Drug Detail:Symproic (Naldemedine [ nal-dem-e-deen ])
Drug Class: Peripheral opioid receptor antagonists
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SYMPROIC® (naldemedine tablets for oral use)
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Indications and Usage for Symproic
SYMPROIC is an opioid antagonist indicated for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation (OIC) in adult patients with chronic non-cancer pain, including patients with chronic pain related to prior cancer or its treatment who do not require frequent (e.g., weekly) opioid dosage escalation (1)
Symproic Dosage and Administration
Administration (2.1):
- Alteration of analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating SYMPROIC is not required
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to SYMPROIC
- Discontinue SYMPROIC if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued
Dosage (2.2):
- In adults, the recommended dosage is 0.2 mg once daily with or without food
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 0.2 mg naldemedine (3)
Contraindications
- Patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction or at increased risk of recurrent obstruction (4, 5.1)
- Patients with a history of a hypersensitivity reaction to naldemedine (6.1)
Warnings and Precautions
- Gastrointestinal perforation: Consider the overall risk benefit in patients with known or suspected lesions of the GI tract. Monitor for severe, persistent, or worsening abdominal pain; discontinue if development of symptoms (5.1)
- Opioid withdrawal: Consider the overall risk benefit in patients with disruptions to the blood-brain barrier. Monitor symptoms of opioid withdrawal (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) are: abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and gastroenteritis (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. at 1-800-469-0261 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
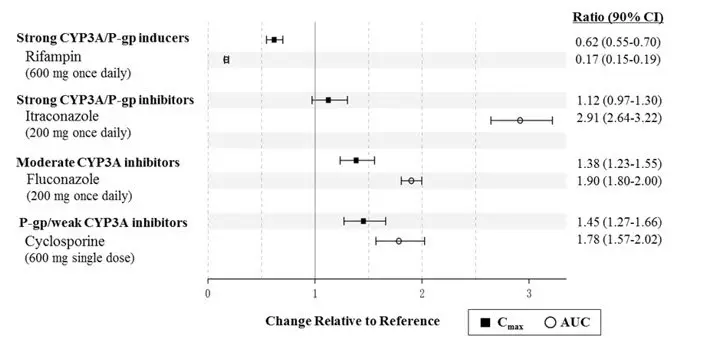
- Strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin): Decreased naldemedine concentrations; avoid concomitant use (7)
- Other opioid antagonists: Potential for additive effect and increased risk of opioid withdrawal; avoid concomitant use (7)
- Moderate (e.g., fluconazole) and strong (e.g., itraconazole) CYP3A4 inhibitors: Increased naldemedine concentrations; monitor for adverse reactions (7)
- P-gp inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine): Monitor for adverse reactions (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May precipitate opioid withdrawal in a fetus (8.1)
- Lactation: Discontinue drug or breastfeeding taking into consideration importance of drug to mother (8.2)
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid in severe impairment (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2021
Related/similar drugs
Amitiza, lubiprostone, Movantik, Relistor, naloxegol, methylnaltrexoneFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Symproic
SYMPROIC is indicated for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation (OIC) in adult patients with chronic non-cancer pain, including patients with chronic pain related to prior cancer or its treatment who do not require frequent (e.g., weekly) opioid dosage escalation.
2. Symproic Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration
- Alteration of analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating SYMPROIC is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to SYMPROIC [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Discontinue SYMPROIC if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 0.2 mg naldemedine; supplied as yellow, round, film-coated, debossed with Shionogi marking above the identifier code 222 on one side and 0.2 on the other side.
4. Contraindications
SYMPROIC is contraindicated in:
- Patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction and patients at increased risk of recurrent obstruction, due to the potential for gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Patients with a history of a hypersensitivity reaction to naldemedine. Reactions have included bronchospasm and rash [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Gastrointestinal Perforation
Cases of gastrointestinal perforation have been reported with use of another peripherally acting opioid antagonist in patients with conditions that may be associated with localized or diffuse reduction of structural integrity in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., peptic ulcer disease, Ogilvie's syndrome, diverticular disease, infiltrative gastrointestinal tract malignancies, or peritoneal metastases). Take into account the overall risk-benefit profile when using SYMPROIC in patients with these conditions or other conditions which might result in impaired integrity of the gastrointestinal tract wall (e.g., Crohn's disease). Monitor for the development of severe, persistent, or worsening abdominal pain; discontinue SYMPROIC in patients who develop this symptom [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Opioid Withdrawal
Clusters of symptoms consistent with opioid withdrawal, including hyperhidrosis, chills, increased lacrimation, hot flush/flushing, pyrexia, sneezing, feeling cold, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting have occurred in patients treated with SYMPROIC [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients having disruptions to the blood-brain barrier may be at increased risk for opioid withdrawal or reduced analgesia. Take into account the overall risk-benefit profile when using SYMPROIC in such patients. Monitor for symptoms of opioid withdrawal in such patients.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Serious and important adverse reactions described elsewhere in labeling include:
- Gastrointestinal perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Opioid withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to SYMPROIC in 1163 patients in clinical trials, including 487 patients with exposures greater than six months and 203 patients with exposures of 12 months.
The following safety data are derived from three double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients with OIC and chronic non-cancer pain: two 12-week studies (Studies 1 and 2) and one 52-week study (Study 3) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
In Studies 1 and 2, patients on laxatives were required to discontinue their use prior to study enrollment. All patients were restricted to bisacodyl rescue treatment during the study. In Study 3, approximately 60% of patients in both treatment groups were on a laxative regimen at baseline; patients were allowed to continue using their laxative regimen throughout the study duration. The safety profile of SYMPROIC relative to placebo was similar regardless of laxative use.
Tables 1 and 2 list common adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of patients receiving SYMPROIC and at an incidence greater than placebo. Table 1 shows pooled 12-week data from Studies 1 and 2. Table 2 shows 12-week data from Study 3.
| Adverse Reaction | SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily N=542 | Placebo N=546 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Abdominal pain† | 8% | 2% |
| Diarrhea | 7% | 2% |
| Nausea | 4% | 2% |
| Gastroenteritis | 2% | 1% |
| Adverse Reaction | SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily N=621 | Placebo N=619 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Abdominal pain† | 11% | 5% |
| Diarrhea | 7% | 3% |
| Nausea | 6% | 5% |
| Vomiting | 3% | 2% |
| Gastroenteritis | 3% | 1% |
Adverse reactions up to 12 months in Study 3 are similar to those listed in Tables 1 and 2 (diarrhea: 11% vs. 5%, abdominal pain: 8% vs. 3%, and nausea: 8% vs. 6% for SYMPROIC and placebo, respectively).
7. Drug Interactions
Table 3 includes drugs with clinically important drug interactions with SYMPROIC and instructions for preventing or managing the interaction.
| Strong CYP3A Inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John's Wort) | |
| Clinical Impact | Significant decrease in plasma naldemedine concentrations, which may reduce efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] |
| Intervention | Avoid use of SYMPROIC with strong CYP3A inducers. |
| Other Opioid Antagonists | |
| Clinical Impact | Potential for additive effect of opioid receptor antagonism and increased risk of opioid withdrawal. |
| Intervention | Avoid use of SYMPROIC with another opioid antagonist. |
| Moderate (e.g., fluconazole, atazanavir, aprepitant, diltiazem, erythromycin) and Strong (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir, saquinavir) CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Increase in plasma naldemedine concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] |
| Intervention | Monitor for potential naldemedine-related adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. |
| P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibitors (e.g., amiodarone, captopril, cyclosporine, quercetin, quinidine, verapamil) | |
| Clinical Impact | Increase in plasma naldemedine concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] |
| Intervention | Monitor for potential naldemedine-related adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SYMPROIC have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1163 patients exposed to SYMPROIC in clinical studies, 183 (16%) were 65 years of age and over, while 37 (3%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness between these and younger patients were observed, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, no age-related alterations in the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine were observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine has not been evaluated. Avoid use of SYMPROIC in patients with severe hepatic impairment. No dose adjustment of SYMPROIC is required in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Single doses of naldemedine up to 100 mg (500 times the recommended dose) and multiple doses of up to 30 mg (150 times the recommended dose) for 10 days have been administered to healthy subjects in clinical studies. Dose-dependent increases in gastrointestinal-related adverse reactions, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea, were observed.
Single doses of naldemedine up to 3 mg (15 times the recommended dose) and multiple doses of 0.4 mg (twice the recommended dose) for 28 days have been administered to patients with OIC in clinical studies. Dose-dependent increases in gastrointestinal-related adverse reactions, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, were observed. Also, chills, hyperhidrosis, and dizziness were reported more frequently at 1 and 3 mg doses and hyperhidrosis at the 0.4 mg dose.
No antidote for naldemedine is known. Hemodialysis is not an effective means to remove naldemedine from the blood [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Symproic Description
SYMPROIC (naldemedine), an opioid antagonist, contains naldemedine tosylate as the active ingredient.
The chemical name for naldemedine tosylate is: 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5α-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-[2-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]morphinan-7-carboxamide 4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid.
The structural formula is:
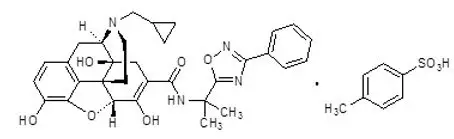
The empirical formula for naldemedine tosylate is C32H34N4O6∙C7H8O3S and the molecular weight is 742.84.
Naldemedine tosylate is a white to light tan powder, soluble in dimethylsulfoxide and methanol, slightly soluble in alcohol and water, and independent of pH.
SYMPROIC (naldemedine) tablets for oral use contain 0.2 mg naldemedine (equivalent to 0.26 mg of naldemedine tosylate).
Excipients are: D-mannitol, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, talc, and yellow ferric oxide.
12. Symproic - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Naldemedine is an opioid antagonist with binding affinities for mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. Naldemedine functions as a peripherally-acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist in tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract, thereby decreasing the constipating effects of opioids.
Naldemedine is a derivative of naltrexone to which a side chain has been added that increases the molecular weight and the polar surface area, thereby reducing its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Naldemedine is also a substrate of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux transporter. Based on these properties, the CNS penetration of naldemedine is expected to be negligible at the recommended dose levels, limiting the potential for interference with centrally-mediated opioid analgesia.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Use of opioids induces slowing of gastrointestinal motility and transit. Antagonism of gastrointestinal mu-opioid receptors by naldemedine inhibits opioid-induced delay of gastrointestinal transit time.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Drug Interaction Studies
14. Clinical Studies
SYMPROIC was evaluated in two replicate, 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Study 1 and Study 2) in which SYMPROIC was used without laxatives in patients with OIC and chronic non-cancer pain.
Patients receiving a stable opioid morphine equivalent daily dose of at least 30 mg for at least 4 weeks before enrollment and self-reported OIC were eligible for clinical trial participation.
Patients with evidence of significant structural abnormalities of the GI tract were not enrolled in these trials.
In Studies 1 and 2, patients had to either be not using laxatives or willing to discontinue laxative use at the time of screening and willing to use only the provided rescue laxatives during the screening and treatment periods.
In Studies 1 and 2, OIC was confirmed through a two-week run in period and was defined as no more than 4 spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) total over 14 consecutive days and less than 3 SBMs in a given week with at least 25% of the SBMs associated with one or more of the following conditions: (1) straining; (2) hard or lumpy stools; (3) having a sensation of incomplete evacuation; and (4) having a sensation of anorectal obstruction/blockage.
An SBM was defined as a bowel movement (BM) without rescue laxative taken within the past 24 hours. Patients with no BMs over the 7 consecutive days prior to and during the 2-week screening period or patients who had never taken laxatives were excluded.
In the screening and treatment periods, bisacodyl was used as rescue laxative if patients had not had a BM for 72 hours and were allowed one-time use of an enema, if after 24 hours of taking bisacodyl they still had not had a BM.
A total of 547 patients in Study 1 and 553 patients in Study 2 were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily or placebo for 12 weeks. Study medication was administered without regard to meals.
The mean age of subjects in Studies 1 and 2 was 54 years; 59% were women; and 80% were white. The most common types of pain in Studies 1 and 2 were back or neck pain (61%). The mean baseline number of SBMs was 1.3 and 1.2 per week for Studies 1 and 2, respectively.
Prior to enrollment, patients were using their current opioid for a mean duration of approximately 5 years. A wide range of types of opioids were used. The mean baseline opioid morphine equivalent daily dosage was 132 mg and 121 mg per day for Studies 1 and 2, respectively.
The efficacy of SYMPROIC was assessed in Studies 1 and 2 using a responder analysis. A responder was defined as a patient who had at least 3 SBMs per week and a change from baseline of at least 1 SBM per week for at least 9 out of the 12 weeks and 3 out of the last 4 weeks in Studies 1 and 2.
The responder rates in Studies 1 and 2 are shown in Table 4.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily (N=273) | Placebo (N=272) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily (N=276) | Placebo (N=274) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] |
|
| CI=Confidence Interval | ||||||
|
||||||
| Responder* | 130 (48%) | 94 (35%) | 13% [5%, 21%] | 145 (53%) | 92 (34%) | 19% [11%, 27%] |
| p value† | 0.0020 | <0.0001 | ||||
In Studies 1 and 2, the mean increase in frequency of SBMs per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of the 12-week treatment period was 3.1 for SYMPROIC vs. 2.0 for placebo (difference 1.0, 95% CI 0.6, 1.5), and 3.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 2.1 for placebo (difference 1.2, 95% CI 0.8, 1.7), respectively.
During week 1 of the treatment period, the mean increase in frequency of SBMs per week from baseline was 3.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.3 for placebo (difference 2.0, 95% CI 1.5, 2.5) in Study 1 and 3.7 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.6 for placebo (difference 2.1, 95% CI 1.5, 2.6) in Study 2.
The mean increase in the frequency of complete SBM (CSBM) per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of 12-week treatment period was 2.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.5 for placebo (difference 0.8, 95% CI 0.4, 1.2) in Study 1 and 2.6 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.6 for placebo (difference 1.1, 95% CI 0.6, 1.5) in Study 2. A CSBM was defined as a SBM that was associated with a sense of complete evacuation.
The change in the frequency of SBMs without straining per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of the treatment period was 1.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 0.7 for placebo (difference 0.6, 95% CI 0.2, 0.9) in Study 1 and 1.8 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.1 for placebo (difference 0.7, 95% CI 0.3, 1.2) in Study 2.
16. How is Symproic supplied
SYMPROIC is supplied as 0.2 mg naldemedine tablets as follows:
- bottle of 30 tablets - NDC 59385-041-30
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: May 2020 |
| MEDICATION GUIDE SYMPROIC® (sim proe' ik) (naldemedine) tablets, for oral use |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about SYMPROIC? |
|
SYMPROIC may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
| What is SYMPROIC? | |
| SYMPROIC is a prescription medicine used to treat constipation that is caused by prescription pain medicines called opioids in adults with long-lasting (chronic) pain that is not caused by active cancer. It is not known if SYMPROIC is safe and effective in children. |
|
Do not take SYMPROIC if you:
|
|
Before you take SYMPROIC, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Other medicines may affect the way SYMPROIC works. | |
How should I take SYMPROIC?
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of SYMPROIC? | |
| See "What is the most important information I should know about SYMPROIC?" | |
| The most common side effects of SYMPROIC include stomach (abdomen) pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting (gastroenteritis). Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of SYMPROIC. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store SYMPROIC?
|
|
| Keep SYMPROIC and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
| General information about the safe and effective use of SYMPROIC. | |
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those in a Medication Guide. Do not take SYMPROIC for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SYMPROIC to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SYMPROIC that is written for health professionals. | |
| What are the ingredients in SYMPROIC? | |
| Active Ingredient: naldemedine tosylate | |
| Inactive ingredients: D-mannitol, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, talc, and yellow ferric oxide. Manufactured for: BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. Raleigh, NC 27612 |
|
| SYM-001-MG-MAY2020 SYMPROIC is a registered trademark of Shionogi & Co., Ltd. For more information, go to www.symproic.com or call 1-800-469-0261. |
|
| SYMPROIC
naldemedine tablet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BioDelivery Sciences International Inc (016058955) |