Drug Detail:Tracleer (Bosentan [ boe-sen-tan ])
Drug Class: Agents for pulmonary hypertension
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TRACLEER ®(bosentan) tablets, for oral use
TRACLEER ®(bosentan) tablets for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
WARNING: RISKS OF HEPATOTOXICITY and EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
TRACLEER is available only through a restricted distribution program called the Bosentan REMS Program because of these risks ( 5.3):
Elevations of liver aminotransferases (ALT, AST) and liver failure have been reported with TRACLEER ( 5.1).
- Measure liver aminotransferases prior to initiation of treatment and then monthly ( 2.1, 5.1).
- Discontinue TRACLEER if aminotransferase elevations are accompanied by signs or symptoms of liver dysfunction or injury or increases in bilirubin ≥2×ULN ( 2.4, 5.1).
Based on animal data, TRACLEER is likely to cause major birth defects if used during pregnancy ( 4.1, 5.2, 8.1).
- Must exclude pregnancy before and during treatment ( 2.1, 4.1, 8.1).
- To prevent pregnancy, females of reproductive potential must use two reliable forms of contraception during treatment and for one month after stopping TRACLEER ( 4.1, 5.2, 8.1).
Indications and Usage for Tracleer
TRACLEER is an endothelin receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1):
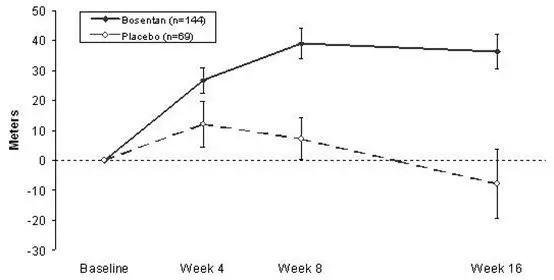
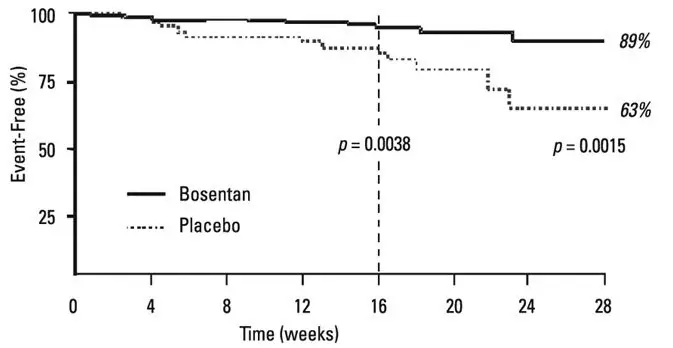
- in adults to improve exercise ability and to decrease clinical worsening. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominantly patients with WHO Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (60%), PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (21%), and PAH associated with congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunts (18%) ( 1).
- in pediatric patients aged 3 years and older with idiopathic or congenital PAH to improve pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), which is expected to result in an improvement in exercise ability ( 1).
Tracleer Dosage and Administration
- Patients older than 12 years of age: initiate at 62.5 mg orally twice daily; for patients weighing greater than 40 kg, increase to 125 mg orally twice daily after 4 weeks ( 2.2).
- Patients 12 years of age and younger: dosage is based on weight, see Table 1( 2.2).
- Reduce the dose and closely monitor patients developing aminotransferase elevations more than 3×Upper Limit of Normal (ULN) ( 2.1).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Film-coated tablet: 62.5 mg and 125 mg ( 3)
- Tablet for oral suspension: 32 mg ( 3)
Contraindications
- Pregnancy ( 4.1)
- Use with Cyclosporine A ( 4.2)
- Use with Glyburide ( 4.3)
- Hypersensitivity ( 4.4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Fluid retention: May require intervention ( 5.4).
- Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD): If signs of pulmonary edema occur, consider the diagnosis of associated PVOD and consider discontinuing TRACLEER ( 5.5).
- Decreased sperm counts ( 5.6).
- Decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit: Monitor hemoglobin levels after 1 and 3 months of treatment, then every 3 months thereafter ( 5.7).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Common adverse reactions (≥3% more than placebo) for the film-coated tablet are respiratory tract infection and anemia ( 6.1).
- Common adverse reactions (≥15%) for the dispersible tablet are upper respiratory tract infections and pyrexia ( 6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen at 1-800-526-7736 (1-800-JANSSEN) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
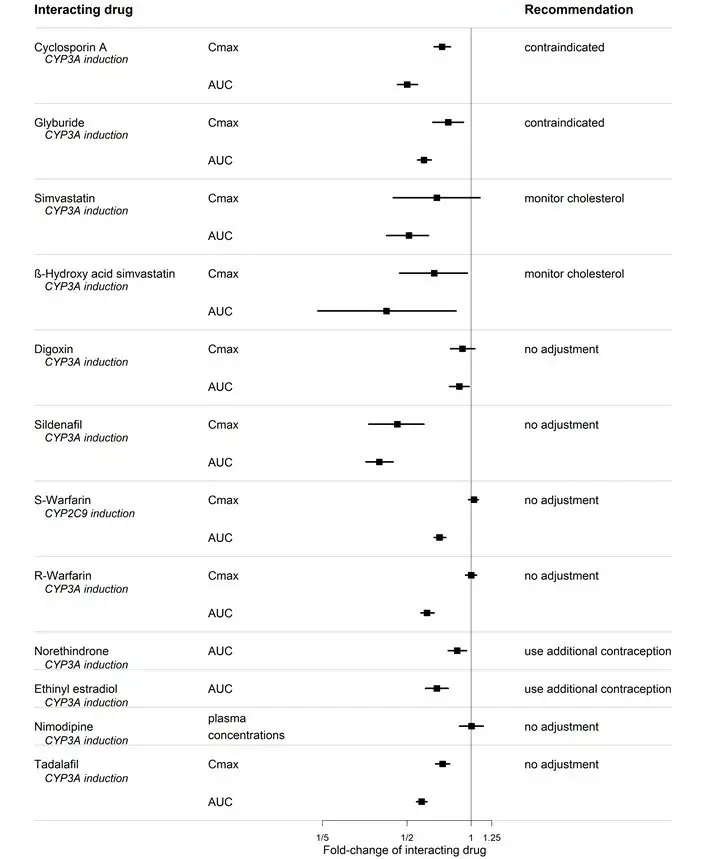
- Cytochrome P450: Coadministration of TRACLEER with drugs metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A can increase exposure to TRACLEER and/or the coadministered drug ( 4.2, 4.3, 7.1).
- Hormonal contraceptives: TRACLEER use decreases contraceptive exposure and reduces effectiveness ( 7.2).
Use In Specific Populations
- Nursing mothers: Choose breastfeeding or TRACLEER ( 8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2022
Related/similar drugs
sildenafil, tadalafil, Adcirca, Revatio, Opsumit, ambrisentanFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISKS OF HEPATOTOXICITY and EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY
Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, TRACLEER is available only through a restricted program called the Bosentan REMS Program. Under the Bosentan REMS, prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must enroll in the program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
1. Indications and Usage for Tracleer
TRACLEER is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1):
- in adults to improve exercise ability and to decrease clinical worsening. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominantly patients with WHO Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (60%), PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (21%), and PAH associated with congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunts (18%) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] .
- in pediatric patients aged 3 years and older with idiopathic or congenital PAH to improve pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), which is expected to result in an improvement in exercise ability.
2. Tracleer Dosage and Administration
2.1 Required Monitoring
Healthcare professionals who prescribe TRACLEER must enroll in the Bosentan REMS Program and must comply with the required monitoring to minimize the risks associated with TRACLEER [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
Obtain a pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential prior to TRACLEER treatment, monthly during treatment and one month after stopping TRACLEER. Initiate treatment with TRACLEER in females of reproductive potential only after a negative pregnancy test [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
Measure liver aminotransferase levels prior to initiation of treatment and then monthly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Administer TRACLEER orally following the dosing recommendations in Table 1. Doses above 125 mg twice daily did not appear to confer additional benefit sufficient to offset the increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
| Initial 4 weeks | Maintenance (after 4 weeks) | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients >12 years of age and >40 kg | 62.5 mg twice daily | 125 mg twice daily |
| Patients >12 years of age and <40 kg | 62.5 mg twice daily | 62.5 mg twice daily |
| Patients ≤12 years of age | ||
| ≥4–8 kg | 16 mg twice daily | 16 mg twice daily |
| >8–16 kg | 32 mg twice daily | 32 mg twice daily |
| >16–24 kg | 48 mg twice daily | 48 mg twice daily |
| >24–40 kg | 64 mg twice daily | 64 mg twice daily |
2.3 Administration
TRACLEER film-coated tablets and tablets for oral suspension (dispersible tablets) should be administered orally twice daily.
Disperse tablets for oral suspension, or dispersible tablet half, in a minimal amount of water immediately before administration.
Store divided dispersible tablet pieces at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF) in the opened blister for up to 7 days.
2.4 Dosage Adjustments for Aminotransferase Elevations
If aminotransferase levels increase, adjust monitoring and treatment plan according to Table 2.
Discontinue TRACLEER if liver aminotransferase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity (such as nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, or unusual lethargy or fatigue) or bilirubin ≥2 ×Upper Limit of Normal (ULN). There is no experience with the reintroduction of TRACLEER in these circumstances.
| ALT/AST levels | Treatment and monitoring recommendations |
|---|---|
| >3 and ≤5 ×ULN | Confirm by another aminotransferase test; if confirmed,
|
| >5 and ≤8 ×ULN | Confirm by another aminotransferase test; if confirmed, stop treatment and monitor aminotransferase levels at least every 2 weeks. Once the aminotransferase levels return to pretreatment values,
|
| >8 ×ULN | Stop treatment permanently. There is no experience with reintroduction of TRACLEER in these circumstances. |
2.6 Use in Patients with Pre-existing Hepatic Impairment
Avoid initiation of TRACLEER in patients with aminotransferases >3 ×ULN. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mildly impaired liver function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
62.5 mg tablets: round, biconvex, orange-white tablets, debossed with identification marking "62,5"
125 mg tablets: oval, biconvex, orange-white tablets, debossed with identification marking "125"
32 mg tablets for oral suspension:
- quadrisected: clover-shaped, quadrisected, pale yellow to off-white tablets, debossed with identification marking "32" on the side opposite the quadrisection lines,
- bisected: round, pale yellow to off-white tablets, bisected on one side and debossed with identification marking "32" on the other side.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Pregnancy
Use of TRACLEER is contraindicated in females who are or may become pregnant. To prevent pregnancy, females of reproductive potential must use two reliable forms of contraception during treatment and for one month after stopping TRACLEER [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
4.2 Use with Cyclosporine A
Co-administration of cyclosporine A and bosentan resulted in markedly increased plasma concentrations of bosentan. Therefore, concomitant use of TRACLEER and cyclosporine A is contraindicated [see Cytochrome P450 Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
4.3 Use with Glyburide
An increased risk of liver enzyme elevations was observed in patients receiving glyburide concomitantly with bosentan. Therefore co-administration of glyburide and TRACLEER is contraindicated [see Cytochrome P450 Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
4.4 Hypersensitivity
TRACLEER is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to bosentan or any component of the product. Observed reactions include Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), anaphylaxis, rash, and angioedema [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Description (11)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
ALT or AST >3 ×ULN were observed in 11% of TRACLEER-treated patients (n=658) compared to 2% of placebo-treated patients (n=280). Three-fold increases were seen in 12% of 95 pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) patients on 125 mg twice daily and 14% of 70 PAH patients on 250 mg twice daily. Eight-fold increases were seen in 2% of PAH patients on 125 mg twice daily and 7% of PAH patients on 250 mg twice daily. Bilirubin increases to ≥3 ×ULN were associated with aminotransferase increases in 2 of 658 (0.3%) of patients treated with TRACLEER. In a pooled analysis of four pediatric studies conducted in PAH (n =100), elevations in liver aminotransferases ≥3×ULN were observed in 2% of patients. The combination of hepatocellular injury (increases in aminotransferases of >3 ×ULN) and increases in total bilirubin (≥2 ×ULN) is a marker for potential serious hepatotoxicity.
Elevations of AST or ALT associated with TRACLEER are dose-dependent, occur both early and late in treatment, usually progress slowly, are typically asymptomatic, and usually have been reversible after treatment interruption or cessation. Aminotransferase elevations also may reverse spontaneously while continuing treatment with TRACLEER.
Liver aminotransferase levels must be measured prior to initiation of treatment and then monthly and therapy adjusted accordingly [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4)] . Discontinue TRACLEER if liver aminotransferase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity (such as nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, or unusual lethargy or fatigue) or increases in bilirubin ≥2 ×ULN.
Avoid initiation of TRACLEER in patients with elevated aminotransferases (>3 ×ULN) prior to drug initiation because monitoring hepatotoxicity in these patients may be more difficult [see Boxed Warning, Dosage and Administration (2.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] .
In WHO Functional Class II patients, consider whether the benefits of TRACLEER are sufficient to offset the risk of hepatotoxicity, which may preclude future use as their disease progresses.
5.2 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal reproduction studies, TRACLEER may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated in females who are pregnant. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Obtain a pregnancy test prior to TRACLEER treatment, monthly during treatment and for one month after stopping treatment. Advise females of reproductive potential to use two reliable forms of contraception during treatment with TRACLEER and for at least one month after the last dose [see Dosage and Administration (2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)] .
TRACLEER is only available for females through a restricted program under REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
5.3 Prescribing and Distribution Program for Bosentan
Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, TRACLEER is available only through a restricted program called the Bosentan REMS Program. As a component of the Bosentan REMS, prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must enroll in the program [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2), Contraindications (4.1)] .
Required components of the Bosentan REMS are:
- Healthcare professionals who prescribe TRACLEER must review the prescriber educational materials, enroll in the Bosentan REMS Program and comply with its requirements.
- Healthcare professionals must (1) review serum aminotransferases (ALT/AST) and bilirubin, and agree to order and monitor these tests monthly; and (2) for females of reproductive potential, confirm that the patient is not pregnant, and agree to order and monitor pregnancy tests monthly.
- To receive TRACLEER, all patients must understand the risks and benefits, and complete a patient enrollment form.
- Pharmacies that dispense TRACLEER must enroll in the program and agree to comply with the Bosentan REMS Program requirements.
Further information about TRACLEER and the Bosentan REMS Program is available at www.BosentanREMSProgram.com or 1-866-359-2612.
5.4 Fluid Retention
Peripheral edema is a known clinical consequence of PAH and worsening PAH and is also a known effect of TRACLEER and other endothelin receptor antagonists. In PAH clinical trials with TRACLEER, combined adverse events of fluid retention or edema were reported in 1.7% (placebo-corrected) of patients.
In addition, there have been numerous postmarketing reports of fluid retention in patients with pulmonary hypertension occurring within weeks after starting TRACLEER. Patients required intervention with a diuretic, fluid management, or hospitalization for decompensating heart failure.
If clinically significant fluid retention develops, with or without associated weight gain, further evaluation should be undertaken to determine the cause, such as TRACLEER or underlying heart failure, and the possible need for treatment or discontinuation of TRACLEER [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14.2)] .
5.5 Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease
If signs of pulmonary edema occur, consider the possibility of associated pulmonary veno-occlusive disease and consider whether TRACLEER should be discontinued.
5.6 Decreased Sperm Counts
Decreased sperm counts have been observed in patients receiving TRACLEER. Preclinical data also suggest that TRACLEER, similar to other endothelin receptor antagonists, may have an adverse effect on spermatogenesis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)] .
5.7 Decreases in Hemoglobin and Hematocrit
Treatment with TRACLEER can cause a dose-related decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit. There have been postmarketing reports of decreases in hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit that have resulted in anemia requiring transfusion. It is recommended that hemoglobin concentrations be checked after 1 and 3 months, and every 3 months thereafter. If a marked decrease in hemoglobin concentration occurs, further evaluation should be undertaken to determine the cause and need for specific treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following important adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Fluid Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Safety data on TRACLEER were obtained from 13 clinical studies (9 placebo-controlled and 4 open-label) in 870 adult patients with PAH and other diseases. Doses up to 8 times the currently recommended clinical dose (125 mg twice daily) were administered for a variety of durations. The exposure to TRACLEER in these trials ranged from 1 day to 4.1 years (n=94 for 1 year; n=61 for 1.5 years; and n=39 for more than 2 years). Exposure of PAH patients (n=328) to TRACLEER ranged from 1 day to 1.7 years (n=174 more than 6 months and n=28 more than 12 months).
Treatment discontinuations due to adverse events other than those related to pulmonary hypertension during the clinical trials in adult patients with PAH were more frequent on TRACLEER (6%; 15/258 patients) than on placebo (3%; 5/172 patients). In this database the only cause of discontinuations >1% and occurring more often on TRACLEER was abnormal liver function.
The adverse drug events that occurred in ≥3% of the TRACLEER-treated patients and were more common on TRACLEER in placebo-controlled trials in PAH at doses of 125 or 250 mg twice daily are shown in Table 3:
| Adverse Event | TRACLEER
n=258 | Placebo
n=172 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | |
|
||||
| Respiratory Tract Infection † | 56 | 22% | 30 | 17% |
| Headache | 39 | 15% | 25 | 14% |
| Edema | 28 | 11% | 16 | 9% |
| Chest Pain | 13 | 5% | 8 | 5% |
| Syncope | 12 | 5% | 7 | 4% |
| Flushing | 10 | 4% | 5 | 3% |
| Hypotension | 10 | 4% | 3 | 2% |
| Sinusitis | 9 | 4% | 4 | 2% |
| Arthralgia | 9 | 4% | 3 | 2% |
| Serum Aminotransferases, abnormal | 9 | 4% | 3 | 2% |
| Palpitations | 9 | 4% | 3 | 2% |
| Anemia | 8 | 3% | - | - |
TRACLEER was evaluated for safety in 119 pediatric patients in uncontrolled studies. The safety profile was similar to that observed in adult patients with PAH.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
There have been several postmarketing reports of angioedema associated with the use of TRACLEER. The onset of the reported cases occurred within a range of 8 hours to 21 days after starting therapy. Some patients were treated with an antihistamine and their signs of angioedema resolved without discontinuing TRACLEER.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported during the postapproval use of TRACLEER. Because these adverse reactions are reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to TRACLEER exposure:
- Unexplained hepatic cirrhosis [see Boxed Warning]
- Liver failure [see Boxed Warning]
- Hypersensitivity, DRESS, and anaphylaxis [see Contraindications (4.4)]
- Thrombocytopenia
- Rash
- Jaundice
- Anemia requiring transfusion
- Neutropenia and leukopenia
- Nasal congestion
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Cytochrome P450 Drug Interactions
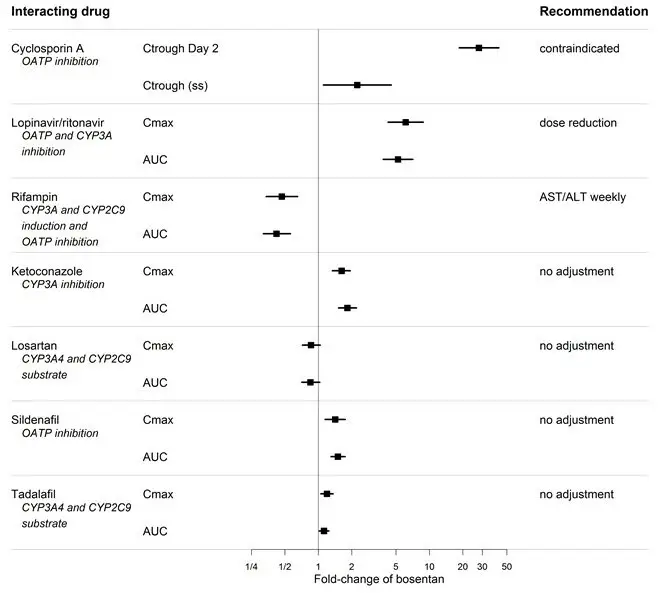
Bosentan is metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A. Inhibition of these enzymes may increase the plasma concentration of bosentan [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)] . Concomitant administration of both a CYP2C9 inhibitor (such as fluconazole or amiodarone) and a strong CYP3A inhibitor (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) or a moderate CYP3A inhibitor (e.g., amprenavir, erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem) with TRACLEER will likely lead to large increases in plasma concentrations of bosentan. Co-administration of such combinations of a CYP2C9 inhibitor plus a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor with TRACLEER is not recommended.
Bosentan is an inducer of CYP3A and CYP2C9. Consequently plasma concentrations of drugs metabolized by these two isozymes will be decreased when TRACLEER is co-administered. Bosentan had no relevant inhibitory effect on any CYP isozyme in vitro(CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A). Consequently, TRACLEER is not expected to increase the plasma concentrations of drugs metabolized by these enzymes.
Figure 1. CYP3A induction-mediated effect of bosentan on other drugs

Figure 2. Effect of other drugs on bosentan
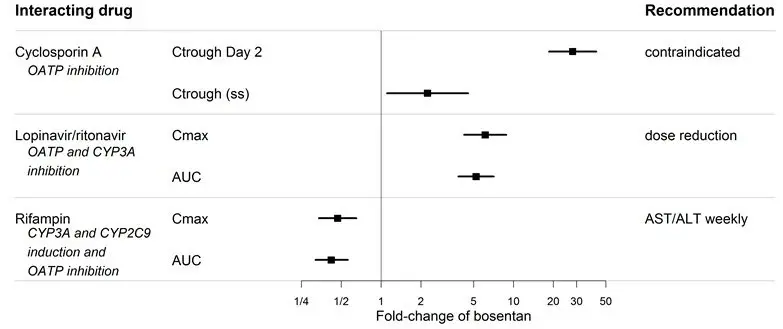
7.2 Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives, including oral, injectable, transdermal, and implantable forms, may not be reliable when TRACLEER is co-administered. Females should practice additional methods of contraception and not rely on hormonal contraception alone when taking TRACLEER [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)] .
An interaction study demonstrated that co-administration of bosentan and a combination oral hormonal contraceptive produced average decreases of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol levels of 14% and 31%, respectively. However, decreases in exposure were as much as 56% and 66%, respectively, in individual subjects.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
Animal Data
Bosentan was teratogenic in rats given oral doses two times the MRHD (on a mg/m 2basis). In an embryo-fetal toxicity study in rats, bosentan showed dose-dependent teratogenic effects, including malformations of the head, mouth, face and large blood vessels. Bosentan increased stillbirths and pup mortality at oral doses 2 and 10 times the MRHD (on a mg/m 2basis). Although birth defects were not observed in rabbits given oral doses of up to the equivalent of 10.5 g/day in a 70 kg person, plasma concentrations of bosentan in rabbits were lower than those reached in the rat. The similarity of malformations induced by bosentan and those observed in endothelin-1 knockout mice and in animals treated with other endothelin receptor antagonists indicates that embryo-fetal toxicity is a class effect of these drugs.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The efficacy of TRACLEER in patients <18 years is supported by data from an uncontrolled trial in which 19 pediatric patients were treated with TRACLEER. In this study, cardiopulmonary hemodynamic improvements were similar to those seen in adults treated with TRACLEER [see Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (14.1)] . Safety in pediatric patients is supported by data from 100 pediatric patients treated with TRACLEER for a median of 17 months [see Clinical Studies Experience (6.1), Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (14.1)] .
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of TRACLEER did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Because there is in vitroand in vivoevidence that the main route of excretion of bosentan is biliary, liver impairment could be expected to increase exposure (C maxand AUC) of bosentan. The pharmacokinetics of TRACLEER have not been evaluated in patients with severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), the systemic exposures to bosentan and its active metabolite increased significantly. TRACLEER should generally be avoided in patients with moderate or severe liver impairment. Pharmacokinetics of bosentan were not altered in patients with mild impairment of hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class A) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Pharmacokinetics (12.3)] .
10. Overdosage
Bosentan has been given as a single dose of up to 2400 mg in normal volunteers, or up to 2000 mg/day for 2 months in patients, without any major clinical consequences. The most common side effect was headache of mild to moderate intensity. In the cyclosporine A interaction study, in which doses of 500 and 1000 mg twice daily of bosentan were given concomitantly with cyclosporine A, trough plasma concentrations of bosentan increased 30-fold, resulting in severe headache, nausea, and vomiting, but no serious adverse events. Mild decreases in blood pressure and increases in heart rate were observed.
In the postmarketing period, there was one reported overdose of 10,000 mg of TRACLEER taken by an adolescent male patient. He had symptoms of nausea, vomiting, hypotension, dizziness, sweating, and blurred vision. He recovered within 24 hours with blood pressure support.
Bosentan is unlikely to be effectively removed by dialysis due to the high molecular weight and extensive plasma protein binding.
11. Tracleer Description
TRACLEER ®is the proprietary name for bosentan, an endothelin receptor antagonist that belongs to a class of highly substituted pyrimidine derivatives, with no chiral centers. It is designated chemically as 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-5-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-[2,2´]-bipyrimidin-4-yl]- benzenesulfonamide monohydrate and has the following structural formula:
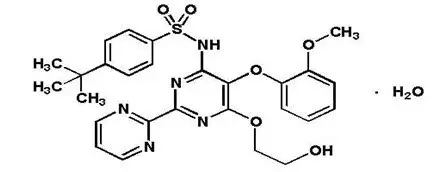
Bosentan has a molecular weight of 569.64 and a molecular formula of C 27H 29N 5O 6S∙H 2O. Bosentan is a white to yellowish powder. It is poorly soluble in water (1.0 mg/100 mL) and in aqueous solutions at low pH (0.1 mg/100 mL at pH 1.1 and 4.0; 0.2 mg/100 mL at pH 5.0). Solubility increases at higher pH values (43 mg/100 mL at pH 7.5). In the solid state, bosentan is very stable, is not hygroscopic and is not light sensitive.
TRACLEER is available as 62.5 mg and 125 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration, and contains the following excipients: corn starch, ethylcellulose, glyceryl behenate, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, povidone, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Each TRACLEER 62.5 mg tablet contains 64.54 mg of bosentan monohydrate, equivalent to 62.5 mg of anhydrous bosentan. Each TRACLEER 125 mg tablet contains 129.08 mg of bosentan monohydrate, equivalent to 125 mg of anhydrous bosentan.
TRACLEER is also available as a 32 mg tablet for oral suspension and contains the following excipients: acesulfame potassium, aspartame (E951), calcium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous, cellulose microcrystalline, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, silica colloidal anhydrous, tartaric acid, and tutti frutti flavor. Each dispersible tablet contains 1.87 mg of phenylalanine. Each dispersible tablet contains 33.045 mg of bosentan monohydrate, equivalent to 32 mg anhydrous bosentan.
12. Tracleer - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bosentan is a specific and competitive antagonist at endothelin receptor types ET Aand ET B. Bosentan has a slightly higher affinity for ET Areceptors than for ET Breceptors. The clinical impact of dual endothelin blockage is unknown.
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a neurohormone, the effects of which are mediated by binding to ET Aand ET Breceptors in the endothelium and vascular smooth muscle. ET-1 concentrations are elevated in plasma and lung tissue of patients with PAH, suggesting a pathogenic role for ET-1 in this disease.
14. Clinical Studies
14.2 Lack of Benefit in Congestive Heart Failure
TRACLEER is not effective in the treatment of congestive heart failure with left ventricular dysfunction. In a pair of studies, 1613 subjects with NYHA Class III-IV heart failure, left ventricular ejection fraction <35%, on diuretics, ACE inhibitor, and other therapies, were randomized to placebo or TRACLEER (62.5 mg twice daily titrated as tolerated to 125 mg twice daily) and followed for up to 70 weeks. Use of TRACLEER was associated with no benefit on patient global assessment (the primary end point) or mortality. However, hospitalizations for heart failure were more common during the first 4 to 8 weeks after TRACLEER was initiated. In a placebo-controlled trial of patients with severe chronic heart failure, there was an increased incidence of hospitalization for CHF associated with weight gain and increased leg edema during the first 4–8 weeks of treatment with TRACLEER. Patients required intervention with a diuretic, fluid management, or hospitalization for decompensating heart failure.
16. How is Tracleer supplied
62.5 mgfilm-coated, round, biconvex, orange-white tablets, debossed with identification marking "62,5", packaged in a white high-density polyethylene bottle and a white polypropylene child-resistant cap or in foil blister-strips for hospital unit-dosing.
NDC 66215-101-06: Bottle containing 60 tablets.
NDC 66215-101-03: Carton of 30 tablets in 10 blister strips of 3 tablets.
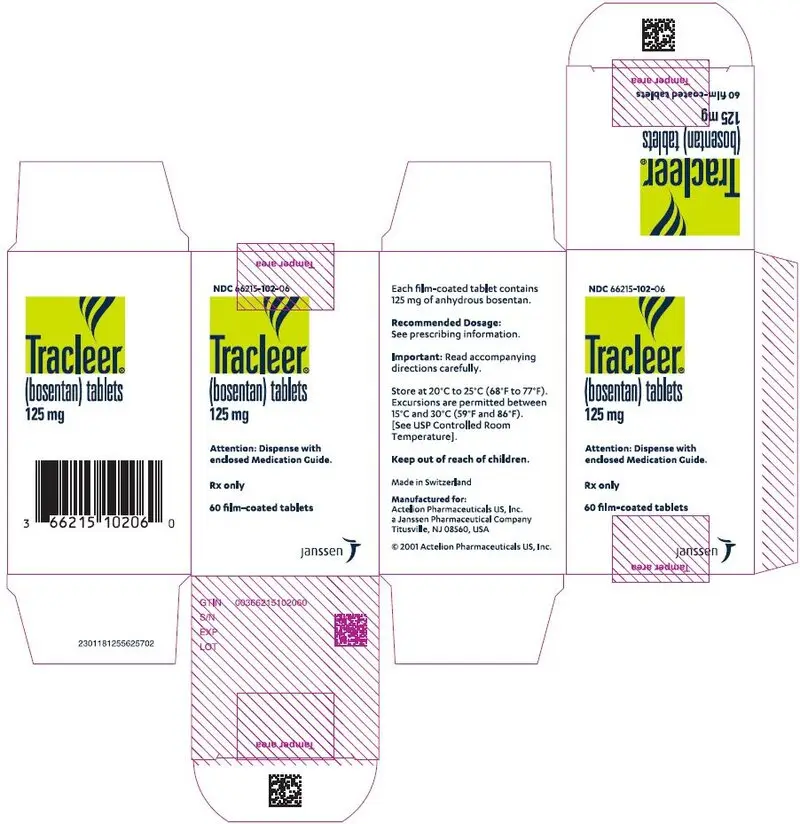
125 mgfilm-coated, oval, biconvex, orange-white tablets, debossed with identification marking "125", packaged in a white high-density polyethylene bottle and a white polypropylene child-resistant cap or in foil blister-strips for hospital unit-dosing.
NDC 66215-102-06: Bottle containing 60 tablets.
NDC 66215-102-03: Carton of 30 tablets in 10 blister strips of 3 tablets.
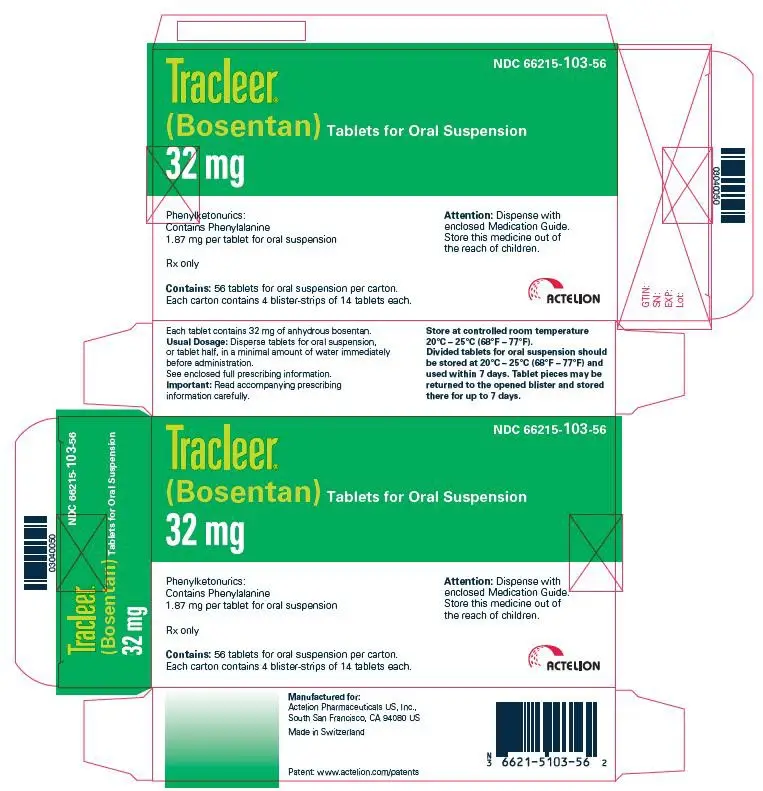
32 mgtablets for oral suspension, pale yellow to off-white, clover-shaped, quadrisected on one side and debossed with identification marking "32" on the other side, packaged in child resistant Aluminum/Aluminum peel-push blisters.
NDC 66215-103-56: Carton of 56 tablets for oral suspension in 4 blister-strips of 14 tablets.
NDC 66215-103-14: Blister strip of 14 tablets for oral suspension.
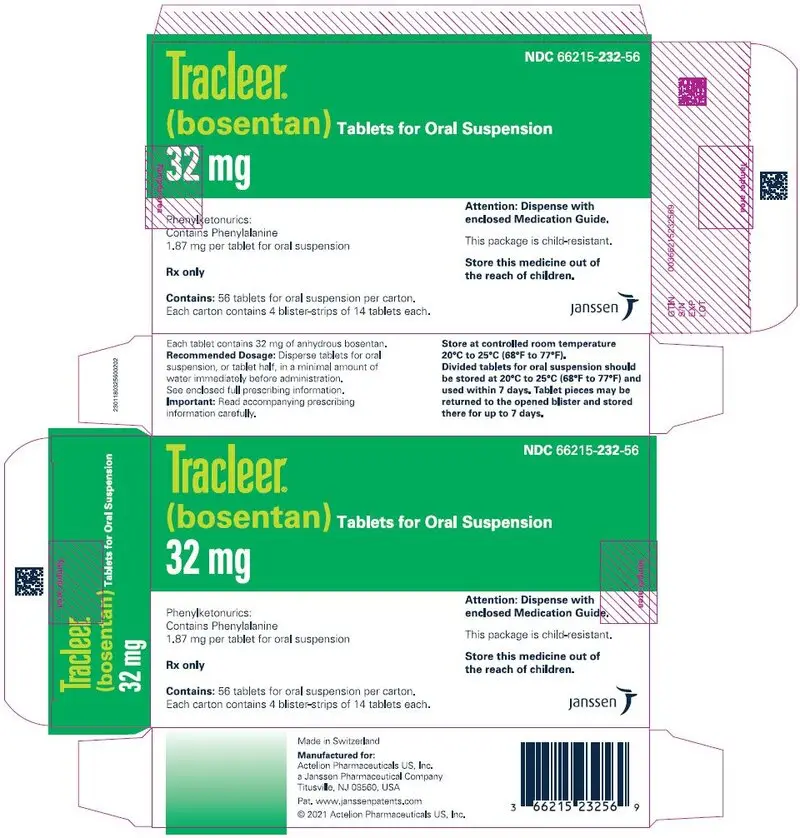
32 mgtablets for oral suspension, pale yellow to off-white, round, bisected on one side and debossed with identification marking "32" on the other side, packaged in child resistant Aluminum/Aluminum peel-push blisters.
NDC 66215-232-56: Carton of 56 tablets for oral suspension in 4 blister-strips of 14 tablets.
NDC 66215-232-14: Blister strip of 14 tablets for oral suspension.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
| Medication Guide
TRACLEER ®(TRA-KLEER) (BOSENTAN) TABLETS |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 07/2022 | |||||||
| Read the Medication Guide that comes with TRACLEER before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Option 1 | Option 2 | Option 3 | Option 4 | |||||
| One method from this list: | or | One method from this list: | or | One method from this list: | or | One method from this list: | ||
| Standard intrauterine device (Copper T 380A IUD)
Intrauterine system (LNg 20 IUS: progesterone IUS) Tubal sterilization | Estrogen and progesterone oral contraceptives ("the pill")
Estrogen and progesterone transdermal patch Vaginal ring Progesterone injection Progesterone implant | Diaphragm with spermicide
Cervical cap with spermicide | Partner's vasectomy | |||||
| PLUS
One method from this list: | ||||||||
| PLUS
One method from this list: | Male condom
Diaphragm with spermicide Cervical cap with spermicide Estrogen and progesterone oral contraceptives ("the pill") Estrogen and progesterone transdermal patch Vaginal ring Progesterone injection Progesterone implant | |||||||
| Male condom | ||||||||
| PLUS
One method from this list: | ||||||||
| Male condom
Diaphragm with spermicide Cervical cap with spermicide | ||||||||
| TRACLEER 32 mg dispersible tablets contain Aspartame. Phenylketonurics: Contains Phenylalanine 1.87 mg per 32 mg dispersible tablet.
See " What are the possible side effects of TRACLEER?" for more information about side effects. |
||||||||
| What is TRACLEER?
TRACLEER is a prescription medicine used to treat people with certain types of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), which is high blood pressure in the vessels of the lungs. TRACLEER can improve your ability to exercise and can slow the worsening of your physical condition and symptoms. TRACLEER lowers high blood pressure in your lungs and lets your heart pump blood more efficiently. TRACLEER is only: Prescribed by healthcare providers who are enrolled in the Bosentan REMS Program. Available to people who understand and agree to enroll in the Bosentan REMS Program. |
||||||||
| Who should not take TRACLEER?
Do not take TRACLEER if you:
|
||||||||
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking TRACLEER?
TRACLEER may not be right for you. Tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| There may be more than one brand name medicine. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
||||||||
| How should I take TRACLEER?
Your healthcare provider will give you detailed information about the Bosentan REMS Program.
|
||||||||
|
What are the possible side effects of TRACLEER?
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||||||||
How should I store TRACLEER?
|
||||||||
| General information about TRACLEER
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TRACLEER for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TRACLEER to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about TRACLEER. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TRACLEER that is written for health professionals. For more information call 1-800-526-7736 (1-800-JANSSEN), go to www.TRACLEER.com. |
||||||||
| What are the ingredients in TRACLEER?
Active ingredient: bosentan Inactive ingredients in 62.5 mg and 125 mg film-coated tablets: corn starch, ethylcellulose, glyceryl behenate, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, povidone, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Inactive ingredients in 32 mg dispersible tablets: acesulfame potassium, aspartame (E951), calcium hydrogen, cellulose microcrystalline, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, phosphate anhydrous, silica colloidal anhydrous, tartaric acid, and tutti frutti flavor. Manufactured for: Actelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc. a Janssen Pharmaceutical Company Titusville, NJ 08560, USA For patent information: www.janssenpatents.com © 2001 – 2019 Actelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc. JN20220715 |
||||||||
| TRACLEER
bosentan tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRACLEER
bosentan tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRACLEER
bosentan tablet, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| TRACLEER
bosentan tablet, for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Actelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc. (002641228) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Inc. | 240769596 | manufacture(66215-103, 66215-232) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haupt Pharma Wuelfing GmbH | 333274975 | manufacture(66215-101, 66215-102) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAS Healthcare Advanced Synthesis SA | 481296960 | api manufacture(66215-101, 66215-102, 66215-103, 66215-232) , analysis(66215-101, 66215-102, 66215-103, 66215-232) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jetpharma SA | 481885861 | particle size reduction(66215-101, 66215-102, 66215-103, 66215-232) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allpack Group AG | 484572565 | pack(66215-101, 66215-102, 66215-103, 66215-232) , label(66215-101, 66215-102, 66215-103, 66215-232) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divi's Laboratories Limited | 676446492 | api manufacture(66215-101, 66215-102) , analysis(66215-101, 66215-102) | |