Drug Detail:Tindamax (Tinidazole [ tye-nye-da-zole ])
Drug Class: Amebicides
Highlights of Prescribing Information
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Tindamax ® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Tindamax. Tindamax ® (tinidazole) oral tablets for oral solution. Initial U.S. Approval 2004
WARNING: POTENTIAL RISK FOR CARCINOGENICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Carcinogenicity has been seen in mice and rats treated chronically with metronidazole, another nitroimidazole agent ( 13.1). Although such data have not been reported for tinidazole, the two drugs are structurally related and have similar biologic effects. Use should be limited to approved indications only.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Tindamax and other antibacterial drugs, Tindamax should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (11.3)
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage, Bacterial Vaginosis ( 1.4) 5/2007
Dosage and Administration, Bacterial Vaginosis ( 2.6) 5/2007
Indications and Usage for Tindamax
Tindamax is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial indicated for:
- Trichomoniasis ( 1.1)
- Giardiasis: in patients age 3 and older ( 1.2)
- Amebiasis: in patients age 3 and older ( 1.3)
- Bacterial Vaginosis: in non-pregnant, adult women ( 1.4, 8.1)
Tindamax Dosage and Administration
- Trichomoniasis: a single 2 g oral dose taken with food. Treat sexual partners with the same dose and at the same time ( 2.3)
- Giardiasis: Adults: a single 2 g dose taken with food. Pediatric patients older than three years of age: a single dose of 50 mg/kg (up to 2 g) with food ( 2.4)
- Amebiasis, Intestinal: Adults: 2 g per day for 3 days with food. Pediatric patients older than three years of age: 50 mg/kg/day (up to 2 g per day) for 3 days with food ( 2.5). Amebic liver abscess: Adults: 2 g per day for 3-5 days with food. Pediatric patients older than three years of age: 50 mg/kg/day (up to 2 g per day) for 3-5 days with food ( 2.5)
- Bacterial vaginosis: Non-pregnant, adult women: 2 g once daily for 2 days taken with food, or 1 g once daily for 5 days taken with food ( 2.6)
Contraindications
- Prior history of hypersensitivity to tinidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives ( 4, 6.1, 6.2)
- First trimester of pregnancy ( 4, 8.1)
- Nursing mothers, unless breast-feeding is interrupted during tinidazole therapy and for 3 days following the last dose ( 4, 8.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Seizures and neuropathy have been reported. Discontinue Tindamax if abnormal neurologic signs develop ( 5.1)
- Vaginal candidiasis may develop with Tindamax and require treatment with an antifungal agent ( 5.2)
- Use Tindamax with caution in patients with blood dyscrasias. Tindamax may produce transient leukopenia and neutropenia ( 5.3, 7.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions for a single 2 g dose of tinidazole (incidence >1%) are metallic/bitter taste, nausea, weakness/fatigue/malaise, dyspepsia/cramps/epigastric discomfort, vomiting, anorexia, headache, dizziness and constipation ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mission Pharmacal Company at 1-855-778-0177or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
The following drug interactions were reported for metronidazole, a chemically-related nitroimidazole and may therefore occur with tinidazole:
- Warfarin and other oral coumarin anticoagulants: Anticoagulant dosage may need adjustment during and up to 8 days after tinidazole therapy ( 7.1)
- Alcohol-containing beverages/preparations: Avoid during and up to 3 days after tinidazole therapy ( 7.1)
- Lithium: Monitor serum lithium concentrations ( 7.1)
- Cyclosporine, tacrolimus: Monitor for toxicities of these immunosuppressive drugs ( 7.1)
- Fluorouracil: Monitor for fluorouracil-associated toxicities ( 7.1)
- Phenytoin, fosphenytoin: Adjustment of anticonvulsant and/or tinidazole dose(s) may be needed ( 7.1, 7.2)
- CYP3A4 inducers/inhibitors: Monitor for decreased tinidazole effect or increased adverse reactions ( 7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pediatric Use: Data on tinidazole use in children is limited to treatment of giardiasis and amebiasis in patients age 3 and older ( 8.4)
- Hemodialysis patients: If tinidazole is administered the same day and prior to hemodialysis, administer an additional ½ dose after end of hemodialysis ( 8.6, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Revised: 5/2007
Revised: 11/2016
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tindamax
2. Tindamax Dosage and Administration
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- 500 mg tablets are pink, oval, scored tablets, with TM debossed on one side and 500 on the other
4. Contraindications
The use of tinidazole is contraindicated:
- In patients with a previous history of hypersensitivity to tinidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives. Reported reactions have ranged in severity from urticaria to Stevens-Johnson syndrome [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1, 6.2)].
- During first trimester of pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)].
- In nursing mothers: Interruption of breast-feeding is recommended during tinidazole therapy and for 3 days following the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Other adverse reactions reported with tinidazole include:
Gastrointestinal: tongue discoloration, stomatitis, diarrhea
| 2 g single dose | Multi-day dose | |
| GI: Metallic/bitter taste | 3.7% | 6.3% |
| Nausea | 3.2% | 4.5% |
| Anorexia | 1.5% | 2.5% |
| Dyspepsia/cramps/epigastric discomfort | 1.8% | 1.4% |
| Vomiting | 1.5% | 0.9% |
| Constipation | 0.4% | 1.4% |
| CNS: Weakness/fatigue/malaise | 2.1% | 1.1% |
| Dizziness | 1.1% | 0.5% |
| Other: Headache | 1.3% | 0.7% |
| Total patients with adverse reactions | 11.0%
(403/3669) | 13.8%
(244/1765) |
7. Drug Interactions
7.2 Potential Effects of Other Drugs on Tinidazole
Oxytetracycline: Oxytetracycline was reported to antagonize the therapeutic effect of metronidazole.
8. Use In Specific Populations
11. Tindamax Description
Tinidazole is a synthetic antiprotozoal and antibacterial agent. It is 1-[2-(ethylsulfonyl)ethyl]-2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole, a second-generation 2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole, which has the following chemical structure:
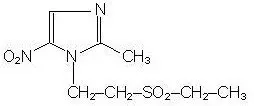
Tindamax pink oral tablets contain 500 mg of tinidazole. Inactive ingredients include croscarmellose sodium, FD&C Red 40 lake, FD&C Yellow 6 lake, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized corn starch, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
12. Tindamax - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tinidazole is an antiprotozoal, antibacterial agent. [See Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The potential of tinidazole to induce the metabolism of other drugs has not been evaluated.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.5 Bacterial Vaginosis
| Outcome | Tindamax
1 g × 5 days (n=76) | Tindamax
2 g × 2 days (n=73) | Placebo
(n=78) |
| % Cure | % Cure | % Cure | |
|
Therapeutic Cure Difference 2 97.5% CI 3 |
36.8 31.7 (16.8, 46.6) |
27.4 22.3 (8.0, 36.6) |
5.1 |
|
Clinical Cure Difference 2 97.5% CI 3 |
51.3 39.8 (23.3, 56.3) |
35.6 24.1 (7.8, 40.3) |
11.5 |
|
Nugent Score Cure Difference 2 97.5% CI 3 |
38.2 33.1 (18.1, 48.0) |
27.4 22.3 (8.0, 36.6) |
5.1 |
| TINDAMAX
tinidazole tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Department of State Health Services, Pharmacy Branch (781992540) |
| Registrant - Department of State Health Services, Pharmacy Branch (781992540) |





