Drug Detail:Tamiflu (Oseltamivir [ os-el-tam-ih-veer ])
Drug Class: Neuraminidase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TAMIFLU® (oseltamivir phosphate) capsules, for oral use
TAMIFLU® (oseltamivir phosphate) for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 1999
Indications and Usage for Tamiflu
TAMIFLU is an influenza neuraminidase inhibitor (NAI) indicated for:
- Treatment of acute, uncomplicated influenza A and B in patients 2 weeks of age and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours. (1.1)
- Prophylaxis of influenza A and B in patients 1 year and older. (1.2)
Limitations of Use:
- Not a substitute for annual influenza vaccination. (1.3)
- Consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use. (1.3)
- Not recommended for patients with end-stage renal disease not undergoing dialysis. (1.3)
Tamiflu Dosage and Administration
Treatment of influenza
- Adults and adolescents (13 years and older): 75 mg twice daily for 5 days (2.2)
- Pediatric patients 1 to 12 years of age: Based on weight twice daily for 5 days (2.2)
- Pediatric patients 2 weeks to less than 1 year of age: 3mg/kg twice daily for 5 days (2.2)
- Renally impaired adult patients (creatinine clearance >30-60 mL/min): Reduce to 30 mg twice daily for 5 days (2.4)
- Renally impaired adult patients (creatinine clearance >10-30 mL/min): Reduce to 30 mg once daily for 5 days (2.4)
- ESRD patients on hemodialysis: Reduce to 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg after every hemodialysis cycle. Treatment duration not to exceed 5 days (2.4)
- ESRD patients on CAPD: Reduce to a single 30 mg dose immediately (2.4)
Prophylaxis of influenza
- Adults and adolescents (13 years and older): 75 mg once daily for at least 10 days (2.3)
- -
- Community outbreak: 75 mg once daily for up to 6 weeks (2.3)
- Pediatric patients 1 to 12 years of age: Based on weight once daily for 10 days (2.3)
- -
- Community outbreak: Based on weight once daily for up to 6 weeks (2.3)
- Renally impaired adult patients (creatinine clearance >30-60 mL/min): Reduce to 30 mg once daily (2.4)
- Renally impaired adult patients (creatinine clearance >10-30 mL/min): Reduce to 30 mg once every other day (2.4)
- ESRD patients on hemodialysis: Reduce to 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg after alternate hemodialysis cycles for the recommended duration of prophylaxis (2.4)
- ESRD patients on CAPD: Reduce to 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg once weekly for the recommended duration of prophylaxis (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Capsules: 30 mg, 45 mg, 75 mg (3)
- For oral suspension: 360 mg oseltamivir base supplied as powder (constituted to a final concentration of 6 mg/mL) (3)
Contraindications
Patients with known serious hypersensitivity to oseltamivir or any of the components of TAMIFLU (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious skin/hypersensitivity reactions such as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme: Discontinue TAMIFLU and initiate appropriate treatment if allergic-like reactions occur or are suspected. (5.1)
- Neuropsychiatric events: Patients with influenza, including those receiving TAMIFLU, particularly pediatric patients, may be at an increased risk of confusion or abnormal behavior early in their illness. Monitor for signs of abnormal behavior. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (>1% and more common than with placebo):
- Treatment studies – Nausea, vomiting, headache. (6.1)
- Prophylaxis studies – Nausea, vomiting, headache, pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV), intranasal:
Avoid administration of LAIV within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after TAMIFLU use, unless medically indicated. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tamiflu
1.1 Treatment of Influenza
TAMIFLU is indicated for the treatment of acute, uncomplicated illness due to influenza A and B infection in patients 2 weeks of age and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours.
1.2 Prophylaxis of Influenza
TAMIFLU is indicated for the prophylaxis of influenza A and B in patients 1 year and older.
1.3 Limitations of Use
- TAMIFLU is not a substitute for early influenza vaccination on an annual basis as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
- Influenza viruses change over time. Emergence of resistance substitutions could decrease drug effectiveness. Other factors (for example, changes in viral virulence) might also diminish clinical benefit of antiviral drugs. Prescribers should consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use TAMIFLU [see Microbiology (12.4)].
- TAMIFLU is not recommended for patients with end-stage renal disease not undergoing dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
2. Tamiflu Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage and Administration Overview
Administer TAMIFLU for the treatment of influenza in patients 2 weeks of age or older [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] or for prophylaxis of influenza in patients 1 year and older [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] using:
- TAMIFLU capsules or
- TAMIFLU for oral suspension (supplied as a powder). This is the preferred formulation (6 mg per mL) for patients who cannot swallow capsules. Prior to use, the supplied TAMIFLU powder must be constituted with water by the pharmacist to produce the oral suspension [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
The capsules and oral suspension may be taken with or without food; however, tolerability may be enhanced if TAMIFLU is taken with food.
Adjust the TAMIFLU dosage in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
For patients who cannot swallow capsules, TAMIFLU for oral suspension is the preferred formulation. When TAMIFLU for oral suspension is not available from wholesaler or the manufacturer, TAMIFLU capsules may be opened and mixed with sweetened liquids such as regular or sugar-free chocolate syrup, corn syrup, caramel topping, or light brown sugar (dissolved in water). During emergency situations and when neither the oral suspension or the age-appropriate strengths of TAMIFLU capsules to mix with sweetened liquids are available, then a pharmacist may prepare an emergency supply of oral suspension from TAMIFLU 75 mg capsules [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Treatment of Influenza
Initiate treatment with TAMIFLU within 48 hours of influenza symptom onset.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Prophylaxis of Influenza
Initiate post-exposure prophylaxis with TAMIFLU within 48 hours following close contact with an infected individual. Initiate seasonal prophylaxis with TAMIFLU during a community outbreak.
Pediatric Patients (1 year to 12 years of age)
Table 1 displays the recommended oral dosage of TAMIFLU for prophylaxis of influenza in pediatric patients 1 year to 12 years of age based on body weight and provides information about prescribing the capsule or the formulation for oral suspension. Prophylaxis in pediatric patients is recommended for 10 days following close contact with an infected individual and up to 6 weeks during a community outbreak [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
| Weight | Treatment Dosage for 5 days | Prophylaxis Dosage for 10 days* | Volume of Oral Suspension (6 mg/mL) for each Dose† | Number of Bottles of Oral Suspension to Dispense | Number of Capsules to Dispense (Strength)‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Patients from 2 Weeks to less than 1 Year of Age | |||||
| Any weight | 3 mg/kg twice daily | Not applicable | 0.5 mL/kg§ | 1 bottle | Not applicable |
| Patients 1 to 12 Years of Age Based on Body Weight | |||||
| 15 kg or less | 30 mg twice daily | 30 mg once daily | 5 mL | 1 bottle | 10 capsules (30 mg) |
| 15.1 kg to 23 kg | 45 mg twice daily | 45 mg once daily | 7.5 mL | 2 bottles | 10 capsules (45 mg) |
| 23.1 kg to 40 kg | 60 mg twice daily | 60 mg once daily | 10 mL | 2 bottles | 20 capsules (30 mg) |
| 40.1 kg or more | 75 mg twice daily | 75 mg once daily | 12.5 mL | 3 bottles | 10 capsules (75 mg) |
2.4 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
Table 2 displays the dosage recommendations for the treatment and prophylaxis of influenza in adults with various stages of renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of less than or equal to 90 mL per minute). Dosage modifications are recommended in adults with an estimated creatinine clearance less than or equal to 60 mL per minute [see Use in Specific Population (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Renal Impairment (Creatinine Clearance) | Recommended Treatment Regimen* | Recommended Prophylaxis Regimen*† |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Mild (>60-90 mL/minute) | 75 mg twice daily for 5 days | 75 mg once daily |
| Moderate (>30-60 mL/minute) | 30 mg twice daily for 5 days | 30 mg once daily |
| Severe (>10-30 mL/minute) | 30 mg once daily for 5 days | 30 mg every other day |
| ESRD Patients on Hemodialysis (≤ 10 mL/minute) | 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg after every hemodialysis cycle (treatment duration not to exceed 5 days) | 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg after alternate hemodialysis cycles |
| ESRD Patients on Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis‡
(≤10 mL/minute) | A single 30 mg dose administered immediately | 30 mg immediately and then 30 mg once weekly |
| ESRD Patients not on Dialysis | TAMIFLU is not recommended | TAMIFLU is not recommended |
2.5 Preparation and Storage of Constituted TAMIFLU Oral Suspension
Prior to dispensing to the patient, constitute TAMIFLU for oral suspension (supplied as powder):
- a)
- Tap the closed bottle containing the supplied TAMIFLU white powder several times to loosen the powder.
- b)
- Measure 55 mL of water in a graduated cylinder.
- c)
- Add the total amount of water for constitution to the bottle.
- d)
- Close bottle with child-resistant cap tightly and shake the closed bottle well for 15 seconds.
- e)
- Label the bottle with instructions to "Shake Well Before Use".
- f)
- The constituted oral suspension contains 360 mg of oseltamivir base per 60 mL of volume (6 mg per mL) and is white, tutti-frutti–flavored). Use the constituted oral suspension within 17 days of preparation when stored under refrigeration, 2º to 8ºC (36º to 46ºF), or within 10 days if stored at controlled room temperature, 25ºC (77ºF). Write the expiration date of the constituted oral suspension on the bottle label.
- g)
- Ensure patients have an oral dosing dispenser that measures the appropriate volume in milliliters. Counsel patients on how to utilize the oral dosing dispenser and correctly measure the oral suspension as prescribed (see Tables 1 and 2).
2.6 Emergency Preparation of Oral Suspension from 75 mg TAMIFLU Capsules
The following directions are provided for use only during emergency situations and when FDA-approved, commercially manufactured TAMIFLU for oral suspension is not available from wholesalers or the manufacturer.
The following emergency preparation instructions will provide one patient with enough TAMIFLU for a 5-day course of treatment of influenza or a 10-day course of prophylaxis of influenza:
Step #1: Determine the dosage of TAMIFLU for the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, and 2.4)] then determine the total volume of oral suspension needed to be prepared (see Table 3).
| TAMIFLU Dose* | Total Volume to Prepare per Patient |
|---|---|
|
|
| 15 mg or less | 37.5 mL |
| 30 mg | 75 mL |
| 45 mg | 100 mL |
| 60 mg | 125 mL |
| 75 mg | 150 mL |
Step #2: Preparation must be performed with only one of the following vehicles (other vehicles have not been studied): Cherry Syrup (Humco®), Ora-Sweet® SF (sugar-free) (Paddock Laboratories), or simple syrup. Determine the number of capsules and the amount of water and vehicle needed to prepare the total volume (see Table 3) of prepared oral suspension (6 mg per mL) for a complete treatment or prophylaxis course (see Table 4).
| Total Volume of Prepared Oral Suspension | 37.5 mL | 75 mL | 100 mL | 125 mL | 150 mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Number of TAMIFLU 75 mg Capsules (Total Strength)* | 3 (225 mg) | 6 (450 mg) | 8 (600 mg) | 10 (750 mg) | 12 (900 mg) |
| Amount of Water | 2.5 mL | 5 mL | 7 mL | 8 mL | 10 mL |
| Volume of Vehicle Cherry Syrup (Humco®) OR Ora-Sweet® SF (Paddock Laboratories) OR simple syrup | 34.5 mL | 69 mL | 91 mL | 115 mL | 137 mL |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TAMIFLU Capsules:
- 30-mg (30 mg free base equivalent of the phosphate salt): light yellow, hard gelatin, with "ROCHE" printed in blue ink on the light yellow body and "30 mg" printed in blue ink on the light yellow cap.
- 45-mg (45 mg free base equivalent of the phosphate salt): grey, hard gelatin, with "ROCHE" printed in blue ink on the grey body and "45 mg" printed in blue ink on the grey cap.
- 75-mg (75 mg free base equivalent of the phosphate salt): grey/light yellow, hard gelatin, with "ROCHE" is printed in blue ink on the grey body and "75 mg" printed in blue ink on the light yellow cap.
TAMIFLU for Oral Suspension: 6 mg per mL (final concentration when constituted)
- White powder blend for constitution.
4. Contraindications
TAMIFLU is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to oseltamivir or any component of the product. Severe allergic reactions have included anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and erythema multiforme [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reactions
Cases of anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and erythema multiforme have been reported in postmarketing experience with TAMIFLU. Stop TAMIFLU and institute appropriate treatment if an allergic-like reaction occurs or is suspected. The use of TAMIFLU is contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to TAMIFLU [see Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Neuropsychiatric Events
There have been postmarketing reports of delirium and abnormal behavior leading to injury, and in some cases resulting in fatal outcomes, in patients with influenza who were receiving TAMIFLU [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Because these events were reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made but they appear to be uncommon based on TAMIFLU usage data. These events were reported primarily among pediatric patients and often had an abrupt onset and rapid resolution. The contribution of TAMIFLU to these events has not been established. Influenza can be associated with a variety of neurologic and behavioral symptoms that can include events such as hallucinations, delirium, and abnormal behavior, in some cases resulting in fatal outcomes. These events may occur in the setting of encephalitis or encephalopathy but can occur without obvious severe disease. Closely monitor TAMIFLU-treated patients with influenza for signs of abnormal behavior. If neuropsychiatric symptoms occur, evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing TAMIFLU for each patient.
5.3 Risk of Bacterial Infections
There is no evidence for efficacy of TAMIFLU in any illness caused by pathogens other than influenza viruses. Serious bacterial infections may begin with influenza-like symptoms or may coexist with or occur as complications during the course of influenza. TAMIFLU has not been shown to prevent such complications. Prescribers should be alert to the potential for secondary bacterial infections and treat them as appropriate.
5.4 Fructose Intolerance in Patients with Hereditary Fructose Intolerance
Fructose can be harmful to patients with hereditary fructose intolerance. One dose of 75 mg TAMIFLU for oral suspension delivers 2 grams of sorbitol. This is above the daily maximum limit of sorbitol for patients with hereditary fructose intolerance and may cause dyspepsia and diarrhea.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious skin and hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neuropsychiatric events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions from Treatment and Prophylaxis Trials in Adult and Adolescent Subjects (13 years of age and older)
The overall safety profile of TAMIFLU is based on data from 2,646 adult and adolescent subjects that received the recommended dosage of 75 mg orally twice daily for 5 days for treatment of influenza and 1,943 adult and adolescent subjects that received the recommended dosage of 75 mg orally once daily for up to 6 weeks for prophylaxis of influenza in clinical trials.
The most common adverse reactions in the pooled treatment and pooled prophylaxis trials in adults and adolescents are displayed in Table 5. The majority of these adverse reactions were reported on a single occasion, occurred on either the first or second treatment day and resolved spontaneously within 1-2 days. This summary includes otherwise healthy adults/adolescents and subjects "at risk" (subjects at higher risk of developing complications associated with influenza, e.g., elderly patients and patients with chronic cardiac or respiratory disease). In general, the safety profile in the subjects "at risk" was qualitatively similar to that in otherwise healthy adults/adolescents.
| System Organ Class | Treatment Trials | Prophylaxis Trials | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | TAMIFLU 75 mg twice daily (n = 2646) | Placebo (n = 1977) | TAMIFLU 75 mg once daily (n = 1943) | Placebo (n = 1586) |
|
||||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 10% | 6% | 8% | 4% |
| Vomiting | 8% | 3% | 2% | 1% |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Headache | 2% | 1% | 17% | 16% |
| General Disorders | ||||
| Pain | <1% | <1% | 4% | 3% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of TAMIFLU. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to TAMIFLU exposure.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Swelling of the face or tongue, allergy, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, hypothermia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, dermatitis, urticaria, eczema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, erythema multiforme [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gastrointestinal bleeding, hemorrhagic colitis
Cardiac Disorders: Arrhythmia
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatitis, abnormal liver function tests
Nervous System Disorders: Seizure
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Aggravation of diabetes
Psychiatric Disorders: Abnormal behavior, delirium, including symptoms such as hallucinations, agitation, anxiety, altered level of consciousness, confusion, nightmares, delusions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.2 Drugs Without Clinically Significant Drug Interaction with TAMIFLU
No dose adjustments are needed for either oseltamivir or the concomitant drug when coadministering oseltamivir with amoxicillin, acetaminophen, aspirin, cimetidine, antacids (magnesium and aluminum hydroxides and calcium carbonates), rimantadine, amantadine, or warfarin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.6 Renal Impairment
Patients with renal impairment had higher blood levels of oseltamivir carboxylate compared to patients with normal renal function which may increase the risk of TAMIFLU-associated adverse reactions. Therefore, dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with a serum creatinine clearance between 10 and 60 mL/minute and for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing routine hemodialysis or continuous peritoneal dialysis treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. TAMIFLU is not recommended for patients with ESRD not undergoing dialysis [see Indications and Usage (1.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The safety and pharmacokinetics in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been evaluated [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Use in Patients with Chronic Conditions
Efficacy of TAMIFLU in the treatment of influenza in patients with chronic cardiac disease and/or respiratory disease was evaluated in one randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Efficacy in this population, as measured by time to alleviation of all symptoms, was not established, but no new safety signals were identified [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
No clinical trial data are available regarding treatment of influenza in patients with any medical condition sufficiently severe or unstable to be considered at imminent risk of requiring hospitalization.
8.9 Immunocompromised Patients
Efficacy of TAMIFLU for the treatment or prophylaxis of influenza has not been established in immunocompromised patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Safety of TAMIFLU has been demonstrated for up to 12 weeks for prophylaxis of influenza in immunocompromised patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
10. Overdosage
Reports of overdoses with TAMIFLU have been received from clinical trials and during postmarketing experience. In the majority of cases reporting overdose, no adverse reactions were reported. Adverse reactions reported following overdose were similar in nature to those observed with therapeutic doses of TAMIFLU [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
11. Tamiflu Description
TAMIFLU (oseltamivir phosphate), an influenza neuraminidase inhibitor (NAI), is available as:
- Capsules containing 30 mg, 45 mg, or 75 mg of oseltamivir for oral use, in the form of oseltamivir phosphate, and
- A powder for oral suspension, which when constituted with water as directed contains 6 mg per mL oseltamivir base.
In addition to the active ingredient, each capsule contains croscarmellose sodium, povidone K30, pregelatinized starch, sodium stearyl fumarate and talc. The 30 mg capsule shell contains gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The 45 mg capsule shell contains black iron oxide, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. The 75 mg capsule shell contains black iron oxide, gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. Each capsule is printed with blue ink, which includes FD&C Blue No. 2 as the colorant.
In addition to the active ingredient, the powder for oral suspension contains monosodium citrate, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sorbitol, titanium dioxide, tutti-frutti flavoring, and xanthan gum.
Oseltamivir phosphate is a white crystalline solid with the chemical name (3R,4R,5S)-4-acetylamino-5-amino-3(1-ethylpropoxy)-1-cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester, phosphate (1:1). The chemical formula is C16H28N2O4 (free base). The molecular weight is 312.4 for oseltamivir free base and 410.4 for oseltamivir phosphate salt. The structural formula is as follows:
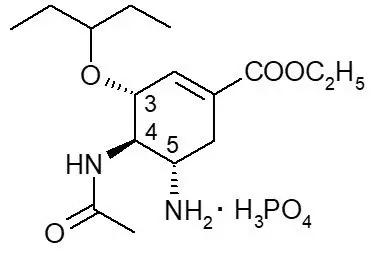
12. Tamiflu - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Oseltamivir is an antiviral drug with activity against influenza virus [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Bioavailability
Oseltamivir is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration of TAMIFLU (oseltamivir phosphate) and is extensively converted predominantly by hepatic esterases to oseltamivir carboxylate. At least 75% of an oral dose reaches the systemic circulation as oseltamivir carboxylate and less than 5% of the oral dose reaches the systemic circulation as oseltamivir (see Table 6).
| Parameter | Oseltamivir | Oseltamivir Carboxylate |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 65 (26) | 348 (18) |
| AUC0-12h (ng∙h/mL) | 112 (25) | 2719 (20) |
Plasma concentrations of oseltamivir carboxylate are proportional to doses up to 500 mg given twice daily (about 6.7 times the maximum recommended TAMIFLU dosage) [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Coadministration with food had no significant effect on the peak plasma concentration (551 ng/mL under fasted conditions and 441 ng/mL under fed conditions) and the area under the plasma concentration time curve (6218 ng∙h/mL under fasted conditions and 6069 ng∙h/mL under fed conditions) of oseltamivir carboxylate.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
Administration of 100 mg of TAMIFLU twice daily (about 1.3 times the maximum recommended dosage) for 5 days to subjects with various degrees of renal impairment showed that exposure to oseltamivir carboxylate is inversely proportional to declining renal function.
Population-derived pharmacokinetic parameters were determined for patients with varying degrees of renal function including ESRD patients on hemodialysis. Median simulated exposures of oseltamivir carboxylate for recommended treatment and prophylaxis regimens are provided in Table 7. The pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir have not been studied in ESRD patients not undergoing dialysis [see Indications and Usage (1.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
| Renal Function/Impairment | Normal Creatinine Clearance 90-140 mL/min (n=57) | Mild Creatinine Clearance 60-90 mL/min (n=45) | Moderate Creatinine Clearance 30-60 mL/min (n=13) | Severe Creatinine Clearance 10-30 mL/min (n=11) | ESRD Creatinine Clearance <10 mL/min on Hemodialysis (n=24) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Recommended Treatment Regimens | |||||
| PK exposure parameter | 75 mg twice daily | 75 mg twice daily | 30 mg twice daily | 30 mg once daily | 30 mg every HD cycle |
| Cmin (ng/mL) | 145 | 253 | 180 | 219 | 221 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 298 | 464 | 306 | 477 | 1170 |
| AUC48 (ng∙h/mL)* | 11224 | 18476 | 12008 | 16818 | 23200 |
| Recommended Prophylaxis Regimens | |||||
| PK exposure parameter | 75 mg once daily | 75 mg once daily | 30 mg once daily | 30 mg every other day | 30 mg alternate HD cycle |
| Cmin (ng/mL) | 39 | 62 | 57 | 70 | 42 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 213 | 311 | 209 | 377 | 903 |
| AUC48 (ng∙hr/mL)* | 5294 | 8336 | 6262 | 9317 | 11200 |
In continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients, the peak concentration of oseltamivir carboxylate following a single 30 mg dose of oseltamivir or once weekly oseltamivir was approximately 3-fold higher than in patients with normal renal function who received 75 mg twice daily. The plasma concentration of oseltamivir carboxylate on Day 5 (147 ng/mL) following a single 30 mg dose in CAPD patients is similar to the predicted Cmin (160 ng/mL) in patients with normal renal function following 75 mg twice daily. Administration of 30 mg once weekly to CAPD patients resulted in plasma concentrations of oseltamivir carboxylate at the 168 hour blood sample of 63 ng/mL, which were comparable to the Cmin in patients with normal renal function receiving the approved regimen of 75 mg once daily (40 ng/mL).
12.4 Microbiology
Resistance
Clinical studies: Reduced susceptibility isolates have been obtained during treatment with oseltamivir and from sampling during community surveillance studies. Changes in the viral neuraminidase that have been associated with reduced susceptibility to oseltamivir carboxylate are summarized in Table 8. The clinical impact of this reduced susceptibility is unknown.
Hemagglutinin (HA) substitutions selected in cell culture and associated with reduced susceptibility to oseltamivir include (influenza virus subtype-specific numbering) A11T, K173E, and R453M in H3N2; and H99Q in influenza B virus (Yamagata lineage). In some cases, HA substitutions were selected in conjunction with known NA resistance substitutions and may contribute to reduced susceptibility to oseltamivir; however, the impact of HA substitutions on antiviral activity of oseltamivir in humans is unknown and likely to be strain-dependent.
| Amino Acid Substitution* |
|---|
| Influenza A N1 (N1 numbering in brackets) |
|
| I117V (I117V), E119V (E119V), R152K (R152K), Y155H (Y155H), F173V (F174V), D198G/N (D199G/N), I222K/R/T/V (I223K/R/T/V), S246G/N (S247G/N), G248R+I266V (G249R+I267V), H274Y (H275Y), N294S (N295S), Q312R+I427T (Q313R+I427T), N325K (N325K), R371K (R368K) |
| Influenza A N2 |
| E41G, E119I/V, D151V, I222L/V, Q226H, SASG245-248 deletion, S247P, R292K, N294S |
| Influenza B (B numbering in brackets) |
| E119A (E117A), P141S (P139S), G142R (G140R), R152K (R150K), D198E/N/Y (D197E/N/Y), I222L/T/V (I221L/T/V), A246D/S/T (A245D/S/T), H274Y (H273Y), N294S (N294S), R371K (R374K), G402S (G407S) |
Selection of influenza A viruses resistant to oseltamivir can occur at higher frequencies in children. Oseltamivir treatment-associated resistance in pediatric treatment studies has been detected at frequencies of 27 to 37% and 3 to 18% (3/11 to 7/19 and 1/34 to 9/50 post-treatment isolates, respectively) for influenza A/H1N1 virus and influenza A/H3N2 virus, respectively.
In immunocompromised adults and pediatrics (1 year of age and older), selection of influenza viruses resistant to oseltamivir can occur at higher frequencies than in the otherwise healthy population. In a treatment study of immunocompromised subjects, treatment-associated genotypic resistance was detected in 27% (8/30), 12% (6/52), and 0% (0/42) of influenza A/H1N1, A/H3N2, and B virus infections, respectively. Treatment-emergent resistance was observed at a higher frequency in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients (32%; 6/19).
The frequency of resistance selection to oseltamivir and the prevalence of such resistant virus vary seasonally and geographically.
Circulating seasonal influenza strains expressing neuraminidase resistance-associated substitutions have been observed in individuals who have not received oseltamivir treatment. The oseltamivir resistance-associated substitution H275Y was found in more than 99% of US-circulating 2008 H1N1 influenza virus isolates. The 2009 H1N1 influenza virus ("swine flu") was almost uniformly susceptible to oseltamivir; however, the frequency of circulating resistant variants can change from season to season. Prescribers should consider available information from the CDC on influenza virus drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use TAMIFLU.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In 2-year carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats given daily oral doses of the prodrug oseltamivir phosphate up to 400 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg, respectively, the prodrug and the active form oseltamivir carboxylate induced no statistically significant increases in tumors over controls. The mean maximum daily exposures to the prodrug in mice and rats were approximately 130- and 320-fold, respectively, greater than those in humans at the recommended clinical dose based on AUC comparisons. The respective safety margins of the exposures to the active oseltamivir carboxylate were 15- and 50-fold.
Oseltamivir was found to be non-mutagenic in the Ames test and the human lymphocyte chromosome assay with and without enzymatic activation and negative in the mouse micronucleus test. It was found to be positive in a Syrian Hamster Embryo (SHE) cell transformation test. Oseltamivir carboxylate was non-mutagenic in the Ames test and the L5178Y mouse lymphoma assay with and without enzymatic activation and negative in the SHE cell transformation test.
In a fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, doses of oseltamivir at 50, 250, and 1500 mg/kg/day were administered to females for 2 weeks before mating, during mating and until day 6 of pregnancy. Males were dosed for 4 weeks before mating, during mating, and for 2 weeks after mating. There were no effects on fertility, mating performance or early embryonic development at any dose level. The highest dose in this study was approximately 115 times the human systemic exposure (AUC0-24h) of oseltamivir carboxylate that occurs after administration of the maximum recommended human dose.
16. How is Tamiflu supplied
| TAMIFLU
oseltamivir phosphate capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TAMIFLU
oseltamivir phosphate capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TAMIFLU
oseltamivir phosphate capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TAMIFLU
oseltamivir phosphate powder, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd | 485244961 | ANALYSIS(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genentech, Inc. | 080129000 | ANALYSIS(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | 482242971 | API MANUFACTURE(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) , ANALYSIS(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) , MANUFACTURE(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) , PACK(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) , LABEL(0004-0800, 0004-0801, 0004-0802, 0004-0822) | |








