Drug Detail:Vermox (Mebendazole [ me-ben-da-zole ])
Drug Class: Anthelmintics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VERMOX™ (mebendazole) chewable tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1974
Indications and Usage for Vermox
VERMOX™ is an anthelmintic indicated for the treatment of patients two years of age and older with gastrointestinal infections caused by:
- Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm),
- Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm),
- Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm),
- Necator americanus (hookworm), and
- Trichuris trichiura (whipworm), (1).
Vermox Dosage and Administration
Adults and Pediatrics: The tablet may be chewed, swallowed, or crushed and mixed with food (2).
| Pinworm (enterobiasis) | Whipworm (trichuriasis) | Roundworm (ascariasis) | Hookworm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | 1 tablet once | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days |
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Chewable Tablet: 100 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its excipients (4).
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Convulsions: Convulsions in infants below the age of 1 year have been reported (5.1).
- Hematologic Effects: Neutropenia and agranulocytosis have been reported in patients receiving mebendazole at higher doses and for prolonged duration. Monitor blood counts in these patients (5.2)
- Metronidazole and Serious Skin Reactions: Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) have been reported with the concomitant use of mebendazole and metronidazole. Avoid concomitant use of mebendazole and metronidazole (5.3).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Adverse reactions reported in clinical trials were anorexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting and rash. (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2017
Related/similar drugs
albendazole, mebendazole, nitazoxanide, Alinia, piperazine, pyrantel, EmvermFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vermox
VERMOX™ is indicated for the treatment of patients two years of age and older with gastrointestinal infections caused by Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm), Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm), Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm), Necator americanus (hookworm), and Trichuris trichiura (whipworm).
2. Vermox Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage for VERMOX™ is described in Table 1 below. The same dosage schedule applies to adults and pediatric patients two years of age and older. The tablet may be chewed, swallowed, or crushed and mixed with food.
| Pinworm (enterobiasis) | Whipworm (trichuriasis) | Roundworm (ascariasis) | Hookworm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | 1 tablet Once | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days | 1 tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days |
If the patient is not cured three weeks after treatment, a second course of treatment is advised. No special procedures, such as fasting or purging, are required.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Chewable Tablet: 100 mg, round, flat radius-edged white to yellowish chewable tablet that is debossed with "M/100" on one side and "J" on the other side.
4. Contraindications
VERMOX™ is contraindicated in persons with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its excipients.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Convulsions
Although VERMOX™ is approved for use in children two years of age and older, convulsions have been reported in infants below the age of 1 year during post-marketing experience with mebendazole, including VERMOX™ [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.2 Hematologic Effects
Agranulocytosis and neutropenia have been reported with mebendazole use at higher doses and for more prolonged durations than is recommended for the treatment of soil-transmitted helminth infections. Monitor blood counts if VERMOX™ is used at higher doses or for prolonged duration.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Studies
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of mebendazole was evaluated in 6276 subjects who participated in 39 clinical trials for treatment of single or mixed parasitic infections of the gastrointestinal tract. In these trials, the formulations, dosages and duration of mebendazole treatment varied. Adverse reactions reported in mebendazole-treated subjects from the 39 clinical trials are shown in Table 2 below.
| Adverse Reaction(s) |
|---|
|
| Gastrointestinal Disorders |
| Anorexia |
| Abdominal Pain |
| Diarrhea |
| Flatulence |
| Nausea |
| Vomiting |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders |
| Rash |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified in adult and pediatric patients postmarketing with mebendazole formulations and dosages other than the VERMOX™ 100 mg chewable tablet. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
| Adverse Reaction(s) | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | Agranulocytosis, Neutropenia |
| Immune System Disorders | Hypersensitivity including anaphylactic reactions |
| Nervous System Disorders | Convulsions, Dizziness |
| Hepatobiliary Disorders | Hepatitis, Abnormal liver tests |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | Glomerulonephritis |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Exanthema, Angioedema, Urticaria, Alopecia |
7. Drug Interactions
Concomitant use of mebendazole, including VERMOX™, and metronidazole should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VERMOX™ 100 mg chewable tablets has not been established in pediatric patients less than two years of age. Convulsions have been reported with mebendazole use in children less than one year of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
10. Overdosage
In patients treated at dosages substantially higher than recommended or for prolonged periods of time, the following adverse reactions have been reported: alopecia, reversible transaminase elevations, hepatitis, agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and glomerulonephritis.
11. Vermox Description
VERMOX™ (mebendazole) is an orally administered, synthetic anthelmintic available as chewable tablets, each containing 100 mg of mebendazole. Inactive ingredients are: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, hydrogenated vegetable oil, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium saccharin, sodium starch glycolate, talc, tetrarome orange, and FD&C yellow No.6.
Chemically, mebendazole is methyl 5-benzoylbenzimidazole-2-carbamate with a molecular formula of C16H13N3O3 and the following structural formula:
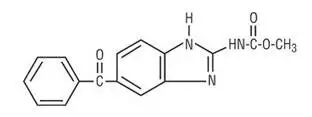
Mebendazole is a white to slightly yellow powder with a molecular weight of 295.29. It is less than 0.05% soluble in water, dilute mineral acid solutions, alcohol, ether and chloroform, but is soluble in formic acid.
12. Vermox - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mebendazole, a benzimidazole, is an anthelmintic drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In carcinogenicity tests of mebendazole in mice and rats, no carcinogenic effects were seen at doses as high as 40 mg/kg (one to two times the human dose, based on mg/m2) given daily over two years. No mutagenic activity was observed with mebendazole in a bacterial reverse gene mutation test. Mebendazole was mutagenic in the absence of S-9 when tested using a continuous (24 hour) treatment incubation period in the mouse lymphoma thymidine kinase assay. Mebendazole was aneugenic in vitro in mammalian somatic cells. In the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, orally administered mebendazole induced an increased frequency of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes with evidence suggestive of aneugenicity. Doses up to 40 mg/kg in rats (2 times the total daily human dose, based on mg/m2), given to males for 60 days and to females for 14 days prior to gestation, had no effect upon fetuses and offspring.
14. Clinical Studies
Efficacy rates derived from various studies are shown in Table 4 below:
| Pinworm (enterobiasis) | Whipworm (trichuriasis) | Roundworm (ascariasis) | Hookworm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cure rates mean | 95% | 68% | 98% | 96% |
| Egg reduction mean | - | 93% | 99% | 99% |
16. How is Vermox supplied
VERMOX™ (mebendazole) is available as 100 mg, round, flat radius-edged white to yellowish chewable tablets that are debossed with "M/100" on one side and "J" on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
| Blister package of 12 tablets | NDC 50580-070-12 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Advise patients that:
- Taking VERMOX™ and metronidazole together may cause serious skin reactions and should be avoided. [see Warning and Precautions (5.3)]
- VERMOX™ can be taken with or without food. [see Dosage and Administration (2)]
| VERMOX
mebendazole tablet, chewable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc, McNeil Consumer Healthcare Division (878046358) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV | 370005019 | API MANUFACTURE(50580-070) , MANUFACTURE(50580-070) | |





