Drug Detail:Thiola (Tiopronin [ tye-oh-proe-nin ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous genitourinary tract agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
THIOLA (tiopronin) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
Indications and Usage for Thiola Tablets
THIOLA is a reducing and complexing thiol indicated, in combination with high fluid intake, alkali, and diet modification, for the prevention of cystine stone formation in adults and pediatric patients 20 kg and greater with severe homozygous cystinuria, who are not responsive to these measures alone. (1)
Thiola Tablets Dosage and Administration
- The recommended initial dosage in adult patients is 800 mg/day. In clinical studies, the average dosage was about 1,000 mg/day. (2.1)
- The recommended initial dosage in pediatric patients 20 kg and greater is 15 mg/kg/day. Avoid dosages greater than 50 mg/kg per day in pediatric patients. (2.1, 5.1, 8.4)
- Administer THIOLA in 3 divided doses at the same times each day at least one hour before or 2 hours after meals. (2.1)
- Measure urinary cystine 1 month after initiation of THIOLA and every 3 months thereafter. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 100 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to tiopronin or any component of THIOLA (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Proteinuria, including nephrotic syndrome, and membranous nephropathy, has been reported with tiopronin use. Pediatric patients receiving greater than 50 mg/kg of tiopronin per day may be at increased risk for proteinuria. (2.1, 5.1, 8.4)
- Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during tiopronin treatment. (4, 5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥10%) are nausea, diarrhea or soft stools, oral ulcers, rash, fatigue, fever, arthralgia, proteinuria, and emesis. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mission Pharmacal Company at toll-free phone # 1-800-298-1087 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended. (8.2)
- Geriatric: Choose dose carefully and monitor renal function in the elderly. (8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2019
Related/similar drugs
penicillamine, Cuprimine, tiopronin, D-Penamine, Depen, Thiola ECFull Prescribing Information
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets for oral use:
100 mg tablets: round, white and imprinted in red with “M” on one
side
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Table 1 presents adverse reactions ≥5% in either treatment group occurring in this trial.
| Table 1: | Adverse Reactions Occurring in One or More Patients | |||
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Group 1
Previously treated with d‑penicillamine (N = 49) | Group 2
Naïve to d‑penicillamine (N = 17) |
|
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | anemia | 1 (2%) | 1 (6%) | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | nausea | 12 (25%) | 2 (12%) | |
| emesis | 5 (10%) | – | ||
| diarrhea/soft stools | 9 (18%) | 1 (6%) | ||
| abdominal pain | – | 1 (6%) | ||
| oral ulcers | 6 (12%) | 3 (18%) | ||
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | fever | 4 (8%) | – | |
| weakness | 2 (4%) | 2 (12%) | ||
| fatigue | 7 (14%) | – | ||
| peripheral (edema) | 3 (6%) | 1 (6%) | ||
| chest pain | – | 1 (6%) | ||
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | anorexia | 4 (8%) | – | |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | arthralgia | – | 2 (12%) | |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | proteinuria | 5 (10%) | 1 (6%) | |
| impotence | – | 1 (6%) | ||
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | cough | – | 1 (6%) | |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | rash | 7 (14%) | 2 (12%) | |
| ecchymosis | 3 (6%) | – | ||
| pruritus | 2 (4%) | 1 (6%) | ||
| urticaria | 4 (8%) | – | ||
| skin wrinkling | 3 (6%) | 1 (6%) | ||
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
| Table 2: | Adverse Reactions Reported for THIOLA Pharmacovigilance by System Organ Class and Preferred Term | |
| System Organ Class | Preferred Term | |
| Cardiac Disorders | congestive heart failure | |
| Ear and Labyrinth Disorder | vertigo | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | abdominal discomfort; abdominal distension; abdominal pain; chapped lips; diarrhea; dry mouth; dyspepsia; eructation; flatulence; gastrointestinal disorder; gastroesophageal reflux disease; nausea; vomiting; jaundice; liver transaminitis | |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | asthenia; chest pain; fatigue; malaise; pain; peripheral swelling; pyrexia; swelling | |
| Investigations | glomerular filtration rate decreased; weight increased | |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | decreased appetite; dehydration; hypophagia | |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | arthralgia; back pain; flank pain; joint swelling; limb discomfort; musculoskeletal discomfort; myalgia; neck pain; pain in extremity | |
| Nervous System Disorders | ageusia; burning sensation; dizziness; dysgeusia; headache; hypoesthesia | |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | nephrotic syndrome; proteinuria; renal failure | |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | dry skin; hyperhidrosis; pemphigus foliaceus; pruritus; rash; rash pruritic; skin irritation; skin texture abnormal; skin wrinkling; urticaria | |
11. Thiola Tablets Description
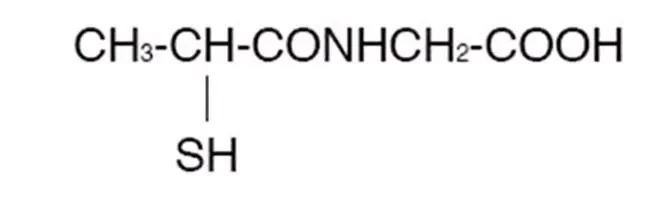
Tiopronin is a white crystalline powder, which is freely soluble in water.
12. Thiola Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
| THIOLA
tiopronin tablet, sugar coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Mission Pharmacal Company (008117095) |
| Registrant - Mission Pharmacal Company (927726893) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mission Pharmacal Company | 927726893 | MANUFACTURE(0178-0900) | |





