Drug Detail:Sporanox (Itraconazole [ it-ra-kon-a-zole ])
Drug Class: Azole antifungals
BOXED WARNING
Drug Interactions
Coadministration of the following drugs are contraindicated with SPORANOX ®Oral Solution: methadone, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine, isavuconazole, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine)), irinotecan, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam, felodipine, nisoldipine, ivabradine, ranolazine, eplerenone, cisapride, naloxegol, lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin, avanafil, ticagrelor. In addition, coadministration with colchicine, fesoterodine and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment, and coadministration with eliglustat is contraindicated in subjects that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. Coadministration with venetoclax is contraindicated in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) during the dose initiation and ramp-up phase of venetoclax. See PRECAUTIONS: Drug InteractionsSection for specific examples. Coadministration with itraconazole can cause elevated plasma concentrations of these drugs and may increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs. For example, increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. See CONTRAINDICATIONSand WARNINGSSections, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug InteractionsSection for specific examples.
Sporanox Description
SPORANOX ®is the brand name for itraconazole, an azole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the following structural formula and nomenclature:
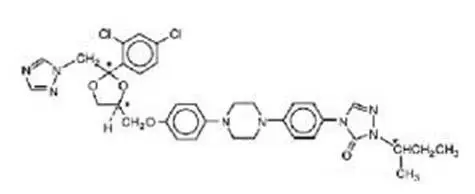
(±)-1-[( R*)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 R*,4 S*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one mixture with (±)-1-[( R*)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 S*,4 R*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
or
(±)-1-[( RS)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 R,4 S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one.
Itraconazole has a molecular formula of C 35H 38Cl 2N 8O 4and a molecular weight of 705.64. It is a white to slightly yellowish powder. It is insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohols, and freely soluble in dichloromethane. It has a pKa of 3.70 (based on extrapolation of values obtained from methanolic solutions) and a log (n-octanol/water) partition coefficient of 5.66 at pH 8.1.
SPORANOX ®(itraconazole) Oral Solution contains 10 mg of itraconazole per mL, solubilized by hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (400 mg/mL) as a molecular inclusion complex. SPORANOX ®Oral Solution is clear and yellowish in color with a target pH of 2. Other ingredients are hydrochloric acid, propylene glycol, purified water, sodium hydroxide, sodium saccharin, sorbitol, cherry flavor 1, cherry flavor 2 and caramel flavor.
Related/similar drugs
ciprofloxacin, Augmentin, fluconazole, amoxicillin / clavulanate, nystatin topical, nystatin, vancomycinSporanox - Clinical Pharmacology
Indications and Usage for Sporanox
SPORANOX ®(itraconazole) Oral Solution is indicated for the treatment of oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis.
(See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, WARNINGS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experiencefor more information.)
Contraindications
Drug Interactions
Coadministration of a number of CYP3A4 substrates are contraindicated with SPORANOX ®. Plasma concentrations increase for the following drugs: levaceytlmethadol (levomethadyl), methadone, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine, isavuconazole, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine)), irinotecan, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam, felodipine, nisoldipine, ivabradine, ranolazine, eplerenone, cisapride, naloxegol, lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin, avanafil, ticagrelor. In addition, coadministration with colchicine, fesoterodine, and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment, and coadministration with eliglustat is contraindicated in subjects that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug InteractionsSection for specific examples.) This increase in drug concentrations caused by coadministration with itraconazole may increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs. For example, increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsade de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. Specific examples are listed in PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.
Coadministration with venetoclax is contraindicated in patients with CLL/SLL during the dose initiation and ramp-up phase of venetoclax due to the potential for an increased risk of tumor lysis syndrome.
SPORANOX ®is contraindicated for patients who have shown hypersensitivity to itraconazole. There is limited information regarding cross-hypersensitivity between itraconazole and other azole antifungal agents. Caution should be used when prescribing SPORANOX ®to patients with hypersensitivity to other azoles.
Warnings
Hepatic Effects
SPORANOX ®has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition, and some of these cases developed within the first week of treatment. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, treatment should be discontinued and liver function testing performed. Continued SPORANOX ®use or reinstitution of treatment with SPORANOX ®is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. (See PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patientsand ADVERSE REACTIONS. )
Precautions
Hepatotoxicity
Rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity have been observed with SPORANOX ®treatment, including some cases within the first week. It is recommended that liver function monitoring be considered in all patients receiving SPORANOX ®. Treatment should be stopped immediately and liver function testing should be conducted in patients who develop signs and symptoms suggestive of liver dysfunction.
Information for Patients
- Only SPORANOX ®Oral Solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis.
- SPORANOX ®Oral Solution contains the excipient hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin which produced adenocarcinomas in the large intestine and exocrine pancreatic adenocarcinomas in a rat carcinogenicity study. These findings were not observed in a similar mouse carcinogenicity study. The clinical relevance of these adenocarcinomas is unknown. (See Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility.)
- Taking SPORANOX ®Oral Solution under fasted conditions improves the systemic availability of itraconazole. Instruct patients to take SPORANOX ®Oral Solution without food, if possible.
- SPORANOX ®Oral Solution should not be used interchangeably with SPORANOX ®Capsules.
- Instruct patients about the signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure, and if these signs or symptoms occur during SPORANOX ®administration, they should discontinue SPORANOX ®and contact their healthcare provider immediately.
- Instruct patients to stop SPORANOX ®treatment immediately and contact their healthcare provider if any signs and symptoms suggestive of liver dysfunction develop. Such signs and symptoms may include unusual fatigue, anorexia, nausea and/or vomiting, jaundice, dark urine, or pale stools.
- Instruct patients to contact their physician before taking any concomitant medications with itraconazole to ensure there are no potential drug interactions.
- Instruct patients that hearing loss can occur with the use of itraconazole. The hearing loss usually resolves when treatment is stopped, but can persist in some patients. Advise patients to discontinue therapy and inform their physicians if any hearing loss symptoms occur.
- Instruct patients that dizziness or blurred/double vision can sometimes occur with itraconazole. Advise patients that if they experience these events, they should not drive or use machines.
Drug Interactions
Effect of SPORANOX ®on Other Drugs
Itraconazole and its major metabolite, hydroxy-itraconazole, are potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. Itraconazole is an inhibitor of the drug transporters P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Consequently, SPORANOX ®has the potential to interact with many concomitant drugs resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of the concomitant drugs. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drug which can be severe or life-threatening in some cases (e.g., QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes, respiratory depression, hepatic adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, myelosuppression, hypotension, seizures, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, priapism). Reduced concentrations of concomitant drugs may reduce their efficacy. The table below lists examples of drugs that may have their concentrations affected by itraconazole, but is not a comprehensive list.
Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways risk potential and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with SPORANOX ®.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 1 below are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with SPORANOX ®.
| Concomitant Drug Within Class | Prevention or Management | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Drug Interactions with SPORANOX ®that Increase Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with the Concomitant Drug | ||
| Alpha Blockers | ||
| Alfuzosin
Silodosin Tamsulosin | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Analgesics | ||
| Methadone | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Fentanyl | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Alfentanil
Buprenorphine (IV and sublingual) Oxycodone * Sufentanil | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antiarrhythmics | ||
| Disopyramide
Dofetilide Dronedarone Quinidine * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Digoxin * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antibacterials | ||
| Bedaquiline † | Concomitant SPORANOX ®not recommended for more than 2 weeks at any time during bedaquiline treatment. | |
| Rifabutin | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. See also Table 2. | |
| Clarithromycin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 2. | |
| Trimetrexate | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Anticoagulants and Antiplatelets | ||
| Ticagrelor | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Apixaban
Rivaroxaban Vorapaxar | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Cilostazol
Dabigatran Warfarin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| Carbamazepine | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. See also Table 2. | |
| Antidiabetic Drugs | ||
| Repaglinide
*
Saxagliptin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antihelminthics, Antifungals and Antiprotozoals | ||
| Isavuconazonium | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Praziquantel | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Artemether-lumefantrine Quinine * | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Antimigraine Drugs | ||
| Ergot alkaloids (e.g., dihydroergotamine, ergotamine) | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Eletriptan | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary | |
| Antineoplastics | ||
| Irinotecan | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Venetoclax | Contraindicated during the dose initiation and ramp-up phase in patients with CLL/SLL. Refer to the venetoclax prescribing information for dosing and safety monitoring instructions. | |
| Axitinib
Bosutinib Cabazitaxel Cabozantinib Ceritinib Cobimetinib * Crizotinib Dabrafenib Dasatinib Docetaxel | Ibrutinib
Lapatinib Nilotinib Olaparib * Pazopanib Sunitinib Trabectedin Trastuzumab-emtansine Vinca alkaloids | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. |
| Talazoparib * | Refer to the talazoparib prescribing information for dosing instructions if concomitant use cannot be avoided. | |
| Glasdegib | Refer to the glasdegib prescribing information for safety monitoring if concomitant use cannot be avoided. | |
| Bortezomib
Brentuximab-vedotin Busulfan Erlotinib Gefitinib * Idelalisib Imatinib Ixabepilone | Nintedanib
Panobinostat Ponatinib Ruxolitinib Sonidegib Tretinoin (oral) Vandetanib * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For idelalisib: see also Table 2. |
| Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics and Hypnotics | ||
| Alprazolam
*
Aripiprazole * Buspirone * Cariprazine Diazepam * Haloperidol * | Midazolam (IV)
*
Quetiapine Ramelteon Risperidone * Suvorexant | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Zopiclone * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Lurasidone
Midazolam (oral) * Pimozide Triazolam * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Antivirals | ||
| Daclatasvir
Indinavir * Maraviroc | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For indinavir: see also Table 2. | |
| Cobicistat
Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted) Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir with or without Dasabuvir Ritonavir Saquinavir (unboosted) * | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Elbasvir/grazoprevir | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | Monitor for adverse reactions.
Monitor for adverse reactions. |
|
| Beta Blockers | ||
| Nadolol * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | ||
| Felodipine
*
Nisoldipine | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Diltiazem
Other dihydropyridines Verapamil | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For diltiazem: see also Table 2. | |
| Cardiovascular Drugs, Miscellaneous | ||
| Ivabradine
Ranolazine | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Aliskiren
*
Riociguat Sildenafil (for pulmonary hypertension) Tadalafil (for pulmonary hypertension) | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Urologic Drugsbelow. | |
| Bosentan
Guanfacine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Contraceptives‡ | ||
| Dienogest
Ulipristal | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Diuretics | ||
| Eplerenone | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | ||
| Cisapride
Naloxegol | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Aprepitant
Loperamide * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Netupitant | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Immunosuppressants | ||
| Everolimus
Sirolimus Temsirolimus (IV) | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Budesonide (inhalation)
*
Budesonide (non-inhalation) Ciclesonide (inhalation) Cyclosporine (IV) * Cyclosporine (non-IV) Dexamethasone * | Fluticasone (inhalation)
*
Fluticasone (nasal) Methylprednisolone * Tacrolimus (IV) * Tacrolimus (oral) | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Lipid-Lowering Drugs | ||
| Lomitapide
Lovastatin * Simvastatin * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Atorvastatin * | Monitor for drug adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary . | |
| Respiratory Drugs | ||
| Salmeterol | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| SSRIs, Tricyclics and Related Antidepressants | ||
| Venlafaxine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Urologic Drugs | ||
| Avanafil | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Fesoterodine | Patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX
®treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
|
| Solifenacin | Patients with severe renal or moderate to severe hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX
®treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
|
| Darifenacin
Vardenafil | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Dutasteride
Oxybutynin * Sildenafil (for erectile dysfunction) Tadalafil (for erectile dysfunction and benign prostatic hyperplasia) Tolterodine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Cardiovascular Drugsabove. | |
| Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances | ||
| Colchicine | Patients with renal or hepatic impairment:Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX
®treatment.
Other patients: Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. |
|
| Eliglustat | CYP2D6 EMs
§taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor, CYP2D6 IMs
§, or CYP2D6 PMs
§: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX
®treatment.
CYP2D6 EMs §not taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor : Monitor for adverse reactions. Eliglustat dose reduction may be necessary. |
|
| Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Alitretinoin (oral)
Cabergoline Cannabinoids Cinacalcet Galantamine Ivacaftor | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists | ||
| Conivaptan
Tolvaptan | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Drug Interactions with SPORANOX ®that Decrease Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of the Concomitant Drug | ||
| Antineoplastics | ||
| Regorafenib | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | ||
| Saccharomyces boulardii | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. | |
| Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs | ||
| Meloxicam * | Concomitant drug dose increase may be necessary. | |
Effect of Other Drugs on SPORANOX ®
Itraconazole is mainly metabolized through CYP3A4. Other substances that either share this metabolic pathway or modify CYP3A4 activity may influence the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole. Some concomitant drugs have the potential to interact with SPORANOX ®resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of SPORANOX ®. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with SPORANOX ®. Decreased concentrations may reduce SPORANOX ®efficacy.
The table below lists examples of drugs that may affect itraconazole concentrations, but is not a comprehensive list. Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways, risk potential and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with SPORANOX ®.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 2 below are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with SPORANOX ®.
| Concomitant Drug Within Class | Prevention or Management |
|---|---|
|
|
| Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Increase SPORANOX®Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with SPORANOX ® | |
| Antibacterials | |
| Ciprofloxacin
*
Erythromycin * Clarithromycin * | Monitor for adverse reactions. SPORANOX ®dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Antineoplastics | |
| Idelalisib | Monitor for adverse reactions. SPORANOX ®dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 1. |
| Antivirals | |
| Cobicistat
Darunavir (ritonavir-boosted) Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted) Fosamprenavir (ritonavir-boosted) Indinavir * Ombitasvir/ Paritaprevir/ Ritonavir with or without Dasabuvir Ritonavir Saquinavir | Monitor for adverse reactions. SPORANOX ®dose reduction may be necessary. For Boceprevir, cobicistat, elvitegravir, indinavir, ombitasvir/ paritaprevir/ ritonavir with or without dasabuvir, ritonavir and saquinavir, see also Table 1. |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | |
| Diltiazem | Monitor for adverse reactions. SPORANOX ®dose reduction may be necessary. See also the table above. |
| Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Decrease SPORANOX ®Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of SPORANOX ® | |
| Antibacterials | |
| Isoniazid
Rifampicin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during SPORANOX ®treatment. |
| Rifabutin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. See also Table 1. |
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Phenobarbital
Phenytoin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during SPORANOX ®treatment. |
| Carbamazepine | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. See also Table 1. |
| Antivirals | |
| Efavirenz
*
Nevirapine * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during SPORANOX ®treatment. |
| Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances | |
| Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after SPORANOX ®treatment. |
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects
Itraconazole was found to cause a dose-related increase in maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats at dosage levels of approximately 40–160 mg/kg/day (5–20 times the MRHD), and in mice at dosage levels of approximately 80 mg/kg/day (10 times the MRHD). Itraconazole has been shown to cross the placenta in a rat model. In rats, the teratogenicity consisted of major skeletal defects; in mice, it consisted of encephaloceles and/or macroglossia.
SPORANOX ®Oral Solution contains the excipient hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD). HP-β-CD has no direct embryotoxic and no teratogenic effect.
There are no studies in pregnant women. SPORANOX ®should be used in pregnancy only if the benefit outweighs the potential risk. Highly effective contraception should be continued throughout SPORANOX ®therapy and for 2 months following the end of treatment.
During post-marketing experience, cases of congenital abnormalities have been reported. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience.)
Nursing Mothers
Itraconazole is excreted in human milk; therefore, the expected benefits of SPORANOX ®therapy for the mother should be weighed against the potential risk from exposure of itraconazole to the infant. The U.S. Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advises HIV-infected women not to breast-feed to avoid potential transmission of HIV to uninfected infants.
Pediatric Use
The efficacy and safety of SPORANOX ®have not been established in pediatric patients.
The long-term effects of itraconazole on bone growth in children are unknown. In three toxicology studies using rats, itraconazole induced bone defects at dosage levels as low as 20 mg/kg/day (2.5 times the MRHD). The induced defects included reduced bone plate activity, thinning of the zona compacta of the large bones, and increased bone fragility. At a dosage level of 80 mg/kg/day (10 times the MRHD) over 1 year or 160 mg/kg/day (20 times the MRHD) for 6 months, itraconazole induced small tooth pulp with hypocellular appearance in some rats.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of SPORANOX ®Oral Solution did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. It is advised to use SPORANOX ®Oral Solution in these patients only if it is determined that the potential benefit outweighs the potential risks. In general, it is recommended that the dose selection for an elderly patient should be taken into consideration, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Transient or permanent hearing loss has been reported in elderly patients receiving treatment with itraconazole. Several of these reports included concurrent administration of quinidine which is contraindicated (see BOXED WARNING: Drug Interactions, CONTRAINDICATIONS: Drug Interactionsand PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Renal Impairment
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. The exposure of itraconazole may be lower in some patients with renal impairment. Caution should be exercised when itraconazole is administered in this patient population and dose adjustment may be needed. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populationsand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Hepatic Impairment
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. It is recommended that patients with impaired hepatic function be carefully monitored when taking SPORANOX ®. It is recommended that the prolonged elimination half-life of itraconazole observed in the single oral dose clinical trial with itraconazole capsules in cirrhotic patients be considered when deciding to initiate therapy with other medications metabolized by CYP3A4.
In patients with elevated or abnormal liver enzymes or active liver disease, or who have experienced liver toxicity with other drugs, treatment with SPORANOX ®is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. It is recommended that liver function monitoring be done in patients with pre-existing hepatic function abnormalities or those who have experienced liver toxicity with other medications. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populationsand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
SPORANOX ®has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, treatment should be discontinued and liver function testing performed. The risks and benefits of SPORANOX ®use should be reassessed. (See WARNINGS: Hepatic Effectsand PRECAUTIONS: Hepatotoxicityand Information for Patients.)
Adverse Events Reported in Oropharyngeal or Esophageal Candidiasis Trials
U.S. adverse experience data are derived from 350 immunocompromised patients (332 HIV seropositive/AIDS) treated for oropharyngeal or esophageal candidiasis. Table 3 below lists adverse events reported by at least 2% of patients treated with SPORANOX ®Oral Solution in U.S. clinical trials. Data on patients receiving comparator agents in these trials are included for comparison.
| Itraconazole | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body System/ Adverse Event | Total
(n = 350 *) % | All controlled studies
(n = 272) % | Fluconazole
(n = 125 †) % | Clotrimazole (n = 81 ‡) % |
|
||||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 11 | 10 | 11 | 5 |
| Diarrhea | 11 | 10 | 10 | 4 |
| Vomiting | 7 | 6 | 8 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain | 6 | 4 | 7 | 7 |
| Constipation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Body as a whole | ||||
| Fever | 7 | 6 | 8 | 5 |
| Chest pain | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Pain | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Respiratory disorders | ||||
| Coughing | 4 | 4 | 10 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 |
| Pneumonia | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Sinusitis | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Sputum increased | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Skin and appendages disorders | ||||
| Rash | 4 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Increased sweating | 3 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| Skin disorder unspecified | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Central/peripheral nervous system | ||||
| Headache | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 |
| Dizziness | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Resistance mechanism disorders | ||||
| Pneumocystis carinii infection | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||||
| Depression | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Adverse events reported by less than 2% of patients in U.S. clinical trials with SPORANOX ®included: adrenal insufficiency, asthenia, back pain, dehydration, dyspepsia, dysphagia, flatulence, gynecomastia, hematuria, hemorrhoids, hot flushes, implantation complication, infection unspecified, injury, insomnia, male breast pain, myalgia, pharyngitis, pruritus, rhinitis, rigors, stomatitis ulcerative, taste perversion, tinnitus, upper respiratory tract infection, vision abnormal, and weight decrease. Edema, hypokalemia and menstrual disorders have been reported in clinical trials with itraconazole capsules.
Post-marketing Experience
Adverse drug reactions that have been first identified during post-marketing experience with SPORANOX ®(all formulations) are listed in Table 4 below. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, reliably estimating their frequency or establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not always possible.
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: | Leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia |
| Immune System Disorders: | Anaphylaxis; anaphylactic, anaphylactoid and allergic reactions; serum sickness; angioneurotic edema |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: | Hypertriglyceridemia |
| Nervous System Disorders: | Peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, tremor |
| Eye Disorders: | Visual disturbances, including vision blurred and diplopia |
| Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: | Transient or permanent hearing loss |
| Cardiac Disorders: | Congestive heart failure |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: | Pulmonary edema |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders: | Pancreatitis |
| Hepatobiliary Disorders: | Serious hepatotoxicity (including some cases of fatal acute liver failure), hepatitis, reversible increases in hepatic enzymes |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: | Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, alopecia, photosensitivity, urticaria |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: | Arthralgia |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders: | Urinary incontinence, pollakiuria |
| Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: | Erectile dysfunction |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: | Peripheral edema |
| Investigations: | Blood creatine phosphokinase increased |
There is limited information on the use of SPORANOX ®during pregnancy. Cases of congenital abnormalities including skeletal, genitourinary tract, cardiovascular and ophthalmic malformations as well as chromosomal and multiple malformations have been reported during post-marketing experience. A causal relationship with SPORANOX ®has not been established. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactionsfor more information.)
Overdosage
Itraconazole is not removed by dialysis. In the event of accidental overdosage, supportive measures should be employed. Contact a certified poison control center for the most up to date information on the management of SPORANOX ®(itraconazole) Oral Solution overdosage (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org). In general, adverse events reported with overdose have been consistent with adverse drug reactions already listed in this package insert for itraconazole. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
How is Sporanox supplied
SPORANOX ®(itraconazole) Oral Solution is available in 150 mL amber glass bottles (NDC 50458-295-15) containing 10 mg of itraconazole per mL.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC50458-295-15
150 mL
SPORANOX
®
(ITRACONAZOLE)
ORAL SOLUTION
10 mg/mL
Each 1 mL contains:
10 mg of itraconazole in an aqueous solution.
Dosage:For information concerning dosage and
administration of SPORANOX
®(itraconazole) oral
solution, please read accompanying
Package Insert.
Storage:Store bottle at or below
25°C (77°F). Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
For any questions concerning this product please call: (1-800) 526-7736.
Rx only
Product of Belgium
Manufactured by:
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Beerse, Belgium
Manufactured for:
Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Titusville, NJ 08560
© 2003 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies
673455

| SPORANOX
itraconazole solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutical Sciences Unlimited Company | 985639841 | api manufacture(50458-295) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica, NV | 400345889 | api manufacture(50458-295) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica, NV | 370005019 | manufacture(50458-295) , analysis(50458-295) | |




