Drug Detail:Tafinlar (Dabrafenib [ da-braf-e-nib ])
Drug Class: Multikinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TAFINLAR® (dabrafenib) capsules, for oral use
TAFINLAR® (dabrafenib) tablets for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Solid Tumors (1.6) | 6/2022 |
| Indications and Usage, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma (1.7) | 3/2023 |
| Indications and Usage, Limitations of Use (1.8) | 6/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration, Patient Selection (2.1) | 3/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration, Recommended Dosage (2.2) | 3/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration, Administration (2.3) | 3/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration, Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions (2.4) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, New Primary Malignancies (5.1) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hemorrhage (5.3) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Cardiomyopathy (5.4) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Uveitis (5.5) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Serious Febrile Reactions (5.6) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Serious Skin Toxicities (5.7) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hyperglycemia (5.8) | 3/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (5.11) | 5/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Tafinlar
TAFINLAR is a kinase inhibitor indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.1, 2.1)
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for:
- the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.2, 2.1)
- the adjuvant treatment of patients with melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and involvement of lymph node(s), following complete resection. (1.3, 2.1)
- the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1.4, 2.1)
- the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) with BRAF V600E mutation and with no satisfactory locoregional treatment options. (1.5, 2.1)
- the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with BRAF V600E mutation who have progressed following prior treatment and have no satisfactory alternative treatment options. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1.6, 2.1)
- the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with low-grade glioma (LGG) with a BRAF V600E mutation who require systemic therapy. (1.7, 2.1)
Limitations of Use: TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with colorectal cancer because of known intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibition. (1.8, 12.1). TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF solid tumors. (5.2)
Tafinlar Dosage and Administration
- The recommended dosage of TAFINLAR in adult patients is 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) orally twice daily. The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR in pediatric patients is based on body weight. Take TAFINLAR at least 1 hour before or at least 2 hours after a meal. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
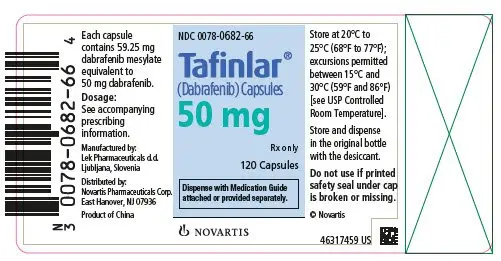
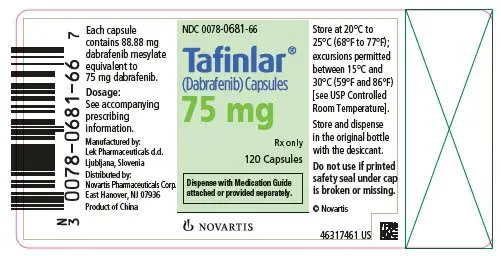
TAFINLAR Capsules: 50 mg, 75 mg (3)
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension: 10 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- New Primary Malignancies, Cutaneous and Non-Cutaneous: Can occur when TAFINLAR is administered as a single agent or with trametinib. Monitor patients for new malignancies prior to, or while on therapy, and following discontinuation of treatment. (5.1, 2.4)
- Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-type Tumors: Increased cell proliferation can occur with BRAF inhibitors. (5.2, 2.1)
- Hemorrhage: Major hemorrhagic events can occur in patients receiving TAFINLAR with trametinib. Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding. (5.3)
- Cardiomyopathy: Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib, after one month of treatment, then every 2 to 3 months thereafter. (5.4, 2.4)
- Uveitis: Perform ophthalmological evaluation for any visual disturbances. (5.5, 2.4)
- Serious Febrile Reactions: Incidence and severity of pyrexia are increased with TAFINLAR and trametinib. (5.6, 2.4)
-
Serious Skin Toxicities: Monitor for skin toxicities. Discontinue for intolerable Grade 2 or for Grade 3 or 4 rash not improving within 3 weeks despite interruption of TAFINLAR. Permanently discontinue for severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs). (5.7, 2.4)
- Hyperglycemia: Monitor serum glucose levels in patients with preexisting diabetes or hyperglycemia. (5.8)
- Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (G6PD): Closely monitor for hemolytic anemia. (5.9)
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): Interrupt treatment for suspected HLH. Discontinue treatment if HLH is confirmed. (5.11)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective non-hormonal method of contraception. (5.12, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) for TAFINLAR as a single agent are hyperkeratosis, headache, pyrexia, arthralgia, papilloma, alopecia, and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome. (6.1)
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) for TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib include:
- Unresectable or metastatic melanoma: pyrexia, rash, chills, headache, arthralgia, and cough. (6.1)
- Adjuvant treatment of melanoma: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, headache, rash, chills, diarrhea, vomiting, arthralgia, and myalgia. (6.1)
- NSCLC: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin, decreased appetite, edema, rash, chills, hemorrhage, cough, and dyspnea. (6.1)
- Adult patients with solid tumors: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, rash, chills, headache, hemorrhage, cough, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, myalgia, arthralgia, and edema. (6.1)
- Pediatric patients with solid tumors: pyrexia, rash, vomiting, fatigue, dry skin, cough, diarrhea, dermatitis acneiform, headache, abdominal pain, nausea, hemorrhage, constipation, and paronychia. (6.1)
- Pediatric patients with LGG: pyrexia, rash, headache, vomiting, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, diarrhea, dry skin, nausea, hemorrhage, abdominal pain, and dermatitis acneiform. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Avoid concurrent administration of strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8. (7.1)
- Concomitant use with agents that are sensitive substrates of CYP3A4, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2B6 may result in loss of efficacy of these agents. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
-
Lactation: Do not breastfeed. (8.2)
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: May impair fertility. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tafinlar
1.1 BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
TAFINLAR® is indicated as a single agent for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test.
1.2 BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.3 Adjuvant Treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the adjuvant treatment of patients with melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and involvement of lymph node(s), following complete resection [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.4 BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with BRAF V600E mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.5 BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) with BRAF V600E mutation and with no satisfactory locoregional treatment options [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.6 BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Solid Tumors
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with BRAF V600E mutation who have progressed following prior treatment and have no satisfactory alternative treatment options [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) [see Clinical Studies (14.6)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
1.7 BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma
TAFINLAR is indicated, in combination with trametinib, for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with low-grade glioma (LGG) with a BRAF V600E mutation who require systemic therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.8 Limitations of Use
- TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with colorectal cancer because of known intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibition [see Indications and Usage (1.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
- TAFINLAR is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF solid tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2. Tafinlar Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Melanoma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR as a single agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)].
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
NSCLC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
- Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
ATC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in ATC is not currently available.
Solid Tumors
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.6)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in solid tumors other than melanoma and NSCLC is not currently available.
Low-Grade Glioma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with TAFINLAR and trametinib [see Clinical Studies (14.7)]. An FDA-approved test for the detection of BRAF V600E mutation in LGG is not currently available.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
TAFINLAR Capsules
Adult Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in adult patients is 150 mg taken orally twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Pediatric Patients
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR capsules in pediatric patients who weigh at least 26 kg is based on body weight (Table 1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. A recommended dosage of TAFINLAR capsules has not been established in patients who weigh less than 26 kg.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 26 to 37 kg | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| 38 to 50 kg | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| 51 kg or greater | 150 mg orally twice daily |
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
The recommended dosage for TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension is based on body weight (Table 2) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
| 8 to 9 kg | 20 mg twice daily |
| 10 to 13 kg | 30 mg twice daily |
| 14 to 17 kg | 40 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg | 50 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg | 60 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg | 70 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg | 80 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg | 90 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg | 100 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg | 110 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg | 130 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg | 150 mg twice daily |
- The recommended duration of treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma or solid tumors, metastatic NSCLC, or locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer is until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
- The recommended duration of treatment in the adjuvant melanoma setting is until disease recurrence or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year.
- The recommended duration of treatment for pediatric patients with LGG is until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for recommended trametinib dosing information.
2.3 Administration
- Take TAFINLAR at the same time each day, approximately 12 hours apart.
- Take TAFINLAR at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Do not take a missed dose of TAFINLAR within 6 hours of the next dose of TAFINLAR.
- If vomiting occurs after TAFINLAR administration, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose at its scheduled time.
TAFINLAR Capsules
- Do not open, crush, or break TAFINLAR capsules.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension
- Prior to use of the oral suspension, instruct caregivers (and if appropriate, patients) on proper dosing and administration of TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
- Do not swallow whole, chew or crush TAFINLAR tablets for oral suspension.
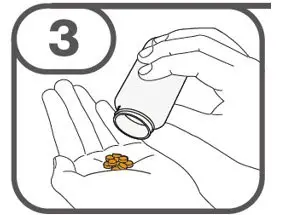
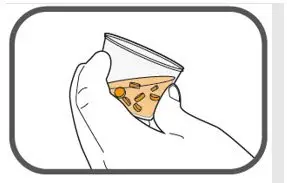
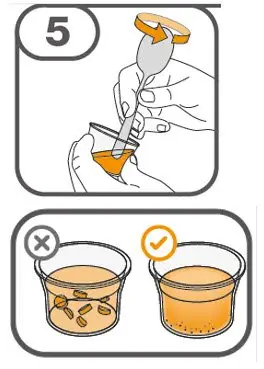
Preparation and Administration
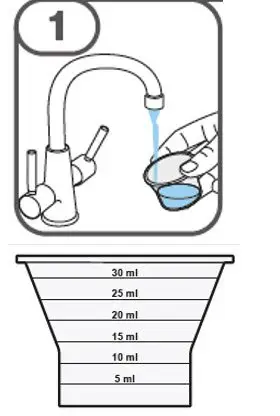
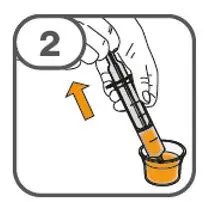
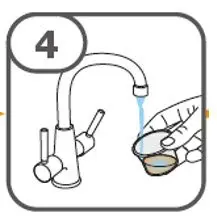
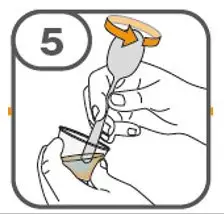
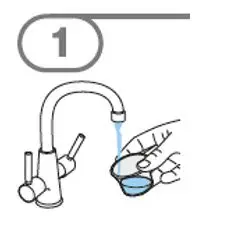
- Prepare suspension with approximately 5 mL of water for 1 to 4 tablets, and approximately 10 mL of water for 5 to 15 tablets in the provided cup.
- Gently stir the water and prescribed number of tablets with the handle of a teaspoon until the tablets are fully dissolved. It may take at least 3 minutes to fully dissolve the tablets. Once the tablets for oral suspension are dissolved, the suspension will be cloudy white.
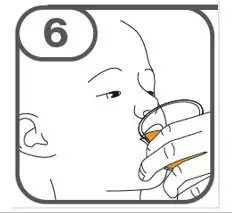
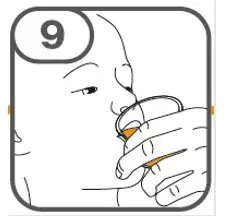
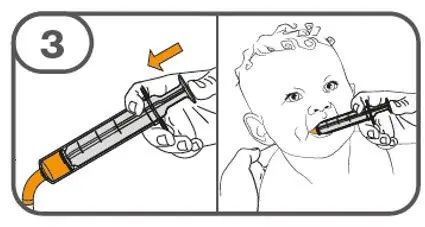
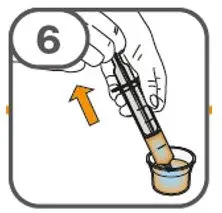
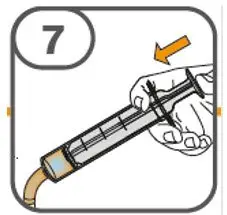
- Administer suspension immediately after preparation from cup, oral dosing syringe or feeding tube.
- Discard suspension if not administered within 30 minutes after preparation.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Tables 3 and 4.
| Recommended Dosage | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily | 150 mg orally twice daily |
| First dose reduction | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily | 100 mg orally twice daily |
| Second dose reduction | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily | 75 mg orally twice daily |
| Third dose reduction | N/A | N/A | 50 mg orally twice daily |
| Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate TAFINLAR capsules 50 mg orally twice daily. | ||
| Body Weight
(Recommended dosage) | First Dose Reduction | Second Dose Reduction | Third Dose Reduction |
| Tablets for oral suspension twice daily | |||
| 8 to 9 kg (20 mg twice daily) | 10 mg twice daily | N/A | N/A |
| 10 to 13 kg (30 mg twice daily) | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | N/A |
| 14 to 17 kg (40 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 18 to 21 kg (50 mg twice daily) | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily |
| 22 to 25 kg (60 mg twice daily) | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 26 to 29 kg (70 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 20 mg twice daily |
| 30 to 33 kg (80 mg twice daily) | 50 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 34 to 37 kg (90 mg twice daily) | 60 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 38 to 41 kg (100 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily |
| 42 to 45 kg (110 mg twice daily) | 70 mg twice daily | 60 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| 46 to 50 kg (130 mg twice daily) | 90 mg twice daily | 70 mg twice daily | 40 mg twice daily |
| ≥ 51 kg (150 mg twice daily) | 100 mg twice daily | 80 mg twice daily | 50 mg twice daily |
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with TAFINLAR are presented in Table 5.
| a National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.0. b See Tables 3 and 4 for recommended dose reductions of TAFINLAR. c Dose modifications are not recommended for TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib for the following adverse reactions of trametinib: retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis, and uncomplicated venous thromboembolism. Dose modification of TAFINLAR is not required for new primary cutaneous malignancies. |
|
| Severity of Adverse Reactiona | Dosage Modification for TAFINLARb |
| New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Non-Cutaneous RAS Mutation-positive Malignancies | Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until LVEF improves to at least the institutional LLN and absolute decrease to less than or equal to 10% compared to baseline, then resume at same dose. |
| Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| For mild or moderate uveitis does not respond to ocular therapy, or for severe uveitis, withhold TAFINLAR for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Febrile Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR until fever resolves, then resume TAFINLAR at same or lower dose. |
|
|
| Skin Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR for up to 3 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
| Other Adverse Reactionsc, including Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Withhold TAFINLAR.
|
|
|
| Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR. |
Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with trametinib.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TAFINLAR Capsules:
- 50 mg: Dark red capsule imprinted with ‘GS TEW’ and ‘50 mg’.
- 75 mg: Dark pink capsule imprinted with ‘GS LHF’ and ‘75 mg’.
TAFINLAR Tablets for Oral Suspension:
- 10 mg: White to slightly yellow, round, biconvex 6 mm tablet debossed with “D” on one side and “NVR” on the other, contains berry flavor.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 New Primary Malignancies
Cutaneous Malignancies
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (cuSCC), and keratoacanthomas occurred in 11% and 4% of patients, respectively. Basal cell carcinoma and new primary melanoma occurred in 4% and 1% of patients, respectively.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], the incidence of cuSCC (including keratoacanthomas) occurred in 2% of patients. Basal cell carcinoma and new primary melanoma occurred in 3% and < 1% of patients, respectively.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, new primary melanoma occurred in < 1% of patients.
Perform dermatologic evaluations prior to initiation of TAFINLAR, every 2 months while on therapy, and for up to 6 months following discontinuation of TAFINLAR.
Non-Cutaneous Malignancies
Based on its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR may promote the growth and development of malignancies with activation of RAS through mutation or other mechanisms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
In the pooled adult safety populations of TAFINLAR monotherapy and TAFINLAR administered with trametinib [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], non-cutaneous malignancies occurred in 1% of patients.
Monitor patients receiving TAFINLAR for signs or symptoms of non-cutaneous malignancies. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for RAS mutation-positive non-cutaneous malignancies [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors
In vitro experiments have demonstrated paradoxical activation of MAP-kinase signaling and increased cell proliferation in BRAF wild-type cells which are exposed to BRAF inhibitors. Confirm evidence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation status prior to initiation of TAFINLAR as a single agent or in combination with trametinib [see Indications and Usage (1.6), Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.3 Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage, including major hemorrhage defined as symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ, can occur when TAFINLAR is administered with trametinib. Fatal cases have been reported.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], hemorrhagic events occurred in 17% of patients; gastrointestinal hemorrhage occurred in 3% of patients; intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 0.6% of patients; fatal hemorrhage occurred in 0.5% of patients. The fatal events were cerebral hemorrhage and brainstem hemorrhage.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, hemorrhagic events occurred in 25% of patients; the most common type of bleeding was epistaxis (16%). Serious events of bleeding occurred in 3.6% of patients and included gastrointestinal hemorrhage (1.2%), cerebral hemorrhage (0.6%) uterine hemorrhage (0.6%), post-procedural hemorrhage (0.6%), and epistaxis (0.6%).
Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for all Grade 4 hemorrhagic events and for any Grade 3 hemorrhagic events that do not improve. Withhold TAFINLAR for Grade 3 hemorrhagic events; if improved, resume at the next lower dose level.
5.4 Cardiomyopathy
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], cardiomyopathy, defined as a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥ 10% from baseline and below the institutional lower limit of normal (LLN), occurred in 6% of patients. Development of cardiomyopathy resulted in dose interruption or discontinuation of TAFINLAR in 3% and < 1% of patients, respectively. Cardiomyopathy resolved in 45 of 50 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, cardiomyopathy, defined as a decrease in LVEF ≥ 10% from baseline and below the institutional LLN, occurred in 9% of patients.
Assess LVEF by echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan before initiation of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib, one month after initiation, and then at 2- to 3-month intervals while on treatment. Withhold TAFINLAR for symptomatic cardiomyopathy or asymptomatic LV dysfunction of > 20% from baseline that is below institutional LLN. Resume TAFINLAR at the same dose level upon recovery of cardiac function to at least the institutional LLN for LVEF and absolute decrease ≤ 10% compared to baseline [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.5 Uveitis
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], uveitis occurred in 1% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], uveitis occurred in 2% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, uveitis occurred in 1.2% of patients.
Treatment employed in clinical trials included steroid and mydriatic ophthalmic drops. Monitor patients for visual signs and symptoms of uveitis (e.g., change in vision, photophobia, eye pain). If iritis is diagnosed, administer ocular therapy and continue TAFINLAR without dose modification. If severe uveitis (i.e., iridocyclitis) or if mild or moderate uveitis does not respond to ocular therapy, withhold TAFINLAR and treat as clinically indicated. Resume TAFINLAR at the same or lower dose if improves to Grade 0 or 1. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for persistent Grade 2 or greater uveitis of > 6 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Serious Febrile Reactions
Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure, can occur with TAFINLAR.
The incidence and severity of pyrexia are increased when TAFINLAR is administered with trametinib compared with TAFINLAR as a single agent [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], fever (serious and non-serious) occurred in 30% of patients. Approximately 13% of these patients experienced 3 or more discrete episodes. Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills occurred in 6% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], fever occurred in 58% of patients. Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration or renal failure occurred in 5% of patients. Fever was complicated by hypotension in 4%, dehydration in 3%, syncope in 2%, renal failure in 1%, and severe chills/rigors in < 1% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], pyrexia occurred in 66% of patients.
Withhold TAFINLAR when used as monotherapy, and both TAFINLAR and trametinib when used in combination, if the patient’s temperature is ≥ 100.4°F. In case of recurrence, therapy can also be interrupted at the first symptom of pyrexia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Fever may be complicated by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure. Evaluate for signs and symptoms of infection and monitor serum creatinine and other evidence of renal function during and following severe pyrexia. If appropriate, TAFINLAR, or both TAFINLAR and trametinib when used in combination, may be restarted if the patient has recovered from the febrile reaction for at least 24 hours, either at the same or lower dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Administer antipyretics as secondary prophylaxis when resuming TAFINLAR if patient had a prior episode of severe febrile reaction or fever associated with complications. Administer corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone 10 mg daily) for at least 5 days for second or subsequent pyrexia if temperature does not return to baseline within 3 days of onset of pyrexia, or for pyrexia associated with complications, such as dehydration, hypotension, renal failure, or severe chills/rigors, and there is no evidence of active infection.
5.7 Serious Skin Toxicities
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), which can be life-threatening or fatal, have been reported during treatment with TAFINLAR administered with trametinib [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], other serious skin toxicity occurred in < 1% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, serious adverse events of skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders occurred in 1.8% of patients.
Monitor for new or worsening serious skin reactions. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR for SCARs [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. For other skin toxicities, withhold TAFINLAR for intolerable or severe skin toxicity. Resume TAFINLAR at a lower dose in patients with improvement or recovery from skin toxicity within 3 weeks. Permanently discontinue TAFINLAR if skin toxicity has not improved within 3 weeks [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.8 Hyperglycemia
TAFINLAR Monotherapy (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], 14% of patients with a history of diabetes that received TAFINLAR required more intensive hypoglycemic therapy. Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia occurred in 3% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Adult): In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], 15% of patients with a history of diabetes who had received TAFINLAR with trametinib required more intensive hypoglycemic therapy. Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia occurred in 2% of patients.
TAFINLAR Administered with Trametinib (Pediatric): In the pooled safety population, Grade 3 and Grade 4 hyperglycemia events occurred in < 1% of patients.
Monitor serum glucose levels upon initiation and as clinically appropriate when TAFINLAR is administered in patients with preexisting diabetes or hyperglycemia. Initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as clinically indicated.
5.9 Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
TAFINLAR, which contains a sulfonamide moiety, confers a potential risk of hemolytic anemia in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Monitor patients with G6PD deficiency for signs of hemolytic anemia while taking TAFINLAR.
5.10 Risks Associated with Combination Treatment
TAFINLAR is indicated for use in combination with trametinib. Review the prescribing information for trametinib for information on the serious risks of trametinib prior to initiation of TAFINLAR with trametinib.
5.11 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) has been observed in the post-marketing setting when TAFINLAR was administered with trametinib. If HLH is suspected, interrupt treatment. If HLH is confirmed, discontinue treatment and initiate appropriate management of HLH.
5.12 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Dabrafenib was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at doses three times greater than the human exposure at the recommended adult clinical dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective non-hormonal contraception, since TAFINLAR can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective, during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Serious Febrile Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Serious Skin Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
There are additional adverse reactions associated with trametinib. Refer to the trametinib prescribing information for additional information.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Safety Pools
The TAFINLAR monotherapy pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to TAFINLAR 150 mg orally, taken twice daily as a single agent in 586 patients with various solid tumors, including BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma, enrolled in BREAK-2, BREAK-3, BREAK-MB, BRF113220, and BRF112680. Among these 586 patients who received TAFINLAR as a single agent, 46% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 15% were exposed for greater than one year.
The pooled safety population for TAFINLAR administered with trametinib (Adult) described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to TAFINLAR 150 mg orally, twice daily administered in combination with trametinib 2 mg orally, once daily, in 1087 patients enrolled in METRIC, MEK113583, MEK111504, COMBI-d, COMBI-v, COMBI-AD, and BRF113928 with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, adjuvant melanoma or NSCLC. Among these 1087 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib, 70% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 21% were exposed for greater than one year.
Pediatric Safety Pool
The pediatric pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to weight-based TAFINLAR orally, twice daily administered in combination with trametinib in 166 pediatric patients across two trials: a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive glioma requiring systemic therapy (Study G2201; n = 123) and a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients with refractory or recurrent solid tumors with MAPK pathway activation (Study X2101; n = 43) [see Clinical Studies (14.6, 14.7)]. Among 166 patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib, 84% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 70% were exposed for greater than one year. The most common (> 20%) adverse reactions were pyrexia (66%), rash (54%), headache (40%), vomiting (38%), musculoskeletal pain (36%), fatigue (31%), dry skin (31%), diarrhea (30%), nausea (26%), epistaxis and other bleeding events (25%), abdominal pain (24%), and dermatitis acneiform (23%). The most common (> 2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased neutrophil count (20%), increased alanine aminotransferase (3.1%), and increased aspartate aminotransferase (3.1%).
Unresectable or Metastatic BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
TAFINLAR as a Single Agent
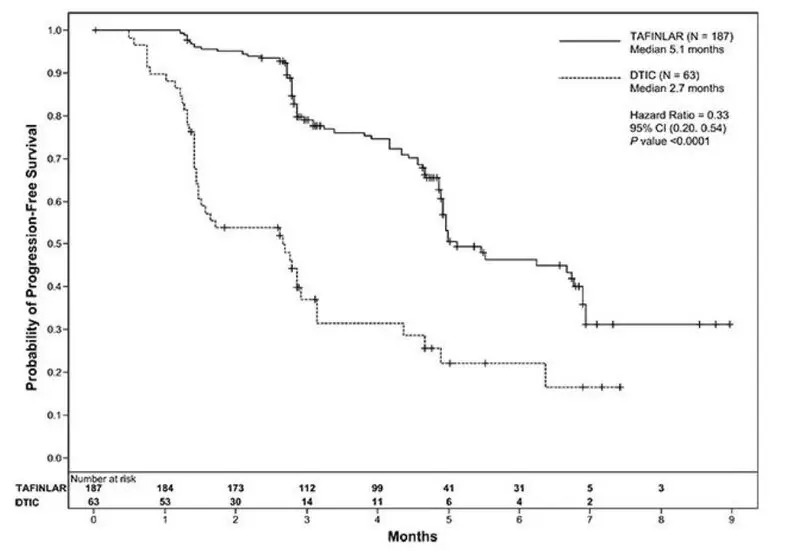
The safety of TAFINLAR was evaluated in BREAK-3, a multi-center, international, open-label, randomized (3:1), controlled trial allocated 250 patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E mutation-positive melanoma to receive TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily (n = 187) or dacarbazine 1000 mg/m2 intravenously every 3 weeks (n = 63) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF or cardiac valve morphology (≥ Grade 2), corrected QT interval ≥ 480 milliseconds on electrocardiogram, or a known history of G6PD deficiency. The median duration on treatment was 4.9 months for patients treated with TAFINLAR and 2.8 months for dacarbazine-treated patients. The population exposed to TAFINLAR was 60% male, 99% White, and had a median age of 53 years.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients treated with TAFINLAR were, in order of decreasing frequency: hyperkeratosis, headache, pyrexia, arthralgia, papilloma, alopecia, and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES).
The incidence of adverse events resulting in permanent discontinuation of study medication in the BREAK-3 study was 3% for patients treated with TAFINLAR and 3% for patients treated with dacarbazine. The most frequent (≥ 2%) adverse reactions leading to dose reduction of TAFINLAR were pyrexia (9%), PPES (3%), chills (3%), fatigue (2%), and headache (2%). Table 6 and Table 7 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, of TAFINLAR as a single agent in the BREAK-3 study.
| Abbreviations: cuSCC, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, includes squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and keratoacanthoma; NA, not applicable. a Adverse reactions, reported using MedDRA and graded using NCI CTCAE version 4.0 for assessment of toxicity. b Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to hyperkeratosis (n = 1) and constipation (n = 1). c Includes skin papilloma and papilloma. d Cases of cuSCC were required to be reported as Grade 3 per protocol. |
||||
| TAFINLAR
N = 187 | Dacarbazine
N = 59 |
|||
| Adverse Reactions | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4b (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Hyperkeratosis | 37 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 22 | NA | 2 | NA |
| Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Rash | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headache | 32 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexia | 28 | 3 | 10 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Arthralgia | 27 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Back pain | 12 | 3 | 7 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Neoplasms | ||||
| Papillomac | 27 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| cuSCCd | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||||
| Cough | 12 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Constipation | 11 | 2 | 14 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 10 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| a Adverse reactions, reported using MedDRA and graded using NCI CTCAE version 4.0 for assessment of toxicity. b Grade 4 laboratory abnormality limited to hypophosphatemia (n = 1). |
||||
| TAFINLAR
N = 187 | Dacarbazine N = 59 |
|||
| Laboratory Abnormality | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
| Hyperglycemia | 50 | 6 | 43 | 0 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 37 | 6b | 14 | 2 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 19 | 0 | 14 | 2 |
| Hyponatremia | 8 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions observed in less than 10% of patients (N = 586) treated with TAFINLAR were:
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis
Immune System: Hypersensitivity manifesting as bullous rash
Renal and Urinary: Interstitial nephritis
TAFINLAR with Trametinib
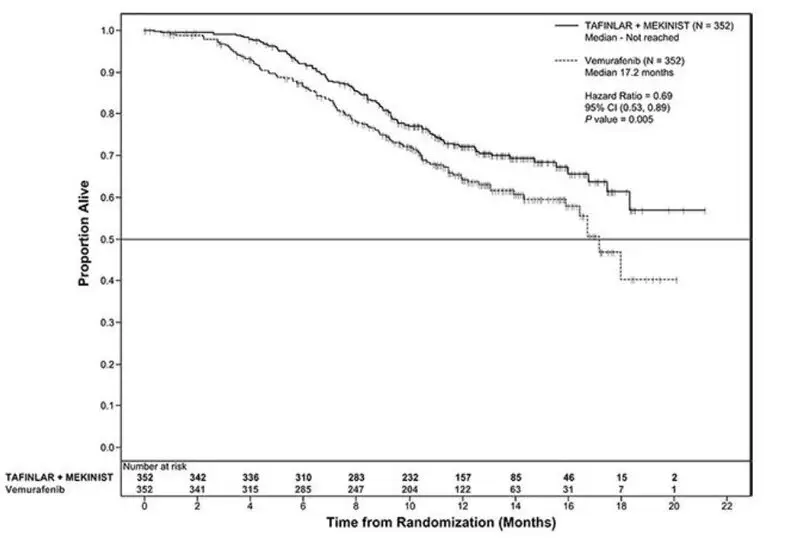
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 559 patients with previously untreated, unresectable or metastatic, BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma who received TAFINLAR in two trials, the COMBI-d study (n = 209), a multi-center, double-blind, randomized (1:1), active-controlled trial and the COMBI-v study (n = 350), a multi-center, open-label, randomized (1:1), active-controlled trial. In both trials, patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Both trials excluded patients with abnormal LVEF, history of acute coronary syndrome within 6 months, history of Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association), history of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) or retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED), QTcB interval ≥ 480 msec, treatment refractory hypertension, uncontrolled arrhythmias, active brain metastases, or known history of G6PD deficiency [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Among these 559 patients, 199 (36%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months to 12 months while 185 (33%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 55 years (range: 18 to 91), 57% were male, 98% were White, 72% had baseline ECOG performance status 0 and 28% had ECOG performance status 1, 64% had M1c stage disease, 35% had elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) at baseline, and 0.5% had a history of brain metastases.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) for TAFINLAR in patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib in the COMBI-d and COMBI-v studies were: pyrexia, rash, chills, headache, arthralgia, and cough. The demographics and baseline tumor characteristics of patients enrolled in the COMBI-d study are summarized in Clinical Studies [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib had a median duration of exposure of 11 months (range: 3 days to 30 months) to TAFINLAR. Among the 209 patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib, 26% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months to 12 months while 46% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 1 year.
In the COMBI-d study, adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TAFINLAR occurred in 11% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent was pyrexia (1.9%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of TAFINLAR occurred in 26% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent were pyrexia (14%), neutropenia (1.9%), rash (1.9%), and chills (1.9%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of TAFINLAR occurred in 56% of patients who received TAFINLAR plus trametinib; the most frequent were pyrexia (35%), chills (11%), vomiting (7%), nausea (5%), and decreased ejection fraction (5%).
Table 8 and Table 9 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, observed in the COMBI-d study.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to headache (n = 1). c Includes rash generalized, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash vesicular, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, and rash folliculitis. |
||||||
| Pooled TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 559 | COMBI-d Study | |||||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 209 | TAFINLAR
N = 211 |
|||||
| Adverse Reactions | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4b (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
| General | ||||||
| Pyrexia | 54 | 5 | 57 | 7 | 33 | 1.9 |
| Chills | 31 | 0.5 | 31 | 0 | 17 | 0.5 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||||
| Rashc | 32 | 1.1 | 42 | 0 | 27 | 1.4 |
| Dry skin | 10 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||||
| Headache | 30 | 0.9 | 33 | 0.5 | 30 | 1.4 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 0.2 | 14 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||||
| Arthralgia | 25 | 0.9 | 26 | 0.9 | 31 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 15 | 0.2 | 13 | 0.5 | 13 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||||||
| Cough | 20 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||||
| Constipation | 13 | 0.2 | 13 | 0.5 | 10 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||||
| Nasopharyngitis | 12 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR across the COMBI-d and COMBI-v studies (N = 559) observed in less than 10% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were:
Gastrointestinal: Colitis, gastrointestinal perforation, pancreatitis
Immunologic: Sarcoidosis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: Panniculitis
| a For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 556. b For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 208 for the combination arm, 208-209 for the TAFINLAR arm. c Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to hyperglycemia (n = 4), hyponatremia and hypophosphatemia (each n = 1) in the pooled combination arm; hyperglycemia (n = 1) in the COMBI-d study combination arm; hypophosphatemia (n = 1) in the TAFINLAR arm. |
||||||
| Laboratory Abnormalities | Pooled TAFINLAR plus Trametinib N = 559a | COMBI-d Study | ||||
| TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 209b | TAFINLAR
N = 211b |
|||||
| All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4c (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4c (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4c (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||||||
| Hyperglycemia | 60 | 4.7 | 65 | 6 | 57 | 4.3 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 38 | 6 | 38 | 3.8 | 35 | 7 |
| Hyponatremia | 25 | 8 | 24 | 6 | 14 | 2.9 |
| Hepatic | ||||||
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 49 | 2.7 | 50 | 1.0 | 25 | 0.5 |
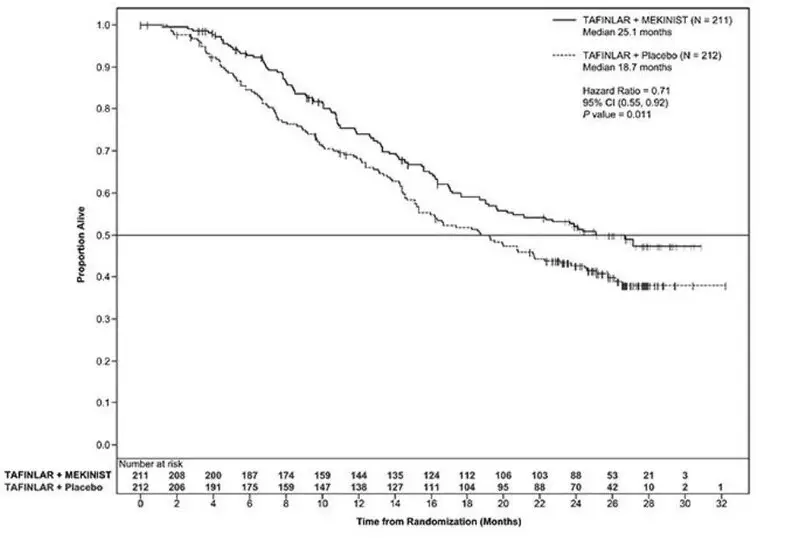
Adjuvant Treatment of BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Melanoma
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 435 patients with Stage III melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations following complete resection who received at least one dose of study therapy in the COMBI-AD study [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily for 12 months. The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF; history of acute coronary syndromes, coronary angioplasty, or stenting within 6 months; Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association); QTc interval ≥ 480 msec; treatment refractory hypertension; uncontrolled arrhythmias; or history of RVO.
Patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib had a median duration of exposure of 11 months (range: 0 to 12) to TAFINLAR. Among the 435 patients receiving TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib, 71% were exposed to TAFINLAR for > 6 months. The median age of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib was 50 years (range: 18 to 89), 56% were male, 99% were White, 92% had baseline ECOG performance status 0, and 8% had baseline ECOG performance status of 1.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, headache, rash, chills, diarrhea, vomiting, arthralgia, and myalgia.
Adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation, dose reduction, or dose interruption of TAFINLAR occurred in 25%, 35%, and 66% of patients, respectively; the most frequent for each were pyrexia and chills.
Table 10 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 20% of patients who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes pyrexia and hyperpyrexia. c Includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. d Includes headache and tension headache. e Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash macular, rash generalized, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash pruritic, nodular rash, rash vesicular, and rash pustular. f Includes myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, and musculoskeletal chest pain. |
||||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 435 | Placebo
N = 432 |
||
| All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
|
| General | ||||
| Pyrexiab | 63 | 5 | 11 | < 1 |
| Fatiguec | 59 | 5 | 37 | < 1 |
| Chills | 37 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 40 | < 1 | 20 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 33 | < 1 | 15 | < 1 |
| Vomiting | 28 | < 1 | 10 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headached | 39 | 1 | 24 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Rashe | 37 | < 1 | 16 | < 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Arthralgia | 28 | < 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Myalgiaf | 20 | < 1 | 14 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions observed in less than 20% of patients in the COMBI-AD study who received TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were: blurred vision (6%), ejection fraction decreased (5%), rhabdomyolysis (< 1%), and sarcoidosis (< 1%).
The laboratory abnormalities are summarized in Table 11.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The incidence is based on the number of patients who had both a baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement: TAFINLAR plus Trametinib (range: 429 to 431) and placebo arm (range: 426 to 428). |
||||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametiniba
N = 435 | Placeboa
N = 432 |
||
| All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) | All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||||
| Hyperglycemia | 63 | 3 | 47 | 2 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 42 | 7 | 10 | < 1 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 25 | < 1 | < 1 | 0 |
| Hepatic | ||||
| Increased AST | 57 | 6 | 11 | < 1 |
| Increased ALT | 48 | 5 | 18 | < 1 |
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 38 | 1 | 6 | < 1 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Neutropenia | 47 | 6 | 12 | < 1 |
| Lymphopenia | 26 | 5 | 6 | < 1 |
| Anemia | 25 | < 1 | 6 | < 1 |
Trial COMBI-APlus (Pyrexia Management Study)
COMBI-APlus evaluated the impact of pyrexia-related outcomes of a revised pyrexia management algorithm in patients who received dabrafenib administered with trametinib in the adjuvant treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma after complete resection. The pyrexia management algorithm interrupted both dabrafenib and trametinib when patient’s temperature is ≥ 100.4°F.
Grade 3-4 pyrexia occurred in 4.3% of patients, hospitalizations due to pyrexia occurred in 5.1% of patients, pyrexia with complications (dehydration, hypotension, renal dysfunction, syncope, severe chills) occurred in 2.2% of patients, and treatment discontinuation due to pyrexia occurred in 2.5% of patients.
Metastatic, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in 93 patients with previously untreated (n = 36) and previously treated (n = 57) metastatic BRAF V600E mutation-positive NSCLC in a multi-center, multi-cohort, non-randomized, open-label trial (Study BRF113928). Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The trial excluded patients with abnormal LVEF, history of acute coronary syndrome within 6 months, history of Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association), QTc interval ≥ 480 msec, treatment refractory hypertension, uncontrolled arrhythmias, active brain metastases, history of interstitial lung disease or pneumonitis, or history or current RVO [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Among these 93 patients, 53 (57%) were exposed to TAFINLAR and trametinib for > 6 months and 27 (29%) were exposed to TAFINLAR and trametinib for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 65 years (range: 41 to 91); 46% were male; 85% were White; 32% had baseline ECOG performance status 0 and 61% had ECOG performance status 1; 98% had non-squamous histology; and 12% were current smokers, 60% were former smokers, and 28% had never smoked.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 93 patients were: pyrexia, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin, decreased appetite, edema, rash, chills, hemorrhage, cough, and dyspnea.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of TAFINLAR occurred in 18% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (2.2%), decreased ejection fraction (2.2%), and respiratory distress (2.2%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of TAFINLAR occurred in 35% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (10%), diarrhea (4.3%), nausea (4.3%), vomiting (4.3%), and neutropenia (3.2%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of TAFINLAR occurred in 62% of patients; the most frequent were pyrexia (27%), vomiting (11%), neutropenia (8%), and chills (6%).
Table 12 and Table 13 present adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, of TAFINLAR administered with trametinib in Study BRF113928.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes fatigue, malaise, and asthenia. c Includes peripheral edema, edema, and generalized edema. d Includes rash, rash generalized, rash papular, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, and rash pustular. e Includes hemoptysis, hematoma, epistaxis, purpura, hematuria, subarachnoid hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, urinary bladder hemorrhage, contusion, hematochezia, injection site hemorrhage, pulmonary hemorrhage, and retroperitoneal hemorrhage. |
||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 93 |
|
| All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
|
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 55 | 5 |
| Fatigueb | 51 | 5 |
| Edemac | 28 | 0 |
| Chills | 23 | 1.1 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea | 45 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 33 | 3.2 |
| Diarrhea | 32 | 2.2 |
| Decreased appetite | 29 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Dry skin | 31 | 1.1 |
| Rashd | 28 | 3.2 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhagee | 23 | 3.2 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Cough | 22 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 20 | 5 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions for TAFINLAR observed in less than 10% of patients with NSCLC receiving TAFINLAR administered with trametinib were:
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis
Renal and Urinary: Tubulointerstitial nephritis
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 90. b For these laboratory tests, the denominator is 91. |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 93 |
|
| All
Grades (%) | Grades
3 and 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistrya | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 71 | 9 |
| Hyponatremia | 57 | 17 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 36 | 7 |
| Increased creatinine | 21 | 1.1 |
| Hepatica | ||
| Increased blood alkaline phosphatase | 64 | 0 |
| Increased AST | 61 | 4.4 |
| Increased ALT | 32 | 6 |
| Hematologyb | ||
| Leukopenia | 48 | 8 |
| Anemia | 46 | 10 |
| Neutropenia | 44 | 8 |
| Lymphopenia | 42 | 14 |
Advanced BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Tumors
Study BRF117019
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in a multi-cohort, multi-center, non-randomized, open-label study in adult patients with cancers with the BRAF V600E mutation (Study BRF117019). A total of 206 patients were enrolled in the trial, 36 of whom were enrolled in the ATC cohort, 105 were enrolled in specific solid tumor cohorts, and 65 in other malignancies [see Clinical Studies (14.5, 14.6)]. Patients received TAFINLAR 150 mg orally twice daily and trametinib 2 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Among these 206 patients, 103 (50%) were exposed to TAFINLAR for ≥ 1 year and 101 (49%) were exposed to trametinib for ≥ 1 year. The median age was 60 years (range: 18 to 89); 56% were male; 79% were White; and 34% had baseline ECOG performance status 0 and 60% had ECOG performance status 1.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Serious adverse reactions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (11%) and pneumonia (6%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.9% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Fatal adverse reactions that occurred in > 1% of patients included sepsis (1.9%).
Permanent treatment discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 13% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent treatment discontinuation in > 1% of patients included nausea (1.5%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 55% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (22%), chills (9%), fatigue (6%), neutropenia (6%), and nausea (5%).
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 44% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (18%), chills (8%), and fatigue (6%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are listed in Table 14 and Table 15.
Table 14 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study BRF117019.
| aNCI CTCAE version 4.0. bIncludes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. cIncludes peripheral edema and peripheral swelling. dIncludes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash pustular, and rash papular. eIncludes epistaxis, hematuria, contusion, hematoma, hemoptysis, conjunctival hemorrhage, hematochezia, rectal hemorrhage, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, melena, purpura, eye contusion, eye hemorrhage, gastric hemorrhage, gingival bleeding, hematemesis, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhagic stroke, hemothorax, increased tendency to bruise, large intestinal hemorrhage, mouth hemorrhage, petechiae, pharyngeal hemorrhage, prothrombin time prolonged, pulmonary hematoma, retinal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, and vitreous hemorrhage. fIncludes cough and productive cough. gIncludes myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, and musculoskeletal pain. |
||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametiniba
(N = 206) |
|
| All Grades
(%) | Grade 3 or 4
(%) |
|
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 55 | 4.9 |
| Fatigueb | 50 | 5 |
| Chills | 30 | 0.5 |
| Peripheral edemac | 22 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea | 40 | 1.5 |
| Constipation | 27 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 27 | 1.5 |
| Diarrhea | 26 | 2.9 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Rashd | 40 | 2.4 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Headache | 30 | 1.5 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhagee | 29 | 4.4 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Coughf | 29 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||
| Myalgiag | 24 | 0.5 |
| Arthralgia | 23 | 0.5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 20% of adult patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib included ejection fraction decreased (8%), uveitis (1.9%) and hypersensitivity (1.9%).
Table 15 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study BRF117019.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 199 to 202 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametiniba | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 61 | 8 |
| Decreased sodium | 35 | 10 |
| Decreased magnesium | 24 | 0 |
| Increased creatinine | 21 | 1.5 |
| Hepatic | ||
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 51 | 5 |
| Increased AST | 51 | 4.6 |
| Increased ALT | 39 | 3 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 44 | 9 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Solid Tumors in Pediatric Patients
Study CTMT212X2101 (X2101)
The safety of TAFINLAR when administered with trametinib was evaluated in Study X2101, a multi-center, open-label, multi-cohort study in pediatric patients (n = 48) with refractory or recurrent solid tumors [see Clinical Studies (14.6)]. The median duration of exposure to TAFINLAR in Parts C (dose escalation) and D (cohort expansion) was 20.8 and 24.9 months, respectively. The median duration of exposure to trametinib in Parts C and D was 20.8 and 24.4 months, respectively. The median age of pediatric patients who received TAFINLAR with trametinib was 9 years (range: 1 to 17).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients who received TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Serious adverse reactions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (25%) and ejection fraction decreased (6%). Permanent treatment discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 21% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent treatment discontinuation in > 3% of patients included ALT increased (6%), AST increased (4.2%) and ejection fraction decreased (4.2%). Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (56%), vomiting (19%), neutropenia (13%), rash (13%), ejection fraction decreased (6%), and uveitis (6%). Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 25% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (13%).
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are listed in Table 16 and Table 17.
Table 16 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study X2101.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.0. b Includes fatigue, asthenia, and malaise. c Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash papular, rash pustular, and rash macular. d Includes dermatitis acneiform and acne. e Includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper. f Includes epistaxis, hematuria, contusion, hematoma, petechiae, rectal hemorrhage, and red blood cell count decreased. |
||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametiniba
(N = 48) |
|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| General | ||
| Pyrexia | 75 | 17 |
| Fatigueb | 48 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
| Rashc | 73 | 2.1 |
| Dry skin | 48 | 0 |
| Dermatitis acneiformd | 40 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Vomiting | 52 | 4.2 |
| Diarrhea | 42 | 2.1 |
| Abdominal paine | 33 | 4.2 |
| Nausea | 33 | 2.1 |
| Constipation | 23 | 0 |
| Respiratory system | ||
| Cough | 44 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Headache | 35 | 0 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhagef | 33 | 0 |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Paronychia | 23 | 0 |
Table 17 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study X2101.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. aThe denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 39 to 48 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametiniba | |
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 65 | 2.2 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 48 | 2.1 |
| Hypocalcemia | 40 | 2.1 |
| Decreased phosphate | 38 | 0 |
| Decreased magnesium | 33 | 2.1 |
| Hypernatremia | 27 | 0 |
| Hypokalemia | 21 | 2.1 |
| Hepatic | ||
| Increased AST | 55 | 4.2 |
| Increased ALT | 40 | 6 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 28 | 6 |
| Increased total bilirubin | 21 | 2.1 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 60 | 6 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 49 | 28 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Low-Grade Glioma in Pediatric Patients
Study CDRB436G2201 (G2201)
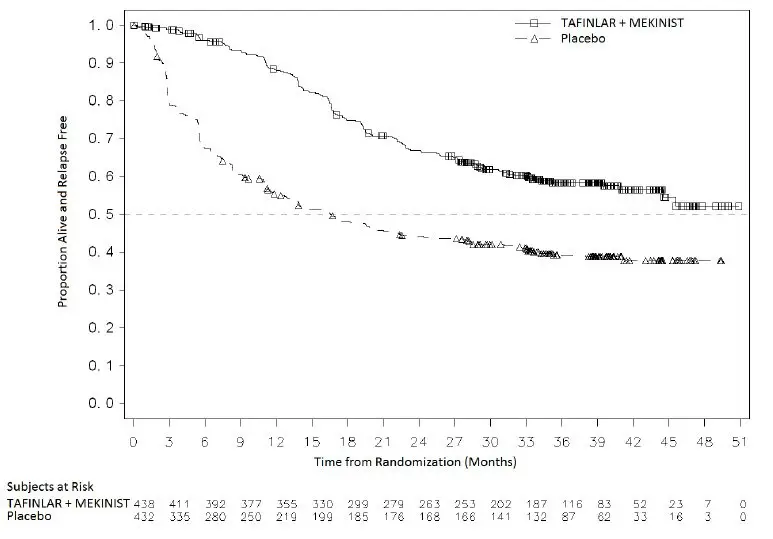
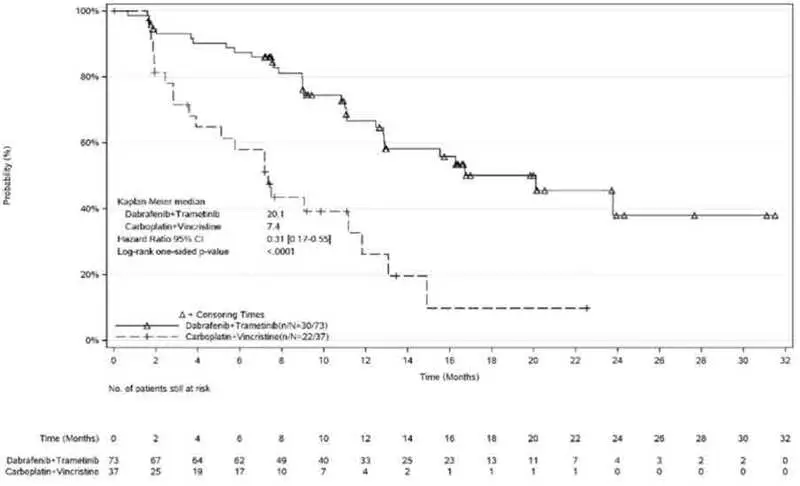
The safety of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib was evaluated in pediatric patients 1 to < 18 years of age in Study G2201. Patients with low-grade glioma (LGG) who required first systemic therapy were randomized (2:1) to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 73) or carboplatin plus vincristine (n = 33). Nine patients crossed over from the carboplatin plus vincristine arm to the TAFINLAR and trametinib arm. Pediatric patients received weight-based TAFINLAR orally twice daily administered in combination with trametinib until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Patients in the control arm received carboplatin and vincristine at doses of 175 mg/m2 and 1.5 mg/m2, respectively in 10-week induction course followed by eight 6-week cycles of maintenance therapy or until disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Among patients with low-grade glioma who were randomized to TAFINLAR plus trametinib (n = 73), 95% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 71% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of these patients was 10 years (range: 1 to 17); 60% female; 75% White, 7% Asian, 2.7% Black or African American, 4% other race and 11% where race was unknown or not reported.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 40% of these patients. Serious adverse reactions in > 3% of patients included pyrexia (14%) and vomiting (4%).
Permanent discontinuation of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 4% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of TAFINLAR included chills, fatigue, pyrexia, weight increased, and headache.
Dosage interruptions of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 73% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included pyrexia (53%).
Dose reductions of TAFINLAR due to an adverse reaction occurred in 48% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 2% of patients included rash (2.7%). The most common (≥ 15%) adverse reactions were pyrexia (68%), rash (51%), headache (47%), vomiting (34%), musculoskeletal pain (34%), fatigue (33%), diarrhea (29%), dry skin (26%), nausea (25%), hemorrhage (25%), abdominal pain (25%), dermatitis acneiform (22%), dizziness (15%), upper respiratory tract infection (15%), and weight increased (15%).
The most common (≥ 20%) laboratory abnormalities that worsened from baseline were leukopenia (59%), increased alkaline phosphatase (55%), anemia (46%), decreased neutrophils (44%), increased AST (37%), decreased magnesium (34%), increased magnesium (32%), decreased platelets (30%), increased ALT (29%), and increased lymphocytes (24%).
Table 18 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study G2201.
| a NCI CTCAE version 4.03. b Includes diarrhea, colitis, enterocolitis, and enteritis. c Includes abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain. d Includes stomatitis, cheilitis, mouth ulceration, aphthous ulcer, and glossitis. e Includes pyrexia and body temperature increased. f Includes fatigue and asthenia. g Includes headache and migraine with aura. h Includes dizziness and vertigo. i Includes peripheral neuropathy, peripheral motor neuropathy, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy, paresthesia, neuralgia, hypoaesthesia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy. j Includes epistaxis, post-procedural hemorrhage, hematuria, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and hemorrhage intracranial. k Includes rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash pustular, rash papular, rash erythematous, eczema, erythema multiforme, dermatitis, dermatitis exfoliative, skin exfoliation, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, and dermatitis bullous. l Includes dermatitis acneiform, acne, and acne pustular. m Includes back pain, myalgia, pain in extremity, arthralgia, bone pain, non-cardiac chest pain, neck pain, and musculoskeletal stiffness. |
||||
| Adverse Reactions | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 73 | Carboplatin plus Vincristine
N = 33 |
||
| All Grades
(%) | Grade ≥ 3
(%) | All Grades
(%) | Grade ≥ 3
(%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Vomiting | 34 | 1 | 48 | 3 |
| Diarrheab | 29 | 0 | 18 | 6 |
| Nausea | 25 | 0 | 45 | 0 |
| Abdominal painc | 25 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Constipation | 12 | 0 | 36 | 0 |
| Stomatitisd | 10 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| General | ||||
| Pyrexiae | 68 | 8 | 18 | 3 |
| Fatiguef | 33 | 0 | 39 | 0 |
| Nervous system | ||||
| Headacheg | 47 | 1 | 33 | 3 |
| Dizzinessh | 15 | 0 | 9 | 3 |
| Peripheral neuropathyi | 7 | 0 | 45 | 6 |
| Vascular | ||||
| Hemorrhagej | 25 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||||
| Rashk | 51 | 2.7 | 18 | 3 |
| Dry skin | 26 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Dermatitis acneiforml | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 3 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||||
| Musculoskeletal painm | 34 | 0 | 30 | 0 |
| Pain in jaw | 1.4 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | ||||
| Decreased appetite | 5 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal | ||||
| Oropharyngeal pain | 11 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Psychiatric | ||||
| Anxiety | 1.4 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Immune system | ||||
| Hypersensitivity | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Infections and infestations | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 15 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications | ||||
| Infusion related reaction | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| Investigations | ||||
| Weight increased | 15 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
Table 19 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study G2201.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase. a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 70 to 73 in D + T arm and 9 to 33 in C + V arm based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. |
||||
| Laboratory Abnormality | TAFINLAR plus Trametinib
N = 73 | Carboplatin plus Vincristine
N = 33 |
||
| All Grades
(%) | Grade 3 or 4
(%) | All Grades
(%) | Grade 3 or 4
(%) |
|
| Hepatic | ||||
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 55 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Increased AST | 37 | 1.4 | 55 | 0 |
| Increased ALT | 29 | 3 | 61 | 9 |
| Chemistry | ||||
| Decreased magnesium | 34 | 4.1 | 76 | 6 |
| Increased magnesium | 32 | 0 | 24 | 3 |
| Increased potassium | 15 | 4.2 | 21 | 6 |
| Decreased calcium | 14 | 4.1 | 22 | 9 |
| Decreased potassium | 8 | 1.4 | 70 | 0 |
| Decreased phosphate | 7 | 2.7 | 33 | 3 |
| Decreased sodium | 5 | 1.4 | 27 | 6 |
| Increased serum fasting glucose | 0 | 0 | 44 | 0 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Decreased leukocytes | 59 | 0 | 91 | 18 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 46 | 0 | 94 | 36 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 44 | 17 | 84 | 75 |
| Decreased platelets | 30 | 0 | 73 | 18 |
| Increased lymphocytes | 24 | 0 | 13 | 3.1 |
| Decreased lymphocytes | 16 | 1.4 | 56 | 6 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of TAFINLAR in combination with trametinib. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: SCAR (including DRESS and SJS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Immune System: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on TAFINLAR
Strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 may increase the concentration of dabrafenib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Substitution of strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 is recommended during treatment with TAFINLAR. If concomitant use of strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 is unavoidable, monitor patients closely for adverse reactions when taking strong inhibitors.
7.2 Effects of TAFINLAR on Other Drugs
Dabrafenib decreased the systemic exposures of midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate), S-warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate), and R-warfarin (a CYP3A4/CYP1A2 substrate) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor international normalized ratio (INR) levels more frequently in patients receiving warfarin during initiation or discontinuation of dabrafenib. Coadministration of TAFINLAR with other substrates of these enzymes, including dexamethasone or hormonal contraceptives, can result in decreased concentrations and loss of efficacy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]. Substitute for these medications or monitor patients for loss of efficacy if use of these medications is unavoidable.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There is insufficient data in pregnant women exposed to TAFINLAR to assess the risks. Dabrafenib was teratogenic and embryotoxic in rats at doses three times greater than the human exposure at the recommended adult clinical dose of 150 mg twice daily (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined female fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats conducted during the period of organogenesis, developmental toxicity consisted of embryo-lethality, ventricular septal defects, and variation in thymic shape at a dabrafenib dose of 300 mg/kg/day [approximately three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on area under the curve (AUC)]. At doses of 20 mg/kg/day or greater (equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC), rats demonstrated delays in skeletal development and reduced fetal body weight.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dabrafenib in human milk, or the effects of dabrafenib on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks following the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TAFINLAR.
Contraception
Based on data from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TAFINLAR can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose. Counsel patients to use a non-hormonal method of contraception since TAFINLAR can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Males
To avoid potential drug exposure to pregnant partners and female partners of reproductive potential, advise male patients (including those who have had vasectomies) with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with TAFINLAR and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential that TAFINLAR may impair fertility. A reduction in fertility was observed in female rats at dose exposures equivalent to the human exposure at the recommended adult dose. A reduction in the number of corpora lutea was noted in pregnant rats at dose exposures approximately three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Advise male patients of the potential risk for impaired spermatogenesis which may be irreversible. Effects on spermatogenesis have been observed in animals treated with dabrafenib at dose exposures up to three times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
12. Tafinlar - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dabrafenib is an inhibitor of some mutated forms of BRAF kinases with in vitro IC50 values of 0.65, 0.5, and 1.84 nM for BRAF V600E, BRAF V600K, and BRAF V600D enzymes, respectively. Dabrafenib also inhibits wild-type BRAF and CRAF kinases with IC50 values of 3.2 and 5.0 nM, respectively, and other kinases, such as SIK1, NEK11, and LIMK1 at higher concentrations. Some mutations in the BRAF gene, including those that result in BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth [see Indications and Usage (1)]. Dabrafenib inhibits cell growth of various BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo.
Dabrafenib and trametinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Use of dabrafenib and trametinib in combination resulted in greater growth inhibition of BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor cell lines in vitro and prolonged inhibition of tumor growth in BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumor xenografts compared with either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway re-activation has been identified as a mechanism of intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibitors [see Indications and Usage (1.8)].
| TAFINLAR
dabrafenib capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| TAFINLAR
dabrafenib capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| TAFINLAR
dabrafenib tablet, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |




![The following chemical structure for Dabrafenib mesylate is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name for dabrafenib mesylate is N-{3-[5-(2-amino-4-pyrimidinyl)-2-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]-2-fluorophenyl}-2,6-difluorobenzene sulfonamide, methanesulfonate salt. It has the molecular formula C23H20F3N5O2S2•CH4O3S and a molecular weight of 615.68.](https://cdn.themeditary.com/images/2023/09/05/tafinlar-01.webp)