Drug Detail:Spevigo (Spesolimab-sbzo)
Drug Class: Interleukin inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SPEVIGO® (spesolimab-sbzo) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
Indications and Usage for Spevigo Injection
SPEVIGO is an interleukin-36 receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis flares in adults. (1)
Spevigo Injection Dosage and Administration
- Administer as a single 900 mg dose by intravenous infusion over 90 minutes. If flare symptoms persist, may administer an additional intravenous 900 mg dose one week after the initial dose. (2.1)
- Must be diluted before use. See full prescribing information for preparation and administration instructions and storage of the diluted solution. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 450 mg/7.5 mL (60 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial (3)
Contraindications
Severe or life-threatening hypersensitivity to spesolimab-sbzo or to any of the excipients in SPEVIGO (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Infections: SPEVIGO may increase the risk of infections. Do not initiate SPEVIGO during any clinically important active infection. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur after treatment with SPEVIGO. (5.1)
- Tuberculosis (TB): Evaluate patients for TB prior to initiating treatment with SPEVIGO. (5.2)
- Hypersensitivity and Infusion-Related Reactions: Hypersensitivity including drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and infusion-related reactions may occur. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue SPEVIGO immediately and initiate appropriate treatment. (5.3)
- Vaccinations: Do not administer live vaccines concurrently with SPEVIGO. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥5%) are asthenia and fatigue, nausea and vomiting, headache, pruritus and prurigo, infusion site hematoma and bruising, and urinary tract infection. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at (800) 542-6257 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2022
Related/similar drugs
Kenalog, Kenalog-40, Dovonex, Bryhali, Impoyz, Trianex, ClodermFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Spevigo Injection
SPEVIGO is indicated for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) flares in adults.
2. Spevigo Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dose
Administer SPEVIGO as a single 900 mg dose by intravenous infusion over 90 minutes.
If GPP flare symptoms persist, an additional intravenous 900 mg dose (over 90 minutes) may be administered one week after the initial dose.
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
SPEVIGO must be diluted before use.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permits. SPEVIGO is a colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains large or colored particulates.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
SPEVIGO is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution.
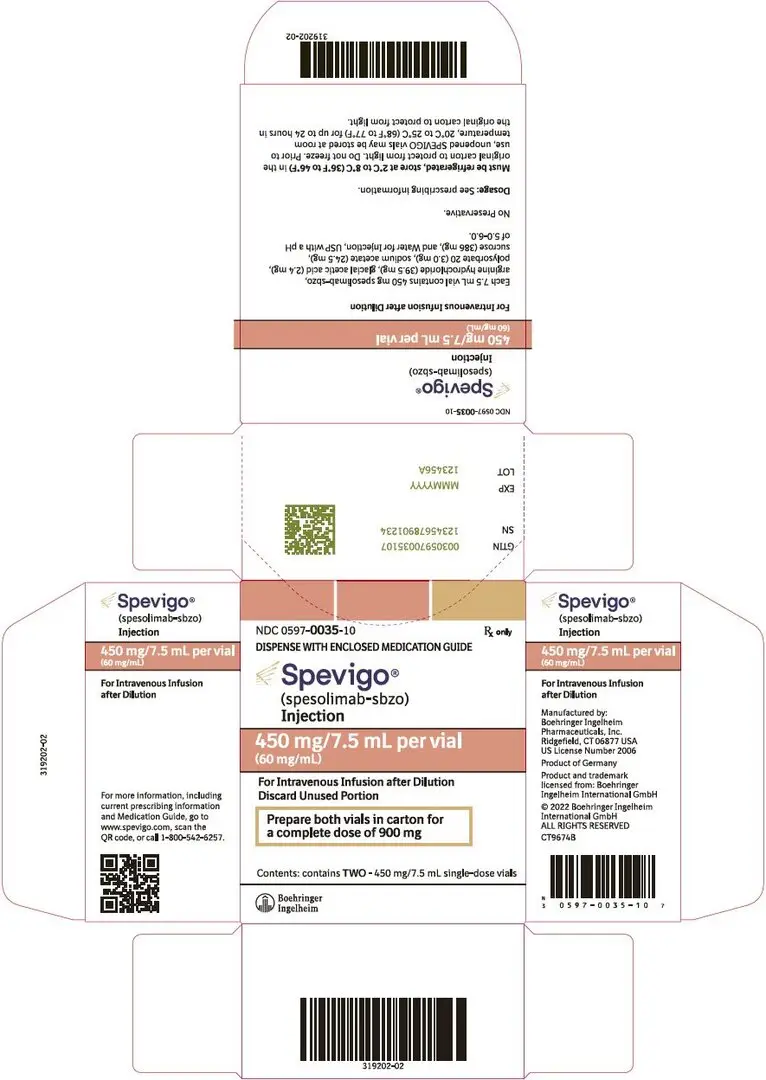
Injection: 450 mg/7.5 mL (60 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial
4. Contraindications
SPEVIGO is contraindicated in patients with severe or life-threatening hypersensitivity to spesolimab-sbzo or to any of the excipients in SPEVIGO. Reactions have included drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Infections
SPEVIGO may increase the risk of infections. During the one-week placebo-controlled period in the Effisayil-1 trial, infections were reported in 14% of subjects treated with SPEVIGO compared with 6% of subjects treated with placebo [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection, consider the potential risks and expected clinical benefits of treatment prior to prescribing SPEVIGO. Treatment with SPEVIGO is not recommended for use in patients with any clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur after treatment with SPEVIGO.
5.2 Risk of Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SPEVIGO. Do not administer SPEVIGO to patients with active TB infection.
Consider initiating anti-TB therapy prior to initiating SPEVIGO in patients with latent TB or a history of TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after SPEVIGO treatment.
5.3 Hypersensitivity and Infusion-Related Reactions
SPEVIGO-associated hypersensitivity reactions may include immediate reactions such as anaphylaxis and delayed reactions such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in clinical trials with spesolimab-sbzo in subjects with GPP [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
If a patient develops signs of anaphylaxis or other serious hypersensitivity, discontinue SPEVIGO immediately and initiate appropriate treatment [see Contraindications (4)].
If a patient develops mild or moderate infusion-related reactions, stop SPEVIGO infusion and consider appropriate medical therapy (e.g., systemic antihistamines and/or corticosteroids). Upon resolution of the reaction, the infusion may be restarted at a slower infusion rate with gradual increase to complete the infusion.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
SPEVIGO was studied in Study Effisayil-1, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing a single intravenous 900 mg dose of SPEVIGO (n=35) with placebo (n=18) in subjects with generalized pustular psoriasis flare. Subjects in either treatment group who continued to experience flare symptoms at Week 1 were eligible to receive a single open-label intravenous dose of 900 mg of SPEVIGO (second dose and first dose for subjects in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively). At Week 1, 12 (34%) subjects and 15 subjects (83%) in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively, received open-label SPEVIGO. After Week 1 to Week 12, subjects in either treatment group whose GPP flare reoccurred after achieving a clinical response were eligible to receive a single open-label rescue intravenous dose of 900 mg of SPEVIGO, with a maximum of 3 total doses of SPEVIGO throughout the study. Six subjects received a single open-label rescue dose of SPEVIGO. Thirty-six subjects received 1 dose of SPEVIGO, 13 subjects received 2 doses of SPEVIGO, and 2 subjects received 3 doses of SPEVIGO throughout the study [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Subjects ranged in age from 21 to 69 years (mean age of 43 years); 45% were White and 55% were Asian; and 68% were female.
Table 1 summarizes selected adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% and at a higher rate in the SPEVIGO group than in the placebo group through Week 1.
| Adverse Reaction | SPEVIGO N = 35 n (%) | Placebo N = 18 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Asthenia and Fatigue | 3 (9) | 0 |
| Nausea and Vomiting | 3 (9) | 1 (6) |
| Headache | 3 (9) | 1 (6) |
| Pruritus and prurigo | 2 (6) | 0 |
| Infusion site hematoma and bruising | 2 (6) | 0 |
| Urinary tract infection | 2 (6) | 0 |
| Bacteremia | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Bacteriuria | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Cellulitis | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Herpes dermatitis and oral herpes | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Eye edema | 1 (3) | 0 |
| Urticaria | 1 (3) | 0 |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SPEVIGO in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In Study Effisayil-1, 2 (6%) of SPEVIGO-treated subjects were 65 to 74 years of age and no subjects were 75 years of age or older. Clinical studies of SPEVIGO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
11. Spevigo Injection Description
Spesolimab-sbzo, an interleukin-36 receptor antagonist, is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody (mAb) against human IL-36R produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells by recombinant DNA technology. Spesolimab-sbzo has a molecular weight of approximately 146 kDa.
SPEVIGO (spesolimab-sbzo) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution supplied in a single-dose vial for intravenous infusion. Each 7.5 mL vial contains 450 mg spesolimab-sbzo, arginine hydrochloride (39.5 mg), glacial acetic acid (2.4 mg), polysorbate 20 (3.0 mg), sodium acetate (24.5 mg), sucrose (386 mg), and Water for Injection, USP with a pH of 5.0-6.0.
12. Spevigo Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Spesolimab-sbzo is a humanized monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that inhibits interleukin-36 (IL-36) signaling by specifically binding to the IL36R. Binding of spesolimab-sbzo to IL36R prevents the subsequent activation of IL36R by cognate ligands (IL-36 α, β and γ) and downstream activation of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pathways. The precise mechanism linking reduced IL36R activity and the treatment of flares of GPP is unclear.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of SPEVIGO in the treatment of patients with GPP have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
A population pharmacokinetic model was developed based on data collected from healthy subjects, patients with GPP, and patients with other diseases. After a single intravenous dose of 900 mg of SPEVIGO, the population PK model-estimated AUC0-∞ (95% CI) and Cmax (95% CI) in a typical anti-drug antibody (ADA)-negative patient with GPP were 4750 (4510, 4970) mcg∙day/mL and 238 (218, 256) mcg/mL, respectively.
Spesolimab-sbzo AUC increased dose-proportionally from 0.3 to 20 mg/kg, and CL and terminal half-life were independent of dose.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of spesolimab-sbzo or of other spesolimab products.
In subjects with GPP treated with SPEVIGO in Effisayil-1, ADAs formed with a median onset of 2.3 weeks. Following administration of 900 mg intravenous SPEVIGO, (12/50) 24% of subjects had a maximum ADA titer greater than 4000 and were neutralizing antibody-positive by the end of the trial (Weeks 12 to 17). Females appeared to have higher immunogenicity response; the percentage of subjects with ADA titer greater than 4000 was 30% in females, and 12% in males, respectively.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with spesolimab-sbzo.
No adverse effects on fertility were observed in male or female mice that were intravenously administered a surrogate antibody to IL36R at doses up to 50 mg/kg twice weekly.
14. Clinical Studies
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (Study Effisayil-1) [NCT03782792] was conducted to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of SPEVIGO in adult subjects with flares of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). Subjects were randomized if they had a flare of GPP of moderate-to-severe intensity, as defined by:
- A Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPPGA) total score of at least 3 (moderate) [the total GPPPGA score ranges from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe)],
- The presence of fresh pustules (new appearance or worsening of pustules),
- GPPPGA pustulation sub score of at least 2 (mild), and
- At least 5% of body surface area covered with erythema and the presence of pustules.
Subjects were required to discontinue systemic and topical therapy for GPP prior to receiving study drug.
A total of 53 subjects were randomized (2:1) to receive a single intravenous dose of 900 mg SPEVIGO (N=35) or placebo (N=18) (administered over 90 minutes) during the double-blind portion of the study.
The study population consisted of 32% men and 68% women. The mean age was 43 years (range: 21 to 69 years); 55% of subjects were Asian and 45% were White. Most subjects included in the study had a GPPPGA pustulation sub score of 3 (43%) or 4 (36%), and subjects had a GPPPGA total score of 3 (81%) or 4 (19%). In this study, 25% of subjects had been previously treated with biologic therapy for GPP. At baseline acute flare, of the subjects with white blood cell count (WBC) assessments, 45% and 31% of subjects in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively, had (WBC) >12 × 109/L. Seventeen percent and 11% of subjects in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively, had temperature >38° Celsius. Of the subjects with WBC assessments, 12% and 6% of subjects in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively, had both WBC >12 × 109/L and temperature >38° Celsius [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The primary endpoint of the study was the proportion of subjects with a GPPPGA pustulation sub score of 0 (indicating no visible pustules) at Week 1 after treatment. The results of the primary endpoint are presented in Table 2.
| SPEVIGO (N=35) | Placebo (N=18) |
|
|---|---|---|
| GPPPGA = Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment | ||
| Subjects achieving a GPPPGA pustulation sub score of 0, n (%) | 19 (54) | 1 (6) |
| Risk difference versus placebo, % (95% CI) | 49 (21, 67) | |
In Study Effisayil-1, subjects in either treatment group who continued to experience flare symptoms at Week 1 were eligible to receive a single open-label intravenous dose of 900 mg of SPEVIGO (second dose and first dose for subjects in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively). At Week 1, 12 (34%) subjects and 15 subjects (83%) in the SPEVIGO and placebo groups, respectively, received open-label SPEVIGO. In subjects who were randomized to SPEVIGO and received an open-label dose of SPEVIGO at Week 1, 5 (42%) subjects had a GPPPGA pustulation sub score of 0 at Week 2 (one week after their second dose of SPEVIGO).
This study did not include sufficient numbers of subjects to determine if there are differences in response according to biological sex, age, race, baseline GPPPGA pustulation sub score, and baseline GPPPGA total score.
16. How is Spevigo Injection supplied
SPEVIGO is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution for intravenous infusion.
NDC Number 0597-0035-10: Each carton contains two single-dose 450 mg/7.5 mL (60 mg/mL) glass vials.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE SPEVIGO® (spea VEE go) (spesolimab-sbzo) injection, for intravenous use |
||
|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: September 2022 | |
| What is the most important information I should know about SPEVIGO? | ||
SPEVIGO may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
| See "What are the possible side effects of SPEVIGO?" for more information about side effects. | ||
| What is SPEVIGO? | ||
| SPEVIGO is a prescription medicine used to treat generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) flares in adults. | ||
| It is not known if SPEVIGO is safe and effective in children. | ||
| Do not receive SPEVIGO if you have had a severe or life-threatening allergic reaction to spesolimab-sbzo or any of the ingredients in SPEVIGO. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in SPEVIGO. | ||
Before you receive SPEVIGO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||
How will I receive SPEVIGO?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of SPEVIGO? | ||
| SPEVIGO may cause serious side effects. See "What is the most important information I should know about SPEVIGO?" | ||
| The most common side effects of SPEVIGO include: | ||
|
|
|
| These are not all of the possible side effects of SPEVIGO. | ||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SPEVIGO. | ||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SPEVIGO that is written for health professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in SPEVIGO? | ||
| Active ingredient: spesolimab-sbzo | ||
| Inactive ingredients: arginine hydrochloride, glacial acetic acid, polysorbate 20, sodium acetate, sucrose, and Water for Injection, USP | ||
| Manufactured by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA | ||
| US License Number 2006 | ||
| Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany | ||
| SPEVIGO is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. | ||
| Copyright © 2022 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | ||
| COL9614AH012022 | ||
| For more information about SPEVIGO, including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.SPEVIGO.com, scan the code below, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257. | ||
|
|
||
| SPEVIGO
spesolimab-sbzo injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 340700520 | MANUFACTURE(0597-0035) , API MANUFACTURE(0597-0035) , PACK(0597-0035) , LABEL(0597-0035) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | PACK(0597-0035) | |