Drug Detail:Tepmetko (Tepotinib)
Drug Class: Multikinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TEPMETKO® (tepotinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 03/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Tepmetko
TEPMETKO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping alterations. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. (1)
Tepmetko Dosage and Administration
- Select patients for treatment with TEPMETKO on the presence of METex14 skipping. (2.1, 14)
- Recommended dosage: 450 mg orally once daily with food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 225 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Immediately withhold TEPMETKO in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO in patients diagnosed with ILD/pneumonitis of any severity. (2.4, 5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests. Withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TEPMETKO based on severity. (5.2)
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: TEPMETKO can cause fetal harm. Advise of potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 2%) were decreased lymphocytes, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, increased gamma-glutamyltransferase, increased amylase, increased ALT, increased lipase, increased AST, and decreased hemoglobin. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact EMD Serono at 1-800-283-8088 ext. 5563 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Certain P-gp substrates: Avoid coadministration of TEPMETKO with P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2023
Related/similar drugs
Opdivo, Retevmo, Rybrevant, Lumakras, methotrexate, Keytruda, AvastinFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tepmetko
TEPMETKO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping alterations.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
2. Tepmetko Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection for METex14 Skipping Alterations
Select patients for treatment with TEPMETKO based on the presence of MET exon 14 skipping alterations in plasma or tumor specimens. Testing for the presence of MET exon 14 skipping alterations in plasma specimens is recommended only in patients for whom a tumor biopsy cannot be obtained. If an alteration is not detected in a plasma specimen, re-evaluate the feasibility of biopsy for tumor tissue testing. An FDA-approved test for detection of MET exon 14 skipping alterations in NSCLC for selecting patients for treatment with TEPMETKO is not available.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TEPMETKO is 450 mg orally once daily with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Instruct patients to take their dose of TEPMETKO at approximately the same time every day and to swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush or split tablets.
Advise patients not to make up a missed dose within 8 hours of the next scheduled dose.
If vomiting occurs after taking a dose of TEPMETKO, advise patients to take the next dose at the scheduled time.
2.3 Administration to Patients Who Have Difficulty Swallowing Solids
Place TEPMETKO tablet(s) in a glass containing 30 mL (1 ounce) of non-carbonated water. No other liquids should be used or added. Stir, without crushing, until the tablet(s) is dispersed into small pieces (tablets will not completely dissolve) and drink immediately or within 1 hour. Swallow the tablet dispersion. Do not chew pieces of the tablet. Rinse the glass with an additional 30 mL and drink immediately ensuring no residue remains in the glass and the full dose is administered.
If an administration via a naso-gastric tube (with at least 8 French gauge) is required, disperse the tablet(s) in 30 mL of non-carbonated water as described above. Administer the 30 mL of liquid immediately or within 1 hour as per naso-gastric tube manufacturer's instructions. Immediately rinse twice with 30 mL each time to ensure that no residue remains in the glass or syringe and the full dose is administered.
2.4 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reduction of TEPMETKO for the management of adverse reactions is 225 mg orally once daily.
Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO in patients who are unable to tolerate 225 mg orally once daily.
The recommended dosage modifications of TEPMETKO for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity | Dose Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) /Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Any grade | Withhold TEPMETKO if ILD is suspected. Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO if ILD is confirmed. |
| Increased ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TEPMETKO until recovery to baseline ALT/AST. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TEPMETKO at the same dose; otherwise resume TEPMETKO at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO. | |
| Increased ALT and/or AST with increased total bilirubin in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | ALT and/or AST greater than 3 times ULN with total bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN | Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO. |
| Increased total bilirubin without concurrent increased ALT and/or AST [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade 3 | Withhold TEPMETKO until recovery to baseline bilirubin. If recovered to baseline within 7 days, then resume TEPMETKO at a reduced dose; otherwise permanently discontinue. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO. | |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 2 | Maintain dose level. If intolerable, consider withholding TEPMETKO until resolved, then resume TEPMETKO at a reduced dose. |
| Grade 3 | Withhold TEPMETKO until resolved, then resume TEPMETKO at a reduced dose. | |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue TEPMETKO. |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 225 mg, white-pink, oval, biconvex film-coated tablets with embossment "M" on one side and plain on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
ILD/pneumonitis, which can be fatal, occurred in patients treated with TEPMETKO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 2.2% patients treated with TEPMETKO, with one patient experiencing a Grade 3 or higher event; this event resulted in death. Four patients (0.9%) discontinued TEPMETKO due to ILD/pneumonitis.
Monitor patients for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Immediately withhold TEPMETKO in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity occurred in patients treated with TEPMETKO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 13% of patients treated with TEPMETKO. Grade 3 or 4 increased ALT/AST occurred in 4.2% of patients. A fatal adverse reaction of hepatic failure occurred in one patient (0.2%). Three patients (0.7%) discontinued TEPMETKO due to increased ALT/AST. The median time-to-onset of Grade 3 or higher increased ALT/AST was 30 days (range 1 to 178).
Monitor liver function tests (including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin) prior to the start of TEPMETKO, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months of treatment, then once a month or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop increased transaminases or bilirubin. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold, dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TEPMETKO [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action TEPMETKO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Oral administration of tepotinib to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in malformations (teratogenicity) and anomalies at exposures less than the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the 450 mg daily clinical dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential or males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TEPMETKO and for one week after the final dose. [See Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)]
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail elsewhere in the labeling:
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to TEPMETKO in 448 patients with solid tumors enrolled in five open-label, single-arm studies receiving TEPMETKO as single agent at a dose of 450 mg once daily. This included 255 patients with NSCLC positive for METex14 skipping alterations, who received TEPMETKO in VISION. Among 448 patients who received TEPMETKO, 32% were exposed for 6 months or longer, and 12% were exposed for greater than one year.
The data described below reflect exposure to TEPMETKO 450 mg once daily in 255 patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with METex14 skipping alterations in VISION [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received TEPMETKO. Serious adverse reactions in > 2% of patients included pleural effusion (7%), pneumonia (5%), edema (3.9%), dyspnea (3.9%), general health deterioration (3.5%), pulmonary embolism (2%), and musculoskeletal pain (2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in one patient (0.4%) due to pneumonitis, one patient (0.4%) due to hepatic failure, and one patient (0.4%) due to dyspnea from fluid overload.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 20% of patients who received TEPMETKO. The most frequent adverse reactions (> 1%) leading to permanent discontinuations of TEPMETKO were edema (5%), pleural effusion (2%), dyspnea (1.6%), general health deterioration (1.6%), and pneumonitis (1.2%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 44% of patients who received TEPMETKO. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 2% of patients who received TEPMETKO included edema (23%), increased blood creatinine (6%), pleural effusion (4.3%), increased ALT (3.1%), and pneumonia (2.4%).
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 30% of patients who received TEPMETKO. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 2% of patients who received TEPMETKO included edema (19%), pleural effusion (2.7%), and increased blood creatinine (2.7%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients who received TEPMETKO were edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 2%) were decreased lymphocytes, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, increased gamma-glutamyltransferase, increased amylase, increased ALT, increased lipase, increased AST, and decreased hemoglobin.
Table 2 summarizes the adverse reactions in VISION.
| Adverse Reactions | TEPMETKO (N = 255) |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) |
|
|
||
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | ||
| Edema * | 70 | 9 |
| Fatigue † | 27 | 1.6 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Nausea | 27 | 0.8 |
| Diarrhea | 26 | 0.4 |
| Abdominal Pain ‡ | 16 | 0.8 |
| Constipation | 16 | 0 |
| Vomiting § | 13 | 1.2 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal Pain ¶ | 24 | 2.4 |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Dyspnea # | 20 | 2 |
| Cough Þ | 15 | 0.4 |
| Pleural effusion | 13 | 5 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | ||
| Decreased appetite | 16 | 1.2 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||
| Pneumonia ß | 11 | 3.9 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received TEPMETKO included ILD/pneumonitis, rash, fever, dizziness, pruritus, and headache.
Table 3 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities observed in VISION.
| Laboratory Abnormalities | TEPMETKO* | |
|---|---|---|
| Grades 1 to 4 (%) | Grades 3 to 4 (%) |
|
|
||
| Chemistry | ||
| Decreased albumin | 76 | 9 |
| Increased creatinine | 55 | 0.4 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase aminotransferase | 50 | 1.6 |
| Increased alanine aminotransferase | 44 | 4.1 |
| Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 35 | 2.5 |
| Decreased sodium | 31 | 8 |
| Increased potassium | 25 | 1.6 |
| Increased gamma-glutamyltransferase | 24 | 5 |
| Increased amylase | 23 | 4.6 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 48 | 11 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 27 | 2 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 23 | 0.8 |
A clinically relevant laboratory abnormality in < 20% of patients who received TEPMETKO was increased lipase in 18% of patients, including 3.7% Grades 3 to 4.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, TEPMETKO can cause malformations at doses less than the human exposure based on AUC at the 450 mg clinical dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of TEPMETKO in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 255 patients with METex14 skipping alterations in VISION who received 450 mg TEPMETKO once daily, 79% were 65 years or older, and 43% were 75 years or older. No clinically important differences in safety or efficacy were observed between patients aged 65 years or older and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 30 to 89 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The recommended dosage has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended in patients with mild (Child Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics and safety of tepotinib in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh Class C) have not been studied [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Tepmetko Description
Tepotinib is a kinase inhibitor. TEPMETKO (tepotinib) tablets for oral use are formulated with tepotinib hydrochloride hydrate. The chemical name for tepotinib hydrochloride hydrate is 3-{1-[(3-{5-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]pyrimidin-2-yl}phenyl)methyl]-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yl}benzonitrile hydrochloride hydrate. The molecular formula is C29H28N6O2∙HCl∙H2O and the molecular weight is 547.05 g/mol for tepotinib hydrochloride hydrate and 492.58 g/mol for tepotinib (free base). The chemical structure is shown below:
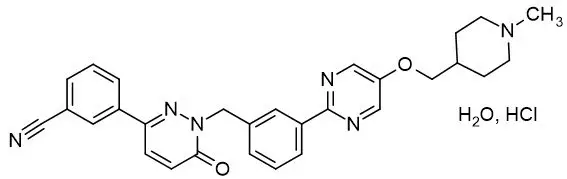
Tepotinib hydrochloride hydrate is a white to off-white powder with a pKa of 9.5.
TEPMETKO is supplied as film-coated tablets containing 225 mg of tepotinib (equivalent to 250 mg tepotinib hydrochloride hydrate). Inactive ingredients in the tablet core are mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and colloidal silicon dioxide. The tablet coating consists of hypromellose, titanium dioxide, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol, triacetin, and red iron oxides.
12. Tepmetko - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tepotinib is a kinase inhibitor that targets MET, including variants with exon 14 skipping alterations. Tepotinib inhibits hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-dependent and -independent MET phosphorylation and MET-dependent downstream signaling pathways. Tepotinib also inhibited melatonin 2 and imidazoline 1 receptors at clinically achievable concentrations.
In vitro, tepotinib inhibited tumor cell proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, and migration of MET-dependent tumor cells. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines with oncogenic activation of MET, including METex14 skipping alterations, tepotinib inhibited tumor growth, led to sustained inhibition of MET phosphorylation, and, in one model, decreased the formation of metastases.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of tepotinib were evaluated in patients with cancer administered 450 mg once daily unless otherwise specified. Tepotinib exposure (AUC0-12h and Cmax) increases dose-proportionally over the dose range of 27 mg (0.06 times the recommended daily dosage) to 450 mg. At the recommended dosage, the geometric mean (coefficient of variation [CV] %) steady state Cmax was 1,291 ng/mL (48.1%) and the AUC0-24h was 27,438 ng∙h/mL (51.7%). The oral clearance of tepotinib did not change with respect to time. The median accumulation was 2.5-fold for Cmax and 3.3-fold for AUC0-24h after multiple daily doses of tepotinib.
Drug Interaction Studies
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with tepotinib. Tepotinib and its major circulating metabolite were not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, or a mouse lymphoma assay. In vivo, tepotinib was not genotoxic in a rat micronucleus test.
Fertility studies of tepotinib have not been performed. There were no morphological changes in male or female reproductive organs in repeat-dose toxicity studies in dogs.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of TEPMETKO was evaluated in a single-arm, open-label, multicenter, non-randomized, multicohort study (VISION, NCT02864992). Eligible patients were required to have advanced or metastatic NSCLC harboring METex14 skipping alterations, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) wild-type and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) negative status, at least one measurable lesion as defined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status of 0 to 1. Patients with symptomatic CNS metastases, clinically significant uncontrolled cardiac disease, or who received treatment with any MET or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibitor were not eligible for the study.
Identification of METex14 skipping alterations was prospectively determined using central laboratories employing either a PCR-based or next-generation sequencing-based clinical trial assay using tissue (58%) and/or plasma (65%) samples.
Patients received TEPMETKO 450 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measure was confirmed overall response rate (ORR) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST v1.1) as evaluated by a Blinded Independent Review Committee (BIRC). An additional efficacy outcome measure was duration of response (DOR) by BIRC.
The efficacy population included 69 treatment naïve patients and 83 previously treated patients. The median age was 73 years (range 41 to 94 years); 48% female; 71% White, 25% Asian; 27% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status (PS) 0 and 73% had ECOG PS 1; 43% never smoked; 86% had adenocarcinoma; 98% had metastatic disease; and 10% had CNS metastases. Amongst previously treated patients, 89% received prior platinum-based chemotherapy.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 4.
| Efficacy parameter | Treatment-Naïve N = 69 | Previously Treated N = 83 |
|---|---|---|
| CI=confidence interval, NE=Not estimable | ||
|
||
| Overall response rate, % (95% CI) *,† | 43 (32, 56) | 43 (33, 55) |
| Median duration of response, months ‡ (95% CI) | 10.8 (6.9, NE) | 11.1 (9.5, 18.5) |
| Patients with DOR ≥ 6 months, % | 67 | 75 |
| Patients with DOR ≥ 9 months, % | 30 | 50 |
16. How is Tepmetko supplied
TEPMETKO (tepotinib) tablets: 225 mg tepotinib, white-pink, oval, biconvex film-coated tablet with embossment "M" on one side and plain on the other side.
| NDC number | Size |
|---|---|
| 44087-5000-3 | Box of 30 tablets: 3 blister cards each containing 10 tablets |
| 44087-5000-6 | Box of 60 tablets: 6 blister cards each containing 10 tablets |
The blister cards consist of a child-resistant blister foil.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised 03/2023 | |
| PATIENT INFORMATION
TEPMETKO® (tep-MET-co) (tepotinib) tablets, for oral use |
||
|
||
| What is TEPMETKO?
TEPMETKO is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that:
|
||
Before you receive TEPMETKO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
How should I take TEPMETKO?
|
||
|
What are the possible side effects of TEPMETKO?
|
||
|
|
|
| The most common side effects of TEPMETKO include: | ||
|
|
|
| Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with TEPMETKO if you develop serious side effects during treatment. These are not all of the possible side effects of TEPMETKO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store TEPMETKO?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TEPMETKO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use TEPMETKO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TEPMETKO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TEPMETKO that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in TEPMETKO?
Active ingredient: tepotinib Inactive ingredients: mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and colloidal silicon dioxide. Tablet coating: hypromellose, titanium dioxide, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol, triacetin, and red iron oxides. Manufactured for: EMD Serono, Inc., Rockland, MA 02370, U.S.A. TEPMETKO is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. Product of Germany. For more information, call toll-free 1-844-662-3631 or go to www.TEPMETKO.com. |
||
| TEPMETKO
tepotinib hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - EMD Serono, Inc. (088514898) |





