Drug Detail:Tolsura (Itraconazole [ it-ra-kon-a-zole ])
Drug Class: Azole antifungals
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TOLSURA ®(itraconazole capsules), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1992
WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE and DRUG INTERACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
-
Congestive Heart Failure
TOLSURA can cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure (CHF). When itraconazole was administered intravenously to healthy human volunteers and dogs, negative inotropic effects were seen. If signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure occur or worsen during administration of TOLSURA, reassess the benefit-risk of continuing treatment. ( 5.1, 6). -
Drug Interactions
- Co-administration of certain drugs that are metabolized by human CYP3A4 enzymes are contraindicated with TOLSURA because plasma concentrations of such drugs are increased. ( 4.1, 5.4, 7.1)
- Co-administration with colchicine, fesoterodine and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment. ( 4.1, 7.1)
- Co-administration with eliglustat is contraindicated in poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors. ( 4.1, 7.1)
- Increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia. ( 4.1, 5.4, 7.1)
Indications and Usage for Tolsura
TOLSURA is an azole antifungal indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromisedadult patients ( 1):
- Blastomycosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary
- Histoplasmosis, including chronic cavitary pulmonary disease and disseminated, non-meningeal histoplasmosis, and
- Aspergillosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary, in patients who are intolerant of or who are refractory to amphotericin B therapy.
Limitations of Use:
TOLSURA is not indicated for the treatment of onychomycosis ( 1)
TOLSURA is NOTinterchangeable or substitutable with other itraconazole products ( 1)
Tolsura Dosage and Administration
- Blastomycosis and Histoplasmosis - 130 mg to 260 mg daily ( 2)
- Aspergillosis - 130 mg to 260 mg daily ( 2)
- See full prescribing information for additional dosing for life-threatening situations. ( 2)
- TOLSURA must be administered with food. ( 2)
- Swallow whole. Do not chew crush or break. ( 2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 65 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- Co-administration with certain drugs that either affect metabolism of itraconazole or whose metabolism is affected by itraconazole. ( 4.1)
- Hypersensitivity to itraconazole ( 4.2)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death were reported with the use of itraconazole. Discontinue treatment if signs of liver dysfunction occur ( 5.1)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmias: Life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias and/or sudden death have occurred in patients using certain drugs that are metabolized by human CYP450 enzymes concomitantly with oral itraconazole and/or other CYP3A4 inhibitors. ( 4, 5.3, 5.4)
- Peripheral Neuropathy: This has been reported in patients on long-term therapy with itraconazole. Monitor and promptly evaluate neurologic symptoms. ( 5.5)
- Hearing Loss: Reversible or permanent has been reported in patients. Discontinue treatment if hearing loss occurs ( 5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 1%) are nausea, rash, vomiting, edema, headache, diarrhea, fatigue, fever, pruritus, hypertension, abnormal hepatic function, abdominal pain, dizziness, hypokalemia, anorexia, malaise, decreased libido, somnolence, albuminuria, impotence ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mayne Pharma at 1-844-825-8500 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Itraconazole is mainly metabolized through CYP3A4. Other drugs that either share this metabolic pathway or modify CYP3A4 activity may influence the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole. ( 4, 5, 7.1, 7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tolsura
TOLSURA is indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromisedadult patients:
- Blastomycosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary
- Histoplasmosis, including chronic cavitary pulmonary disease and disseminated, non-meningeal histoplasmosis, and
- Aspergillosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary, in patients who are intolerant of or who are refractory to amphotericin B therapy.
Specimens for fungal cultures and other relevant laboratory studies (wet mount, histopathology, serology) should be obtained before therapy to isolate and identify causative organisms. Therapy may be instituted before the results of the cultures and other laboratory studies are known; however, once these results become available, anti-fungal therapy should be adjusted accordingly
2. Tolsura Dosage and Administration
TOLSURA must be administered with food.
TOLSURA capsules must be swallowed whole. Do not chew, crush or break TOLSURA capsules.
Table 1 below describes the recommended dosage for TOLSURA.
| Indications | Daily Dosing |
|---|---|
| Treatment of Blastomycosis and Histoplasmosis | |
| Recommended dose | 130 mg (2 × 65 mg capsules) once daily
If no obvious improvement, or there is evidence of progressive fungal disease, the dose should be increased in 65 mg increments to a maximum of 260 mg/day (130 mg (2 × 65 mg capsules) twice daily). Doses above 130 mg/day should be given in two divided doses. |
| Treatment of Aspergillosis | |
| Recommended dose | 130 mg (2 × 65 mg capsules) once daily |
| 260 mg/day (130 mg (2 × 65 mg capsules) twice daily) | |
| Treatment in Life-Threatening Situations | |
| Although clinical studies did not provide for a loading dose, it is recommended, based on pharmacokinetic data, that a loading dose should be used. | A loading dose of 130 mg (2 × 65 mg capsules) three times daily (390 mg/day) is recommended to be given for the first 3 days, followed by the appropriate recommended dosing based on indication. Treatment should be continued for a minimum of three months and until clinical parameters and laboratory tests indicate that the active fungal infection has subsided. An inadequate period of treatment may lead to recurrence of active infection. |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TOLSURA (itraconazole capsules) is available in a size 1, hard gelatin capsules with light blue cap and white body, imprinted with "i-65" in black on the cap and containing 65 mg of itraconazole.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Drug Interactions
- Co-administration of certain drugs that are metabolized by human CYP3A4 substrates are contraindicated with TOLSURA because plasma concentrations of such drugs are increased, which may also increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs [see Warnings and Precaution (5.4)and Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
- Co-administration with colchicine, fesoterodine and solifenacin is contraindicated in subjects with varying degrees of renal or hepatic impairment.
- Co-administration with eliglustat is contraindicated in subjects that are poor or intermediate metabolizers of CYP2D6 and in subjects taking strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
- Increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs due to co-administration of TOLSURA can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsade de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Congestive Heart Failure
TOLSURA can cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure (CHF) [see Boxed Warningand Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. For patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as CHF, history or risk factors for CHF, physicians should carefully review the risks and benefits of TOLSURA therapy. These risk factors include cardiac disease such as ischemic and valvular disease; significant pulmonary disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and renal failure and other edematous disorders. Inform such patients of the signs and symptoms of CHF and monitor carefully for signs and symptoms of CHF during treatment. If signs or symptoms of CHF appear or worsen during administration of TOLSURA, reassess the benefit-risk of continuing treatment.
When itraconazole was administered intravenously to anesthetized dogs, a dose-related negative inotropic effect was demonstrated. In a healthy volunteer study of itraconazole intravenous infusion, transient, asymptomatic decreases in left ventricular ejection fraction were observed using gated SPECT imaging; these resolved before the next infusion, 12 hours later.
Itraconazole has been associated with reports of CHF, peripheral edema, and pulmonary edema. In post-marketing experience, heart failure was more frequently reported in patients receiving higher total daily doses of itraconazole of 400 mg although there were also cases reported among those receiving lower total daily doses [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
Calcium channel blockers can have negative inotropic effects which may be additive to those of itraconazole. In addition, itraconazole can inhibit the metabolism of calcium channel blockers. Therefore, when co-administering itraconazole and calcium channel blockers, monitor carefully for signs and symptoms of CHF during treatment due to an increased risk of CHF. Concomitant administration of TOLSURA and felodipine or nisoldipine is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.1), Drug Interactions (7.1)and Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Itraconazole has been associated with cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition, and some of these cases developed within the first week of treatment. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, discontinue treatment and perform testing for liver disease. Continued TOLSURA use or reinstitution of treatment with TOLSURA is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Cardiac Dysrhythmias
Life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias and/or sudden death have occurred in patients using drugs such as, pimozide, methadone, or quinidine concomitantly with oral itraconazole and/or other CYP3A4 inhibitors. Concomitant administration of these drugs with TOLSURA is contraindicated [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4)and Drug Interactions (7)].
5.4 Drug Interaction Potential
Itraconazole has a potential for clinically important drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)] . Co-administration of specific drugs with TOLSURA may result in changes in the efficacy of itraconazole and/or the co-administered drug, life-threatening effects and/or sudden death. [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4.1)and Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
5.5 Peripheral Neuropathy
Cases of peripheral neuropathy have been reported in patients on long-term therapy with itraconazole. Monitor for and promptly evaluate neurologic symptoms. If neuropathy attributable to TOLSURA occurs, discontinue treatment.
5.6 Hearing Loss
Reversible or permanent hearing loss has been reported in patients receiving treatment with itraconazole. Several of these reports included concurrent administration of quinidine which is contraindicated [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4.2)and Drug Interactions (7)] . The hearing loss usually resolves when treatment is stopped but can persist in some patients.
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
TOLSURA is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to itraconazole [see Contraindications (4.2)]. Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with the use of itraconazole [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] . Due to the limited information regarding cross-hypersensitivity between itraconazole and other azole antifungal drugs, careful enquiry about previous hypersensitivity to other azole antifungal drugs should be made when prescribing TOLSURA. If hypersensitivity reactions to TOLSURA occurs, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate therapy.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Congestive Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac Dysrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse reactions that have been identified during post-marketing experience with itraconazole are listed in Table 3. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, reliably estimating their frequency or establishing a causal relationship to drug exposure is not always possible.
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: | Leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia |
| Immune System Disorders: | Anaphylaxis; anaphylactic, anaphylactoid and allergic reactions; serum sickness; angioneurotic edema |
| Nervous System Disorders: | Peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, tremor |
| Eye Disorders: | Visual disturbances, including blurred vision and diplopia |
| Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: | Transientor permanent hearing loss |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: | Pulmonary edema, dyspnea |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders: | Pancreatitis, dysgeusia |
| Hepatobiliary Disorders: | Serious hepatotoxicity (including some cases of fatal acute liver failure), hepatitis |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: | Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, alopecia, photosensitivity, urticaria |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: | Arthralgia |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders: | Urinary incontinence, pollakiuria |
| Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: | Erectile dysfunction |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: | Peripheral edema |
| Investigations: | Blood creatine phosphokinase increased |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of TOLSURA on Other Drugs
Itraconazole and its major metabolite, hydroxy-itraconazole, are potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. Itraconazole is an inhibitor of the drug transporters P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Consequently, itraconazole has the potential to interact with many concomitant drugs resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of the concomitant drugs. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drug which can be severe or life-threatening in some cases (e.g., QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes, respiratory depression, hepatic adverse reactions, hypersensitivity reactions, myelosuppression, hypotension, seizures, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, priapism). Reduced concentrations of concomitant drugs may reduce their efficacy. Table 4 lists examples of drugs that may have their concentrations affected by itraconazole, but is not a comprehensive list. Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways, risk potential, and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with itraconazole.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 4 are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with itraconazole.
| Concomitant Drug Within Class | Prevention or Management | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Drug Interactions with TOLSURA that Increase Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with the Concomitant Drug | ||
| Alpha Blockers | ||
| Alfuzosin
Silodosin Tamsulosin | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Analgesics | ||
| Methadone | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Fentanyl | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Alfentanil
Buprenorphine (IV and sublingual) Oxycodone * Sufentanil | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antiarrhythmics | ||
| Disopyramide
Dofetilide Dronedarone Quinidine * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Digoxin * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antibacterials | ||
| Bedaquiline † | Concomitant TOLSURA not recommended for more than 2 weeks at any time during bedaquiline treatment. | |
| Rifabutin | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. See also Table 5. | |
| Clarithromycin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 5. | |
| Trimetrexate | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Anticoagulants and Antiplatelets | ||
| Ticagrelor | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Apixaban
Rivaroxaban Vorapaxar | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Cilostazol
Dabigatran Warfarin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| Carbamazepine | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. See also Table 5. | |
| Antidiabetic Drugs | ||
| Repaglinide
*
Saxagliptin | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Antihelminthics, Antifungals and Antiprotozoals | ||
| Isavuconazonium | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Praziquantel | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Artemether-lumefantrine
Quinine * | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Antimigraine Drugs | ||
| Ergot alkaloids (e.g., dihydroergotamine, ergotamine) | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Eletriptan | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary | |
| Antineoplastics | ||
| Irinotecan | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Axitinib
Bosutinib Cabazitaxel Cabozantinib Ceritinib Cobimetinib * Crizotinib Dabrafenib Dasatinib | Docetaxel
Ibrutinib Lapatinib Nilotinib Olaparib * Pazopanib Sunitinib Trabectedin Trastuzumab-emtansine Vinca alkaloids | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. |
| Bortezomib
Brentuximab-vedotin Busulfan * Erlotinib Gefitinib * Idelalisib Imatinib Ixabepilone | Nintedanib
Panobinostat Ponatinib Ruxolitinib Sonidegib Vandetanib * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For Idelalisib, see also Table 5. |
| Antipsychotics, Anxiolytics and Hypnotics | ||
| Alprazolam
*
Aripiprazole * Buspirone * Diazepam * Haloperidol * | Midazolam (IV)
*
Quetiapine Ramelteon Risperidone * Suvorexant | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Zopiclone * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Lurasidone
Midazolam (oral) * Pimozide Triazolam * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Antivirals | ||
| Simeprevir | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Daclatasvir
Indinavir * Maraviroc | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For indinavir, see also Table 5. | |
| Cobicistat
Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted) Ritonavir Saquinavir (unboosted) * | Monitor for adverse reactions. See also Table 5. | |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Beta Blockers | ||
| Nadolol * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | ||
| Felodipine
*
Nisoldipine | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Diltiazem
Other dihydropyridines Verapamil | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For diltiazem, see also Table 5. | |
| Cardiovascular Drugs, Miscellaneous | ||
| Ivabradine
Ranolazine | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Aliskiren
*
Riociguat Sildenafil (for pulmonary hypertension) Tadalafil (for pulmonary hypertension) | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Urologic Drugsbelow. | |
| Bosentan
Guanfacine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Contraceptives | ||
| Dienogest
Ulipristal | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Diuretics | ||
| Eplerenone | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | ||
| Naloxegol | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Aprepitant
Loperamide * | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Netupitant | Monitor for adverse reactions. | |
| Immunosuppressants | ||
| Everolimus
Sirolimus Temsirolimus (IV) | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Budesonide (inhalation)
*
Budesonide (noninhalation) Ciclesonide (inhalation) Cyclosporine (IV) * Cyclosporine (non-IV) Dexamethasone * | Fluticasone (inhalation)
*
Fluticasone (nasal) Methylprednisolone * Tacrolimus (IV) * Tacrolimus (oral) | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Lipid-Lowering Drugs | ||
| Lomitapide
Lovastatin * Simvastatin * | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Atorvastatin * | Monitor for drug adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary . | |
| Respiratory Drugs | ||
| Salmeterol | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| SSRIs, Tricyclics and Related Antidepressants | ||
| Venlafaxine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Urologic Drugs | ||
| Avanafil | Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Fesoterodine | Patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary |
|
| Solifenacin | Patients with severe renal or moderate to severe hepatic impairment: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment.
Other patients: Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. |
|
| Darifenacin
Vardenafil | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Dutasteride
Oxybutynin * Sildenafil (for erectile dysfunction) Tadalafil (for erectile dysfunction and benign prostatic hyperplasia) Tolterodine | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. For sildenafil and tadalafil, see also Cardiovascular Drugsabove. | |
| Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances | ||
| Colchicine | Patients with renal or hepatic impairment:Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment.
Other patients: Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. |
|
| Eliglustat | CYP2D6 EMs
‡taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor, CYP2D6 IMs
‡, or CYP2D6 PMs
‡: Contraindicated during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment.
CYP2D6 EMs ‡not taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor : Monitor for adverse reactions. Eliglustat dose reduction may be necessary. |
|
| Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Alitretinoin (oral)
Cabergoline Cannabinoids Cinacalcet Ivacaftor | Monitor for adverse reactions. Concomitant drug dose reduction may be necessary. | |
| Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists | ||
| Conivaptan
Tolvaptan | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Drug Interactions with TOLSURA that Decrease Concomitant Drug Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of the Concomitant Drug | ||
| Antineoplastics | ||
| Regorafenib | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | ||
| Saccharomyces boulardii | Not recommended during and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. | |
| Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs | ||
| Meloxicam * | Concomitant drug dose increase may be necessary. | |
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on TOLSURA
Itraconazole is mainly metabolized through CYP3A4. Other substances that either share this metabolic pathway or modify CYP3A4 activity may influence the pharmacokinetics of itraconazole. Some concomitant drugs have the potential to interact with TOLSURA resulting in either increased or sometimes decreased concentrations of TOLSURA. Increased concentrations may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with TOLSURA. Decreased concentrations may reduce TOLSURA efficacy.
Table 4 lists examples of drugs that may affect itraconazole concentrations, but is not a comprehensive list. Refer to the approved product labeling to become familiar with the interaction pathways, risk potential and specific actions to be taken with regards to each concomitant drug prior to initiating therapy with TOLSURA.
Although many of the clinical drug interactions in Table 5 are based on information with a similar azole antifungal, ketoconazole, these interactions are expected to occur with TOLSURA.
| Concomitant Drug Within Class | Prevention or Management |
|---|---|
|
|
| Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Increase TOLSURA Concentrations and May Increase Risk of Adverse Reactions Associated with TOLSURA | |
| Antibacterials | |
| Ciprofloxacin
*
Erythromycin * Clarithromycin * | Monitor for adverse reactions. TOLSURA dose reduction may be necessary. |
| Antineoplastics | |
| Idelalisib | Monitor for adverse reactions. TOLSURA dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 4. |
| Antivirals | |
| Cobicistat
Darunavir (ritonavir-boosted) Elvitegravir (ritonavir-boosted) Fosamprenavir (ritonavir-boosted) Indinavir * Ritonavir Saquinavir | Monitor for adverse reactions. TOLSURA dose reduction may be necessary. For, cobicistat, elvitegravir, indinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir, see also Table 4. |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | |
| Diltiazem | Monitor for adverse reactions. TOLSURA dose reduction may be necessary. See also Table 4. |
| Gastrointestinal Drugs | |
| Drugs that reduce gastric acidity e.g. acid neutralizing medicines such as aluminum hydroxide, or acid secretion suppressors such as H 2- receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole). | Co-administration of these drugs, including omeprazole, with TOLSURA increases the systemic exposure to itraconazole. Monitor for adverse reactions. TOLSURA dose reduction may be necessary [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Drug Interactions with Other Drugs that Decrease TOLSURA Concentrations and May Reduce Efficacy of TOLSURA | |
| Antibacterials | |
| Isoniazid
Rifampicin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during TOLSURA treatment. |
| Rifabutin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. See also Table 4. |
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Phenobarbital
Phenytoin * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during TOLSURA treatment. |
| Carbamazepine | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. See also Table 4. |
| Antivirals | |
| Efavirenz
*
Nevirapine * | Not recommended 2 weeks before and during TOLSURA treatment. |
| Miscellaneous Drugs and Other Substances | |
| Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor | Not recommended 2 weeks before, during, and 2 weeks after TOLSURA treatment. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
The long-term effects of itraconazole on bone growth in children are unknown. Bone lesions were observed in the young adult rats dosed with oral itraconazole for 3 to 12 months [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)] .
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of itraconazole did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. It is advised to use TOLSURA Capsules in these patients only if it is determined that the potential benefit outweighs the potential risks. In general, it is recommended that the dose selection for an elderly patient should be taken into consideration, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Reversible or permanent hearing loss has been reported in elderly patients receiving treatment with itraconazole. Several of these reports included concurrent administration of quinidine which is contraindicated [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4.1)and Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
8.6 Renal Impairment
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. It is recommended that patients with renal impairment be carefully monitored when taking TOLSURA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Limited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with hepatic impairment. It is recommended that patients with impaired hepatic function be carefully monitored when taking TOLSURA. It is recommended that the prolonged elimination half-life of itraconazole observed in the single oral dose clinical trial with itraconazole capsules in cirrhotic patients be considered when deciding to initiate therapy with other medications metabolized by CYP3A4 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
In patients with elevated or abnormal liver enzymes or active liver disease, or who have experienced liver toxicity with other drugs, treatment with TOLSURA is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. It is recommended that liver function monitoring be done in patients with pre-existing hepatic function abnormalities or those who have experienced liver toxicity with other medications [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
10. Overdosage
Itraconazole is not removed by dialysis. In the event of accidental overdosage, supportive measures should be employed. Activated charcoal may be given if considered appropriate.
11. Tolsura Description
TOLSURA (itraconazole capsules) is an azole antifungal drug for oral use. Itraconazole is an equal mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the following structural formula and nomenclature:
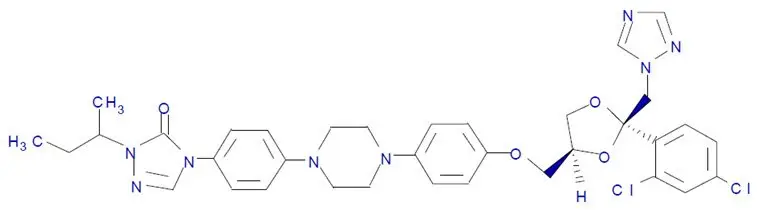
(±)-1-[( R*)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 R*,4 S*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one mixture with (±)-1-[( R*)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 S*,4 R*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
or
(±)-1-[( RS)- sec-butyl]-4-[ p-[4-[ p-[[(2 R,4 S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ 2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one.
Itraconazole has a molecular formula of C 35H 38Cl 2N 8O 4and a molecular weight of 705.64. It is a white to slightly yellowish powder. It is insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohols, and freely soluble in dichloromethane. It has a pKa of 3.70 (based on extrapolation of values obtained from methanolic solutions) and a log (n-octanol/water) partition coefficient of 5.66 at pH 8.1.
Each TOLSURA capsule contains 65 mg of itraconazole dispersed in a polymer matrix and encapsulated in a hard gelatin capsule. The inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose phthalate, magnesium stearate and sodium starch glycolate.
12. Tolsura - Clinical Pharmacology
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
When itraconazole was administered intravenously to anesthetized dogs, a dose-related negative inotropic effect was documented.
In three toxicology studies using rats, itraconazole (dosed in feed or via oral gavage) induced bone defects at dosage levels as low as 20 mg/kg/day (3×MRHD, based on mg/kg comparisons). The induced defects included reduced bone plate activity, thinning of the zona compacta of the large bones, and increased bone fragility. At a dosage level of 80 mg/kg/day (12×MRHD) over 1 year or 160 mg/kg/day (25×MRHD) for 6 months, itraconazole induced small tooth pulp with hypocellular appearance in some rats.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Blastomycosis
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=73 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status treated with the100 mg itraconazole capsules. The median dose was 200 mg/day (2 × 100 mg). A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 6 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of blastomycosis compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
14.2 Histoplasmosis
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=34 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status (not including HIV-infected patients) treated with the 100 mg itraconazole capsules. The median dose was 200 mg/day (2 × 100 mg). A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 12 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of histoplasmosis, compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
14.3 Histoplasmosis in HIV-infected Patients
Data from a small number of HIV-infected patients treated with the 100 mg itraconazole capsules suggested that the response rate of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is similar to that of non-HIV-infected patients. The clinical course of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is more severe and usually requires maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
14.4 Aspergillosis
Analyses were conducted on data from an open-label, "single-patient-use" protocol designed to make itraconazole available in the U.S. for patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy (N=190). The findings were corroborated by two smaller open-label studies (N=31 combined) in the same patient population. Most adult patients were treated with a daily dose of 200 (2 × 100 mg) to 400 (4 × 100 mg) mg, with a median duration of 3 months. Results of these studies demonstrated substantial evidence of effectiveness of the 100 mg itraconazole capsules as a second-line therapy for the treatment of aspergillosis compared with the natural history of the disease in patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy.
16. How is Tolsura supplied
TOLSURA (itraconazole capsules) is supplied in a size 1, hard gelatin capsules with light blue cap and white body, imprinted with "i-65" in black on the cap and containing 65 mg of itraconazole.
TOLSURA capsules are supplied as follows:
| Bottles of 8 capsules | Bottles of 60 capsules |
| NDC 51862-462-88 | NDC 51862-462-60 |
| TOLSURA
itraconazole capsule, gelatin coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Mayne Pharma Commercial LLC (867220261) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mayne Pharma International Pty Ltd | 756003745 | manufacture(51862-462) , analysis(51862-462) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Greenville, Inc. | 118812386 | label(51862-462) , pack(51862-462) , analysis(51862-462) | |





