonychia,
- Reproductive system and breast disorders: oligospermia, azoospermia, amenorrhea
7. Drug Interactions
7.2 Concomitant Use of Live Virus Vaccine
Concomitant use of SIKLOS with a live virus vaccine may potentiate the replication of the vaccine virus and/or may increase the adverse reactions of the vaccine virus, because normal defense mechanisms may be suppressed by SIKLOS therapy. Vaccination with a live vaccine in a patient taking SIKLOS may result in severe infections. Generally, the patient's antibody response to vaccines may be decreased. Treatment with SIKLOS and concomitant immunization with live virus vaccines should only be performed if benefits clearly outweigh potential risks. Consider consultation with a specialist.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SIKLOS have been established in pediatric patients aged 2-18 years with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crises. Use of SIKLOS in these age groups is supported by evidence from a non-interventional cohort study, the European Sickle Cell Disease prospective Cohort study, ESCORT-HU, in which 405 pediatric patients ages 2 to <18 were enrolled. Among the 405 pediatric patients treated with SIKLOS, 274 were children (2-11) and 108 were adolescents (12-16) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Continuous follow-up of the growth of treated children is recommended.
Pediatric patients aged 2-16 years had a higher risk of neutropenia than patients more than 16 years old.
The safety and effectiveness of SIKLOS have not been established in pediatric patients less than 2 years of age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The exposure to SIKLOS is higher in patients with creatinine clearance of less than 60 mL/min. Reduce dosage and closely monitor the hematologic parameters when SIKLOS is to be administered to these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Acute mucocutaneous toxicity has been reported in patients receiving hydroxyurea at doses several times above the therapeutic dose. Soreness, violet erythema, oedema on palms and soles followed by scaling of hand and feet, severe generalized hyperpigmentation of the skin and stomatitis have been observed. In patients with sickle cell anemia, neutropenia was reported in isolated cases of hydroxyurea overdose (1.43 times and 8.57 times of the maximum recommended dose of 35 mg/kg b.w./day). Monitor blood counts weekly until recovery. Treatment of overdose consists of gastric lavage, followed by symptomatic treatment and control of bone marrow function.
11. Siklos Description
SIKLOS (hydroxyurea) is an antimetabolite that is available for oral use as functionally scored 100 mg film-coated tablet and functionally triple-scored 1,000 mg film-coated tablet containing 100 and 1,000 mg of hydroxyurea, respectively. Inactive ingredients include silicified microcrystalline cellulose, sodium stearyl fumarate, and film-coating agent amino methacrylate copolymer.
Hydroxyurea is a white crystalline powder. It has a molecular weight of 76.05. Its structural formula is:
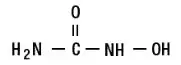
12. Siklos - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism by which hydroxyurea produces its cytotoxic and cytoreductive effects is not known. However, various studies support the hypothesis that hydroxyurea causes an immediate inhibition of DNA synthesis by acting as a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor, without interfering with the synthesis of ribonucleic acid or of protein.
The mechanisms by which SIKLOS produces its beneficial effects in patients with sickle cell Anemia (SCA) are uncertain. Known pharmacologic effects of SIKLOS that may contribute to its beneficial effects include increasing hemoglobin F levels in red blood cells (RBCs), decreasing neutrophils, increasing the water content of RBCs, increasing deformability of sickled cells, and altering the adhesion of RBCs to endothelium.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The correlation between hydroxyurea concentrations, reduction of crisis rate, and increase in HbF, is not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mean peak plasma concentrations and AUCs increase more than proportionally with increase of dose. There is no drug accumulation upon once daily dosing of hydroxyurea.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Conventional long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of hydroxyurea have not been performed. However, hydroxyurea is presumed to be a transspecies carcinogen. Intraperitoneal administration of 125 to 250 mg/kg hydroxyurea (about 0.6-1.2 times the maximum recommended human oral daily dose on a mg/m2 basis) thrice weekly for 6 months to female rats increased the incidence of mammary tumors in rats surviving to 18 months compared to control. Hydroxyurea is mutagenic in vitro to bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and mammalian cells. Hydroxyurea is clastogenic in vitro (hamster cells, human lymphoblasts) and in vivo (SCE assay in rodents, mouse micronucleus assay). Hydroxyurea causes the transformation of rodent embryo cells to a tumorigenic phenotype [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
Hydroxyurea administered to male rats at 60 mg/kg /day (about 0.3 times the maximum recommended human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis) produced testicular atrophy, decreased spermatogenesis and significantly reduced their ability to impregnate females [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
14. Clinical Studies
Adult Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
In ESCORT-HU 1077 adult patients were included of which 436 patients were naïve to HU treatment. There were 370 evaluable patients who had at least 12 months follow-up (Median [range] 41 months [29, 54].
Median (range) hemoglobin F percentages were 5.2% (0.2, 30.9) at baseline and 14.2% (0.5, 41.5) at least 6 months (the value closest to 6 months collected between 5 and 14 months) after initiation of SIKLOS treatment, with a median (range) change of 8% (-8.0, 33.3) in 181 patients. Among adult patients previously not treated with hydroxyurea prior to enrollment and analyzable for efficacy (N=370), the incidence and number of vaso-occlusive events, hospitalizations, acute chest syndrome and blood transfusions in the 12 month period before treatment and after initiation of treatment decreased after 12 months of SIKLOS treatment. Table 5 provides the efficacy results for ESCORT-HU.
| SCD events | Adult Patients previously not treated with hydroxyurea with at least 12 months follow-up data available for clinical efficacy (N=369) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| In the 12 months prior to enrolment | After 12 months of Siklos® treatment | Change | |
| Number of patients with at least one vaso-occlusive episode (in 367 evaluable patients) | |||
| No | 133 (36.2%) | 226 (61.6%) | |
| Yes | 234 (63.8%) | 141 (38.4%) | |
| Number of vasoocclusive episodes over 12 months (in 343 evaluable patients) | |||
| Median (range) | 1.0 (0.0, 20.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 30.0) | 0.0 (-20.0, 24.0) |
| Number of patients with at least one episode of acute chest syndrome (in 365 evaluable patients) | |||
| No | 273 (74.8%) | 338 (92.6%) | |
| Yes | 92 (25.2%) | 27 (7.4%) | |
| Number of episodes of acute chest syndrome over 12 months (in 364 evaluable patients) | |||
| Median (range) | 1.0 (0.0, 5.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 3.0) | 0.0 (-5.0 ; 2.0) |
| Number of patients with at least one hospitalization related to SCD (in 366 evaluable patients) | |||
| No | 152 (41.5%) | 252 (68.9%) | |
| Yes | 214 (58.5%) | 114 (31.1%) | |
| Number of hospitalizations related to SCD over 12 months (in 360 evaluable patients) | |||
| Median (range) | 1 (0.0, 15.0) | 0 (0.0, 10.0) | 0 (-15.0, 8.0) |
| Number of days of hospitalizations related to SCD over 12 months (in 313 evaluable patients) | |||
| Median (range) | 2 (0.0, 90.0) | 0 (0.0, 77.0) | 0 (-90.0, 57.0) |
| Number of patients with at least one blood transfusion (in 365 evaluable patients) | |||
| No | 207 (56.7%) | 296 (81.1%) | |
| Yes | 158 (43.3%) | 69 (18.9%) | |
16. How is Siklos supplied
16.1 How Supplied
SIKLOS (hydroxyurea) film-coated tablet is supplied in high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with polypropylene child-resistant cap with a desiccant unit containing 30 (SIKLOS 1,000 mg) or 60 (SIKLOS 100 mg) film coated tablets. Each bottle containing SIKLOS 100 mg tablets or SIKLOS 1000 mg tablets is supplied in a carton.
SIKLOS is supplied in the following strengths:
- -
- 100 mg off-white, capsule-shaped, film-coated, functionally scored tablet with scoring on both sides which can be divided into two equal parts, each part is debossed with "H" on one side.
- -
- 1,000 mg off-white, capsule-shaped, film-coated, functionally triple-scored tablet with scoring on both sides which can be divided into four equal parts, each part is debossed with "T" on one side.
| Bottles of 30 | Bottles of 60 | |
|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | N/A | NDC 71770-105-60 |
| 1,000 mg | NDC 71770-120-30 | N/A |
16.2 Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep tightly closed.
Broken tablets must be stored in the bottle and must be used within three months.
16.3 Handling and Disposal
SIKLOS is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures [see References (15)].
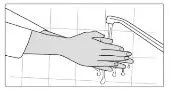
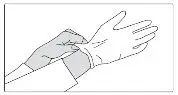
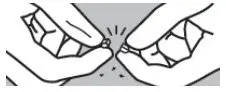
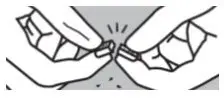
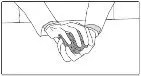
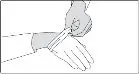
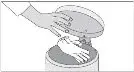
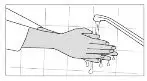
To decrease the risk of contact, advise caregivers to wear disposable gloves when handling SIKLOS or bottles containing SIKLOS. Wash hands with soap and water before and after contact with the bottle or tablets when handling SIKLOS. Avoid exposure to crushed tablets. If contact with crushed tablets occurs on the skin, wash affected area immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. If contact with crushed tablets occurs on the eye(s), the affected area should be flushed thoroughly with water or isotonic eyewash designated for that purpose for at least 15 minutes.
Powder spilled from the broken tablet should be wiped up with a damp disposable towel which must be thrown away in a closed container such as a plastic bag to avoid ingestion of powder by other people. The spill areas should then be cleaned using a detergent solution followed by clean water.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use and Medication Guide).
- There is a risk of myelosuppression. Emphasize the importance of monitoring blood counts every two weeks throughout the duration of therapy to patients taking SIKLOS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise patients to report signs and symptoms of infection or bleeding immediately.
- Advise patients that there is a risk of cutaneous vasculitic toxicities and secondary malignancies including leukemia. Advise use of sun protection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus should they become pregnant while taking SIKLOS. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use contraception during and after treatment with SIKLOS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Advise females to discontinue breastfeeding during treatment with SIKLOS [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- Advise male patients of potential risk to fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise patients with HIV infection to contact their physician for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis, hepatic events, and peripheral neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Advise patients of the risk of hemolytic anemia. Advise patients that they will have blood tests to evaluate for this if they develop persistent anemia not related to sickle cell anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
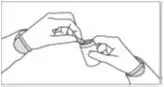
- Because SIKLOS tablets are scored, advise patients on how to take SIKLOS properly.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 12/2021 | ||
| MEDICATION GUIDE
SIKLOS (See – k – los) (hydroxyurea) tablets |
|||
|
What is the most important information I should know about SIKLOS? SIKLOS can cause serious side effects including:
|
|||
|
|
||
See "What are the possible side effects of SIKLOS?" for more information about side effects. |
|||
| What is SIKLOS?
SIKLOS is a prescription medicine that is used to reduce the frequency of painful crises and reduce the need for blood transfusions in adults and children, 2 years of age and older, with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crises. It is not known if SIKLOS is safe and effective in children less than 2 years of age. |
|||
| Do not take SIKLOS if you are allergic to hydroxyurea or any of the ingredients in SIKLOS. See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of the ingredients in SIKLOS. | |||
|
Before taking SIKLOS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
|||
|
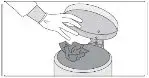
How should I take SIKLOS? Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Medication Guide for step-by-step instructions on how to prepare a dose of SIKLOS. If you have any questions, talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
|
|||
|
|||
The most common side effects of SIKLOS in children include:
|
|||
The most common side effects of SIKLOS in adults include:
|
|||
| These are not all the possible side effects of SIKLOS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
How should I store SIKLOS?
|
|||
| Keep SIKLOS and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SIKLOS.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SIKLOS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SIKLOS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about SIKLOS that is written for health professionals. |
|||
| What are the ingredients of SIKLOS?
Active ingredient: hydroxyurea Inactive ingredients: silicified microcrystalline cellulose, sodium stearyl fumarate, and film-coating agent amino methacrylate copolymer. Distributed by: Medunik USA, 919 Conestoga Road Building One, Suite 202, Bryn Mawr, PA 19010 Manufactured for: Addmedica 37 rue de Caumartin 75009 Paris France Manufactured by: Delpharm Lille, 22 rue de Toufflers 59452 Lys Lez Lannoy France. SIKLOS is a trademark of Addmedica. For more information, call 1-844-884-5520. |
|||
| SIKLOS
hydroxyurea tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SIKLOS
hydroxyurea tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Medunik (080318531) |
| Registrant - Addmedica (280967790) |