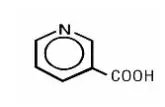
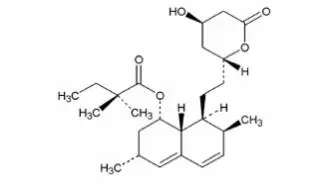
Drug Detail:Simcor (Niacin and simvastatin [ nye-a-sin-and-sim-va-stat-in ])
Drug Class: Antihyperlipidemic combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SIMCOR (niacin extended-release/simvastatin) tablet, film coated for oral use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
Indications and Usage for Simcor
SIMCOR is a combination of simvastatin, an HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor, and niacin extended-release (NIASPAN), nicotinic acid. SIMCOR is indicated to:
- Reduce elevated Total–C, LDL-C, Apo B, non-HDL-C, TG, or to increase HDL-C in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia when treatment with simvastatin monotherapy or niacin extended-release monotherapy is considered inadequate. (1.1)
- Reduce TG in patients with hypertriglyceridemia when treatment with simvastatin monotherapy or niacin extended-release monotherapy is considered inadequate. (1.1)
Limitations of use:
No incremental benefit of SIMCOR on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for simvastatin monotherapy and niacin monotherapy has been established. (1.1)
Niacin extended-release, one of the components of SIMCOR, at doses of 1,500 – 2,000 mg/day, in combination with simvastatin, did not reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events more than simvastatin in a randomized controlled trial of patients with cardiovascular disease and mean baseline LDL-C levels of 74 mg per deciliter (1.1).
Simcor Dosage and Administration
- SIMCOR should be taken at bedtime with a low-fat snack. (2)
- Dose range: 500/20 mg to 2000/40 mg once daily. (2)
- Initial dose for patients naïve to or switching from immediate-release niacin: 500/20 mg once daily. (2)
- The initial dose for patients already receiving niacin extended-release should not exceed 2000/40 mg once daily. (2)
- Maintenance dose: 1000/20 mg to 2000/40 mg once daily. (2)
- Doses greater than 2000/40 mg daily are not recommended. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Unscored film-coated tablets:
500 mg niacin extended-release/20 mg simvastatin (3)
500 mg niacin extended-release/40 mg simvastatin (3)
750 mg niacin extended-release/20 mg simvastatin (3)
1000 mg niacin extended-release/20 mg simvastatin (3)
1000 mg niacin extended-release/40 mg simvastatin (3)
Contraindications
- Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels (4, 5.3)
- Active peptic ulcer disease (4)
- Arterial bleeding (4)
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (4, 5.2)
- Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol (4, 5.2)
- Concomitant administration of verapamil or diltiazem (4,5.2)
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant (4, 8.1)
- Nursing mothers (4, 8.3)
- Known hypersensitivity to product components (4, 6.1)
Warnings and Precautions
- Skeletal muscle effects (e.g., myopathy and rhabdomyolysis): Risks increase with higher doses and concomitant use of certain medicines. Predisposing factors include advanced age (≥ 65), female gender, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and renal impairment. Patients should be advised to report promptly any unexplained and/or persistent muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. SIMCOR therapy should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. (4, 5.2, 8.5, 8.7)
- Liver enzyme abnormalities: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases can occur. Check liver enzyme tests before initiating therapy and as clinically indicated thereafter. (5.3)
- Severe hepatic toxicity has occurred in patients substituting sustained-release niacin for immediate-release niacin at equivalent doses. If switching from niacin preparations other than niacin extended-release (NIASPAN), initiate with lowest SIMCOR dose; niacin extended-release can be converted at equivalent doses. (5.3)
- Niacin extended-release can increase serum glucose levels. Glucose levels should be closely monitored in diabetic or potentially diabetic patients particularly during the first few months of use. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (incidence > 3%) adverse reactions with SIMCOR are flushing, headache, back pain, diarrhea, nausea, and pruritus. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633–9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Severe renal impairment (not on dialysis): SIMCOR should be used with extreme caution. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2013
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Simcor
2. Simcor Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosing
| * After Week 8, titrate to patient response and tolerance. If response to 1000 mg daily is inadequate, increase dose to 1500 mg daily; may subsequently increase dose to 2000 mg daily. Daily dose should not be increased more than 500 mg in a 4-week period, and doses above 2000 mg daily are not recommended. | ||
| Table 1. Recommended niacin extended-release dosing | ||
| Week(s) | Daily dose of niacin extended-release | |
| Initial Titration Schedule | 1 to 4 | 500 mg |
| 5 to 8 | 1000 mg | |
| * | 1500 mg | |
| * | 2000 mg | |
2.2 Coadministration with Other Drugs
Patients taking Amiodarone, Amlodipine or Ranolazine
- The dose of SIMCOR should not exceed 1000/20 mg/day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
SIMCOR tablets are formulated for oral administration in the following strength combinations:
| Table 2. SIMCOR Tablet Strengths | |||||
| 500mg/20mg | 500mg/40mg | 750mg/20mg | 1000mg/20mg | 1000mg/40mg | |
| Niacin extended-release equivalent (mg) | 500 | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1000 |
| simvastatin equivalent (mg) | 20 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 40 |
4. Contraindications
SIMCOR is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Patients with active peptic ulcer disease
- Patients with arterial bleeding
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, HIV protease inhibitors, boceprevir, telaprevir, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin and nefazodone) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Concomitant administration of verapamil or diltiazem [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. SIMCOR may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on long-term outcomes of primary hypercholesterolemia therapy. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of SIMCOR use during pregnancy; however in rare reports congenital anomalies were observed following intrauterine exposure to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. If SIMCOR is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use In Specific Populations (8.1)]. In rat and rabbit animal reproduction studies, simvastatin revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. There are no animal reproductive studies conducted with niacin.
- Nursing mothers. SIMCOR contains simvastatin and nicotinic acid. Nicotinic acid is excreted into human milk and it is not known whether simvastatin is excreted into human milk; however a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require SIMCOR treatment should not breastfeed their infants [see Use In Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Patients with a known hypersensitivity to any component of this product. Hypersensitivity reactions including one of more of the following adverse reactions have been reported for simvastatin and/or niacin extended-release: anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, fever, dyspnea, tongue edema, larynx edema, face edema, peripheral edema, laryngismus, and flushing [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.2 Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
| Table 3
Drug Interactions Associated with Increased Risk of Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis |
|
| Interacting Agents | Prescribing Recommendations |
| Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, e.g., Itraconazole Ketoconazole Posaconazole Erythromycin Clarithromycin Telithromycin HIV protease inhibitors Boceprevir Telaprevir Nefazodone Gemfibrozil Cyclosporine Danazol Verapamil Diltiazem | Contraindicated with SIMCOR |
| Amiodarone Amlodipine Ranolazine | Do not exceed 1000/20 mg SIMCOR daily |
| Grapefruit juice | Avoid large quantities of grapefruit juice (>1 quart daily) |
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
| * SIMCOR overall included all doses from 500/20 mg to 2000/40 mg ** Simvastatin overall included 20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg doses |
||
| Table 4. Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 3% of Patients in a Controlled Clinical Trial | ||
| Adverse Event | SIMCOR overall * | Simvastatin overall ** |
| Total Number of Patients | N=403 | N=238 |
| Headache | 18 (4.5%) | 11 (4.6%) |
| Pruritus | 13 (3.2%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Nausea | 13 (3.2%) | 10 (4.2%) |
| Back Pain | 13 (3.2%) | 5 (2.1%) |
| Diarrhea | 12 (3.0%) | 7 (2.9%) |
Clinical Laboratory Abnormalities:
Reductions in platelet counts and prolongation of PT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SIMCOR in pediatric patients have not been established.
12. Simcor - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
| * Results based on a chemical assay except results with propranolol as indicated. † Results could be representative of the following CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and nefazodone. ‡ Simvastatin acid refers to the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin. § The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied. ¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3. # Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3. Þ Because Chinese patients have an increased risk for myopathy with simvastatin coadministered with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 gram/day niacin) of niacin-containing products, and the risk is dose-related, Chinese patients should not receive simvastatin 80 mg coadministered with lipid-modifying doses of niacin-containing products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
|||||
| Table 5
Effect of Coadministered Drugs or Grapefruit Juice on Simvastatin Systemic Exposure |
|||||
| Coadministered Drug or Grapefruit Juice | Dosing of Coadministered Drug or Grapefruit Juice | Dosing of Simvastatin | Geometric Mean Ratio
(Ratio* with / without coadministered drug) No Effect = 1.00 |
||
| AUC | Cmax | ||||
| Contraindicated with simvastatin [see Contraindications (4) andWarnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |||||
| Telithromycin† | 200 mg QD for 4 days | 80 mg | simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin | 12 8.9 | 15 5.3 |
| Nelfinavir† | 1250 mg BID for 14 days | 20 mg QD for 28 days | simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin |
6 |
6.2 |
| Itraconazole† | 200 mg QD for 4 days | 80 mg | simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin | 13.1 13.1 |
|
| Posaconazole | 100 mg (oral suspension) QD for 13 days | 40 mg | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 7.3 10.3 | 9.2 9.4 |
| 200 mg (oral suspension) QD for 13 days | 40 mg | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 8.5 10.6 | 9.5 11.4 |
|
| Gemfibrozil | 600 mg BID for 3 days | 40 mg | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 2.85 1.35 | 2.18 0.91 |
| Avoid >1 quart of grapefruit juice with simvastatin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |||||
| Grapefruit Juice§ (high dose) | 200 mL of double-strength TID¶ | 60 mg single dose | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 7 16 | |
| Grapefruit Juice§ (low dose) | 8 oz (about 237 mL) of single-strength# | 20 mg single dose | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 1.3 1.9 | |
| Avoid taking with >10 mg simvastatin, based on clinical and/or post-marketing experience [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |||||
| Verapamil SR | 240 mg QD Days 1-7 then 240 mg BID on Days 8-10 | 80 mg on Day 10 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 2.3 2.5 | 2.4 2.1 |
| Diltiazem | 120 mg BID for 10 days | 80 mg on Day 10 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 2.69 3.10 | 2.69 2.88 |
| Diltiazem | 120 mg BID for 14 days | 20 mg on Day 14 | simvastatin | 4.6 | 3.6 |
| Avoid taking with >20 mg simvastatin, based on clinical and/or post-marketing experience [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |||||
| Amiodarone | 400 mg QD for 3 days | 40 mg on Day 3 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 1.75 1.76 | 1.72 1.79 |
| Amlodipine | 10 mg QD for 10 days | 80 mg on Day 10 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 1.58 1.77 | 1.56 1.47 |
| Ranolazine SR | 1000 mg BID for 7 days | 80 mg on Day 1, and Day 6-9 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 2.26 1.86 | 2.28 1.75 |
| No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
| Fenofibrate | 160 mg QD for 14 days | 80 mg QD on Days 8-14 | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 0.64 0.89 | 0.89 0.83 |
| Niacin extended-release Þ | 2 g single dose | 20 mg single dose | simvastatin acid simvastatin | 1.6 1.4 | 1.84 1.08 |
| Propranolol | 80 mg single dose | 80 mg single dose | total inhibitor active inhibitor | 0.79 0.79 | ↓ from 33.6 to 21.1 ng·eq/mL ↓ from 7.0 to 4.7 ng·eq/mL |
Simvastatin effect on other drugs:
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Modifications of Lipid Profiles
| a n=number of subjects with values in the analysis window at each timepoint b The percent change from baseline is the model-based mean from a repeated measures mixed model with no imputation for missing data from study dropouts. † significant vs. simvastatin 20 mg at the primary endpoint (Week 24), p<0.05 |
|||||||||
| Table 6. Non-HDL Treatment Response Following 24-Week Treatment Mean Percent Change from Simvastatin 20-mg Treated Baseline | |||||||||
| Group A | |||||||||
| SIMCOR 2000/20 | SIMCOR 1000/20 | Simvastatin 20 | |||||||
| Week | na | dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb | na | Dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb | na | Dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb |
| Baseline | 56 | --- | 163.1 mg/dL | 108 | --- | 164.8 mg/dL | 102 | --- | 163.7 mg/dL |
| 4 | 52 | 500/20 | -12.9% | 86 | 500/20 | -12.8% | 91 | 20 | -8.3% |
| 8 | 46 | 1000/20 | -17.5% | 91 | 1000/20 | -15.5% | 95 | 20 | -8.3% |
| 12 | 46 | 1500/20 | -18.9% | 90 | 1000/20 | -14.8% | 96 | 20 | -6.4% |
| 24 | 40 | 2000/20 | -19.5%† | 78 | 1000/20 | -13.6%† | 90 | 20 | -5.0% |
| Dropouts by week 24: | 28.6% | 27.8% | 11.8% | ||||||
| a n=number of subjects with values in the analysis window at each timepoint b The percent change from baseline is the model-based mean from a repeated measures mixed model with no imputation for missing data from study dropouts. c non-inferior to Simvastatin 80 arm; 95% confidence interval of mean difference in non-HDL for SIMCOR 2000/40 vs. Simvastatin 80 is (-7.7%, 4.5%) d non-inferior to Simvastatin 80 arm; 95% confidence interval of mean difference in non-HDL for SIMCOR 1000/40 vs. SIMCOR 80 is (-6.6%, 5.3%) |
|||||||||
| Table 7. Non-HDL Treatment Response Following 24-Week Treatment Mean Percent Change from Simvastatin 40-mg Treated Baseline | |||||||||
| Group B | |||||||||
| SIMCOR 2000/40 | SIMCOR 1000/40 | Simvastatin 80 | |||||||
| Week | na | dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb | na | Dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb | na | Dose (mg/mg) | non-HDLb |
| Baseline | 98 | --- | 144.4 mg/dL | 111 | --- | 141.2 mg/dL | 113 | --- | 134.5 mg/dL |
| 4 | 96 | 500/40 | -6.0% | 108 | 500/40 | -5.9% | 110 | 80 | -11.3% |
| 8 | 93 | 1000/40 | -15.5% | 100 | 1000/40 | -16.2% | 104 | 80 | -13.7% |
| 12 | 90 | 1500/40 | -18.4% | 97 | 1000/40 | -12.6% | 100 | 80 | -9.5% |
| 24 | 80 | 2000/40 | -7.6%c | 82 | 1000/40 | -6.7%d | 90 | 80 | -6.0% |
| Dropouts by week 24: | 18.4% | 26.1% | 20.4% | ||||||
| * either treatment naïve or after receiving simvastatin 20 mg a medians are reported for TG |
||||||
| Table 8. Mean Percent Change from Baseline to Week 24 in Lipoprotein Lipid Levels | ||||||
| Treatment Group A | ||||||
| TREATMENT | N | LDL-C | Total-C | HDL-C | TGa | Apo B |
| Baseline (mg/dL)* | 266 | 120 | 207 | 43 | 209 | 102 |
| Simvastatin 20 mg | 102 | -6.7% | -4.5% | 7.8% | -15.3% | -5.6% |
| SIMCOR 1000/20 | 108 | -11.9% | -8.8% | 20.7% | -26.5% | -13.2% |
| SIMCOR 2000/20 | 56 | -14.3% | -11.1% | 29.0% | -38.0% | -18.5% |
| * after receiving simvastatin 40 mg a medians are reported for TG |
||||||
| Table 9. Mean Percent Change from Baseline to Week 24 in Lipoprotein Lipid Levels | ||||||
| Treatment Group B | ||||||
| TREATMENT | N | LDL-C | Total-C | HDL-C | TGa | Apo B |
| Baseline (mg/dL)* | 322 | 108 | 187 | 47 | 145 | 93 |
| Simvastatin 80 mg | 113 | -11.4% | -6.2% | 0.1% | 0.3% | -7.5% |
| SIMCOR 1000/40 | 111 | -7.1% | -3.1% | 15.4% | -22.8% | -7.7% |
| SIMCOR 2000/40 | 98 | -5.1% | -1.6% | 24.4% | -31.8% | -10.5% |
16. How is Simcor supplied
| SIMCOR Tablet Strength | Printed ID | NDC Number |
| 500 mg/20 mg | a 500-20 | 0074-3312-90 |
| 500 mg/40 mg | a 500-40 | 0074-3459-90 |
| 750 mg/20 mg | a 750-20 | 0074-3315-90 |
| 1000 mg/20 mg | a 1000-20 | 0074-3455-90 |
| 1000 mg/40 mg | a 1000-40 | 0074-3457-90 |
Storage: Store at controlled room temperature 20º-25ºC (68º-77ºF).
17. Patient Counseling Information
17.4 Tablet Integrity
SIMCOR tablets should not be broken, crushed or chewed, but should be swallowed whole.
| SIMCOR
niacin and simvastatin tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIMCOR
niacin and simvastatin tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIMCOR
niacin and simvastatin tablet, film coated, extended release |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIMCOR
niacin and simvastatin tablet, film coated, extended release |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIMCOR
niacin and simvastatin tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370) |