Drug Detail:Trokendi xr (Topiramate [ toe-pyre-a-mate ])
Drug Class: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor anticonvulsants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TROKENDI XR (topiramate) extended-release capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.3) | 4/2017 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3) | 4/2017 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.7, 5.10, 5.11) | 4/2017 |
Indications and Usage for Trokendi XR
TROKENDI XR® is indicated for:
- Monotherapy epilepsy: initial monotherapy in patients 6 years of age and older with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (1.1)
- Adjunctive therapy epilepsy: adjunctive therapy in patients 6 years of age and older with partial onset, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, or seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) (1.2)
- Migraine: Prophylaxis of migraine headache in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older (1.3)
Trokendi XR Dosage and Administration
| Initial Dose | Titration | Recommended Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapy: Partial Onset or Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures | |||
| Adults and pediatric patients 10 years and older (2.1) | 50 mg orally once daily | Increase dose weekly by increments of 50 mg for first 4 weeks then 100 mg for weeks 5 to 6 | 400 mg once daily |
| Pediatric patients 6 to less than 10 (2.1) | 25 mg/day nightly for the first week | Titrate over 5 to 7 weeks | Daily doses based on weight (Table 1) |
| Adjunctive Therapy | |||
| Adults with partial onset seizures or LGS (2.2) | 25 mg to 50 mg orally once daily | Increase dose weekly by increments of 25 mg to 50 mg to achieve an effective dose | 200 mg to 400 mg once daily |
| Adults with primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (2.2) | 25 mg to 50 mg orally once daily | Increase dose weekly to an effective dose by increments of 25 mg to 50 mg | 400 mg once daily |
| Pediatric patients 6 years and older with partial onset seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, or LGS (2.2) | 25 mg once at nighttime (based on a range of 1 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg once daily) for first week | Increase dosage at 1- or 2-week intervals by increments of 1 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg Dose titration should be guided by clinical outcome | 5 mg/kg to 9 mg/kg once daily |
| Migraine | |||
| Prophylaxis of migraine headache (2.3) | 25mg once daily administered for first week | Increase dosage weekly by 25mg increments to achieve desired clinical outcome | 100 mg once daily |
Swallow capsule whole and intact. Do not sprinkle on food, chew, or crush (2.10)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg (3)
Contraindications
- With recent alcohol use, ie, within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after TROKENDI XR® use (4), (5.5)
- In patients with metabolic acidosis taking concomitant metformin (4), (5.4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Acute myopia and secondary angle closure glaucoma: Untreated elevated intraocular pressure can lead to permanent visual loss. Discontinue TROKENDI XR® if it occurs (5.1)
- Visual field defects: These have been reported independent of elevated intraocular pressure. Consider discontinuation of TROKENDI XR (5.2)
- Oligohydrosis and hyperthermia: Monitor decreased sweating and increased body temperature, especially in pediatric patients (5.3)
- Metabolic acidosis: Measure baseline and periodic measurement of serum bicarbonate. Consider dose reduction or discontinuation of TROKENDI XR® if clinically appropriate (5.4)
- Suicidal behavior and ideation: Antiepileptic drugs increase the risk of suicidal behavior or ideation (5.6)
- Cognitive/neuropsychiatric: TROKENDI XR® may cause cognitive dysfunction. Use caution when operating machinery including automobiles. Depression and mood problems may occur (5.7)
- Fetal toxicity: Topiramate use during pregnancy can cause cleft lip and/or palate and increases the risk of being small for gestational age (5.8)
- Withdrawal of AEDs: Withdrawal of TROKENDI XR® should be done gradually (5.9)
- Hyperammonemia and encephalopathy: Patients with inborn errors of metabolism or reduced mitochondrial activity may have an increased risk of hyperammonemia. Measure ammonia if encephalopathic symptoms occur (5.10)
- Kidney stones: Avoid use with other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, other drugs causing metabolic acidosis, or in patients on a ketogenic diet (5.11)
- Hypothermia: Reported with concomitant valproic acid use (5.12)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (≥ 10% more frequent than placebo or low-dose topiramate in monotherapy and adjunctive therapy) adverse reactions in adult and pediatric patients were paresthesia, anorexia, weight decrease, speech disorders/related speech problems, fatigue, dizziness, somnolence, nervousness, psychomotor slowing, abnormal vision, difficulty with memory, difficulty with concentration/attention, and fever (6.1).
The most common (≥5% more frequent than placebo) adverse reactions at recommended dosing in adult and adolescent controlled migraine clinical trials were paresthesia , anorexia, weight decrease, difficulty with memory, taste perversion, upper respiratory tract infections, abdominal pain, diarrhea, hypoesthesia, and nausea (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Supernus Pharmaceuticals at 1-866-398-0833 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Oral contraceptives: Decreased contraceptive efficacy and increased breakthrough bleeding, especially at doses greater than 200 mg per day (7.2)
- Phenytoin or carbamazepine: Concomitant administration with topiramate decreased plasma concentrations of topiramate (7.3)
- Lithium: Monitor lithium levels when co-administered with high-dose topiramate (7.7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment: (creatinine clearance less than 70 mL/min/1.73m2), one-half of the adult dose is recommended (8.7)
- Patients undergoing hemodialysis: Topiramate is cleared by hemodialysis. Dosage adjustment is necessary to avoid rapid drops in topiramate plasma concentration during hemodialysis (8.8)
- Pediatric Use: Because the capsule must be swallowed whole, and may not be sprinkled on food, crushed, or chewed, TROKENDI XR® is recommended only for children ages 6 years and older (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 4/2017
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Trokendi XR
1.1 Monotherapy Epilepsy
TROKENDI XR® extended-release capsules are indicated in patients 6 years of age and older as initial monotherapy for partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Safety and effectiveness in patients who were converted to monotherapy from a previous regimen of other anticonvulsant drugs have not been established in controlled trials [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.2 Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy
TROKENDI XR® extended-release capsules are indicated as adjunctive therapy in patients 6 years of age and older with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome [see Clinical Studies (14.3, 14.4, 14.5)].
2. Trokendi XR Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing in Monotherapy Epilepsy
Pediatric Patients Ages 6 to less than 10 Years
Dosing of topiramate as initial monotherapy in pediatric patients 6 to less than 10 years of age with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures was based on a pharmacometric bridging approach [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Dosing in patients 6 to less than 10 years is based on weight. During the titration period, the initial dose of TROKENDI XR® should be 25 mg/day administered nightly for the first week. Based upon tolerability, the dosage can be increased to 50 mg/day in the second week. Dosage can be increased by 25-50 mg/day each subsequent week as tolerated. Titration to the minimum maintenance dose should be attempted over 5-7 weeks of the total titration period. Based upon tolerability and clinical response, additional titration to a higher dose (up to the maximum maintenance dose) can be attempted at 25-50 mg/day weekly increments. The total daily dose should not exceed the maximum maintenance dose for each range of body weight (Table 1).
| Weight (kg) | Total Daily Dose (mg/day) Minimum Maintenance Dose | Total Daily Dose (mg/day) Maximum Maintenance Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 11 | 150 | 250 |
| 12 - 22 | 200 | 300 |
| 23 - 31 | 200 | 350 |
| 32 - 38 | 250 | 350 |
| Greater than 38 | 250 | 400 |
2.3 Dosing in Migraine
The recommended total daily dose of TROKENDI XR® as treatment for prophylaxis of migraine headache in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older is 100 mg once daily. The recommended titration rate for TROKENDI XR® for migraine prophylaxis to 100 mg once daily is:
Migraine Prophylaxis Titration Schedule for Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older
Week 1: 25mg once daily
Week 2: 50mg once daily
Week 3: 75mg once daily
Week 4: 100mg once daily
Dose and titration rate should be guided by clinical outcome. If required, longer intervals between dose adjustments can be used.
2.4 Administration with Alcohol
Alcohol use should be completely avoided within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after TROKENDI XR® administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.5 Dose Modifications in Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 70 mL/min/1.73 m2), one-half of the usual adult dose is recommended. Such patients will require a longer time to reach steady-state at each dose.
Prior to dosing, obtain an estimated GFR measurement in patients at high risk for renal insufficiency (e.g., older patients, or those with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or autoimmune disease).
2.6 Dosage Modifications in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Topiramate is cleared by hemodialysis at a rate that is 4 to 6 times greater than in patients with normal renal function. Accordingly, a prolonged period of dialysis may cause topiramate concentration to fall below that required to maintain an antiseizure effect. To avoid rapid drops in topiramate plasma concentration during hemodialysis, a supplemental dose of topiramate may be required. The actual adjustment should take into account the:
- duration of dialysis period
- clearance rate of the dialysis system being used
- effective renal clearance of topiramate in the patient being dialyzed
2.7 Laboratory Testing Prior to Treatment Initiation
Measurement of baseline and periodic serum bicarbonate during TROKENDI XR® treatment is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.8 Dosing Modifications in Patients Taking Phenytoin and/or Carbamazepine
The co-administration of TROKENDI XR® with phenytoin may require an adjustment of the dose of phenytoin to achieve optimal clinical outcome. Addition or withdrawal of phenytoin and/or carbamazepine during adjunctive therapy with TROKENDI XR® may require adjustment of the dose of TROKENDI XR®.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TROKENDI XR® (topiramate) extended-release capsules are available in the following strengths and colors:
25 mg: Size 2 capsules, light green opaque body/yellow opaque cap (printed "SPN" on the cap, "25" on the body)
50 mg: Size 0 capsules, light green opaque body/orange opaque cap (printed "SPN" on the cap, "50" on the body)
100 mg: Size 00 capsules, green opaque body/blue opaque cap (printed "SPN" on the cap, "100" on the body)
200 mg: Size 00 capsules, pink opaque body/blue opaque cap (printed "SPN" on the cap, "200" on the body)
4. Contraindications
TROKENDI XR® is contraindicated in patients:
- With recent alcohol use ( i.e., within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after TROKENDI XR® use) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- With metabolic acidosis who are taking concomitant metformin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7.6)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma
A syndrome consisting of acute myopia associated with secondary angle closure glaucoma has been reported in patients receiving topiramate. Symptoms include acute onset of decreased visual acuity and/or ocular pain. Ophthalmologic findings can include myopia, anterior chamber shallowing, ocular hyperemia (redness) and increased intraocular pressure. Mydriasis may or may not be present. This syndrome may be associated with supraciliary effusion resulting in anterior displacement of the lens and iris, with secondary angle closure glaucoma. Symptoms typically occur within 1 month of initiating topiramate therapy. In contrast to primary narrow angle glaucoma, which is rare under 40 years of age, secondary angle closure glaucoma associated with topiramate has been reported in pediatric patients as well as adults. The primary treatment to reverse symptoms is discontinuation of TROKENDI XR® as rapidly as possible, according to the judgment of the treating physician. Other measures, in conjunction with discontinuation of TROKENDI XR®, may be helpful.
Elevated intraocular pressure of any etiology, if left untreated, can lead to serious sequelae including permanent vision loss.
5.2 Visual Field Defects
Visual field defects (independent of elevated intraocular pressure) have been reported in clinical trials and in postmarketing experience in patients receiving topiramate. In clinical trials, most of these events were reversible after topiramate discontinuation. If visual problems occur at any time during treatment with TROKENDI XR, consideration should be given to discontinuing the drug.
5.3 Oligohydrosis and Hyperthermia
Oligohydrosis (decreased sweating), resulting in hospitalization in some cases, has been reported in association with topiramate use. Decreased sweating and an elevation in body temperature above normal characterized these cases. Some of the cases were reported after exposure to elevated environmental temperatures.
The majority of the reports have been in pediatric patients. Patients, especially pediatric patients, treated with TROKENDI XR® should be monitored closely for evidence of decreased sweating and increased body temperature, especially in hot weather. Caution should be used when TROKENDI XR® is prescribed with other drugs that predispose patients to heat-related disorders; these drugs include, but are not limited to, other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and drugs with anticholinergic activity [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
5.4 Metabolic Acidosis
Hyperchloremic, non-anion gap, metabolic acidosis (i.e., decreased serum bicarbonate below the normal reference range in the absence of chronic respiratory alkalosis) is associated with topiramate, and can be expected with treatment with TROKENDI XR®. This metabolic acidosis is caused by renal bicarbonate loss due to the inhibitory effect of topiramate on carbonic anhydrase. Such electrolyte imbalance has been observed with the use of topiramate in placebo-controlled clinical trials and in the post-marketing period. Generally, topiramate-induced metabolic acidosis occurs early in treatment although cases can occur at any time during treatment. Bicarbonate decrements are usually mild to moderate (average decrease of 4 mEq/L at daily doses of 400 mg in adults and at approximately 6 mg/kg/day in pediatric patients); rarely, patients can experience severe decrements to values below 10 mEq/L. Conditions or therapies that predispose patients to acidosis (such as renal disease, severe respiratory disorders, status epilepticus, diarrhea, ketogenic diet or specific drugs) may be additive to the bicarbonate lowering effects of topiramate.
5.5 Interaction with Alcohol
In vitro data show that, in the presence of alcohol, the pattern of topiramate release from TROKENDI XR® capsules is significantly altered. As a result, plasma levels of topiramate with TROKENDI XR® may be markedly higher soon after dosing and subtherapeutic later in the day. Therefore, alcohol use should be completely avoided within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after TROKENDI XR® administration.
5.6 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED, including TROKENDI XR® for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 2 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
| Indication | Placebo Patients with Events per 1,000 Patients | Drug Patients with Events per 1,000 Patients | Relative Risk: Incidence of Events in Drug Patients/ Incidence in Placebo Patients | Risk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events per 1,000 Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | 1.0 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
| Psychiatric | 5.7 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| Other | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 0.9 |
| Total | 2.4 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing TROKENDI XR® or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
5.7 Cognitive/Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions most often associated with the use of topiramate, and therefore expected to be associated with the use of TROKENDI XR®, were related to the central nervous system and were observed in both the epilepsy and migraine populations. In adults, the most frequent of these can be classified into three general categories: 1) Cognitive-related dysfunction (e.g., confusion, psychomotor slowing, difficulty with concentration/attention, difficulty with memory, speech or language problems, particularly word-finding difficulties), 2) Psychiatric/behavioral disturbances (e.g.,depression or mood problems), and 3) Somnolence or fatigue.
5.8 Fetal Toxicity
Topiramate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Data from pregnancy registries indicate that infants exposed to topiramate in utero have an increased risk for cleft lip and/or cleft palate (oral clefts) and for being small for gestational age. In multiple species, oral administration of topiramate to pregnant animals at clinically relevant doses resulted in structural malformations, including craniofacial defects, and reduced body weights in offspring [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Consider the benefits and risks of TROKENDI XR® when administering the drug in women of childbearing potential, particularly when TROKENDI XR® is considered for a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. TROKENDI XR® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be informed of the potential hazard to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.9 Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs
In patients with or without a history of seizures or epilepsy, antiepileptic drugs including TROKENDI XR® should be gradually withdrawn to minimize the potential for seizures or increased seizure frequency [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In situations where rapid withdrawal of TROKENDI XR® is medically required, appropriate monitoring is recommended.
5.11 Kidney Stones
A total of 32/2086 (1.5%) of adults exposed to topiramate during its adjunctive epilepsy therapy development reported the occurrence of kidney stones, an incidence about 2 to 4 times greater than expected in a similar, untreated population. In the double-blind monotherapy epilepsy study, a total of 4/319 (1.3%) of adults exposed to topiramate reported the occurrence of kidney stones. As in the general population, the incidence of stone formation among topiramate treated patients was higher in men. Kidney stones have also been reported in pediatric patients taking topiramate for epilepsy or migraine. During long-term (up to 1 year) topiramate treatment in an open-label extension study of 284 pediatric patients 1 month to 24 months old with epilepsy, 7% developed kidney or bladder stones that were diagnosed clinically or by sonogram. TROKENDI XR® is not approved for pediatric patients less than 6 years old [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Kidney stones have also been reported in pediatric patients taking topiramate for migraine prophylaxis. For the double-blind migraine prophylaxis studies, one adverse event (renal calculus) occurred in a topiramate-treated subject in the age 12 to 17 years group. The overall experience with open-label, long-term, topiramate treatment for migraine prophylaxis is limited in pediatric patients.
TROKENDI XR® would be expected to have the same effect as topiramate on the formation of kidney stones. An explanation for the association of topiramate and kidney stones may lay in the fact that topiramate is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) can promote stone formation by reducing urinary citrate excretion and by increasing urinary pH [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. The concomitant use of TROKENDI XR® with any other drug producing metabolic acidosis, or potentially in patients on a ketogenic diet may create a physiological environment that increases the risk of kidney stone formation, and should therefore be avoided.
Increased fluid intake increases the urinary output, lowering the concentration of substances involved in stone formation. Hydration is recommended to reduce new stone formation.
5.12 Hypothermia with Concomitant Valproic Acid Use
Hypothermia, defined as an unintentional drop in body core temperature to less than 35ºC (95ºF) has been reported in association with topiramate use with concomitant valproic acid (VPA) both in the presence and in the absence of hyperammonemia. This adverse reaction in patients using concomitant topiramate and valproate can occur after starting topiramate treatment or after increasing the daily dose of topiramate [see Drug Interactions (7.5)]. Consideration should be given to stopping topiramate or valproate in patients who develop hypothermia, which may be manifested by a variety of clinical abnormalities including lethargy, confusion, coma, and significant alterations in other major organ systems such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Clinical management and assessment should include examination of blood ammonia levels.
5.13 Paresthesia
Paresthesia (usually tingling of the extremities), an effect associated with the use of other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, appears to be a common effect of topiramate. Paresthesia was more frequently reported in the monotherapy epilepsy and migraine prophylaxis trials conducted with topiramate than in the adjunctive therapy epilepsy trials conducted with the same product. In the majority of instances, paresthesia did not lead to treatment discontinuation.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Visual Field Defects [see Warnings and Precautions 5.2]
- Oligohydrosis and Hyperthermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Metabolic Acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Cognitive/Neuropsychiatric Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]]
- Withdrawal of Antiepileptic Drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy (Without and With Concomitant Valproic Acid Use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Kidney Stones [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hypothermia with Concomitant Valproic Acid Use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Paresthesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
The data described in the following sections were obtained using immediate-release topiramate tablets in studies of patients with epilepsy. TROKENDI XR® has not been studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled Phase III clinical study in the epilepsy patient population. However, it is expected that TROKENDI XR® would produce a similar adverse reaction profile as immediate-release topiramate.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Clinical Trials Experience in Epilepsy
Adverse Reactions Observed in Monotherapy Trial for Epilepsy
Pediatric Patients 6 Years to Less Than 16 Years of Age
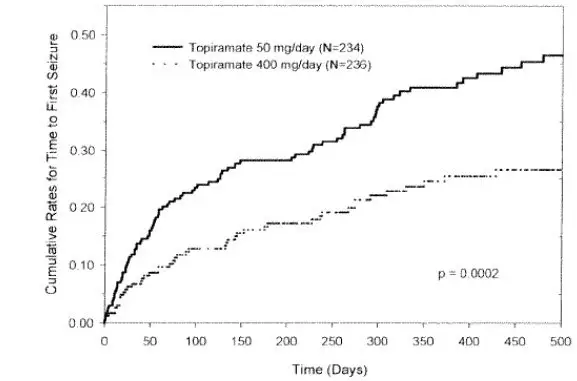
The adverse reactions in the controlled trial (Study 1) that occurred most commonly in pediatric patients in the 400 mg per day topiramate group and at an incidence higher (≥ 5%) than in the 50 mg per day group were fever, weight decrease, paresthesia, mood problems, cognitive problems, infection, and flushing (see Table 4) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Approximately 14% of the 77 pediatric patients in the 400 mg per day group who received topiramate as monotherapy in the controlled clinical trial discontinued therapy due to adverse reactions. The most common (≥ 2% more frequent than in the 50 mg per day group) adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation in this trial were difficulty with concentration/attention, fever, flushing, and confusion.
| Immediate-release topiramate Dosage (mg/day) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Body System/ | 50 | 400 |
| Adverse Reaction | (N=160) | (N=159) |
|
||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | ||
| Asthenia | 4 | 6 |
| Leg Pain | 2 | 3 |
| Chest Pain | 1 | 2 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Paresthesia | 21 | 40 |
| Dizziness | 13 | 14 |
| Hypoesthesia | 4 | 5 |
| Ataxia | 3 | 4 |
| Hypertonia | 0 | 3 |
| Gastro-intestinal System Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 5 | 6 |
| Constipation | 1 | 4 |
| Gastritis | 0 | 3 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 | 3 |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux | 1 | 2 |
| Liver and Biliary System Disorders | ||
| Gamma-GT Increased | 1 | 3 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
| Weight Decrease | 6 | 16 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 9 | 15 |
| Anorexia | 4 | 14 |
| Difficulty with Memory NOS | 5 | 10 |
| Insomnia | 8 | 9 |
| Depression | 7 | 9 |
| Difficulty with Concentration/Attention | 7 | 8 |
| Anxiety | 4 | 6 |
| Psychomotor Slowing | 3 | 5 |
| Mood Problems | 2 | 5 |
| Confusion | 3 | 4 |
| Cognitive Problem NOS | 1 | 4 |
| Libido Decreased | 0 | 3 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Female | ||
| Vaginal Hemorrhage | 0 | 3 |
| Red Blood Cell Disorders | ||
| Anemia | 1 | 2 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||
| Infection Viral | 6 | 8 |
| Infection | 2 | 3 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||
| Bronchitis | 3 | 4 |
| Rhinitis | 2 | 4 |
| Dyspnea | 1 | 2 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||
| Rash | 1 | 4 |
| Pruritus | 1 | 4 |
| Acne | 2 | 3 |
| Special Senses Other, Disorders | ||
| Taste Perversion | 3 | 5 |
| Urinary System Disorders | ||
| Cystitis | 1 | 3 |
| Renal Calculus | 0 | 3 |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 1 | 2 |
| Dysuria | 0 | 2 |
| Micturition Frequency | 0 | 2 |
| Immediate-release topiramate Dosage (mg/day) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Body System/ | 50 | 400 |
| Adverse Reaction | (N=74) | (N=77) |
|
||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | ||
| Fever | 1 | 12 |
| Asthenia | 0 | 3 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Paresthesia | 3 | 12 |
| Muscle Contractions Involuntary | 0 | 3 |
| Vertigo | 0 | 3 |
| Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 8 | 9 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
| Weight Decrease | 7 | 17 |
| Platelet, Bleeding & Clotting Disorders | ||
| Epistaxis | 0 | 4 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Difficulty with Concentration/Attention | 7 | 10 |
| Mood Problems | 1 | 8 |
| Cognitive Problems | 1 | 6 |
| Difficulty with Memory | 1 | 3 |
| Confusion | 0 | 3 |
| Depression | 0 | 3 |
| Personality Disorder (Behavior Problems) | 0 | 3 |
| Red Blood Cell Disorders | ||
| Anemia | 1 | 3 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Female† | ||
| Intermenstrual Bleeding | 0 | 3 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||
| Infection | 3 | 8 |
| Infection Viral | 3 | 6 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 16 | 18 |
| Rhinitis | 5 | 6 |
| Bronchitis | 1 | 5 |
| Sinusitis | 1 | 4 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||
| Rash | 3 | 4 |
| Alopecia | 1 | 4 |
| Urinary System Disorders | ||
| Urinary Incontinence | 1 | 3 |
| Micturition Frequency | 0 | 3 |
| Vascular (Extracardiac) Disorders | ||
| Flushing | 0 | 5 |
Adverse Reactions Observed in Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy Trials
The most commonly observed adverse reactions associated with the use of topiramate at dosages of 200 to 400 mg per day in controlled trials in adults with partial onset seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome that were seen at greater frequency in topiramate-treated patients and did not appear to be dose-related were: somnolence, ataxia, speech disorders and related speech problems, psychomotor slowing, abnormal vision, difficulty with memory, paresthesia and diplopia [see Table 5] [see Clinical Studies (14.3, 14.4, and 14.5)]. The most common dose-related adverse reactions at dosages of 200 mg to 1,000 mg per day were: fatigue, nervousness, difficulty with concentration or attention, confusion, depression, anorexia, language problems, anxiety, mood problems, and weight decrease [see Table 7].
Adverse reactions associated with the use of topiramate at dosages of 5 mg/kg/day to 9 mg/kg/day in controlled trials in pediatric patients with partial onset seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome that were seen at greater frequency in topiramate-treated patients were: fatigue, somnolence, anorexia, nervousness, difficulty with concentration/attention, difficulty with memory, aggressive reaction, and weight decrease [see Table 8].
In controlled clinical trials in adults, 11% of patients receiving topiramate 200 to 400 mg per day as adjunctive therapy discontinued due to adverse reactions. This rate appeared to increase at dosages above 400 mg per day. Adverse events associated with discontinuing therapy included somnolence, dizziness, anxiety, difficulty with concentration or attention, fatigue, and paresthesia and increased at dosages above 400 mg per day. None of the pediatric patients who received topiramate adjunctive therapy at 5 mg/kg/day to 9 mg/kg/day in controlled clinical trials discontinued due to adverse reactions.
Approximately 28% of the 1757 adults with epilepsy who received topiramate at dosages of 200 mg to 1,600 mg per day in clinical studies discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions; an individual patient could have reported more than one adverse reaction. These adverse reactions were: psychomotor slowing (4.0%), difficulty with memory (3.2%), fatigue (3.2%), confusion (3.1%), somnolence (3.2%), difficulty with concentration/attention (2.9%), anorexia (2.7%), depression (2.6%), dizziness (2.5%), weight decrease (2.5%), nervousness (2.3%), ataxia (2.1%), and paresthesia (2.0%). Approximately 11% of the 310 pediatric patients who received topiramate at dosages up to 30 mg/kg/day discontinued due to adverse reactions. Adverse reactions associated with discontinuing therapy included aggravated convulsions (2.3%), difficulty with concentration/attention (1.6%), language problems (1.3%), personality disorder (1.3%), and somnolence (1.3%).
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During Double-Blind Epilepsy Adjunctive Therapy Trials
Other adverse reactions that occurred in more than 1% of adults treated with 200 mg to 400 mg of topiramate in placebo-controlled epilepsy trials but with equal or greater frequency in the placebo group were headache, injury, anxiety, rash, pain, convulsions aggravated, coughing, fever, diarrhea, vomiting, muscle weakness, insomnia, personality disorder, dysmenorrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, and eye pain.
| Topiramate Dosage (mg per day) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Body System/ | Placebo | 200-400 | 600-1,000 |
| Adverse Reaction‡ | (N=291) | (N=183) | (N=414) |
|
|||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | |||
| Fatigue | 13 | 15 | 30 |
| Asthenia | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| Back pain | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Chest pain | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| Influenza-like symptoms | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Leg pain | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Hot flushes | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Allergy | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Edema | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Body odor | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Rigors | 0 | 1 | <1 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | |||
| Dizziness | 15 | 25 | 32 |
| Ataxia | 7 | 16 | 14 |
| Speech disorders/Related speech problems | 2 | 13 | 11 |
| Paresthesia | 4 | 11 | 19 |
| Nystagmus | 7 | 10 | 11 |
| Tremor | 6 | 9 | 9 |
| Language problems | 1 | 6 | 10 |
| Coordination abnormal | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Hypoesthesia | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Gait abnormal | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Muscle contractions involuntary | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Stupor | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Vertigo | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Gastro-intestinal System Disorders | |||
| Nausea | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| Dyspepsia | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Abdominal pain | 4 | 6 | 7 |
| Constipation | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Gastroenteritis | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Dry mouth | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Gingivitis | <1 | 1 | 1 |
| GI disorder | <1 | 1 | 0 |
| Hearing and Vestibular Disorders | |||
| Hearing decreased | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | |||
| Weight decrease | 3 | 9 | 13 |
| Musculoskeletal System Disorders | |||
| Myalgia | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Skeletal pain | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Platelet, Bleeding & Clotting Disorders | |||
| Epistaxis | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | |||
| Somnolence | 12 | 29 | 28 |
| Nervousness | 6 | 16 | 19 |
| Psychomotor slowing | 2 | 13 | 21 |
| Difficulty with memory | 3 | 12 | 14 |
| Anorexia | 4 | 10 | 12 |
| Confusion | 5 | 11 | 14 |
| Depression | 5 | 5 | 13 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 2 | 6 | 14 |
| Mood problems | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| Agitation | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Aggressive reaction | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Emotional liability | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Cognitive problems | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Libido decreased | 1 | 2 | <1 |
| Apathy | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Depersonalization | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Female | |||
| Breast pain | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Amenorrhea | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Menorrhagia | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Menstrual disorder | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Male | |||
| Prostatic disorder | <1 | 2 | 0 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | |||
| Infection | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Infection viral | 1 | 2 | <1 |
| Moniliasis | <1 | 1 | 0 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | |||
| Pharyngitis | 2 | 6 | 3 |
| Rhinitis | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Sinusitis | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Dyspnea | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | |||
| Skin disorder | <1 | 2 | 1 |
| Sweating increased | <1 | 1 | <1 |
| Rash, erythematous | <1 | 1 | <1 |
| Special Senses Other, Disorders | |||
| Taste perversion | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Urinary System Disorders | |||
| Hematuria | 1 | 2 | <1 |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Micturition frequency | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Urinary incontinence | <1 | 2 | 1 |
| Urine abnormal | 0 | 1 | <1 |
| Vision Disorders | |||
| Vision abnormal | 2 | 13 | 10 |
| Diplopia | 5 | 10 | 10 |
| White Cell and RES Disorders | |||
| Leukopenia | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Adverse Reactions Observed in Adjunctive Therapy Trial in Adults with Partial Onset Seizures (Study 7)
Study 7 was a randomized, double-blind, adjunctive, placebo-controlled, parallel group study with 3 treatment arms: 1) placebo; 2) topiramate 200 mg per day with a 25 mg per day starting dose, increased by 25 mg per day each week for 8 weeks until the 200 mg per day maintenance dose was reached; and 3) topiramate 200 mg per day with a 50 mg per day starting dose, increased by 50 mg per day each week for 4 weeks until the 200 mg per day maintenance dose was reached. All patients were maintained on concomitant carbamazepine with or without another concomitant antiepileptic drug.
The incidence of adverse reactions (Table 6) did not differ significantly between the 2 topiramate regimens. Because the frequencies of adverse reactions reported in this study were markedly lower than those reported in the previous epilepsy studies, they cannot be directly compared with data obtained in other studies.
| Topiramate Dosage (mg per day) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System/ | Placebo | 200 |
| Adverse Reaction‡ | (N=92) | (N=171) |
|
||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 4 | 9 |
| Chest pain | 1 | 2 |
| Cardiovascular Disorders, General | ||
| Hypertension | 0 | 2 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Paresthesia | 2 | 9 |
| Dizziness | 4 | 7 |
| Tremor | 2 | 3 |
| Hypoesthesia | 0 | 2 |
| Leg cramps | 0 | 2 |
| Language problems | 0 | 2 |
| Gastro-intestinal System Disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 3 | 5 |
| Constipation | 0 | 4 |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 2 |
| Dyspepsia | 0 | 2 |
| Dry mouth | 0 | 2 |
| Hearing and Vestibular Disorders | ||
| Tinnitus | 0 | 2 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
| Weight decrease | 4 | 8 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 9 | 15 |
| Anorexia | 7 | 9 |
| Nervousness | 2 | 9 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 0 | 5 |
| Insomnia | 3 | 4 |
| Difficulty with memory | 1 | 2 |
| Aggressive reaction | 0 | 2 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||
| Rhinitis | 0 | 4 |
| Urinary System Disorders | ||
| Cystitis | 0 | 2 |
| Vision Disorder | ||
| Diplopia | 0 | 2 |
| Vision abnormal | 0 | 2 |
| (Topiramate) Dosage (mg per day) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | Placebo | 200 | 400 | 600-1,000 |
| (N=216) | (N=45) | (N=68) | (N=414) | |
|
||||
| Fatigue | 13 | 11 | 12 | 30 |
| Nervousness | 7 | 13 | 18 | 19 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 1 | 7 | 9 | 14 |
| Confusion | 4 | 9 | 10 | 14 |
| Depression | 6 | 9 | 7 | 13 |
| Anorexia | 4 | 4 | 6 | 12 |
| Language Problems | <1 | 2 | 9 | 10 |
| Anxiety | 6 | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| Mood Problems | 2 | 0 | 6 | 9 |
| Weight Decrease | 3 | 4 | 9 | 13 |
| Body System/ | Placebo | Topiramate |
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | (N=101) | (N=98) |
|
||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 5 | 16 |
| Injury | 13 | 14 |
| Allergic reaction | 1 | 2 |
| Back pain | 0 | 1 |
| Pallor | 0 | 1 |
| Cardiovascular Disorders, General | ||
| Hypertension | 0 | 1 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Gait abnormal | 5 | 8 |
| Ataxia | 2 | 6 |
| Hyperkinesia | 4 | 5 |
| Dizziness | 2 | 4 |
| Speech disorders/Related speech problems | 2 | 4 |
| Hyporeflexia | 0 | 2 |
| Convulsions grand mal | 0 | 1 |
| Fecal incontinence | 0 | 1 |
| Paresthesia | 0 | 1 |
| Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders | ||
| Nausea | 5 | 6 |
| Saliva increased | 4 | 6 |
| Constipation | 4 | 5 |
| Gastroenteritis | 2 | 3 |
| Dysphagia | 0 | 1 |
| Flatulence | 0 | 1 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 0 | 1 |
| Glossitis | 0 | 1 |
| Gum hyperplasia | 0 | 1 |
| Heart Rate and Rhythm Disorders | ||
| Bradycardia | 0 | 1 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
| Weight decrease | 1 | 9 |
| Thirst | 1 | 2 |
| Hypoglycemia | 0 | 1 |
| Weight increase | 0 | 1 |
| Platelet, Bleeding & Clotting Disorders | ||
| Purpura | 4 | 8 |
| Epistaxis | 1 | 4 |
| Hematoma | 0 | 1 |
| Prothrombin increased | 0 | 1 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0 | 1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 16 | 26 |
| Anorexia | 15 | 24 |
| Nervousness | 7 | 14 |
| Personality disorder (Behavior Problems) | 9 | 11 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 2 | 10 |
| Aggressive reaction | 4 | 9 |
| Insomnia | 7 | 8 |
| Difficulty with memory | 0 | 5 |
| Confusion | 3 | 4 |
| Psychomotor slowing | 2 | 3 |
| Appetite increased | 0 | 1 |
| Neurosis | 0 | 1 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Female | ||
| Leukorrhea | 0 | 2 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||
| Infection viral | 3 | 7 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||
| Pneumonia | 1 | 5 |
| Respiratory disorder | 0 | 1 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||
| Skin Disorder | 2 | 3 |
| Alopecia | 1 | 2 |
| Dermatitis | 0 | 2 |
| Hypertrichosis | 1 | 2 |
| Rash erythematous | 0 | 2 |
| Eczema | 0 | 1 |
| Seborrhea | 0 | 1 |
| Skin discoloration | 0 | 1 |
| Urinary System Disorders | ||
| Urinary incontinence | 2 | 4 |
| Nocturia | 0 | 1 |
| Vision Disorders | ||
| Eye abnormality | 1 | 2 |
| Vision abnormal | 1 | 2 |
| Diplopia | 0 | 1 |
| Lacrimation abnormal | 0 | 1 |
| Myopia | 0 | 1 |
| White Cell and RES Disorders | ||
| Leukopenia | 0 | 2 |
Clinical Trial Experience in Migraine
Adult Patients
In the four multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group migraine prophylaxis clinical trials (which included 35 adolescent patients age 12 to 15 years) conducted with immediate-release topiramate, most of the adverse reactions were mild or moderate in severity. Most adverse reactions occurred more frequently during the titration period than during the maintenance period.
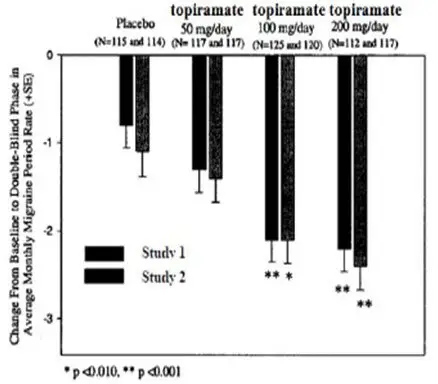
The most common (≥5% more frequent than placebo) adverse reactions associated with the use of the 100 mg topiramate dose in controlled, migraine clinical trials of predominantly adults were paresthesia, anorexia, weight decrease, taste perversion, diarrhea, difficulty with memory, hypoesthesia, and nausea. Table 9 includes those adverse reactions reported for patients in the placebo-controlled trials where the incidence in any immediate-release topiramate group was at least 2% and was greater than that for placebo patients.
| Body System/ | Placebo | Topiramate dosage (mg per day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | ||
| Adverse Reaction | (N=445) % | (N=235) % | (N=386) % | (N=514) % |
|
||||
| Body as a Whole-General Disorders | ||||
| Fatigue | 11 | 14 | 15 | 19 |
| Injury | 7 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| Asthenia | 1 | Less than 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Fever | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Influenza-like symptoms | Less than 1 | Less than 1 | Less than 1 | 2 |
| Allergy | Less than 1 | 2 | Less than 1 | Less than 1 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Paresthesia | 6 | 35 | 51 | 49 |
| Dizziness | 10 | 8 | 9 | 12 |
| Hypoaesthesia | 2 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Language problems | 2 | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| Involuntary muscle contractions | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Ataxia | Less than 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Speech disorders/Related speech problems | Less than 1 | 1 | Less than 1 | 2 |
| Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 8 | 9 | 13 | 14 |
| Diarrhea | 4 | 9 | 11 | 11 |
| Abdominal pain | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| Dyspepsia | 3 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Vomiting | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Gastroenteritis | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Hearing and Vestibular Disorders | ||||
| Tinnitus | 1 | Less than 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||||
| Weight decrease | 1 | 6 | 9 | 11 |
| Thirst | Less than 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal System Disorders | ||||
| Arthralgia | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 |
| Neoplasms | ||||
| Neoplasm | Less than 1 | 2 | Less than 1 | Less than 1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
| Anorexia | 6 | 9 | 15 | 14 |
| Somnolence | 5 | 8 | 7 | 10 |
| Difficulty with memory | 2 | 7 | 7 | 11 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 2 | 3 | 6 | 10 |
| Insomnia | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Anxiety | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Mood Problems | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
| Depression | 4 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Nervousness | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Confusion | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Psychomotor slowing | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| Libido decreased | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Aggravated depression | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Agitation | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Cognitive problems | 1 | Less than 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Female | ||||
| Menstrual disorder | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Reproductive Disorders, Male | ||||
| Ejaculation premature | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||||
| Viral Infection | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Otitis media | Less than 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 12 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
| Sinusitis | 6 | 10 | 6 | 8 |
| Pharyngitis | 4 | 5 | 6 | 2 |
| Coughing | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Bronchitis | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Dyspnea | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Rhinitis | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||||
| Pruritis | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Special Sense Other, Disorders | ||||
| Taste perversion | 1 | 15 | 8 | 12 |
| Taste loss | Less than 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Urinary System Disorders | ||||
| Urinary tract infection | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Renal calculus | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Vision Disorders | ||||
| Vision abnormal | Less than 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Blurred vision | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Conjunctivitis | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Of the 1135 patients exposed to immediate-release topiramate in the placebo-controlled studies, 25% discontinued due to adverse reactions, compared to 10% of the 445 placebo patients. The adverse reactions associated with discontinuing therapy in patients in these studies included paresthesia (7%), fatigue (4%), nausea (4%), difficulty with concentration/attention (3%), insomnia (3%), anorexia (2%) and dizziness (2%).
Patients treated in these studies experienced mean percent reductions in body weight that were dose-dependent. This change was not seen in the placebo group. Mean changes of 0%, -2%, -3%, and -4% were seen for the placebo group, immediate-release topiramate 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg groups, respectively.
Table 10 shows adverse reactions that were dose-dependent. Several central nervous system adverse reactions, including some that represented cognitive dysfunction, were dose-related. The most common dose-related adverse reactions (treatment difference ≥5% for the 100 mg dose) were: paresthesia, nausea, anorexia, difficulty with memory, diarrhea, weight decrease, and hypoesthesia.
| Body System/ | Placebo | Topiramate dosage (mg per day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | ||
| Adverse Reaction | (N=445) % | (N=235) % | (N=386) % | (N=514) % |
|
||||
| Paresthesia | 6 | 35 | 51 | 49 |
| Fatigue | 11 | 14 | 15 | 19 |
| Nausea | 8 | 9 | 13 | 14 |
| Anorexia | 6 | 9 | 15 | 14 |
| Dizziness | 10 | 8 | 9 | 12 |
| Weight decrease | 1 | 6 | 9 | 11 |
| Difficulty with memory | 2 | 7 | 7 | 11 |
| Diarrhea | 4 | 9 | 11 | 11 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 2 | 3 | 6 | 10 |
| Somnolence | 5 | 8 | 7 | 10 |
| Hypoaesthesia | 2 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Anxiety | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Depression | 4 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Mood problems | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
| Dry mouth | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Confusion | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Involuntary muscle contractions | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Abnormal vision | Less than 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Renal calculus | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
Adolescents 12 to 17 Years of Age
In five randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group migraine prophylaxis clinical trials, most of the adverse reactions with immediate-release topiramate were mild or moderate in severity. Most adverse reactions occurred more frequently during the titration period than during the maintenance period. Among adverse reactions with onset during titration, approximately half persisted into the maintenance period.
In four, fixed-dose, double-blind migraine prophylaxis clinical trials in immediate-release topiramate treated adolescent patients, the most commonly observed adverse reactions associated with the use of 100 mg of immediate-release topiramate that were seen at an incidence higher (≥5%) than in the placebo group were: paresthesia, upper respiratory tract infection, anorexia, and abdominal pain (see Table 11). Table 11 shows adverse reactions from the adolescent pivotal trial (Study 3) demonstrating the efficacy of immediate-release topiramate in which there were 103 adolescent patients who were treated with placebo or 50 mg or 100 mg of immediate-release topiramate, and three predominantly adult trials in which there were 49 adolescent patients (12 to 17 years) who were treated with placebo or 50 mg, 100 mg or 200 mg of immediate-release topiramate [see Clinical Studies (14.6)]. Table 11 also shows adverse reactions in adolescents in the controlled migraine trials when the incidence in an immediate-release topiramate dose group was at least 5% or higher than the incidence of placebo. Many adverse reactions shown in Table 11 indicated a dose-dependent relationship.
| Immediate-Release Topiramate Dosage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body System/ Adverse Reaction | Placebo (N=45) % | 50 mg/day (N=46) % | 100 mg/day (N=48) % | 200 mg/day (N=13) % |
|
||||
| Body as a Whole – General Disorders | ||||
| Allergy | 0 | 0 | 4 | 8 |
| Fatigue | 7 | 7 | 8 | 15 |
| Fever | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Leg pain | 0 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||||
| Dizziness | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Headache | 2 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Language problems | 2 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| Muscle contractions involuntary | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Paresthesia | 7 | 20 | 19 | 38 |
| Endocrine Disorders | ||||
| Hyperthyroidism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Gastrointestinal System Disorders | ||||
| Abdominal pain | 9 | 7 | 15 | 15 |
| Diarrhea | 0 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Nausea | 4 | 4 | 8 | 0 |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||||
| Edema pharynx | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Weight decrease | 2 | 7 | 4 | 31 |
| Platelet, Bleeding & Clotting Disorders | ||||
| Epistaxis | 0 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
| Anorexia | 4 | 9 | 10 | 15 |
| Anxiety | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Difficulty with concentration/attention | 0 | 0 | 2 | 15 |
| Difficulty with memory | 2 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Insomnia | 2 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| Mood problems | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Psychomotor slowing | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8 |
| Somnolence | 2 | 2 | 6 | 15 |
| Resistance Mechanism Disorders | ||||
| Infection viral | 4 | 4 | 8 | 15 |
| Otitis media | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||||
| Coughing | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0 |
| Laryngitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Rhinitis | 2 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
| Sinusitis | 2 | 9 | 4 | 15 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 11 | 26 | 23 | 23 |
| Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||||
| Rash erythematous | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Special Senses Other, Disorders | ||||
| Taste perversion | 2 | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| Vision Disorders | ||||
| Conjunctivitis | 4 | 7 | 4 | 0 |
In the double-blind placebo-controlled studies, adverse reactions led to discontinuation of treatment in 8% of placebo patients compared with 6% of immediate-release topiramate-treated patients. Adverse reactions associated with discontinuing therapy that occurred in more than one immediate-release topiramate-treated patient were fatigue (1%), headache (1%), and somnolence (1%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of topiramate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The listing is alphabetized: bullous skin reactions (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), hepatic failure (including fatalities), hepatitis, maculopathy, pancreatitis, and pemphigus.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Alcohol
Alcohol use is contraindicated within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after TROKENDI XR® administration [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7.2 Oral Contraceptives
Exposure to ethinyl estradiol was statistically significantly decreased when topiramate (at doses above 200 mg) was given as adjunctive therapy in patients taking valproic acid. However, norethindrone exposure was not significantly affected.
In another pharmacokinetic interaction study in healthy volunteers with a concomitantly administered combination oral contraceptive product containing 1 mg norethindrone (NET) plus 35 mcg ethinyl estradiol (EE), topiramate, given in the absence of other medications at doses of 50 to 200 mg per day, was not associated with statistically significant changes in mean exposure to either component of the oral contraceptive.
The possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy and increased breakthrough bleeding should be considered in patients taking combination oral contraceptive products with TROKENDI XR®. Patients taking estrogen-containing contraceptives should be asked to report any change in their bleeding patterns. Contraceptive efficacy can be decreased even in the absence of breakthrough bleeding [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Antiepileptic Drugs
Concomitant administration of phenytoin or carbamazepine with topiramate decreased plasma concentrations of topiramate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Concomitant administration of valproic acid and topiramate has been associated with hyperammonemia with and without encephalopathy. Concomitant administration of topiramate with valproic acid has also been associated with hypothermia (with and without hyperammonemia) in patients who have tolerated either drug alone. It may be prudent to examine blood ammonia levels in patients in whom the onset of hypothermia has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10, 5.12) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Numerous AEDs are substrates of the CYP enzyme system. In vitro studies indicate that topiramate does not inhibit enzyme activity for CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4/5 isozymes. In vitro studies indicate that immediate-release topiramate is a mild inhibitor of CYP2C19 and a mild inducer of CYP3A4. The same drug interactions can be expected with the use of TROKENDI XR®.
7.4 CNS Depressants
Topiramate is a CNS depressant. Concomitant administration of topiramate with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol can result in significant CNS depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
7.5 Other Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Concomitant use of topiramate, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, with any other carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide), may increase the severity of metabolic acidosis and may also increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Patient should be monitored for the appearance or worsening of metabolic acidosis when TROKENDI XR® is given concomitantly with another carbonic anhydrase inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
Human Data
Data from the NAAED Pregnancy Registry indicate an increased risk of oral clefts in infants exposed to topiramate monotherapy during the first trimester of pregnancy. The prevalence of oral clefts was 1.2% compared to a prevalence of 0.39% - 0.46% in infants exposed to other AEDs, and a prevalence of 0.12% in infants of mothers without epilepsy or treatment with other AEDs. For comparison, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reviewed available data on oral clefts in the United States and found a similar background rate of 0.17%. The relative risk of oral clefts in topiramate-exposed pregnancies in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry was 9.6 (95% Confidence Interval=[CI] 4.0-23.0) as compared to the risk in a background population of untreated women. The UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register reported a similarly increased prevalence of oral clefts of 3.2% among infants exposed to topiramate monotherapy. The observed rate of oral clefts was 16 times higher than the background rate in the UK, which is approximately 0.2%.
Data from the NAAED pregnancy registry and a population-based birth registry cohort indicate that exposure to topiramate in utero is associated with an increased risk of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns (birth weight <10th percentile). In the NAAED pregnancy registry, 18% of topiramate-exposed newborns were SGA compared to 7% of newborns exposed to a reference AED, and 5% of newborns of mothers without epilepsy and without AED exposure. In the Medical Birth Registry of Norway (MBRN), a population-based pregnancy registry, 25% of newborns in the topiramate monotherapy exposure group were SGA compared to 9 % in the comparison group who were unexposed to AEDs. The long-term consequences of the SGA findings are not known.
Animal Data
When topiramate (20, 100, and 500 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to pregnant mice during the period of organogenesis, the incidence of fetal malformations (primarily craniofacial defects) was increased at all doses. Fetal body weights and skeletal ossification were reduced at the highest dose tested in conjunction with decreased maternal body weight gain. A no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity in mice was not identified. The lowest dose tested, which was associated with teratogenic effects, is less than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for epilepsy (400 mg/day) or migraine (100 mg/day) on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis.
In pregnant rats administered topiramate (20, 100, and 500 mg/kg/day or 0.2, 2.5, 30, and 400 mg/kg/day) orally during the period of organogenesis, the frequency of limb malformations (ectrodactyly, micromelia, and amelia) was increased in fetuses at 400 or 500 mg/kg/day. Embryotoxicity (reduced fetal body weights, increased incidences of structural variations) was observed at doses as low as 20 mg/kg/day. Clinical signs of maternal toxicity were seen at 400 mg/kg/day and above, and maternal body weight gain was reduced at doses of 100 mg/kg/day or greater. The no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity in rats is less than the MRHD for epilepsy or migraine on a mg/m2 basis.
In pregnant rabbits administered topiramate (20, 60, and 180 mg/kg/day or 10, 35, and 120 mg/kg/day) orally during organogenesis, embryofetal mortality was increased at 35 mg/kg/day and teratogenic effects (primarily rib and vertebral malformations) were observed at 120 mg/kg/day. Evidence of maternal toxicity (decreased body weight gain, clinical signs, and/or mortality) was seen at 35 mg/kg/day and above. The no-effect dose (20 mg/kg/day) for embryofetal developmental toxicity in rabbits is equivalent to the MRHD for epilepsy and approximately 4 times the MRHD for migraine on a mg/m2 basis.
When topiramate (0.2, 4, 20, and 100 mg/kg/day or 2, 20, and 200 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to female rats during the latter part of gestation and throughout lactation, offspring exhibited decreased viability and delayed physical development at 200 mg/kg/day and reductions in pre-and/or postweaning body weight gain at 2 mg/kg/day and above. Maternal toxicity (decreased body weight gain, clinical signs) was evident at 100 mg/kg/day or greater.
In a rat embryo/fetal development study which included postnatal assessment of offspring, oral administration of topiramate (0.2, 2.5, 30, and 400 mg/kg/day) to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis resulted in delayed physical development at 400 mg/kg/day and persistent reductions in body weight gain at 30 mg/kg/day and higher in the offspring. The no-effect dose (0.2 mg/kg/day) for pre- and postnatal developmental toxicity is less than the MRHD for epilepsy or migraine on a mg/m2 basis.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of immediate-release topiramate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. Dosage adjustment is necessary for elderly with creatinine clearance less than 70 mL/min/1.73 m2. Estimate GFR should be measured prior to dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Race and Gender Effects
Evaluation of effectiveness and safety of topiramate in clinical trials has shown no race- or gender-related effects.
8.7 Renal Impairment
The clearance of topiramate was reduced by 42% in moderately renally impaired (creatinine clearance 30 to 69 mL/min/1.73m2) and by 54% in severely renally impaired subjects (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2) compared to normal renal function subjects (creatinine clearance greater than 70 mL/min/1.73m2). One-half the usual starting and maintenance dose is recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Topiramate is cleared by hemodialysis at a rate that is 4 to 6 times greater than a normal individual. Accordingly, a prolonged period of dialysis may cause topiramate concentration to fall below that required to maintain an anti-seizure effect. To avoid rapid drops in topiramate plasma concentration during hemodialysis, a supplemental dose of topiramate may be required. The actual adjustment should take into account the duration of dialysis period, the clearance rate of the dialysis system being used, and the effective renal clearance of topiramate in the patient being dialyzed [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
TROKENDI XR® (topiramate) extended-release capsule is not a controlled substance.
10. Overdosage
Overdoses of topiramate have been reported. Signs and symptoms included convulsions, drowsiness, speech disturbance, blurred vision, diplopia, mentation impaired, lethargy, abnormal coordination, stupor, hypotension, abdominal pain, agitation, dizziness and depression. The clinical consequences were not severe in most cases, but deaths have been reported after polydrug overdoses involving topiramate.
Topiramate overdose has resulted in severe metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
A patient who ingested a dose between 96 g and 110 g of topiramate was admitted to hospital with coma lasting 20 to 24 hours followed by full recovery after 3 to 4 days.
Similar signs, symptoms, and clinical consequences are expected to occur with overdosage of TROKENDI XR®. Therefore, in acute TROKENDI XR® overdose, if the ingestion is recent, the stomach should be emptied immediately by lavage or by induction of emesis. Activated charcoal has been shown to adsorb topiramate in vitro. Treatment should be appropriately supportive. Hemodialysis is an effective means of removing topiramate from the body.
11. Trokendi XR Description
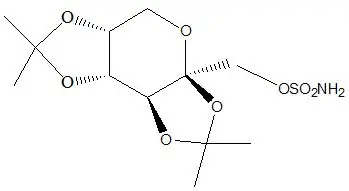
Topiramate, USP, is a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide. TROKENDI XR® (topiramate) extended-release capsules are available as 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg capsules for oral administration.
Topiramate is a white to off-white powder. Topiramate is freely soluble in polar organic solvents such as acetonitrile and acetone; and very slightly soluble to practically insoluble in non-polar organic solvents such as hexanes. Topiramate has the molecular formula C12H21NO8S and a molecular weight of 339.4. Topiramate is designated chemically as 2,3:4,5-Di-O-isopropylidene-β-D-fructopyranose sulfamate and has the following structural formula:
TROKENDI XR® (topiramate) is an extended-release capsule. TROKENDI XR® capsules contain the following inactive ingredients:
Sugar Spheres, NF
Hypromellose (Type 2910), USP
Mannitol, USP
Docusate Sodium, USP
Sodium Benzoate, NF
Ethylcellulose, NF
Oleic Acid, NF
Medium Chain
Triglycerides, NF
Polyethylene Glycol, NF
Polyvinyl Alcohol, USP
Titanium Dioxide, USP
Talc, USP
Lecithin, NF
Xanthan Gum, NF
The capsule shells contain gelatin, USP; Titanium Dioxide, USP; and Colorants.
The colorants are:
FD&C Blue #1 (all strength capsules)
Yellow Iron Oxide, USP (25 mg and 50 mg capsules)
FD&C Red #3 (50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg capsules)
FD&C Yellow #6 (50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg capsules)
Riboflavin, USP (25 mg capsules)
All capsule shells are imprinted with black print that contains shellac, NF, and black iron oxide, NF.
12. Trokendi XR - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanisms by which topiramate exerts its anticonvulsant and migraine prophylaxis effects are unknown; however, preclinical studies have revealed four properties that may contribute to topiramate's efficacy for epilepsy and migraine prophylaxis. Electrophysiological and biochemical evidence suggests that topiramate, at pharmacologically relevant concentrations, blocks voltage-dependent sodium channels, augments the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyrate at some subtypes of the GABA-A receptor, antagonizes the AMPA/kainate subtype of the glutamate receptor, and inhibits the carbonic anhydrase enzyme, particularly isozymes II and IV.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Topiramate has anticonvulsant activity in rat and mouse maximal electroshock seizure (MES) tests. Topiramate is only weakly effective in blocking clonic seizures induced by the GABA-A receptor antagonist, pentylenetetrazole. Topiramate is also effective in rodent models of epilepsy, which include tonic and absence-like seizures in the spontaneous epileptic rat (SER) and tonic and clonic seizures induced in rats by kindling of the amygdala or by global ischemia.
Changes (increases and decreases) from baseline in vital signs (systolic blood pressure-SBP, diastolic blood pressure-DBP, pulse) occurred more frequently in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years) treated with various daily doses of topiramate (50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 2 to 3 mg/kg) than in patients treated with placebo in controlled trials for migraine prophylaxis. The most notable changes were SBP < 90 mm Hg, DBP < 50 mm Hg, SBP or DBP increases or decreases ≥ 20 mm Hg, and pulse increases or decreases ≥ 30 beats per minute. These changes were often dose-related, and were most frequently associated with the greatest treatment difference at the 200 mg dose level. When a position was specified for measurement of vital signs in a trial, measurements were made in a sitting position. Systematic collection of orthostatic vital signs has not been conducted. The clinical significance of these various changes in vital signs has not been clearly established.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Drug-Drug Interaction Studies
Antiepileptic Drugs
Potential interactions between immediate-release topiramate and standard AEDs were assessed in controlled clinical pharmacokinetic studies in patients with epilepsy. The effects of these interactions on mean plasma AUCs are summarized in Table 12. Interaction of TROKENDI XR® and standard AEDs is not expected to differ from the experience with immediate-release topiramate products.
In Table 12, the second column (AED concentration) describes what happened to the concentration of the AED listed in the first column when topiramate was added. The third column (topiramate concentration) describes how the co-administration of a drug listed in the first column modified the concentration of topiramate in experimental settings when topiramate was given alone.
| AED Coadministered | AED Concentration | Topiramate Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| NC=Less than 10% change in plasma concentration | ||
| AED=Antiepileptic drug | ||
| NE=Not evaluated | ||
| TPM=topiramate | ||
|
||
| Phenytoin | NC or 25% increase* | 48% decrease |
| Carbamazepine (CBZ) | NC | 40% decrease |
| CBZ epoxide† | NC | NE |
| Valproic acid | 11% decrease | 14% decrease |
| Phenobarbital | NC | NE |
| Primidone | NC | NE |
| Lamotrigine | NC at TPM doses up to 400mg per day | 13% decrease |
In addition to the pharmacokinetic interaction described in the above table, concomitant administration of valproic acid and topiramate has been associated with hyperammonemia with and without encephalopathy and hypothermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10), (5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.5)].
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Bridging Study to Demonstrate Pharmacokinetic Equivalence between Extended-Release and Immediate-Release Topiramate Formulations
The basis for approval of the extended-release formulation (TROKENDI XR®) included the studies described below using an immediate-release formulation and the demonstration of the pharmacokinetic equivalence of TROKENDI XR® to immediate-release topiramate through the analysis of concentrations and cumulative AUCs at multiple time points [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6)].
The clinical studies described in the following sections were conducted using immediate-release topiramate.
14.2 Monotherapy Treatment in Patients with Partial Onset or Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
14.3 Adjunctive Therapy in Patients with Partial Onset Seizures
Adult Patients with Partial Onset Seizures
The effectiveness of topiramate as an adjunctive treatment for adults with partial onset seizures was established in six multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Studies 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7), two comparing several dosages of topiramate and placebo and four comparing a single dosage with placebo, in patients with a history of partial onset seizures, with or without secondarily generalized seizures.
Patients in these studies were permitted a maximum of two antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in addition to topiramate tablets or placebo. In each study, patients were stabilized on optimum dosages of their concomitant AEDs during baseline phase lasting between 4 and 12 weeks. Patients who experienced a prespecified minimum number of partial onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, during the baseline phase (12 seizures for 12-week baseline, 8 for 8-week baseline or 3 for 4-week baseline) were randomly assigned to placebo or a specified dose of topiramate tablets in addition to their other AEDs.
Following randomization, patients began the double-blind phase of treatment. In five of the six studies, patients received active drug beginning at 100 mg per day; the dose was then increased by 100 mg or 200 mg per day increments weekly or every other week until the assigned dose was reached, unless intolerance prevented increases. In Study 7, the 25 or 50 mg per day initial doses of topiramate were followed by respective weekly increments of 25 or 50 mg per day until the target dose of 200 mg per day was reached. After titration, patients entered a 4, 8 or 12-week stabilization period. The numbers of patients randomized to each dose, and the actual mean and median doses in the stabilization period are shown in Table 13.
| Target Topiramate Dosage (mg per day) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Stabilization Dose | Placebo† | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1,000 |
|
|||||||
| 2 | N | 42 | 42 | 40 | 41 | -- | -- |
| Mean Dose | 5.9 | 200 | 390 | 556 | -- | -- | |
| Median Dose | 6.0 | 200 | 400 | 600 | -- | -- | |
| 3 | N | 44 | -- | -- | 40 | 45 | 40 |
| Mean Dose | 9.7 | -- | -- | 544 | 739 | 796 | |
| Median Dose | 10.0 | -- | -- | 600 | 800 | 1,000 | |
| 4 | N | 23 | -- | 19 | -- | -- | -- |
| Mean Dose | 3.8 | -- | 395 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Median Dose | 4.0 | -- | 400 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 5 | N | 30 | -- | -- | 28 | -- | -- |
| Mean Dose | 5.7 | -- | -- | 522 | -- | -- | |
| Median Dose | 6.0 | -- | -- | 600 | -- | -- | |
| 6 | N | 28 | -- | -- | -- | 25 | -- |
| Mean Dose | 8.0 | -- | -- | -- | 568 | -- | |
| Median Dose | 8.0 | -- | -- | -- | 600 | -- | |
| 7 | N | 90 | 157 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Mean Dose | 8 | 200 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| Median Dose | 8 | 200 | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
14.4 Adjunctive Therapy in Patients with Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
The effectiveness of topiramate as an adjunctive treatment for primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients 2 years old and older was established in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Study 9), comparing a single dosage of topiramate and placebo.
Patients in Study 9 were permitted a maximum of two antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in addition to topiramate or placebo. Patients were stabilized on optimum dosages of their concomitant AEDs during an 8-week baseline phase. Patients who experienced at least three primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures during the baseline phase were randomly assigned to placebo or topiramate in addition to their other AEDs.
Following randomization, patients began the double-blind phase of treatment. Patients received active drug beginning at 50 mg per day for four weeks; the dose was then increased by 50 mg to 150 mg per day increments every other week until the assigned dose of 175, 225 or 400 mg per day based on patients' body weight to approximate a dosage of 6 mg/kg/day was reached, unless intolerance prevented increases. After titration, patients entered a 12-week stabilization period.
14.5 Adjunctive Therapy in Patients with Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
The effectiveness of topiramate as an adjunctive treatment for seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome was established in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing a single dosage of topiramate with placebo in patients 2 years of age and older (Study 10).
Patients in Study 10 were permitted a maximum of two antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in addition to topiramate or placebo. Patients who were experiencing at least 60 seizures per month before study entry were stabilized on optimum dosages of their concomitant AEDs during a 4 week baseline phase. Following baseline, patients were randomly assigned to placebo or topiramate in addition to their other AEDs. Active drug was titrated beginning at 1 mg/kg/day for a week; the dose was then increased to 3 mg/kg/day for one week then to 6 mg/kg/day. After titration, patients entered an 8-week stabilization period. The primary measures of effectiveness were the percent reduction in drop attacks and a parental global rating of seizure severity.
In all adjunctive topiramate trials, the reduction in seizure rate from baseline during the entire double-blind phase was measured. The median percent reductions in seizure rates and the responder rates (fraction of patients with at least a 50% reduction) by treatment group for each study are shown below in Table 14. As described above, a global improvement in seizure severity was also assessed in the Lennox-Gastaut trial.
| Target Topiramate Dosage (mg per day) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study # | # | Placebo | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1,000 | ≈6mg/kg/day* |
| Comparisons with placebo: | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Partial Onset Seizures Studies in Adults | ||||||||
| 2 | N | 45 | 45 | 45 | 46 | -- | -- | -- |
| Median % Reduction | 11.6 | 27.2† | 47.5‡ | 44.7§ | -- | -- | -- | |
| % Responders | 18 | 24 | 44¶ | 46¶ | -- | -- | -- | |
| 3 | N | 47 | -- | -- | 48 | 48 | 47 | -- |
| Median % Reduction | 1.7 | -- | -- | 40.8§ | 41.0§ | 36.0§ | ||
| % Responders | 9 | -- | -- | 40§ | 41§ | 36¶ | -- | |
| 4 | N | 24 | -- | 23 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Median % Reduction | 1.1 | -- | 40.7# | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| % Responders | 8 | -- | 35¶ | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 5 | N | 30 | -- | -- | 30 | -- | -- | -- |
| Median % Reduction | -12.2 | -- | -- | 46.4Þ | -- | -- | -- | |
| % Responders | 10 | -- | -- | 47§ | -- | -- | -- | |
| 6 | N | 28 | -- | -- | -- | 28 | -- | -- |
| Median % Reduction | -20.6 | -- | -- | -- | 24.3§ | -- | -- | |
| % Responders | 0 | -- | -- | -- | 43§ | -- | -- | |
| 7 | N | 91 | 168 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Median % Reduction | 20.0 | 44.2§ | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| % Responders | 24 | 45§ | ||||||
| Studies in Pediatric Patients | ||||||||
| 8 | N | 45 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 41 |
| Median % Reduction | 10.5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 33.1¶ | |
| % Responders | 20 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 39 | |
| Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonicß | ||||||||
| 9 | N | 40 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 39 |
| Median % Reduction | 9.0 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 56.7¶ | |
| % Responders | 20 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 56§ | |
| Lennox-Gastaut Syndromeà | ||||||||
| 10 | N | 49 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 46 |
| Median % Reduction | -5.1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 14.8¶ | |
| % Responders | 14 | 28è | ||||||
| Improvement in Seizure Severityð | 28 | 52¶ | ||||||
Subset analyses of the antiepileptic efficacy of topiramate tablets in these studies showed no differences as a function of gender, race, age, baseline seizure rate, or concomitant AED.
In clinical trials for epilepsy, daily dosages were decreased in weekly intervals by 50 mg per day to 100 mg per day in adults and over a 2- to 8-week period in children; transition was permitted to a new antiepileptic regimen when clinically indicated.
14.6 Migraine Prophylaxis
Adult Patients
The results of 2 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group clinical trials conducted in US (Study 1) or the US and Canada (Study 2) established the effectiveness of immediate-release topiramate in the prophylactic treatment of migraine headache. The design of both trials was identical, enrolling patients with a history of migraine with or without aura, for at least 6 months, according to the International Headache Society (IHS) diagnostic criteria. Patients with a history of cluster headaches or basilar, opthalmoplegic, hemiplegic, or transformed migraine headaches were excluded from the trials. Patients were required to have completed up to a 2-week washout of any prior migraine preventative medications before starting the baseline phase.
Patients who experienced 3 to 12 migraine headaches over the 4 weeks in the baseline phase were randomized to either immediate-release topiramate 50 mg per day, 100 mg per day, 200 mg per day (twice the recommended daily dosage for migraine prophylaxis) or placebo, and treated for a total of 26 weeks (8-week titration period and 18-week maintenance period.). Treatment was initiated at 25 mg per day for one week, and then the daily dosage was increased by 25 mg increments each week until reaching the assigned target dose or maximum tolerated dose (administered twice daily).
Effectiveness of treatment was assessed by the reduction in migraine headache frequency, as measured by the change in 4-week migraine rate (according to migraines classified by IHS criteria) from the baseline phase to double-blind treatment period in each immediate-release topiramate treatment group compared to placebo in the Intent-To-Treat (ITT) population.
In Study 1, a total of 469 patients (416 females, 53 males) ranging in age from 13 to 70 years, were randomized and provided efficacy data. Two hundred sixty-five patients completed the entire 26-week double-blind phase. The median average daily dosages were 48 mg per day, 88 mg per day, and 132 mg per day in the target dose groups of topiramate 50, 100 and 200 mg per day, respectively.
The mean migraine headache frequency rate at baseline was approximately 5.5 migraine headaches per 28 days, and was similar across treatment groups. The change in the mean 4-week migraine headache frequency from baseline to the double-blind phase was -1.3, -2.1, and -2.2 in the immediate-release topiramate 50, 100, and 200 mg per day groups, respectively, versus -0.8 in the placebo group (see Figure 2). The treatment differences between the immediate release topiramate 100 and 200 mg per day groups versus placebo were similar and statistically significant (p less than 0.001 for both comparisons).
In Study 2, a total of 468 patients (406 females, 62 males) ranging in age from 12 to 65 years, were randomized and provided efficacy data. Two hundred fifty-five patients completed the entire 26-week double-blind phase. The median average daily dosages were 47 mg per day, 86 mg per day, and 150 mg per day in the target dose groups of immediate-release topiramate 50, 100, and 200 mg per day, respectively.
The mean migraine headache frequency rate at baseline was approximately 5.5 migraine headaches per 28 days and was similar across treatment groups. The change in the mean 4-week migraine headache period frequency from baseline to the double-blind phase was -1.4, -2.1, and -2.4 in the immediate-release topiramate 50, 100, and 200 mg per day groups, respectively, versus -1.1 in the placebo group (see Figure 2). The differences between the immediate-release topiramate 100 and 200 mg per day groups versus placebo were similar and statistically significant (p equals 0.008 and p less than 0.001, respectively).
In both studies there were no apparent differences in treatment effect within age or gender subgroups. Because most patients were Caucasian, there were insufficient numbers of patients from different races to make a meaningful comparison of race.
For patients withdrawing from immediate-release topiramate, daily dosages were decreased in weekly intervals by 25 to 50 mg per day.
| Figure 2: Reduction in 4-Week Migraine Headache Frequency (Studies 1 and 2 for Adults and Adolescents) |
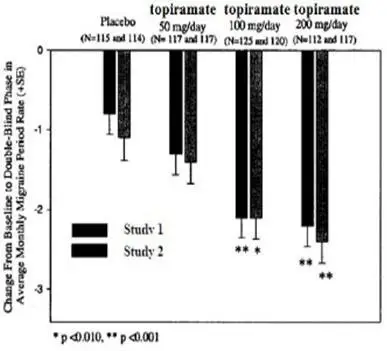 |
Adolescent Patients Age 12 to 17 Years
The effectiveness of immediate-release topiramate as prophylaxis for migraine headache in adolescents was established in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial (Study 3). The study enrolled 103 patients (40 male, 63 female) age 12 to 17 years with episodic migraine headaches with or without aura. Patient selection was based on IHS criteria for migraines (using proposed revisions to the 1988 IHS pediatric migraine criteria [IHS-R criteria]).
Patients who experienced 3 to 12 migraine attacks (according to migraines classified by patient reported diaries) and ≤14 headache days (migraine and non-migraine) during the 4-week prospective baseline period were randomized to either immediate-release topiramate 50 mg/day, 100 mg/day, or placebo and treated for a total of 16 weeks (4-week titration period followed by a 12 week maintenance period). Treatment was initiated at 25 mg/day for one week, and then the daily dosage was increased by 25 mg increments each week until reaching the assigned target dose or maximum tolerated dose (administered twice daily). Approximately 80% or more patients in each treatment group completed the study. The median average daily dosages were 45 and 79 mg/day in the target dose groups of immediate-release topiramate 50 and 100 mg/day, respectively.
Effectiveness of treatment was assessed by comparing each immediate-release topiramate treatment group to placebo (ITT population) for the percent reduction from baseline to the last 12 weeks of the double-blind phase in the monthly migraine attack rate (primary endpoint). The percent reduction from baseline to the last 12 weeks of the double-blind phase in average monthly migraine attack rate is shown in Table 15. The 100 mg immediate-release topiramate dose produced a statistically significant treatment difference relative to placebo of 28% reduction from baseline in the monthly migraine attack rate.
The mean reduction from baseline to the last 12 weeks of the double-blind phase in average monthly attack rate, a key secondary efficacy endpoint in Study 3 (and the primary efficacy endpoint in Studies 1 and 2, of adults) was 3.0 for 100 mg immediate-release topiramate dose and 1.7 for placebo. This 1.3 treatment difference in mean reduction from baseline of montly migraine rate was statistically significant (p=0.0087).
| Category | Placebo (N=33) | Immediate-Release Topiramate 50 mg/day (N=35) | Immediate-Release Topiramate 100 mg/day (N=35) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Baseline | |||
| Median | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Last 12 Weeks of Double-Blind Phase | |||
| Median | 2.3 | 2.3 | 1.0 |
| Percent Reduction (%) | |||
| Median | 44.4 | 44.6 | 72.2 |
| P-value versus Placebo *,† | 0.7975 | 0.0164‡ | |
16. How is Trokendi XR supplied
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 4/2017 | |||
| MEDICATION GUIDE
TROKENDI XR (tro-KEN-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-Release Capsules |
||||
|
What is the most important information I should know about Trokendi XR? Take Trokendi XR® capsules whole. Do not sprinkle Trokendi XR® on food, or break, crush, dissolve, or chew Trokendi XR® capsules before swallowing. If you cannot swallow Trokendi XR® capsules whole, tell your healthcare provider. You may need a different medicine. Do not drink alcohol within 6 hours prior to and 6 hours after Trokendi XR® administration. Trokendi XR may cause eye problems. Serious eye problems include:
Trokendi XR may cause decreased sweating and increased body temperature (fever). People, especially children, should be watched for signs of decreased sweating and fever, especially in hot temperatures. Some people may need to be hospitalized for this condition. If a high fever, a fever that does not go away, or decreased sweating develops, call your healthcare provider right away. Trokendi XR can increase the level of acid in your blood (metabolic acidosis). If left untreated, metabolic acidosis can cause brittle or soft bones (osteoporosis, osteomalacia, osteopenia), kidney stones, can slow the rate of growth in children, and may possibly harm your baby if you are pregnant. Metabolic acidosis can happen with or without symptoms. Sometimes people with metabolic acidosis will:
Your healthcare provider should do a blood test to measure the level of acid in your blood before and during your treatment with Trokendi XR. If you are pregnant, you should talk to your healthcare provider about whether you have metabolic acidosis. Like other antiepileptic drugs, Trokendi XR may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500. Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you: |
||||
|
|
|||
|
Do not stop Trokendi XR without first talking to a healthcare provider.
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
Trokendi XR can harm your unborn baby.
|
||||
|
What is Trokendi XR? Trokendi XR is a prescription medicine used:
|
||||
|
Before taking Trokendi XR , tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially, tell your healthcare provider if you take:
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is listed above. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. Do not start a new medicine without talking with your healthcare provider. |
||||
|
How should I take Trokendi XR?
|
||||
|
What should I avoid while taking Trokendi XR?
|
||||
|
What are the possible side effects of Trokendi XR? Trokendi XR may cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information I should know about Trokendi XR?"
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms above. The most common side effects of Trokendi XR include: |
||||
|
|
|
||
|
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of Trokendi XR. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-398-0833. |
||||
|
How should I store Trokendi XR?
|
||||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of Trokendi XR. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Trokendi XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Trokendi XR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Trokendi XR that is written for health professionals. |
||||
|
What are the ingredients in Trokendi XR? Active ingredient: topiramate Inactive ingredients: Sugar spheres, NF; hypromellose (Type 2910), USP; mannitol, USP; docusate sodium, USP; sodium benzoate, NF; ethylcellulose, NF; oleic acid, NF; medium chain triglycerides, NF; polyethylene glycol, NF; polyvinyl alcohol, USP; titanium dioxide, USP; talc, USP; lecithin, NF; xanthan gum, NF. Capsule shells: Gelatin, USP; titanium dioxide, USP; colorants. Colorants: FD&C Blue #1 (all strength capsules) Yellow iron oxide, USP (25 mg and 50 mg capsules) FD&C red #3 (50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg capsules) FD&C yellow #6 (50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg capsules) Riboflavin, USP (25 mg capsules) All capsule shells are imprinted with black print that contains shellac, NF, and black iron oxide, NF. Manufactured by: Catalent Pharma Solutions, Winchester, KY USA 40391 Manufactured for: Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Rockville, MD USA 20850 © Supernus Pharmaceuticals RA-TRO-MGV5 For more information, go to www.trokendixr.com or call 1-866-398-0833. |
||||
| TROKENDI XR
topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TROKENDI XR
topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TROKENDI XR
topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TROKENDI XR
topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (363066452) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Pharma Solutions (Catalent OTW) | 829672745 | MANUFACTURE(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ScinoPharm Taiwan, Ltd. (ScinoPharm) | 657484726 | API MANUFACTURE(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc | 363066452 | ANALYSIS(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Pharma Solutions (Catalent RTP) | 014167995 | ANALYSIS(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Chemical Laboratories | 071344167 | ANALYSIS(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| AndersonBrecon | 098908572 | PACK(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics, Inc | 867220261 | ANALYSIS(17772-101, 17772-102, 17772-103, 17772-104) | |