Drug Detail:Tuxarin er (Chlorpheniramine and codeine [ klor-fen-ir-a-meed-and-koe-deen ])
Drug Class: Upper respiratory combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TUXARIN ER (codeine phosphate and chlorpheniramine maleate) extended release tablets, CIII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1985
WARNING ULTRA-RAPID METABOLISM OF CODEINE AND OTHER RISK FACTORS FOR LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION IN CHILDREN and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Life threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine; most cases followed tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy and many of the children had evidence of being an ultra-rapid metabolizer of codeine due to a CYP2D6 polymorphism. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. TUXARIN ER is contraindicated in children younger than 12 years of age and in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy [See Contraindications(4)]. Avoid the use of TUXARIN ER in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death [see Warning and Precautions (5.2) Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warning | 8/2017 |
| Contraindications (4) | 8/2017 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1) | 8/2017 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2) | 1/2017 |
Indications and Usage for Tuxarin
TUXARIN ER is a combination of codeine phosphate, an opiate agonist antitussive, and chlorpheniramine maleate, a histamine-1 (H1) receptor antagonist indicated for the relief of cough and symptoms associated with upper respiratory allergies or a common cold. (1) Important Limitations of Use Not indicated for pediatric patients under 18 years of age (8.4))
Tuxarin Dosage and Administration
Adults and children 18 years of age and older: 1 tablet every 12 hours, not to exceed 2 doses in 24 hours. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended release (ER) tablet: contains 54.3 mg of codeine phosphate (equivalent to 40 mg of codeine) and 8 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate (equivalent to 5.6 mg of chlorpheniramine). (3)
Contraindications
- All children younger than 12 years of age (4)
- Post-operative management in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. (4)
- Hypersensitivity to codeine, chlorpheniramine, or any of the product components of TUXARIN ER. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of death in ultra-rapid metabolizers: Conversion of codeine into its active metabolite, morphine, may occur more rapidly and completely resulting in higher than expected morphine levels and respiratory depression or death. (5.1)
- Risks using with Benzodiazepines or other CNS Depressants. (5.2)
- Dose-related respiratory depression. Use with caution. (5.3)
- Drug dependence: Prescribe with caution that is appropriate to the use of other opioids. (5.4)
- Head injury, intra-cranial lesions, or increased intracranial pressure: Avoid in patients with head injury, intra-cranial lesions, or increased intracranial pressure. (5.5)
- Activities requiring mental alertness: Avoid engaging in hazardous tasks requiring complete mental alertness such as driving or operating machinery. Avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants. (5.6)
- Prolonged use may cause Obstructive Bowel Disease (5.7)
- Acute abdominal conditions: Use caution in patients with acute abdominal conditions. (5.8)
- Special risk patients: Caution in elderly patients and those with asthma, persistent or chronic cough, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Common adverse reactions of TUXARIN ER include: Nausea and vomiting, constipation, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, blurred vision, diplopia, visual disturbances, confusion, dizziness, depression, drowsiness, sedation, headache, euphoria, facial dyskinesia, feeling faint, light-headedness, general feeling of discomfort or illness, excitability, nervousness, agitation, restlessness, somnolence, insomnia, dyskinesia, irritability, tremor. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact MainPointe Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 502-709-7544 or go to mainpointepharmaceuticals.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088
Drug Interactions
- Opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety agents, or other CNS depressants: may cause additive CNS depression. (7.1)
- MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants: may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or codeine. (7.2)
- Anticholinergic drugs: Use with caution. Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockage (e.g., xerostomia, blurred vision, or constipation) may occur. (7.3)
- Inhibitors or inducers of metabolic enzymes: Concomitant use of cytochrome P450 2D6 and 3A4 enzyme inhibitors or inducers may result in an altered response to codeine, monitor antitussive activity. Chlorpheniramine may inhibit the hepatic metabolism of phenytoin, monitor phenytoin toxicity. (7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Labor: Use of codeine during labor can produce respiratory depression in the neonate. (8.2)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.3)
- Pediatric patients: Safety and effectiveness of this drug product has not been established for patients under 18. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2018
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING ULTRA-RAPID METABOLISM OF CODEINE AND OTHER RISK FACTORS FOR LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION IN CHILDREN And RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
1. Indications and Usage for Tuxarin
TUXARIN ER is indicated for the relief of cough and symptoms associated with upper respiratory allergies or a common cold in adults 18 years of age and older.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended release tablets: Each tablet contains 54.3 mg of codeine phosphate (equivalent to 40 mg of codeine) and 8 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate (equivalent to 5.6 mg of chlorpheniramine). Each tablet is white to off-white, uncoated, round, debossed with MP on one side and CC on the other side.
4. Contraindications
- TUXARIN ER is contraindicated for:
- All children younger than 12 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Postoperative management in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to codeine, chlorpheniramine or any of the inactive ingredients of TUXARIN ER. Persons known to be hypersensitive to certain other opioids may exhibit cross-sensitivity to codeine.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Other Risk Factors for Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Children
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine. Codeine is subject to variability in metabolism based upon CYP2D6 genotype (described below), which can lead to an increased exposure to the active metabolite morphine. Based upon post-marketing reports, children less than 12 years old appear to be more susceptible to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine, particularly if there are risk factors for respiratory depression. For example, many reported cases of death occurred in the post-operative period following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, and many of the children had evidence of being ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine. Furthermore, children with obstructive sleep apnea who are treated with codeine for post-tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy pain may be particularly sensitive to its respiratory depressant effect. Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death:
- TUXARIN ER is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age [see Contraindications (4)].
- TUXARIN ER is contraindicated for post-operative management in pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy [see Contraindications (4)].
- Avoid the use of TUXARIN ER in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Risk factors include conditions associated with hypoventilation, such as postoperative status, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, severe pulmonary disease, neuromuscular disease, and concomitant use of other medications that cause respiratory depression.
- When prescribing codeine for adolescents, healthcare providers should choose the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time and inform patients and caregivers about these risks and the signs of morphine overdose [see Overdosage (10)].
5.2 Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids, including TUXARIN ER, with benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking Benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. Because of similar pharmacologic properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with concomitant use of opioid cough medications and benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation if TUXARIN ER is used with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other CNS depressants. [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]
5.3 Respiratory Depression
Codeine, one of the active ingredients in TUXARIN ER, produces dose-related respiratory depression by directly acting on brain stem respiratory centers.
Overdose of codeine in adults has been associated with fatal respiratory depression, and the use of codeine in children has been associated with fatal respiratory depression. Exercise caution when administering TUXARIN ER because of the potential for respiratory depression. If respiratory depression occurs, discontinue TUXARIN ER and use naloxone hydrochloride when indicated to antagonize the effect and other supportive measures as necessary. [see Overdosage (10)].
5.4 Drug Dependence
Codeine can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and, therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of TUXARIN ER. Prescribe and administer TUXARIN ER with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other opioid drugs. [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)]
5.5 Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depression effects of opioids and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, opioids produce adverse reactions that may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries. The use of TUXARIN ER should be avoided in these patients.
5.6 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Codeine and chlorpheniramine, the active ingredients in TUXARIN ER, may produce marked drowsiness and impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Advise patients to avoid engaging in hazardous tasks requiring mental alertness and motor coordination after ingestion of TUXARIN ER. Concurrent use of TUXARIN ER with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
5.7 Obstructive Bowel Disease
Chronic use of opioids, including codeine, may result in obstructive bowel disease especially in patients with underlying intestinal motility disorders. Codeine may cause or aggravate constipation. Use with caution in patients with underlying intestinal motility disorders.
5.8 Acute Abdominal Conditions
TUXARIN ER should be used with caution in patients with acute abdominal conditions since the administration of codeine may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions. The concurrent use of other anticholinergics with codeine may produce paralytic ileus. [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]
5.9 Special Risk Patients
As with other opioids, TUXARIN ER should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients and those with asthma, persistent or chronic cough, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Use of codeine, an opioid, may result in the following:
- Respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1); (5.3) and Overdosage (10)]
- Drug dependence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Increased intracranial pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Decreased mental alertness with impaired mental and/or physical abilities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Paralytic ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Use of chlorpheniramine, an antihistamine, may result in:
- Decreased mental alertness with impaired mental and/or physical abilities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Adverse reactions listed below have been reported in the literature for codeine and chlorpheniramine and may be expected to occur with TUXARIN ER. Also included are events that occurred during clinical pharmacokinetic studies (in a total of 66 healthy adult volunteers with either single or multiple dose exposure) with TUXARIN ER and judged by the investigator to be related to study treatment. Because these reactions may be reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Allergic: Allergic laryngospasm, nasal stuffiness, bronchospastic allergic reaction, hives, itching, swelling of face.
Body as a whole: Asthenia, feeling of relaxation, redness or flushing of the face, unusual tiredness, weakness.
Cardiovascular: Fast, or slow heartbeat, hypertension, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, shock-like state, syncope.
Dermatological System: Skin rash, pruritus, erythema, urticaria, excessive perspiration, dermatitis.
Endocrine System: Changes in glucose utilization, decreased lactation, early menses, glycosuria, gynecomastia, hypoglycemia, increased appetite, increased libido, pheochromocytoma stimulation.
Gastrointestinal System: Nausea and vomiting, constipation, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, acute pancreatitis, dry mouth, dyspepsia, epigastric distress, loss of appetite, diarrhea, gastro-esophageal reflux, gastrointestinal hypomotility.
Genitourinary System: Ureteral spasm, urinary retention, dysuria, urinary frequency, urinary hesitancy, irritative bladder symptom.
Nervous System: Blurred vision, diplopia, visual disturbances, confusion, dizziness, depression, drowsiness, sedation, headache, euphoria, facial dyskinesia, false sense of well-being, feeling faint, lightheadedness, general feeling of discomfort or illness, excitability nervousness, agitation, restlessness, somnolence, insomnia, dyskinesia, irritability, tremor.
Respiratory: Dryness of the pharynx and respiratory passages, laryngismus, atelectasis, wheezing, troubled breathing, respiratory depression, hiccups.
Special Senses: labyrinthitis, tinnitus, vertigo, hypermetropia, lacrimation increased, mydriasis, photophobia.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Benzodiazepines, Opioids, Antihistamines, Antipsychotics, Anti-anxiety Agents, or Other CNS Depressants (Including Alcohol)
The use of benzodiazepines, opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with TUXARIN ER may cause an additive CNS depressant effect, profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death and should be avoided. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants
Do not prescribe TUXARIN ER if the patient is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) (i.e., certain drugs used for depression, psychiatric or emotional conditions, or Parkinson's disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping a MAOI drug. The use of MAOIs or tricyclic antidepressants with codeine preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or codeine.
7.3 Anticholinergic Drugs
Codeine and chlorpheniramine should be administered cautiously to persons receiving other anticholinergic drugs in order to avoid paralytic ileus and excessive anticholinergic effects.
Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade (e.g., xerostomia, blurred vision, or constipation) may occur when anticholinergic drugs are administered with chlorpheniramine.
7.4 Inhibitors or Inducers of Metabolic Enzymes
Codeine is metabolized by the CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. The concurrent use of drugs that preferentially induce codeine N-demethylation (via CYP3A4) may increase the plasma concentrations of codeine's inactive metabolite norcodeine. Drugs that inhibit codeine O-demethylation (via CYP2D6), may decrease the plasma concentration of codeine's active metabolites, morphine and morphine-6-glucuronide. The contribution of these active metabolites to the overall antitussive effect of codeine is not known, but should be considered.
Adverse event reports in the literature suggest a possible drug interaction involving increased serum phenytoin levels and phenytoin toxicity when chlorpheniramine and phenytoin are co-administered. The exact mechanism for this interaction is not known, however it is believed that chlorpheniramine may inhibit the hepatic metabolism of phenytoin. Patients should be monitored for evidence of phenytoin toxicity such as ataxia, hyperreflexia, nystagmus and tremor when these two drugs are co-administered.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
8.2 Labor and Delivery
As with all opioids, administration of TUXARIN ER to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TUXARIN ER in patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . In most of the reported cases, these events followed tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, and many of the children had evidence of being ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine (i.e., multiple copies of the gene for cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 2D6 or high morphine concentrations). Children with sleep apnea may be particularly sensitive to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death:
- TUXARIN ER is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age [see Contraindications (4)].
- TUXARIN ER is contraindicated for post-operative management in pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy [see Contraindications (4)].
- Avoid the use of TUXARIN ER in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Risk factors include conditions associated with hypoventilation, such as postoperative status, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, severe pulmonary disease, neuromuscular disease, and concomitant use of other medications that cause respiratory depression. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical efficacy and safety studies have not been conducted with TUXARIN ER. Other reported clinical experience with the individual active ingredients of TUXARIN ER did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be made with caution, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Pharmacokinetics of TUXARIN ER has not been characterized in renal impairment subjects.
Both codeine phosphate and chlorpheniramine maleate are cleared substantially by the kidney. As such, impaired renal function could potentially lead to the risk of decreased clearance and thereby increased retention or systemic levels of both these drugs. TUXARIN ER should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Pharmacokinetics of TUXARIN ER has not been characterized in hepatic impairment subjects. Both codeine and chlorpheniramine maleate are extensively metabolized by liver before elimination from the body. As such, impaired hepatic function could potentially lead to the risk of decreased metabolism and thereby increased systemic levels of both these drugs. TUXARIN ER should be used with caution in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
TUXARIN ER is a Schedule III controlled prescription product containing codeine and should be prescribed and administered with caution.
9.2 Abuse
Codeine can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of TUXARIN ER, and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other opioid drugs.
9.3 Dependence
Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of opioids; therefore, TUXARIN ER should be prescribed and administered with caution.
Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assumes clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued oral opioid use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of opioid therapy.
11. Tuxarin Description
TUXARIN ER are extended release tablets that contain 54.3 mg of codeine phosphate (equivalent to 40 mg of codeine) and 8 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate (equivalent to 5.6 mg of chlorpheniramine).
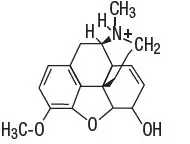
Codeine phosphate [morphine3methyl ether phosphate (1:1) (salt)] hemihydrate, is a narcotic analgesic and antitussive. It has the following structural formula:
|
| H3PO4 ∙ 1/2 H2O |
| Codeine Phosphate Hemihydrate C18H21NO3 ∙ H3PO4 ∙ ½H2O MW 406.37 |
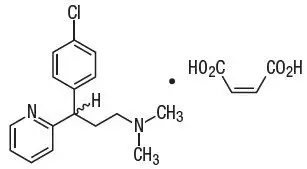
Chlorpheniramine maleate is 2-pyridinepropanamine, γ-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) and has the following chemical structure:
 |
|
| Chlorpheniramine Maleate C16H19ClN2 ∙ C4H4O4 Molecular weight = 390.86 |
|
TUXARIN ER are white to off-white, uncoated, standard round extended release matrix tablets.
Other ingredients: hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, cellulose microcrystalline, polysorbate 80, magnesium stearate, and colloidal silicon dioxide.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of TUXARIN ER is based on previously established findings of effectiveness of codeine and chlorpheniramine at the proposed doses.
16. How is Tuxarin supplied
TUXARIN ER is supplied as white to off-white, uncoated, standard round tablet, debossed with MP on one side and CC on the other side. Supplied in bottles of 100 tablets: NDC 71269-040-10.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE TUXARIN ER™ (tuks a ren) (codeine phosphate and chlorpheniramine maleate) extended release tablets, CIII |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued: August 2017 | ||
|
What is the most important information I should know about TUXARIN ER? |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
| Keep TUXARIN ER in a safe place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and can cause death. If a child accidentally takes TUXARIN ER, get emergency help right away. | |||
| What is TUXARIN ER? | |||
|
|||
| Who should not take TUXARIN ER? | |||
|
|||
| Before taking TUXARIN ER, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | |||
|
|
||
|
|||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Using TUXARIN ER with certain other medicines may affect each other. Using TUXARIN ER with other medicines can cause serious side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you: | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| What should I avoid while taking TUXARIN ER? | |||
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of TUXARIN ER? TUXARIN ER may cause serious side effects, including: |
|||
|
|||
| Stopping TUXARIN ER suddenly could cause withdrawal symptoms. | |||
|
|||
| The most common side effects of TUXARIN ER include: | |||
|
|
|
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of TUXARIN ER. | |||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||
| How should I store TUXARIN ER? | |||
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TUXARIN ER. | |||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TUXARIN ER for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TUXARIN ER to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TUXARIN ER that is written for health professionals. | |||
| What are the ingredients in TUXARIN ER? | |||
| Active ingredients: codeine and chlorpheniramine | |||
| Inactive ingredients: Hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, cellulose microcrystalline, polysorbate 80, magnesium stearate, and colloidal silicon dioxide. | |||
| Distributed By: MainPointe Pharmaceuticals, LLC Louisville, KY, 40202 |
|||
| For more information go to mainpointepharmaceuticals.com or call 502-709-7544 | |||
| TUXARIN
codeine phosphate and chlorpheniramine maleate tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Mainpointe Pharmaceuticals (080544378) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGM Pharma Solutions | 117549200 | MANUFACTURE(71269-040) | |