Drug Detail:Viagra (Sildenafil (oral) [ sil-den-a-fil ])
Drug Class: Impotence agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VIAGRA® (sildenafil citrate) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, Effects on the Eye (5.3) | 08/2017 |
Indications and Usage for Viagra
VIAGRA is a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) (1)
Viagra Dosage and Administration
- For most patients, the recommended dose is 50 mg taken, as needed, approximately 1 hour before sexual activity. However, VIAGRA may be taken anywhere from 30 minutes to 4 hours before sexual activity (2.1)
- Based on effectiveness and toleration, may increase to a maximum of 100 mg or decrease to 25 mg (2.1)
- Maximum recommended dosing frequency is once per day (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Administration of VIAGRA to patients using nitric oxide donors, such as organic nitrates or organic nitrites in any form. VIAGRA was shown to potentiate the hypotensive effect of nitrates (4.1, 7.1, 12.2)
- Known hypersensitivity to sildenafil or any component of tablet (4.2)
- Administration with guanylate cyclase (GC) stimulators, such as riociguat (4.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Patients should not use VIAGRA if sexual activity is inadvisable due to cardiovascular status (5.1)
- Patients should seek emergency treatment if an erection lasts >4 hours. Use VIAGRA with caution in patients predisposed to priapism (5.2)
- Patients should stop VIAGRA and seek medical care if a sudden loss of vision occurs in one or both eyes, which could be a sign of non arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION). VIAGRA should be used with caution, and only when the anticipated benefits outweigh the risks, in patients with a history of NAION. Patients with a "crowded" optic disc may also be at an increased risk of NAION. (5.3)
- Patients should stop VIAGRA and seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing (5.4)
- Caution is advised when VIAGRA is co-administered with alpha-blockers or anti-hypertensives. Concomitant use may lead to hypotension (5.5)
- Decreased blood pressure, syncope, and prolonged erection may occur at higher sildenafil exposures. In patients taking strong CYP inhibitors, such as ritonavir, sildenafil exposure is increased. Decrease in VIAGRA dosage is recommended (2.4, 5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) include headache, flushing, dyspepsia, abnormal vision, nasal congestion, back pain, myalgia, nausea, dizziness and rash (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pfizer at 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- VIAGRA can potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates, alpha blockers, and anti-hypertensives (4.1, 5.5, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 12.2)
- With concomitant use of alpha blockers, initiate VIAGRA at 25 mg dose (2.3)
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin): Increase VIAGRA exposure (2.4, 7.4, 12.3)
- Ritonavir: Do not exceed a maximum single dose of 25 mg in a 48 hour period (2.4, 5.6)
- Erythromycin or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, saquinavir): Consider a starting dose of 25 mg (2.4, 7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
- Geriatric use: Consider a starting dose of 25 mg (2.5, 8.5)
- Severe renal impairment: Consider a starting dose of 25 mg (2.5, 8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: Consider a starting dose of 25 mg (2.5, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2017
Related/similar drugs
sildenafil, tadalafil, Cialis, alprostadil, Levitra, vardenafilFull Prescribing Information
2. Viagra Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage Information
For most patients, the recommended dose is 50 mg taken, as needed, approximately 1 hour before sexual activity. However, VIAGRA may be taken anywhere from 30 minutes to 4 hours before sexual activity.
The maximum recommended dosing frequency is once per day.
Based on effectiveness and toleration, the dose may be increased to a maximum recommended dose of 100 mg or decreased to 25 mg.
2.3 Dosage Adjustments in Specific Situations
VIAGRA was shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates and its administration in patients who use nitric oxide donors such as organic nitrates or organic nitrites in any form is therefore contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.1), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
When VIAGRA is co-administered with an alpha-blocker, patients should be stable on alpha-blocker therapy prior to initiating VIAGRA treatment and VIAGRA should be initiated at 25 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.2), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
2.5 Dosage Adjustments in Special Populations
Consider a starting dose of 25 mg in patients > 65 years, patients with hepatic impairment (e.g., cirrhosis), and patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/minute) because administration of VIAGRA in these patients resulted in higher plasma levels of sildenafil [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6, 8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
VIAGRA is supplied as blue, film-coated, rounded-diamond-shaped tablets containing sildenafil citrate equivalent to 25 mg, 50 mg, or 100 mg of sildenafil. Tablets are debossed with PFIZER on one side and VGR25, VGR50 or VGR100 on the other to indicate the dosage strengths.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Nitrates
Consistent with its known effects on the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1, 12.2)], VIAGRA was shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates, and its administration to patients who are using nitric oxide donors such as organic nitrates or organic nitrites in any form either regularly and/or intermittently is therefore contraindicated.
After patients have taken VIAGRA, it is unknown when nitrates, if necessary, can be safely administered. Although plasma levels of sildenafil at 24 hours post dose are much lower than at peak concentration, it is unknown whether nitrates can be safely co-administered at this time point [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular
There is a potential for cardiac risk of sexual activity in patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease. Therefore, treatments for erectile dysfunction, including VIAGRA, should not be generally used in men for whom sexual activity is inadvisable because of their underlying cardiovascular status. The evaluation of erectile dysfunction should include a determination of potential underlying causes and the identification of appropriate treatment following a complete medical assessment.
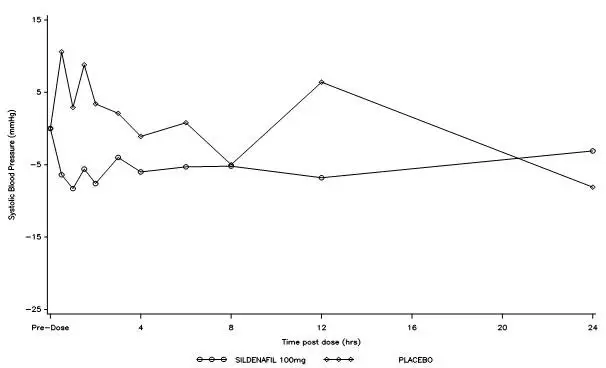
VIAGRA has systemic vasodilatory properties that resulted in transient decreases in supine blood pressure in healthy volunteers (mean maximum decrease of 8.4/5.5 mmHg), [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. While this normally would be expected to be of little consequence in most patients, prior to prescribing VIAGRA, physicians should carefully consider whether their patients with underlying cardiovascular disease could be affected adversely by such vasodilatory effects, especially in combination with sexual activity.
Use with caution in patients with the following underlying conditions which can be particularly sensitive to the actions of vasodilators including VIAGRA – those with left ventricular outflow obstruction (e.g., aortic stenosis, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis) and those with severely impaired autonomic control of blood pressure.
There are no controlled clinical data on the safety or efficacy of VIAGRA in the following groups; if prescribed, this should be done with caution.
- Patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction, stroke, or life-threatening arrhythmia within the last 6 months;
- Patients with resting hypotension (BP <90/50 mmHg) or hypertension (BP >170/110 mmHg);
- Patients with cardiac failure or coronary artery disease causing unstable angina.
5.2 Prolonged Erection and Priapism
Prolonged erection greater than 4 hours and priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) have been reported infrequently since market approval of VIAGRA. In the event of an erection that persists longer than 4 hours, the patient should seek immediate medical assistance. If priapism is not treated immediately, penile tissue damage and permanent loss of potency could result.
VIAGRA should be used with caution in patients with anatomical deformation of the penis (such as angulation, cavernosal fibrosis or Peyronie's disease), or in patients who have conditions which may predispose them to priapism (such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia). However, there are no controlled clinical data on the safety or efficacy of VIAGRA in patients with sickle cell or related anemias.
5.3 Effects on the Eye
Physicians should advise patients to stop use of all phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, including VIAGRA, and seek medical attention in the event of a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes. Such an event may be a sign of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a rare condition and a cause of decreased vision including permanent loss of vision, that has been reported rarely post-marketing in temporal association with the use of all PDE5 inhibitors. Based on published literature, the annual incidence of NAION is 2.5–11.8 cases per 100,000 in males aged ≥ 50. An observational case-crossover study evaluated the risk of NAION when PDE5 inhibitor use, as a class, occurred immediately before NAION onset (within 5 half-lives), compared to PDE5 inhibitor use in a prior time period. The results suggest an approximate 2-fold increase in the risk of NAION, with a risk estimate of 2.15 (95% CI 1.06, 4.34). A similar study reported a consistent result, with a risk estimate of 2.27 (95% CI 0.99, 5.20). Other risk factors for NAION, such as the presence of "crowded" optic disc, may have contributed to the occurrence of NAION in these studies.
Neither the rare post-marketing reports, nor the association of PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION in the observational studies, substantiate a causal relationship between PDE5 inhibitor use and NAION [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Physicians should consider whether their patients with underlying NAION risk factors could be adversely affected by use of PDE5 inhibitors. Individuals who have already experienced NAION are at increased risk of NAION recurrence. Therefore, PDE5 inhibitors, including VIAGRA, should be used with caution in these patients and only when the anticipated benefits outweigh the risks. Individuals with "crowded" optic disc are also considered at greater risk for NAION compared to the general population, however, evidence is insufficient to support screening of prospective users of PDE5 inhibitors, including VIAGRA, for this uncommon condition.
There are no controlled clinical data on the safety or efficacy of VIAGRA in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (a minority of these patients have genetic disorders of retinal phosphodiesterases); if prescribed, this should be done with caution.
5.4 Hearing Loss
Physicians should advise patients to stop taking PDE5 inhibitors, including VIAGRA, and seek prompt medical attention in the event of sudden decrease or loss of hearing. These events, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness, have been reported in temporal association to the intake of PDE5 inhibitors, including VIAGRA. It is not possible to determine whether these events are related directly to the use of PDE5 inhibitors or to other factors [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
5.6 Adverse Reactions with the Concomitant Use of Ritonavir
The concomitant administration of the protease inhibitor ritonavir substantially increases serum concentrations of sildenafil (11-fold increase in AUC). If VIAGRA is prescribed to patients taking ritonavir, caution should be used. Data from subjects exposed to high systemic levels of sildenafil are limited. Decreased blood pressure, syncope, and prolonged erection were reported in some healthy volunteers exposed to high doses of sildenafil (200–800 mg). To decrease the chance of adverse reactions in patients taking ritonavir, a decrease in sildenafil dosage is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Drug Interactions (7.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.7 Combination with other PDE5 Inhibitors or Other Erectile Dysfunction Therapies
The safety and efficacy of combinations of VIAGRA with other PDE5 Inhibitors, including REVATIO or other pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) treatments containing sildenafil, or other treatments for erectile dysfunction have not been studied. Such combinations may further lower blood pressure. Therefore, the use of such combinations is not recommended.
5.8 Effects on Bleeding
There have been postmarketing reports of bleeding events in patients who have taken VIAGRA. A causal relationship between VIAGRA and these events has not been established. In humans, VIAGRA has no effect on bleeding time when taken alone or with aspirin. However, in vitro studies with human platelets indicate that sildenafil potentiates the antiaggregatory effect of sodium nitroprusside (a nitric oxide donor). In addition, the combination of heparin and VIAGRA had an additive effect on bleeding time in the anesthetized rabbit, but this interaction has not been studied in humans.
The safety of VIAGRA is unknown in patients with bleeding disorders and patients with active peptic ulceration.
5.9 Counseling Patients About Sexually Transmitted Diseases
The use of VIAGRA offers no protection against sexually transmitted diseases. Counseling of patients about the protective measures necessary to guard against sexually transmitted diseases, including the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), may be considered.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Prolonged Erection and Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Effects on the Eye [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypotension when Co-administered with Alpha-blockers or Anti-hypertensives [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Adverse Reactions with the Concomitant Use of Ritonavir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Combination with other PDE5 Inhibitors or Other Erectile Dysfunction Therapies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Effects on Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Counseling Patients About Sexually Transmitted Diseases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (≥ 2%) are headache, flushing, dyspepsia, abnormal vision, nasal congestion, back pain, myalgia, nausea, dizziness, and rash.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
VIAGRA was administered to over 3700 patients (aged 19–87 years) during pre-marketing clinical trials worldwide. Over 550 patients were treated for longer than one year.
In placebo-controlled clinical studies, the discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions for VIAGRA (2.5%) was not significantly different from placebo (2.3%).
In fixed-dose studies, the incidence of some adverse reactions increased with dose. The type of adverse reactions in flexible-dose studies, which reflect the recommended dosage regimen, was similar to that for fixed-dose studies. At doses above the recommended dose range, adverse reactions were similar to those detailed in Table 1 below but generally were reported more frequently.
| Adverse Reaction | 25 mg (n=312) | 50 mg (n=511) | 100 mg (n=506) | Placebo (n=607) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Headache | 16% | 21% | 28% | 7% |
| Flushing | 10% | 19% | 18% | 2% |
| Dyspepsia | 3% | 9% | 17% | 2% |
| Abnormal vision* | 1% | 2% | 11% | 1% |
| Nasal congestion | 4% | 4% | 9% | 2% |
| Back pain | 3% | 4% | 4% | 2% |
| Myalgia | 2% | 2% | 4% | 1% |
| Nausea | 2% | 3% | 3% | 1% |
| Dizziness | 3% | 4% | 3% | 2% |
| Rash | 1% | 2% | 3% | 1% |
When VIAGRA was taken as recommended (on an as-needed basis) in flexible-dose, placebo-controlled clinical trials of two to twenty-six weeks duration, patients took VIAGRA at least once weekly, and the following adverse reactions were reported:
| Adverse Reaction | VIAGRA | PLACEBO |
|---|---|---|
| N=734 | N=725 | |
|
||
| Headache | 16% | 4% |
| Flushing | 10% | 1% |
| Dyspepsia | 7% | 2% |
| Nasal Congestion | 4% | 2% |
| Abnormal Vision* | 3% | 0% |
| Back pain | 2% | 2% |
| Dizziness | 2% | 1% |
| Rash | 2% | 1% |
The following events occurred in <2% of patients in controlled clinical trials; a causal relationship to VIAGRA is uncertain. Reported events include those with a plausible relation to drug use; omitted are minor events and reports too imprecise to be meaningful:
Body as a Whole: face edema, photosensitivity reaction, shock, asthenia, pain, chills, accidental fall, abdominal pain, allergic reaction, chest pain, accidental injury.
Cardiovascular: angina pectoris, AV block, migraine, syncope, tachycardia, palpitation, hypotension, postural hypotension, myocardial ischemia, cerebral thrombosis, cardiac arrest, heart failure, abnormal electrocardiogram, cardiomyopathy.
Digestive: vomiting, glossitis, colitis, dysphagia, gastritis, gastroenteritis, esophagitis, stomatitis, dry mouth, liver function tests abnormal, rectal hemorrhage, gingivitis.
Hemic and Lymphatic: anemia and leukopenia.
Metabolic and Nutritional: thirst, edema, gout, unstable diabetes, hyperglycemia, peripheral edema, hyperuricemia, hypoglycemic reaction, hypernatremia.
Musculoskeletal: arthritis, arthrosis, myalgia, tendon rupture, tenosynovitis, bone pain, myasthenia, synovitis.
Nervous: ataxia, hypertonia, neuralgia, neuropathy, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo, depression, insomnia, somnolence, abnormal dreams, reflexes decreased, hypesthesia.
Respiratory: asthma, dyspnea, laryngitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, sputum increased, cough increased.
Skin and Appendages: urticaria, herpes simplex, pruritus, sweating, skin ulcer, contact dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis.
Special Senses: sudden decrease or loss of hearing, mydriasis, conjunctivitis, photophobia, tinnitus, eye pain, ear pain, eye hemorrhage, cataract, dry eyes.
Urogenital: cystitis, nocturia, urinary frequency, breast enlargement, urinary incontinence, abnormal ejaculation, genital edema and anorgasmia.
Analysis of the safety database from controlled clinical trials showed no apparent difference in adverse reactions in patients taking VIAGRA with and without anti-hypertensive medication. This analysis was performed retrospectively, and was not powered to detect any pre-specified difference in adverse reactions.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of VIAGRA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events have been chosen for inclusion either due to their seriousness, reporting frequency, lack of clear alternative causation, or a combination of these factors.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Nitrates
Administration of VIAGRA with nitric oxide donors such as organic nitrates or organic nitrites in any form is contraindicated. Consistent with its known effects on the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway, VIAGRA was shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Contraindications (4.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7.2 Alpha-blockers
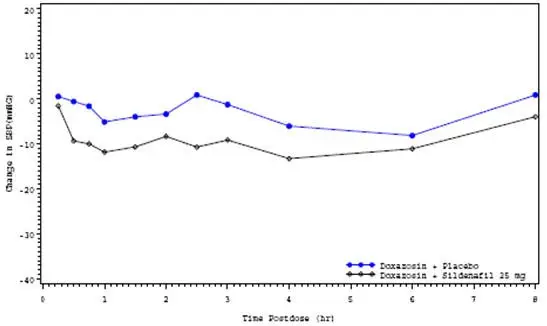
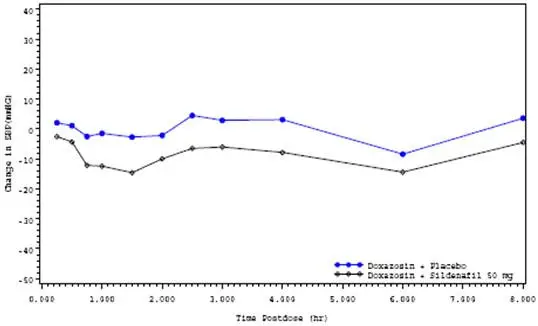
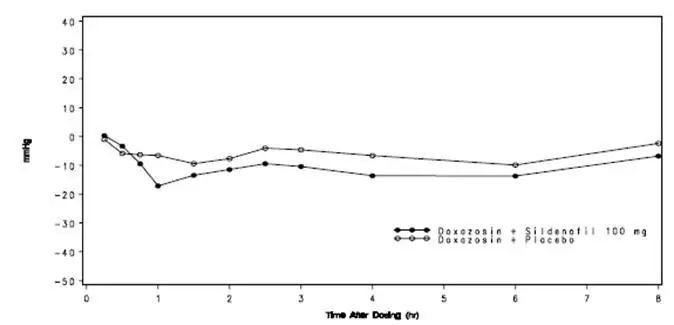
Use caution when co-administering alpha-blockers with VIAGRA because of potential additive blood pressure-lowering effects. When VIAGRA is co-administered with an alpha-blocker, patients should be stable on alpha-blocker therapy prior to initiating VIAGRA treatment and VIAGRA should be initiated at the lowest dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3),Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7.3 Amlodipine
When VIAGRA 100 mg was co-administered with amlodipine (5 mg or 10 mg) to hypertensive patients, the mean additional reduction on supine blood pressure was 8 mmHg systolic and 7 mmHg diastolic [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7.4 Ritonavir and other CYP3A4 inhibitors
Co-administration of ritonavir, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, greatly increased the systemic exposure of sildenafil (11-fold increase in AUC). It is therefore recommended not to exceed a maximum single dose of 25 mg of VIAGRA in a 48 hour period [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Co-administration of erythromycin, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in a 160% and 182% increases in sildenafil Cmax and AUC, respectively. Co-administration of saquinavir, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in 140% and 210% increases in sildenafil Cmax and AUC, respectively. Stronger CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole or itraconazole could be expected to have greater effects than seen with saquinavir. A starting dose of 25 mg of VIAGRA should be considered in patients taking erythromycin or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as saquinavir, ketoconazole, itraconazole) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
VIAGRA is not indicated for use in pediatric patients. Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Healthy elderly volunteers (65 years or over) had a reduced clearance of sildenafil resulting in approximately 84% and 107% higher plasma AUC values of sildenafil and its active N-desmethyl metabolite, respectively, compared to those seen in healthy young volunteers (18–45 years) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Due to age-differences in plasma protein binding, the corresponding increase in the AUC of free (unbound) sildenafil and its active N-desmethyl metabolite were 45% and 57%, respectively [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Viagra, 18% were 65 years and older, while 2% were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between older (≥ 65 years of age) and younger (< 65 years of age) subjects.
However, since higher plasma levels may increase the incidence of adverse reactions, a starting dose of 25 mg should be considered in older subjects due to the higher systemic exposure [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required for mild (CLcr=50–80 mL/min) and moderate (CLcr=30–49 mL/min) renal impairment. In volunteers with severe renal impairment (Clcr<30 mL/min), sildenafil clearance was reduced, resulting in higher plasma exposure of sildenafil (~2 fold), approximately doubling of Cmax and AUC. A starting dose of 25 mg should be considered in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In volunteers with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A and B), sildenafil clearance was reduced, resulting in higher plasma exposure of sildenafil (47% for Cmax and 85% for AUC). The pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in patients with severely impaired hepatic function (Child-Pugh Class C) have not been studied. A starting dose of 25 mg should be considered in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
In studies with healthy volunteers of single doses up to 800 mg, adverse reactions were similar to those seen at lower doses but incidence rates and severities were increased.
In cases of overdose, standard supportive measures should be adopted as required. Renal dialysis is not expected to accelerate clearance as sildenafil is highly bound to plasma proteins and it is not eliminated in the urine.
11. Viagra Description
VIAGRA (sildenafil citrate), an oral therapy for erectile dysfunction, is the citrate salt of sildenafil, a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5).
Sildenafil citrate is designated chemically as 1-[[3-(6,7-dihydro-1-methyl-7-oxo-3-propyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl)-4-ethoxyphenyl]sulfonyl]-4-methylpiperazine citrate and has the following structural formula:
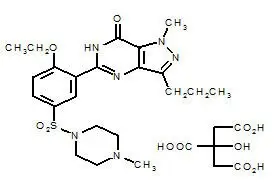
Sildenafil citrate is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a solubility of 3.5 mg/mL in water and a molecular weight of 666.7.
VIAGRA is formulated as blue, film-coated rounded-diamond-shaped tablets equivalent to 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg of sildenafil for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, sildenafil citrate, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, lactose, triacetin, and FD & C Blue #2 aluminum lake.
12. Viagra - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The physiologic mechanism of erection of the penis involves release of nitric oxide (NO) in the corpus cavernosum during sexual stimulation. NO then activates the enzyme guanylate cyclase, which results in increased levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), producing smooth muscle relaxation in the corpus cavernosum and allowing inflow of blood.
Sildenafil enhances the effect of NO by inhibiting phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which is responsible for degradation of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum. Sildenafil has no direct relaxant effect on isolated human corpus cavernosum. When sexual stimulation causes local release of NO, inhibition of PDE5 by sildenafil causes increased levels of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum, resulting in smooth muscle relaxation and inflow of blood to the corpus cavernosum. Sildenafil at recommended doses has no effect in the absence of sexual stimulation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
VIAGRA is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a mean absolute bioavailability of 41% (range 25–63%). The pharmacokinetics of sildenafil are dose-proportional over the recommended dose range. It is eliminated predominantly by hepatic metabolism (mainly CYP3A4) and is converted to an active metabolite with properties similar to the parent, sildenafil. Both sildenafil and the metabolite have terminal half lives of about 4 hours.
Mean sildenafil plasma concentrations measured after the administration of a single oral dose of 100 mg to healthy male volunteers is depicted below:
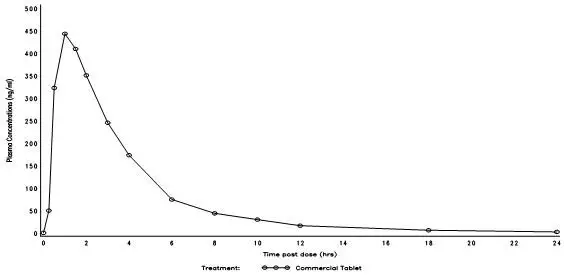
Figure 5: Mean Sildenafil Plasma Concentrations in Healthy Male Volunteers.
Drug Interaction Studies
14. Clinical Studies
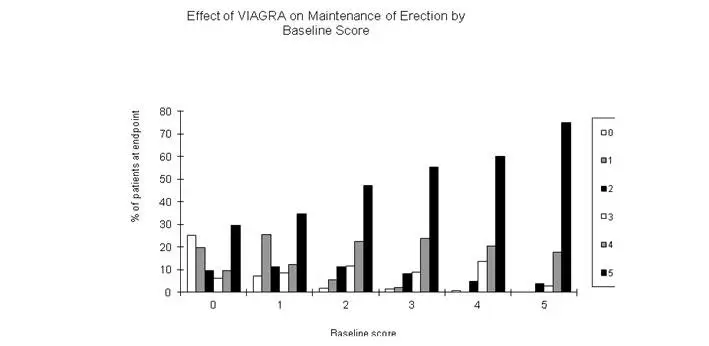
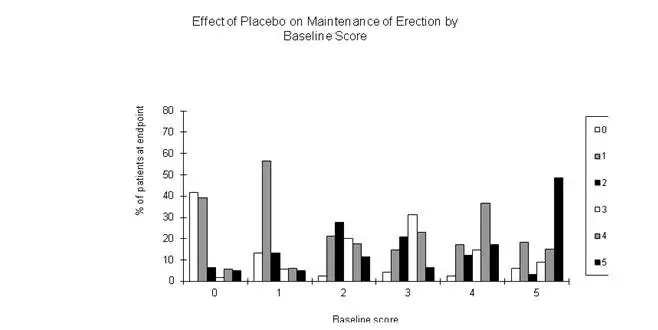
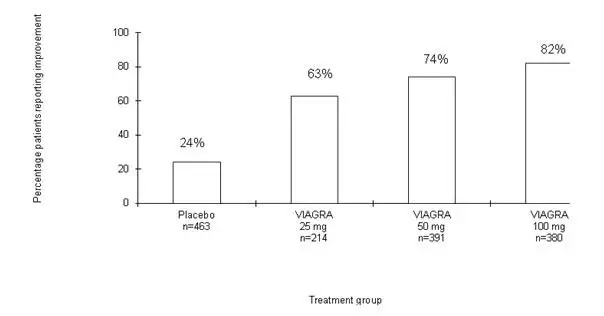
In clinical studies, VIAGRA was assessed for its effect on the ability of men with erectile dysfunction (ED) to engage in sexual activity and in many cases specifically on the ability to achieve and maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual activity. VIAGRA was evaluated primarily at doses of 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg in 21 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of up to 6 months in duration, using a variety of study designs (fixed dose, titration, parallel, crossover). VIAGRA was administered to more than 3,000 patients aged 19 to 87 years, with ED of various etiologies (organic, psychogenic, mixed) with a mean duration of 5 years. VIAGRA demonstrated statistically significant improvement compared to placebo in all 21 studies. The studies that established benefit demonstrated improvements in success rates for sexual intercourse compared with placebo.
16. How is Viagra supplied
VIAGRA (sildenafil citrate) is supplied as blue, film-coated, rounded-diamond-shaped tablets containing sildenafil citrate equivalent to the nominally indicated amount of sildenafil and debossed on the obverse and reverse sides as follows:
| 25 mg | 50 mg | 100 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | VGR25 | VGR50 | VGR100 |
| Reverse | PFIZER | PFIZER | PFIZER |
| Bottle of 30 | NDC-0069-4200-30 | NDC-0069-4210-30 | NDC-0069-4220-30 |
| Bottle of 100 | N/A | NDC-0069-4210-66 | NDC-0069-4220-66 |
| Carton of 30 (1 tablet per Single Pack ) | N/A | NDC 0069-4210-33 | NDC 0069-4220-33 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Patient Information
VIAGRA® (vi-AG-rah)
(sildenafil citrate)
Tablets
What is the most important information I should know about VIAGRA?
VIAGRA can cause your blood pressure to drop suddenly to an unsafe level if it is taken with certain other medicines. Do not take VIAGRA if you take any other medicines called "nitrates." Nitrates are used to treat chest pain (angina). A sudden drop in blood pressure can cause you to feel dizzy, faint, or have a heart attack or stroke.
Do not take VIAGRA if you take medicines called guanylate cyclase stimulators which include:
- Riociguat (Adempas®) a medicine that treats pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic-thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
Tell all your healthcare providers that you take VIAGRA. If you need emergency medical care for a heart problem, it will be important for your healthcare provider to know when you last took VIAGRA.
Stop sexual activity and get medical help right away if you get symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, or nausea during sex.
Sexual activity can put an extra strain on your heart, especially if your heart is already weak from a heart attack or heart disease. Ask your doctor if your heart is healthy enough to handle the extra strain of having sex.
VIAGRA does not protect you or your partner from getting sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV—the virus that causes AIDS.
What is VIAGRA?
VIAGRA is a prescription medicine used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). You will not get an erection just by taking this medicine. VIAGRA helps a man with erectile dysfunction get and keep an erection only when he is sexually excited (stimulated).
VIAGRA is not for use in women or children.
It is not known if VIAGRA is safe and effective in women or children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take VIAGRA?
Do not take VIAGRA if you:
- take medicines called nitrates (such as nitroglycerin)
- use street drugs called "poppers" such as amyl nitrate or amyl nitrite, and butyl nitrate
- take any medicines called guanylate cyclase stimulators such as riociguat (Adempas)
- are allergic to sildenafil, as contained in VIAGRA and REVATIO, or any of the ingredients in VIAGRA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in VIAGRA.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking VIAGRA?
Before you take VIAGRA, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or have had heart problems such as a heart attack, irregular heartbeat, angina, chest pain, narrowing of the aortic valve or heart failure
- have had heart surgery within the last 6 months
- have pulmonary hypertension
- have had a stroke
- have low blood pressure, or high blood pressure that is not controlled
- have a deformed penis shape
- have had an erection that lasted for more than 4 hours
- have problems with your blood cells such as sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia
- have retinitis pigmentosa, a rare genetic (runs in families) eye disease
- have ever had severe vision loss, including an eye problem called non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)
- have bleeding problems
- have or have had stomach ulcers
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems or are having kidney dialysis
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take1, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
VIAGRA may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect the way VIAGRA works causing side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take any of the following:
- medicines called nitrates (see "What is the most important information I should know about VIAGRA?")
- medicines called guanylate cyclase stimulators, such as riociguat (Adempas)
- medicines called alpha blockers such as Hytrin (terazosin HCl), Flomax (tamsulosin HCl), Cardura (doxazosin mesylate), Minipress (prazosin HCl), Uroxatral (alfuzosin HCl), Jalyn (dutasteride and tamsulosin HCl), or Rapaflo (silodosin). Alpha-blockers are sometimes prescribed for prostate problems or high blood pressure. In some patients, the use of VIAGRA with alpha-blockers can lead to a drop in blood pressure or to fainting.
- medicines called HIV protease inhibitors, such as ritonavir (Norvir), indinavir sulfate (Crixivan), saquinavir (Fortovase or Invirase) or atazanavir sulfate (Reyataz)
- some types of oral antifungal medicines, such as ketoconazole (Nizoral), and itraconazole (Sporanox)
- some types of antibiotics, such as clarithromycin (Biaxin), telithromycin (Ketek), or erythromycin
- other medicines that treat high blood pressure
- other medicines or treatments for ED
- VIAGRA contains sildenafil, which is the same medicine found in another drug called REVATIO. REVATIO is used to treat a rare disease called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). VIAGRA should not be used with REVATIO or with other PAH treatments containing sildenafil or any other PDE5 inhibitors (such as Adcirca [tadalafil]).
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take VIAGRA?
- Take VIAGRA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much VIAGRA to take and when to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed.
- Take VIAGRA about 1 hour before sexual activity. You may take VIAGRA between 30 minutes to 4 hours before sexual activity if needed.
- VIAGRA can be taken with or without food. If you take VIAGRA after a high fat meal (such as a cheeseburger and french fries), VIAGRA may take a little longer to start working
- Do not take VIAGRA more than 1 time a day.
- If you accidentally take too much VIAGRA, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of VIAGRA?
VIAGRA can cause serious side effects. Rarely reported side effects include:
- an erection that will not go away (priapism). If you have an erection that lasts more than 4 hours, get medical help right away. If it is not treated right away, priapism can permanently damage your penis.
- sudden vision loss in one or both eyes. Sudden vision loss in one or both eyes can be a sign of a serious eye problem called non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION). It is uncertain whether PDE5 inhibitors directly cause the vision loss. Stop taking VIAGRA and call your healthcare provider right away if you have sudden vision loss in one or both eyes.
- sudden hearing decrease or hearing loss. Some people may also have ringing in their ears (tinnitus) or dizziness. If you have these symptoms, stop taking VIAGRA and contact a doctor right away.
The most common side effects of VIAGRA are:
- headache
- flushing
- upset stomach
- abnormal vision, such as changes in color vision (such as having a blue color tinge) and blurred vision
- stuffy or runny nose
- back pain
- muscle pain
- nausea
- dizziness
- rash
In addition, heart attack, stroke, irregular heartbeats and death have happened rarely in men taking VIAGRA. Most, but not all, of these men had heart problems before taking VIAGRA. It is not known if VIAGRA caused these problems.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of VIAGRA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store VIAGRA?
- Store VIAGRA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep VIAGRA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of VIAGRA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use VIAGRA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VIAGRA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about VIAGRA. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about VIAGRA that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.viagra.com, or call 1-888-4VIAGRA
What are the ingredients in VIAGRA?
Active ingredient: sildenafil citrate
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, lactose, triacetin, and FD & C Blue #2 aluminum lake
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

This product's label may have been updated. For current full prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.
Viagra (sildenafil citrate), Revatio (sildenafil), Cardura (doxazosin mesylate), and Minipress (prazosin HCl) are registered trademarks of Pfizer Inc.
LAB-0220-11.0
Revised: 08/2017
- 1
- The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Pfizer Inc. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse Pfizer Inc or its products.
| VIAGRA
sildenafil citrate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VIAGRA
sildenafil citrate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VIAGRA
sildenafil citrate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc (134489525) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc | 001147495 | ANALYSIS(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC | 829084545 | API MANUFACTURE(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) , MANUFACTURE(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) , PACK(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Inc | 943955690 | ANALYSIS(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC | 829084552 | PACK(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Ireland Pharmaceuticals | 985052076 | ANALYSIS(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) , API MANUFACTURE(0069-4200, 0069-4210, 0069-4220) | |