Drug Detail:Treximet (Naproxen and sumatriptan [ na-prox-en-and-soo-ma-trip-tan ])
Drug Class: Antimigraine agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TREXIMET (sumatriptan and naproxen sodium) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use. (5.1)
- TREXIMET is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events. (5.2)
Recent Major Changes
| Contraindications, pregnancy removal (4) | 4/2021 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.15, 5.16) | 4/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Treximet
TREXIMET is a combination of sumatriptan, a serotonin (5-HT) 1b/1d receptor agonist (triptan), and naproxen sodium, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- Use only if a clear diagnosis of migraine headache has been established. (1)
- Not indicated for the prophylactic therapy of migraine attacks. (1)
- Not indicated for the treatment of cluster headache. (1)
Treximet Dosage and Administration
Adults
- Recommended dosage: 1 tablet of 85/500 mg. (2.1)
- Maximum dosage in a 24-hour period: 2 tablets of 85/500 mg; separate doses by at least 2 hours. (2.1)
Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 years of Age
- Recommended dosage: 1 tablet of 10/60 mg. (2.2)
- Maximum dosage in a 24-hour period: 1 tablet of 85/500 mg.
Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
- Recommended dosage: 1 tablet of 10/60 mg. (2.3, 8.7)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
| Tablets: | 85 mg sumatriptan / 500 mg naproxen sodium (3) |
| 10 mg sumatriptan / 60 mg naproxen sodium (3) |
Contraindications
- History of coronary artery disease or coronary vasospasm. (4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery. (4)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders. (4)
- History of stroke, transient ischemic attack, or hemiplegic or basilar migraine. (4)
- Peripheral vascular disease. (4)
- Ischemic bowel disease. (4)
- Uncontrolled hypertension. (4)
- Recent (within 24 hours) use of another 5-HT1 agonist (e.g., another triptan) or of ergotamine-containing medication. (4)
- Concurrent or recent (past 2 weeks) use of monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor. (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, other allergic type reactions, rhinitis, or nasal polyps syndrome after taking aspirin or other NSAID/analgesic drugs. (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any components of TREXIMET (angioedema and anaphylaxis seen). (4)
- Severe hepatic impairment. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events: Perform cardiac evaluation in patients with cardiovascular risk factors. (5.1)
- Arrhythmias: Discontinue TREXIMET if occurs. (5.3)
- Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure: Generally not associated with myocardial ischemia; evaluate for coronary artery disease in patients at high risk. (5.4)
- Cerebrovascular Events: Discontinue TREXIMET if occurs. (5.5)
- Other Vasospasm Reactions: Discontinue TREXIMET if non-coronary vasospastic reaction occurs. (5.6)
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop. (5.7)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure. (5.8)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of TREXIMET in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure. (5.9)
- Medication Overuse Headache: Detoxification may be necessary. (5.10)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Discontinue TREXIMET if occurs. (5.11)
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of TREXIMET in patients with advanced renal disease. (5.12)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: TREXIMET should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.(5.13)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue TREXIMET at first sign of rash or other signs of hypersensitivity. (5.14)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): Discontinue and evaluate clinically. (5.15)
- Fetal Toxicity: Limit use of NSAIDs, including TREXIMET, between about 20 to 30 weeks in pregnancy due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction. Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy due to the risks of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. (5.16, 8.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia. (5.17)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity). (5.18)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) were:
- Adults: Dizziness, somnolence, nausea, chest discomfort/chest pain, neck/throat/ jaw pain/tightness/pressure, paresthesia, dyspepsia, dry mouth. (6.1)
- Pediatrics: Hot flush (i.e., hot flash[es]) and muscle tightness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Currax Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-800-793-2145 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking TREXIMET with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of TREXIMET and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended. (7.1)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with TREXIMET in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function. (7.1)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of loop and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects. (7.1)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use with TREXIMET can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels. (7.1)
- Lithium: Increases lithium plasma levels. (7.1)
- Methotrexate: Increases methotrexate plasma levels. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
- Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of TREXIMET in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Treximet
TREXIMET is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older.
2. Treximet Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage for adults is 1 tablet ofTREXIMET 85/500 mg.TREXIMET 85/500 mg contains a dose of sumatriptan higher than the lowest effective dose. The choice of the dose of sumatriptan, and of the use of a fixed combination such as in TREXIMET 85/500 mg should be made on an individual basis, weighing the possible benefit of a higher dose of sumatriptan with the potential for a greater risk of adverse reactions.
The maximum recommended dosage in a 24-hour period is 2 tablets, taken at least 2 hours apart.
The safety of treating an average of more than 5 migraine headaches in adults in a 30-day period has not been established.
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
2.2 Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The recommended dosage for pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age is 1 tablet of TREXIMET 10/60 mg.
The maximum recommended dosage in a 24-hour period is 1 tablet of TREXIMET 85/500 mg.
The safety of treating an average of more than 2 migraine headaches in pediatric patients in a 30-day period has not been established.
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
2.3 Dosing in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, the recommended dosage in a 24-hour period is 1 tablet of TREXIMET 10/60 mg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
10 mg sumatriptan/60 mg naproxen sodium, light-blue film-coated tablets, debossed on one side with "TREXIMET" and the other side with "10-60".
85 mg sumatriptan/500 mg naproxen sodium, blue film-coated tablets, debossed on one side with "TREXIMET"
4. Contraindications
TREXIMET is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Ischemic coronary artery disease (CAD) (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction, or documented silent ischemia) or coronary artery vasospasm, including Prinzmetal's angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) or history of hemiplegic or basilar migraine because these patients are at a higher risk of stroke [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Peripheral vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Ischemic bowel disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Recent use (i.e., within 24 hours) of ergotamine-containing medication, ergot-type medication (such as dihydroergotamine or methysergide), or another 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) agonist [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Concurrent administration of a monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A inhibitor or recent (within 2 weeks) use of an MAO-A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- History of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13, 5.14, 5.18)].
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, and serious skin reactions) to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any components of TREXIMET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
- Severe hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
The use of TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with ischemic or vasospastic coronary artery disease (CAD) and in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery due to increased risk of serious cardiovascular events with sumatriptan and NSAIDS [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of TREXIMET, cause serious gastrointestinal adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only 1 in 5 patients who develop a serious upper gastrointestinal adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper gastrointestinal ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs appear to occur in approximately 1% of patients treated daily for 3 to 6 months and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for 1 year. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
Among 3,302 adult patients with migraine who received TREXIMET in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials, 1 patient experienced a recurrence of gastric ulcer after taking 8 doses over 3 weeks, and 1 patient developed a gastric ulcer after treating an average of 8 attacks per month over 7 months.
5.3 Arrhythmias
Life-threatening disturbances of cardiac rhythm, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation leading to death, have been reported within a few hours following the administration of 5-HT1 agonists. Discontinue TREXIMET if these disturbances occur. TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders.
5.4 Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure
Sensations of tightness, pain, pressure, and heaviness in the precordium, throat, neck, and jaw commonly occur after treatment with sumatriptan and are usually non-cardiac in origin. However, perform a cardiac evaluation if these patients are at high cardiac risk. The use of TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with CAD and those with Prinzmetal's variant angina.
5.5 Cerebrovascular Events
Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke have occurred in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the 5-HT1 agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine when they were not. Also, patients with migraine may be at increased risk of certain cerebrovascular events (e.g., stroke, hemorrhage, TIA). Discontinue TREXIMET if a cerebrovascular event occurs.
Before treating headaches in patients not previously diagnosed as migraineurs, and in migraineurs who present with atypical symptoms, exclude other potentially serious neurological conditions. TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with a history of stroke or TIA [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Other Vasospasm Reactions
Sumatriptan may cause non-coronary vasospastic reactions, such as peripheral vascular ischemia, gastrointestinal vascular ischemia and infarction (presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea), splenic infarction, and Raynaud's syndrome. In patients who experience symptoms or signs suggestive of non-coronary vasospasm reaction following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist, rule out a vasospastic reaction before receiving additional TREXIMET.
Reports of transient and permanent blindness and significant partial vision loss have been reported with the use of 5-HT1 agonists. Since visual disorders may be part of a migraine attack, a causal relationship between these events and the use of 5-HT1 agonists have not been clearly established.
5.7 Hepatotoxicity
Borderline elevations of 1 or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients who take NSAIDs including naproxen, a component of TREXIMET. Hepatic abnormalities may be the result of hypersensitivity rather than direct toxicity. These abnormalities may progress, may remain essentially unchanged, or may be transient with continued therapy. Notable (3 times the upper limit of normal) elevations of SGPT (ALT) or SGOT (AST) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare, sometimes fatal cases of severe hepatic injury, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported with NSAIDs.
TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with TREXIMET. TREXIMET should be discontinued if clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash), or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flulike" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue TREXIMET immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
5.8 Hypertension
Significant elevation in blood pressure, including hypertensive crisis with acute impairment of organ systems, has been reported on rare occasions in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, including sumatriptan, a component of TREXIMET. This occurrence has included patients without a history of hypertension.
NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of TREXIMET, can also lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of cardiovascular events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure in patients treated with TREXIMET. TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension [see Contraindications (4)].
5.9 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of naproxen may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of TREXIMET in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If TREXIMET is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
Since each TREXIMET 85/500 mg tablet contains approximately 60 mg of sodium and each TREXIMET 10/60 mg tablet contains approximately 20 mg of sodium, this should be considered in patients whose overall intake of sodium must be severely restricted.
5.10 Medication Overuse Headache
Overuse of acute migraine drugs (e.g., ergotamine, triptans, opioids, or a combination of these drugs for 10 or more days per month) may lead to exacerbation of headache (medication overuse headache). Medication overuse headache may present as migraine-like daily headaches, or as a marked increase in frequency of migraine attacks. Detoxification of patients, including withdrawal of the overused drugs, and treatment of withdrawal symptoms (which often includes a transient worsening of headache) may be necessary.
5.11 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome may occur with TREXIMET, particularly during coadministration with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and MAO inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms usually occurs within minutes to hours of receiving a new or a greater dose of a serotonergic medication. Discontinue TREXIMET if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
5.13 Anaphylactic Reactions
Anaphylactic reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to either component of TREXIMET. Such reactions can be life-threatening or fatal. In general, anaphylactic reactions to drugs are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens although anaphylactic reactions with naproxen have occurred in patient without known hypersensitivity to naproxen or to patients with aspirin sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]. TREXIMET should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in patients with asthma who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any other component of TREXIMET. Naproxen has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients without known hypersensitivity to naproxen and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]. Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.14 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAID-containing products can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions and to discontinue the use of TREXIMET at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.15 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as TREXIMET. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, discontinue TREXIMET and evaluate the patient immediately.
5.17 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in patients receiving NSAIDs. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross gastrointestinal blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with TREXIMET has signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including TREXIMET, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.18 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, TREXIMET is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma [see Contraindications (4)].
When TREXIMET is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.19 Seizures
Seizures have been reported following administration of sumatriptan. Some have occurred in patients with either a history of seizures or concurrent conditions predisposing to seizures. There are also reports in patients where no such predisposing factors are apparent. TREXIMET should be used with caution in patients with a history of epilepsy or conditions associated with a lowered seizure threshold.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cerebrovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Other Vasospasm Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Medication Overuse Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
- Hematological Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]
- Exacerbation Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults
The adverse reactions reported below are specific to the clinical trials with TREXIMET 85/500 mg. See also the full prescribing information for naproxen and sumatriptan products.
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred in 2 placebo controlled clinical trials (Study 1 and 2) in adult patients who received 1 dose of study drug. Only adverse reactions that occurred at a frequency of 2% or more in any group treated with TREXIMET 85/500 mg and that occurred at a frequency greater than the placebo group are included in Table 1.
| Adverse Reactions | TREXIMET 85/500 mg % (n = 737) | Placebo % (n = 752) | Sumatriptan 85 mg % (n = 735) | Naproxen Sodium 500 mg % (n = 732) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nervous system disorders | ||||
| Dizziness | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Somnolence | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Paresthesia | 2 | <1 | 2 | <1 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 3 | 1 | 3 | <1 |
| Dyspepsia | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 1 | 2 | <1 |
| Pain and other pressure sensations | ||||
| Chest discomfort/chest pain | 3 | <1 | 2 | 1 |
| Neck/throat/jaw pain/tightness/pressure | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
The incidence of adverse reactions in controlled clinical trials was not affected by gender or age of the patients. There were insufficient data to assess the impact of race on the incidence of adverse reactions.
Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
In a placebo controlled clinical trial that evaluated pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age who received 1 dose of TREXIMET 10/60 mg, 30/180 mg, or 85/500 mg, adverse reactions occurred in 13% of patients who received 10/60 mg, 9% of patients who received 30/180 mg, 13% who received 85/500 mg, and 8% who received placebo. No patients who received TREXIMET experienced adverse reactions leading to withdrawal from the trial. The incidence of adverse reactions in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was comparable across all 3 doses compared with placebo. Table 2 lists adverse reactions that occurred in a placebo-controlled trial in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age at a frequency of 2% or more with TREXIMET and were more frequent than the placebo group.
| TREXIMET 10/60 mg % | TREXIMET 30/180 mg % | TREXIMET 85/500 mg % | Placebo % |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reactions | (n = 96) | (n = 97) | (n = 152) | (n = 145) |
| Vascular | ||||
| Hot flush (i.e., hot flash[es]) | 0 | 2 | <1 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||||
| Muscle tightness | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with TREXIMET
See Table 3 for clinically significant drug interactions with NSAIDs or Sumatriptan.
| Ergot-Containing Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | Ergot-containing drugs have been reported to cause prolonged vasospastic reactions. |
| Intervention: | Because these effects may be additive, coadministration of TREXIMET and ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medications (like dihydroergotamine or methysergide) within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated. |
| Monoamine Oxidase-A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact: | MAO-A inhibitors increase systemic exposure of orally administered sumatriptan by 7-fold. |
| Intervention: | The use of TREXIMET in patients receiving MAO-A inhibitors is contraindicated. |
| Other 5-HT1 Agonists | |
| Clinical Impact: | 5-HT1 agonist drugs can cause vasospastic effects. |
| Intervention: | Because these effects may be additive, coadministration of TREXIMET and other 5 HT1 agonists (e.g., triptans) within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated. |
| Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of TREXIMET with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]. |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Concomitant use of TREXIMET and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]. |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors/Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors and Serotonin Syndrome | |
| Clinical Impact: | Cases of serotonin syndrome have been reported during coadministration of triptans and SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAO inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. |
| Intervention: | Discontinue TREXIMET if serotonin syndrome is suspected. |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-blockers | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: |
|
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.12)]. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact: | The concomitant use of naproxen with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant administration of some NSAIDs with high-dose methotrexate therapy has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity. Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of naproxen with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | The concomitant use of naproxen with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of TREXIMET and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed. In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration. |
| Probenecid | |
| Clinical Impact: | Probenecid given concurrently increases naproxen anion plasma levels and extends its plasma half-life significantly. The clinical significance of this is unknown. |
| Intervention: | Reduce the frequency of administration of Treximet when given concurrently with probenecid. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
Human Data
There is some evidence to suggest that when inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis are used to delay preterm labor, there is an increased risk of neonatal complications such as necrotizing enterocolitis, patent ductus arteriosus, and intracranial hemorrhage. Naproxen treatment given in late pregnancy to delay parturition has been associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension, renal dysfunction, and abnormal prostaglandin E levels in preterm infants.
The Sumatriptan/Naratriptan/Treximet (sumatriptan and naproxen sodium) Pregnancy Registry, a population-based international prospective study, collected data for sumatriptan from January 1996 to September 2012. The Registry included only 6 pregnancy exposures to TREXIMET, with no major birth defects reported. The Registry documented outcomes of 626 infants and fetuses exposed to sumatriptan during pregnancy (528 with earliest exposure during the first trimester, 78 during the second trimester, 16 during the third trimester, and 4 unknown). The occurrence of major birth defects (excluding fetal deaths and induced abortions without reported defects and all spontaneous pregnancy losses) during first-trimester exposure to sumatriptan was 4.2% (20/478 [95% CI: 2.6% to 6.5%]) and during any trimester of exposure was 4.2% (24/576 [95% CI: 2.7% to 6.2%]). The sample size in this study had 80% power to detect at least a 1.73- to 1.91-fold increase in the rate of major malformations. The number of exposed pregnancy outcomes accumulated during the registry was insufficient to support definitive conclusions about overall malformation risk or to support making comparisons of the frequencies of specific birth defects. Of the 20 infants with reported birth defects after exposure to sumatriptan in the first trimester, 4 infants had ventricular septal defects, including one infant who was exposed to both sumatriptan and naratriptan, and 3 infants had pyloric stenosis. No other birth defect was reported for more than 2 infants in this group.
In a study using data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register, live births to women who reported using triptans or ergots during pregnancy were compared with those of women who did not. Of the 2,257 births with first-trimester exposure to sumatriptan, 107 infants were born with malformations (relative risk 0.99 [95% CI: 0.91 to 1.21]). A study using linked data from the Medical Birth Registry of Norway to the Norwegian Prescription Database compared pregnancy outcomes in women who redeemed prescriptions for triptans during pregnancy, as well as a migraine disease comparison group who redeemed prescriptions for sumatriptan before pregnancy only, compared with a population control group. Of the 415 women who redeemed prescriptions for sumatriptan during the first trimester, 15 had infants with major congenital malformations (OR 1.16 [95% CI: 0.69 to 1.94]) while for the 364 women who redeemed prescriptions for sumatriptan before, but not during, pregnancy, 20 had infants with major congenital malformations (OR 1.83 [95% CI: 1.17 to 2.88]), each compared with the population comparison group. Additional smaller observational studies evaluating use of sumatriptan during pregnancy have not suggested an increased risk of teratogenicity.
Animal Data
Oral administration of sumatriptan alone to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in an increased incidence of fetal blood vessel (cervicothoracic and umbilical) abnormalities. The highest no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity in rats was 60 mg/kg/day, or approximately 3 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 170 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis.
Oral administration of sumatriptan alone to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased incidences of embryolethality and fetal cervicothoracic vascular and skeletal abnormalities. Intravenous administration of sumatriptan to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in an increased incidence of embryolethality. The highest oral and intravenous no-effect doses for developmental toxicity in rabbits were 15 (approximately 2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) and 0.75 mg/kg/day, respectively.
Oral administration of sumatriptan combined with naproxen sodium (5/9, 25/45, or 50/90 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) or each drug alone (50/0, 0/90 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased total incidences of fetal abnormalities at all doses and increased incidences of specific malformations (cardiac interventricular septal defect in the 50/90 mg/kg/day group, fused caudal vertebrae in the 50/0 and 0/90 mg/kg/day groups) and variations (absent intermediate lobe of the lung, irregular ossification of the skull, incompletely ossified sternal centra) at the highest dose of sumatriptan and naproxen alone and in combination. A no-effect dose for developmental toxicity in rabbit was not established. The lowest effect dose of 5/9 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) to sumatriptan and naproxen that were less than those attained at the MRHD of 170 mg sumatriptan and 1000 mg naproxen sodium (two tablets of TREXIMET 85/500 mg in a 24-hour period).
Oral administration of sumatriptan alone to rats prior to and throughout gestation resulted in embryofetal toxicity (decreased body weight, decreased ossification, increased incidence of skeletal abnormalities). The highest no-effect dose was 50 mg/kg/day, or approximately 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. In offspring of pregnant rats treated orally with sumatriptan during organogenesis, there was a decrease in pup survival. The highest no-effect dose for this effect was 60 mg/kg/day, or approximately 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Oral treatment of pregnant rats with sumatriptan during the latter part of gestation and throughout lactation resulted in a decrease in pup survival. The highest no-effect dose for this finding was 100 mg/ kg/day, or approximately 6 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
In reproduction studies of naproxen in rats (20 mg/kg/day), rabbits (20 mg/kg/day, and mice (170 mg/kg/day, no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus was observed. The doses tested in rats, rabbits, and mice were less (≤0.8 times) the MRHD, based on body surface area (mg/m2) comparisons.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The naproxen anion has been found in the milk of lactating women at a concentration equivalent to approximately 1% of maximum naproxen concentration in plasma. Sumatriptan is excreted in human milk following subcutaneous administration (see Data). There is no information regarding sumatriptan concentrations in milk from lactating women following administration of sumatriptan tablets.
There are no data on the effects of naproxen or sumatriptan on the breastfed infant or the effects of naproxen or sumatriptan on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for TREXIMET and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from TREXIMET or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TREXIMET in pediatric patients under 12 years of age have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of TREXIMET for the acute treatment of migraine in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was established in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. TREXIMET is not recommended for use in elderly patients who have decreased renal function, higher risk for unrecognized CAD, and increases in blood pressure that may be more pronounced in the elderly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.8, 5.12) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
A cardiovascular evaluation is recommended for geriatric patients who have other cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to receiving TREXIMET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
TREXIMET is not recommended for use in patients with creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min. Monitor the serum creatinine or creatinine clearance in patients with mild (CrCl = 60 to 89 mL/min) or moderate (CrCL = 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment, preexisting kidney disease, or dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Patients (N = 670) have received single oral doses of 140 to 300 mg of sumatriptan without significant adverse effects. Volunteers (N = 174) have received single oral doses of 140 to 400 mg without serious adverse events.
Overdose of sumatriptan in animals has been fatal and has been heralded by convulsions, tremor, paralysis, inactivity, ptosis, erythema of the extremities, abnormal respiration, cyanosis, ataxia, mydriasis, salivation, and lacrimation.
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Hemodialysis does not decrease the plasma concentration of naproxen because of the high degree of its protein binding. It is unknown what effect hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis has on the serum concentrations of sumatriptan. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
11. Treximet Description
TREXIMET contains sumatriptan (as the succinate), a selective 5 hydroxytryptamine1 (5 HT1) receptor subtype agonist, and naproxen sodium, a member of the arylacetic acid group of NSAIDs.
Sumatriptan succinate is chemically designated as 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-Nmethyl-indole-5-methanesulfonamide succinate (1:1), and it has the following structure:
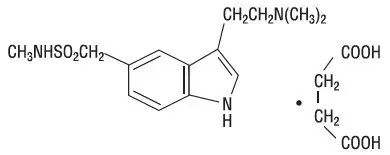
The empirical formula is C14H21N3O2S∙C4H6O4, representing a molecular weight of 413.5. Sumatriptan succinate is a white to off-white powder that is readily soluble in water and in saline.
Naproxen sodium is chemically designated as (S)-6-methoxy-α-methyl-2- naphthaleneacetic acid, sodium salt, and it has the following structure:
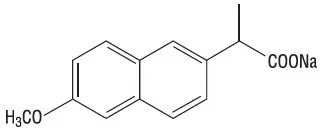
The empirical formula is C14H13NaO3, representing a molecular weight of 252.23. Naproxen sodium is a white-to-creamy white crystalline solid, freely soluble in water at neutral pH.
Each TREXIMET 85/500 mg tablet for oral administration contains 119 mg of sumatriptan succinate equivalent to 85 mg of sumatriptan and 500 mg of naproxen sodium. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, dibasic calcium phosphate, FD&C Blue No. 2, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, sodium bicarbonate, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Each TREXIMET 10/60 mg tablet for oral administration contains 14 mg of sumatriptan succinate equivalent to 10 mg of sumatriptan and 60 mg of naproxen sodium. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, dibasic calcium phosphate, FD&C Blue No. 2, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, sodium bicarbonate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Treximet - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
TREXIMET contains sumatriptan and naproxen.
Sumatriptan binds with high affinity to cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Sumatriptan presumably exerts its therapeutic effects in the treatment of migraine headache through agonist effects at the 5-HT1B/1D receptors on intracranial blood vessels and sensory nerves of the trigeminal system, which result in cranial vessel constriction and inhibition of neuropeptide release.
TREXIMET has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. The mechanism of action of TREXIMET, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Naproxen is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Naproxen concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because naproxen is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Adults
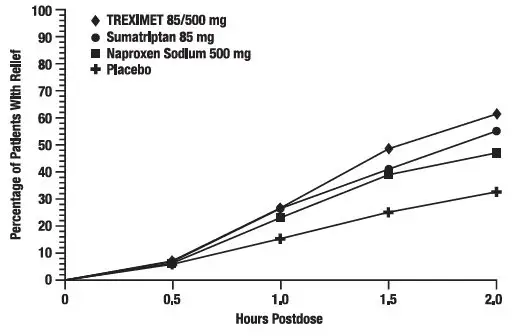
The efficacy of TREXIMET in the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults was demonstrated in 2 randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group trials utilizing placebo and each individual active component of TREXIMET 85/500 mg (sumatriptan and naproxen sodium) as comparison treatments (Study 1 and Study 2). Patients enrolled in these 2 trials were predominately female (87%) and white (88%), with a mean age of 40 years (range: 18 to 65 years). Patients were instructed to treat a migraine of moderate to severe pain with 1 tablet. No rescue medication was allowed within 2 hours postdose. Patients evaluated their headache pain 2 hours after taking 1 dose of study medication; headache relief was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to mild or no pain. Associated symptoms of nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia were also evaluated. Sustained pain free was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to no pain at 2 hours postdose without a return of mild, moderate, or severe pain and no use of rescue medication for 24 hours postdose. The results from Study 1 and 2 are summarized in Table 4. In both trials, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain relief 2 hours after treatment was significantly greater among patients receiving TREXIMET 85/500 mg (65% and 57%) compared with those who received placebo (28% and 29%).
Further, the percentage of patients who remained pain free without use of other medications through 24 hours postdose was significantly greater among patients receiving a single dose of TREXIMET 85/500 mg (25% and 23%) compared with those who received placebo (8% and 7%) or either sumatriptan (16% and 14%) or naproxen sodium (10%) alone.
| TREXIMET 85/500 mg | Sumatriptan 85 mg | Naproxen Sodium 500 mg | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| 2-Hour Pain Relief | ||||
| Study 1 | 65%†
n = 364 | 55% n = 361 | 44% n = 356 | 28% n = 360 |
| Study 2 | 57%†
n = 362 | 50% n = 362 | 43% n = 364 | 29% n = 382 |
| Sustained Pain Free (2-24 Hours) | ||||
| Study 1 | 25%‡
n = 364 | 16% n = 361 | 10% n = 356 | 8% n = 360 |
| Study 2 | 23%‡
n = 362 | 14% n = 362 | 10% n = 364 | 7% n = 382 |
The percentage of patients achieving initial headache pain relief within 2 hours following treatment with TREXIMET 85/500 mg is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Percentage of Adult Patients with Initial Headache Pain Relief within 2 Hours
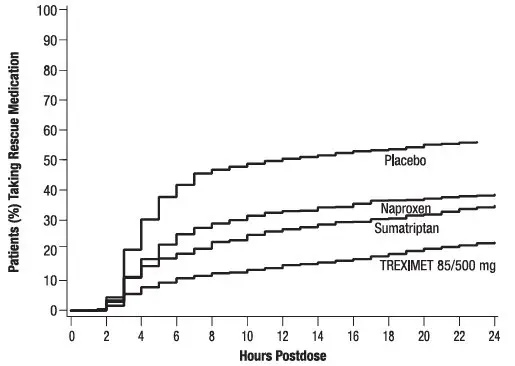
Compared with placebo, there was a decreased incidence of photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea 2 hours after the administration of TREXIMET 85/500 mg. The estimated probability of taking a rescue medication over the first 24 hours is shown in Figure 2.
| Figure 2. Estimated Probability of Adults Taking a Rescue Medication over the 24 Hours following the First Dose* |
|---|
|
|
|
TREXIMET 85/500 mg was more effective than placebo regardless of the presence of aura; duration of headache prior to treatment; gender, age, or weight of the subject; or concomitant use of oral contraceptives or common migraine prophylactic drugs (e.g., beta blockers, anti epileptic drugs, tricyclic antidepressants).
14.2 Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The efficacy of TREXIMET in the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial comparing 3 doses of TREXIMET and placebo (Study 3). Patients enrolled in this trial were mostly female (59%) and white (81%), with a mean age of 15 years.
Patients were required to have at least a 6-month history of migraine attacks with or without aura usually lasting 3 hours or more when untreated. Following a single-blind, placebo run-in phase, placebo nonresponders were randomized to receive a single dose of either TREXIMET 10/60 mg, 30/180 mg, 85/500 mg, or placebo. Patients were instructed to treat a single migraine attack with headache pain of moderate to severe intensity. No rescue medication was allowed within 2 hours postdose. Patients evaluated their headache pain 2 hours after taking 1 dose of study medication. Two-hour pain free was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to no pain at 2 hours postdose.
Results are summarized in Table 5. The percentage of patients who were pain free at 2 hours postdose was significantly greater among patients who received any of the 3 doses of TREXIMET compared with placebo.
| Endpoint | TREXIMET 10/60 mg (n = 96) | TREXIMET 30/180 mg (n = 97) | TREXIMET 85/500 mg (n = 152) | Placebo (n = 145) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| 2-Hour Pain Relief | 29%† | 27%† | 24%† | 10% |
The percentage of pediatric patients who remained pain free without use of other medications 2 through 24 hours postdose was significantly greater after administration of a single dose of TREXIMET 85/500 mg compared with placebo. A greater percentage of pediatric patients who received a single dose of 10/60 mg or 30/180 mg remained pain free 2 through 24 hours postdose compared with placebo.
Compared with placebo, the incidence of photophobia and phonophobia was significantly decreased 2 hours after the administration of a single dose of 85/500 mg, whereas, the incidence of nausea was comparable. There was a decreased incidence of photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea 2 hours after single-dose administration of 10/60 mg or 30/180 mg compared with placebo.
16. How is Treximet supplied
TREXIMET 85/500 mg contains 119 mg of sumatriptan succinate equivalent to 85 mg of sumatriptan and 500 mg of naproxen sodium and is supplied as blue film-coated tablets debossed on one side with TREXIMET in bottles of 9 tablets with desiccant (NDC 42847-850-09).
TREXIMET 10/60 mg contains 14 mg of sumatriptan succinate equivalent to 10 mg of sumatriptan and 60 mg of naproxen sodium and is supplied as light-blue film-coated tablets debossed on one side with TREXIMET and the other side with 10-60 in bottles of 9 tablets with desiccant (NDC 42847-860-09).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with TREXIMET and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 10/2021 |
| MEDICATION GUIDE
TREXIMET® [trex' i-met] Tablets (sumatriptan and naproxen sodium) |
|
| Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TREXIMET and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. | |
| What is the most important information I should know about TREXIMET? TREXIMET may increase your chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. TREXIMET contains 2 medicines: sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug [NSAID]).
Avoid taking TREXIMET after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack. Stop taking TREXIMET and get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of a heart attack or stroke:
Ulcers and bleeding can happen without warning symptoms and may cause death. Your chance of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
TREXIMET already contains an NSAID (naproxen). Do not use TREXIMET with other medicines to lessen pain or fever or with other medicines for colds or sleeping problems without talking to your healthcare provider first, because they may contain an NSAID also. |
|
| What is TREXIMET?
TREXIMET is a prescription medicine that contains sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (an NSAID). TREXIMET is used to treat acute migraine headaches with or without aura in patients 12 years of age and older. TREXIMET is not used to treat other types of headaches such as hemiplegic (that make you unable to move on one side of your body) or basilar (rare form of migraine with aura) migraines. TREXIMET is not used to prevent or decrease the number of migraine headaches you have. It is not known if TREXIMET is safe and effective to treat cluster headaches. |
|
| Who should not take TREXIMET? Do not take TREXIMET if you have:
|
|
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking TREXIMET?
Before you take TREXIMET, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
TREXIMET and certain other medicines can affect each other, causing serious side effects. |
|
How should I take TREXIMET?
|
|
| What should I avoid while taking TREXIMET?
TREXIMET can cause dizziness, weakness, or drowsiness. If you have these symptoms, do not drive a car, use machinery, or do anything where you need to be alert. |
|
| What are the possible side effects of TREXIMET? TREXIMET may cause serious side effects. See "What is the most important information I should know about TREXIMET?" These serious side effects include:
These are not all of the side effects of TREXIMET. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
| How should I store TREXIMET?
Store TREXIMET at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep TREXIMET and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of TREXIMET
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TREXIMET for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TREXIMET to other people, even if they have the same problem you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about TREXIMET. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about TREXIMET that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information call 1-800-793-2145. |
|
| What are the ingredients in TREXIMET?
Active ingredients: sumatriptan succinate and naproxen sodium. Inactive ingredients in all strengths: croscarmellose sodium, dibasic calcium phosphate, FD&C Blue No. 2, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, sodium bicarbonate, talc, and titanium dioxide. 85/500 mg tablets also contain: hypromellose and triacetin. 10/60 mg tablets also contain: polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol. TREXIMET is a registered trademark of Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC. The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC or its products. TRE-LC013.06 Distributed by Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC; Brentwood, TN 37027; © 2021, Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC. All rights reserved. |
|
| TREXIMET
sumatriptan succinate and naproxen sodium tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Currax Pharmaceuticals LLC (117055730) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glaxo Wellcome Manufacturing Pte Ltd | 595295577 | ANALYSIS(42847-850) , API MANUFACTURE(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glaxo Operations UK Ltd | 517226676 | ANALYSIS(42847-850) , MANUFACTURE(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline LLC | 149372109 | ANALYSIS(42847-850) , LABEL(42847-850) , PACK(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divis Laboratories Limited | 676446492 | API MANUFACTURE(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cambrex | 829609168 | ANALYSIS(42847-850) , MANUFACTURE(42847-850) , PACK(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrias Quimicas Falcon de Mexico, S.A. de C.V. (Dr. Reddy's Mexico) | 812915445 | API MANUFACTURE(42847-850) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Limited (India) | 918607727 | API MANUFACTURE(42847-850) | |