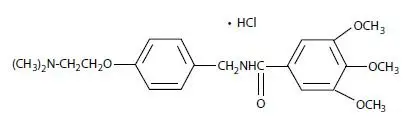
Drug Detail:Trimethobenzamide (monograph) (Tigan)
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
Initial U.S. Approval:1974
Indications and Usage for Trimethobenzamide Capsules
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are an antiemetic indicated in adults for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis. (1)
Limitation of Use:
• Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system (CNS) effects and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's syndrome or other hepatic impairment. (1, 8.4)
Trimethobenzamide Capsules Dosage and Administration
• The recommended adult dosage is 300 mg orally three or four times daily. (2.1)
• Geriatric patients and/or patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 70 mL/min/1.73m2 or less): Reduce the daily dosage by increasing the dosing interval; monitor renal function. (2.2, 8.5, 8.6)
• Select the lowest effective daily dosage and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability. (2.1, 2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsule: 300 mg of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride (3)
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Acute Dystonic Reactions and Other Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) : Depending on the severity of symptoms, reduce the dosage or discontinue the drug. Treat acute dystonic reactions with anticholinergics. Avoid trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in patients receiving other drugs that are likely to cause EPS. (5.1, 7.2)
- Masking of Other Serious Disorders : EPS and other CNS symptoms in patients treated with trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules may be confused with CNS signs of undiagnosed primary disease (e.g., encephalopathy, metabolic imbalance, Reye's Syndrome). If CNS symptoms occur, evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules. (5.2, 7.2)
- Other CNS Reactions : Coma, depression of mood, disorientation, and seizures have been reported. The recent use of other drugs that cause CNS depression or EPS symptoms may also increase the risk; consider reducing the dosage or discontinuing the drug. (5.3, 7.1, 7.2)
- Hepatotoxicity : Avoid use in patients whose signs and symptoms suggest the presence of hepatic impairment. Discontinue trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in patients who develop impaired liver function while on treatment. (5.4, 8.7)
- Effects on the Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery : Mental and/or physical abilities may be impaired. Concomitant use of other drugs that cause CNS depression or EPS symptoms may increase this effect; either trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or the other interacting drug should be chosen, depending on the importance of the drug to the patient. (5.5, 7.1, 7.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adverse reactions include hypersensitivity reactions and Parkinson-like symptoms; blood dyscrasias, blurring of vision, coma, convulsions, depression of mood, diarrhea, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, jaundice, muscle cramps, and opisthotonos. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-403-7592 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or WWW.FDA.GOV/MEDWATCH.
Drug Interactions
• Alcohol: May cause drowsiness; avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
• Other Drugs that Cause CNS Depression or EPS: Either trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or the other interacting drug should be chosen, depending on the importance of the drug to the patient. If CNS-acting drugs cannot be avoided, monitor patients for CNS adverse reactions. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2019
Related/similar drugs
hydroxyzine, ondansetron, lorazepam, meclizine, Benadryl, promethazineFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Trimethobenzamide Capsules
Limitation of Use:
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules is not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system (CNS) effects, and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's syndrome or other hepatic impairment.
2. Trimethobenzamide Capsules Dosage and Administration
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Acute Dystonic Reactions and Other Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
EPS may also include akathisia, restlessness, akinesia, and other parkinsonian-like symptoms (e.g., tremor). Depending on the severity of symptoms, reduce the daily dosage of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules by increasing the dosing interval or discontinue trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Avoid trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in patients receiving other drugs that are likely to cause EPS (e.g. antipsychotics) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Nervous system disorders: Parkinson-like symptoms, coma, convulsions, opisthotonos, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)]
- Psychiatric disorders: disorientation, depression of mood
- Eye disorders: blurred vision
- Hematologic disorders: blood dyscrasias
- Hepatobiliary disorders: jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity, including angioedema and allergic-type skin reactions
- Gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea
- Musculoskeletal disorders: muscle cramps
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
The limited available data with trimethobenzamide in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. No adverse developmental effect was observed in animal reproduction studies with administration of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride during organogenesis in pregnant rats at doses 0.16 and 0.8 times the recommended human dose (RHD) and in pregnant rabbits at doses 1.6 times the RHD [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies with trimethobenzamide hydrochloride were conducted in rats and rabbits following administration of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride during organogenesis and no adverse developmental effect was observed in either species. The only effects observed were an increased percentage of embryonic resorptions or stillborn pups in rats administered 20 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg (0.16 and 0.8 times the RHD of 1200 mg/day, based on body surface area) and increased resorptions in rabbits receiving 100 mg/kg (1.6 times the RHD of 1200 mg/day, based on body surface area). In each study, these adverse effects were attributed to one or two dams.
8.2 Lactation
There is no information on the presence of trimethobenzamide in human milk, the effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules on the breastfed infant or the effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules is not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of EPS and other serious CNS effects, and the risk of exacerbation of underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's Syndrome, or other hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
12. Trimethobenzamide Capsules - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of trimethobenzamide in healthy adult subjects were compared when trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules was administered as a 300 mg oral capsule or a 200 mg (100 mg/mL) intramuscular injection. The time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was about 30 minutes after intramuscular injection compared to about 45 minutes after oral capsule administration. The plasma concentration-time profile of trimethobenzamide was similar between the two formulations.
Elimination
The mean elimination half-life of trimethobenzamide is 7 to 9 hours.
Metabolism
The major pathway of trimethobenzamide metabolism is through oxidation resulting in the formation of trimethobenzamide N-oxide metabolite. The pharmacologic activity of this major metabolite has not been evaluated.
Excretion
Between 30 to 50% of a single dose in humans is excreted unchanged in the urine within 48 to72 hours.
Specific Populations
Sex
Systemic exposure to trimethobenzamide was similar between men (N=40) and women (N=28). Following a single 300 mg capsule oral administration, the respective mean (SD) Cmax of trimethobenzamide were 3.5 (1.1) and 4.2 (1.6) micrograms/mL in male and female subjects. The respective mean (SD) of AUC0-∞ of trimethobenzamide were 10 (2.7) and 10.4 (2.7) micrograms×hour/mL in male and female subjects.
Race
Pharmacokinetics appeared to be similar for Caucasians (N=53) and African Americans (N=12). Following a single 300 mg capsule oral administration, the respective mean (SD) Cmax of trimethobenzamide was 3.8 (1.3) micrograms/mL in Caucasians and 3.9 (1.7) micrograms/mL in African Americans. The respective mean (SD) AUC0-∞ of trimethobenzamide was 10.4 (2.8) micrograms×hour/mL in Caucasians and 9.8 (2.5) micrograms×hour/mL in African Americans.
16. How is Trimethobenzamide Capsules supplied
| Package | NDC Number |
| Bottles of 30 | 43386-660-03 |
| Bottles of 100 | 43386-660-24 |
| Bottles of 500 | 43386-660-26 |
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
[See USP Controlled Room Temperature]
17. Patient Counseling Information
Acute Dystonic Reactions and Other Extrapyramidal Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Other CNS Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Effects on the Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery
Advise patients that trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules can cause drowsiness and may impair their judgment, thinking, or motor skills required for tasks such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery. Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until they are reasonably certain that trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules does not affect them adversely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that use of alcohol or concomitant treatment with other CNS-acting drugs can precipitate or worsen CNS depression and/or EPS [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)]. Instruct patients avoid alcohol and to tell their health care providers when they start taking any concomitant medication.
Manufactured by:
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baltimore, MD 21202
PI6600000206
Rev. 01/2019
| TRIMETHOBENZAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Lupin Pharmaceuticals,Inc. (089153071) |
| Registrant - Lupin Inc. (080038238) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novel Laboratories, Inc. | 793518643 | MANUFACTURE(43386-660) , ANALYSIS(43386-660) , PACK(43386-660) | |