Drug Detail:Tabrecta (Capmatinib (tablets))
Drug Class: Multikinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TABRECTA® (capmatinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 8/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Pancreatic Toxicity (5.3) | 8/2022 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hypersensitivity Reactions (5.4) | 3/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Tabrecta
TABRECTA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1)
Tabrecta Dosage and Administration
- Select patients for treatment with TABRECTA based on presence of a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping. (2.1)
- Recommended Dosage: 400 mg orally twice daily with or without food. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 150 mg and 200 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Monitor for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients with ILD/pneumonitis. (2.3, 5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests. Withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3, 5.2)
- Pancreatic Toxicity: Monitor amylase and lipase levels. Withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3, 5.3)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Withhold or permanently discontinue TABRECTA based on severity. (2.3, 5.4)
- Risk of Photosensitivity: May cause photosensitivity reactions. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure. (5.5)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) are edema, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, and decreased appetite. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tabrecta
TABRECTA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test.
2. Tabrecta Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment with TABRECTA based on the presence of a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping in tumor or plasma specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)]. If a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping is not detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue if feasible. Information on FDA-approved tests is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TABRECTA is 400 mg orally twice daily with or without food.
Swallow TABRECTA tablets whole. Do not break, crush or chew the tablets.
If a patient misses or vomits a dose, instruct the patient not to make up the dose, but to take the next dose at its scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for the management of adverse reactions are listed in Table 1.
| Dose reduction | Dose and schedule |
| First | 300 mg orally twice daily |
| Second | 200 mg orally twice daily |
Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who are unable to tolerate 200 mg orally twice daily.
The recommended dosage modifications of TABRECTA for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ILD, interstitial lung disease; ULN, upper limit of normal. Grading according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. |
||
| Adverse reaction | Severity | Dosage modification |
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline ALT/AST. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased ALT and/or AST with increased total bilirubin in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | ALT and/or AST greater than 3 times ULN with total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Increased total bilirubin without concurrent increased ALT and/or AST [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 2 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at the same dose; otherwise resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
|
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Increased lipase or amylase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until ≤ Grade 2 or baseline. If recovered to baseline or ≤ Grade 2 within 14 days, resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 3 or Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. |
| Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | All Grades | If hypersensitivity is suspected based on clinical judgment, withhold TABRECTA until resolution of the event. Permanently discontinue TABRECTA in patients who develop serious hypersensitivity reactions. |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 2 | Maintain dose level. If intolerable, consider withholding TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TABRECTA until resolved, then resume TABRECTA at a reduced dose. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TABRECTA. | |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets:
- 150 mg: pale orange brown, ovaloid, curved film-coated with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘DU’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side
- 200 mg: yellow, ovaloid, curved film-coated with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘LO’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
ILD/pneumonitis, which can be fatal, occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 4.8% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1, with 1.9% of patients experiencing Grade 3 ILD/pneumonitis and one patient experiencing death (0.3%). Nine patients (2.4%) discontinued TABRECTA due to ILD/pneumonitis. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher ILD/pneumonitis was 1.8 months (range: 0.2 months to 1.7 years).
Monitor for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Immediately withhold TABRECTA in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 15% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1. Grade 3 or 4 increased ALT/AST occurred in 7% of patients. Three patients (0.8%) discontinued TABRECTA due to increased ALT/AST. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher increased ALT/AST was 1.8 months (range: 0.5 to 46.4 months).
Monitor liver function tests (including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin) prior to the start of TABRECTA, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months of treatment, then once a month or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop increased transaminases or bilirubin. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Pancreatic Toxicity
Elevations in amylase and lipase levels occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Increased amylase/lipase occurred in 14% of patients treated with TABRECTA in GEOMETRY mono-1. Grade 3 and 4 increased amylase/lipase occurred in 7% and 1.9% of patients, respectively. Three patients (0.8%) discontinued TABRECTA due to increased amylase/lipase. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher increased amylase/lipase was 2 months (range: 0.03 to 31.1 months). Pancreatitis (Grade 3) occurred in one patient (0.3%); TABRECTA was permanently discontinued for this event.
Monitor amylase and lipase at baseline and regularly during treatment with TABRECTA. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, temporarily withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions occurred in patients treated with TABRECTA in clinical trials other than GEOMETRY mono-1 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity included pyrexia, chills, pruritus, rash, decreased blood pressure, nausea and vomiting. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, temporarily withhold or permanently discontinue TABRECTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Risk of Photosensitivity
Based on findings from animal studies, there is a potential risk of photosensitivity reactions with TABRECTA [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]. In GEOMETRY mono-1, it was recommended that patients use precautionary measures against ultraviolet exposure such as use of sunscreen or protective clothing during treatment with TABRECTA. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure during treatment with TABRECTA.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TABRECTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of capmatinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at exposures less than the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- ILD/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pancreatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The safety of TABRECTA was evaluated in GEOMETRY mono-1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients received TABRECTA 400 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (N = 373). Among patients who received TABRECTA, 37% were exposed for at least 6 months and 22% were exposed for at least one year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 53% of patients who received TABRECTA. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients included dyspnea (7%), pneumonia (7%), pleural effusion (4.3%), musculoskeletal pain (3.8%), general physical health deterioration (2.9%), ILD/pneumonitis (2.7%), edema (2.4%), and vomiting (2.4%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 0.5% of patients who received TABRECTA, including pneumonitis (0.3%) and death, not otherwise specified (0.3%).
Permanent discontinuation of TABRECTA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 17% of patients. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥ 1%) leading to permanent discontinuation of TABRECTA were ILD/pneumonitis (2.4%), edema (2.4%), fatigue (1.3%), and pneumonia (1.1%).
Dose interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 57% of patients who received TABRECTA. Adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in > 2% of patients who received TABRECTA included edema, increased blood creatinine, nausea, increased lipase, vomiting, increased ALT, dyspnea, pneumonia, fatigue, increased amylase, increased AST, musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, and increased blood bilirubin.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 26% of patients who received TABRECTA. Adverse reactions requiring dosage reductions in > 2% of patients who received TABRECTA included edema, increased ALT and increased blood creatinine.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients who received TABRECTA were edema, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, vomiting, dyspnea, cough, and decreased appetite.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in GEOMETRY mono-1.
| aEdema includes edema peripheral, generalized edema, face edema, edema, localized edema, edema genital, eyelid edema, peripheral swelling, scrotal edema, and penile edema. bMusculoskeletal pain includes arthralgia, back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, pain in jaw, spinal pain. cFatigue includes fatigue and asthenia. dPyrexia includes pyrexia and body temperature increased. eCough includes cough, upper airway cough syndrome, and productive cough. fPneumonia includes pneumonia aspiration, pneumonia, pneumonia influenzal, pneumonia bacterial, lower respiratory tract infection, and lung abscess. gRash includes rash, dermatitis acneiform, rash maculo-papular, eczema, erythema multiforme, rash macular, dermatitis, rash erythematous, rash pustular, dermatitis bullous, and rash vesicular. hDizziness includes dizziness, vertigo, and vertigo positional. |
||
| Adverse reactions | TABRECTA (N = 373) |
|
| Grades 1 to 4 (%) | Grades 3 to 4
(%) |
|
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||
| Edemaa | 59 | 13 |
| Musculoskeletal painb | 40 | 4.3 |
| Fatiguec | 34 | 8 |
| Pyrexiad | 14 | 0.8 |
| Weight decreased | 11 | 0.5 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 46 | 2.4 |
| Vomiting | 28 | 2.4 |
| Constipation | 19 | 0.8 |
| Diarrhea | 19 | 0.5 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea | 25 | 7 |
| Coughe | 21 | 0.5 |
| Pneumoniaf | 13 | 6 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 21 | 1.1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Rashg | 13 | 0.5 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizzinessh | 13 | 0.5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in < 10% of patients treated with TABRECTA included pruritus (including allergic pruritus), ILD/pneumonitis, cellulitis, acute kidney injury (including renal failure), urticaria, and acute pancreatitis.
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in GEOMETRY mono-1.
| aThe denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 359 to 364 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||
| Laboratory abnormalities | TABRECTAa | |
| Grades 1 to 4 (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Decreased albumin | 72 | 1.9 |
| Increased creatinine | 65 | 0.5 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 39 | 9 |
| Increased amylase | 34 | 4.7 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 32 | 0.6 |
| Increased gamma-glutamyltransferase | 30 | 6 |
| Increased lipase | 29 | 9 |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 28 | 6 |
| Decreased phosphate | 26 | 4.4 |
| Increased potassium | 25 | 4.1 |
| Decreased sodium | 24 | 6 |
| Decreased glucose | 23 | 0.3 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 45 | 14 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 25 | 1.7 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 24 | 2.8 |
Other Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported following administration of TABRECTA: hypersensitivity.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on TABRECTA
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Coadministration of TABRECTA with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increased capmatinib exposure, which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions of TABRECTA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Closely monitor patients for adverse reactions during coadministration of TABRECTA with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of TABRECTA with a strong CYP3A inducer decreased capmatinib exposure. Coadministration of TABRECTA with a moderate CYP3A inducer may also decrease capmatinib exposure. Decreases in capmatinib exposure may decrease TABRECTA anti-tumor activity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of TABRECTA with strong and moderate CYP3A inducers.
7.2 Effect of TABRECTA on Other Drugs
CYP1A2 Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA increased the exposure of a CYP1A2 substrate, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and CYP1A2 substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the CYP1A2 substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA increased the exposure of a P-gp substrate and a BCRP substrate, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and P-gp or BCRP substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the P-gp or BCRP substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
MATE1 and MATE2K Substrates
Coadministration of TABRECTA may increase the exposure of MATE1 and MATE2K substrates, which may increase the adverse reactions of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If coadministration is unavoidable between TABRECTA and MATE1 or MATE2K substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions, decrease the MATE1 or MATE2K substrate dosage in accordance with the approved prescribing information.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], TABRECTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on TABRECTA use in pregnant women. Oral administration of capmatinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations at maternal exposures less than the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In rats, maternal toxicity (reduced body weight gain and food consumption) occurred at 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose). Fetal effects included reduced fetal weights, irregular/incomplete ossification, and increased incidences of fetal malformations (e.g., abnormal flexure/inward malrotation of hindpaws/forepaws, thinness of forelimbs, lack of/reduced flexion at the humerus/ulna joints, and narrowed or small tongue) at doses of ≥ 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose).
In rabbits, no maternal effects were detected at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.5 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose). Fetal effects included small lung lobe at ≥ 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.016 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose), and reduced fetal weights, irregular/incomplete ossification and increased incidences of fetal malformations (e.g., abnormal flexure/malrotation of hindpaws/forepaws, thinness of forelimbs/hindlimbs, lack of/reduced flexion at the humerus/ulna joints, small lung lobes, narrowed or small tongue) at the dose of 60 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of capmatinib or its metabolites in either human or animal milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, TABRECTA can cause malformations at doses less than the human exposure based on AUC at the 400 mg twice daily clinical dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status for females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with TABRECTA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TABRECTA in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In GEOMETRY mono-1, 61% of the 373 patients were 65 years or older and 18% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in the safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (baseline creatinine clearance [CLcr] 60 to 89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) or moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. TABRECTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min).
11. Tabrecta Description
Capmatinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is 2-Fluoro-N-methyl-4-[7-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)imidazo[1,2-b][1,2,4]triazin-2-yl]benzamide—hydrogen chloride—water (1/2/1). The molecular formula for capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is C23H21Cl2FN6O2. The relative molecular mass is 503.36 g/mol for the dihydrochloride monohydrate salt and 412.43 g/mol for the free base. The chemical structure for capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is shown below:
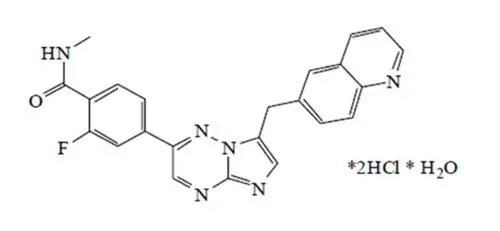
Capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is a yellow powder with a pKa1 of 0.9 (calculated) and pKa2 of 4.5 (experimentally). Capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate is slightly soluble in acidic aqueous solutions at pH 1 and 2 and of further decreasing solubility towards neutral condition. The log of the distribution coefficient (n-octanol/acetate buffer pH 4.0) is 1.2.
TABRECTA is supplied for oral use as ovaloid, curved film-coated tablets with beveled edges, unscored containing 150 mg (pale orange brown color) or 200 mg (yellow color) capmatinib (equivalent to 183.00 mg or 244.00 mg respectively of capmatinib dihydrochloride monohydrate). Each tablet strength contains colloidal silicon dioxide; crospovidone; magnesium stearate; mannitol; microcrystalline cellulose; povidone; and sodium lauryl sulfate as inactive ingredients.
The 150 mg tablet coating contains ferric oxide, red; ferric oxide, yellow; ferrosoferric oxide; hypromellose; polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000; talc; and titanium dioxide. The 200 mg tablet coating contains ferric oxide, yellow; hypromellose; polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000; talc; and titanium dioxide.
16. How is Tabrecta supplied
How Supplied
| Strength | Description | Tablets per bottle | NDC number |
| 150 mg | Pale orange brown, ovaloid, curved film-coated tablet with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘DU’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side. | 56 | 0078-0709-56 |
| 200 mg | Yellow, ovaloid, curved film-coated tablet with beveled edges, unscored, debossed with ‘LO’ on one side and ‘NVR’ on the other side. | 56 | 0078-0716-56 |
Storage
Dispense in the original package with the desiccant cartridge. Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
Discard any unused TABRECTA remaining after 6 weeks of first opening the bottle.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Inform patients of the risks of severe or fatal ILD/pneumonitis. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor liver function. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pancreatic Toxicity
Inform patients that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor pancreatic function. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that there is a risk of hypersensitivity reactions with TABRECTA. Advise patients to stop taking TABRECTA and immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Risk of Photosensitivity
Inform patients that there is a potential risk of photosensitivity reactions with TABRECTA. Advise patients to limit direct ultraviolet exposure by using sunscreen or protective clothing during treatment with TABRECTA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TABRECTA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
T2023-15
| TABRECTA
capmatinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TABRECTA
capmatinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |






