Drug Detail:Voquezna triple pak (Amoxicillin, clarithromycin and vonoprazan)
Drug Class: H. pylori eradication agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK (vonoprazan tablets; amoxicillin capsules; clarithromycin tablets), co-packaged for oral use VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK (vonoprazan tablets; amoxicillin capsules) co-packaged for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
Indications and Usage for Voquezna Pak
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK, is a co-packaged product containing vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB), amoxicillin, a penicillin class antibacterial, and clarithromycin, a macrolide antimicrobial, indicated for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in adults. (1.1)
VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK, is a co-packaged product containing vonoprazan, a PCAB, and amoxicillin, a penicillin class antibacterial, indicated for the treatment of H. pylori infection in adults. (1.1)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK, VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK and other antibacterial drugs, VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.2)
Voquezna Pak Dosage and Administration
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK: The recommended dosage regimen is vonoprazan 20 mg plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg plus clarithromycin 500 mg, each given twice daily (morning and evening, 12 hours apart), with or without food, for 14 days. (2.1)
VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK: The recommended dosage regimen is vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily (morning and evening) plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg, three times a day (morning, mid-day, and evening), with or without food, for 14 days. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK: Carton of 14 daily administration packs for morning and evening dosing, each containing the following three drug products (3.1):
-
- Tablets: Vonoprazan 20 mg
- Tablets: Clarithromycin 500 mg
- Capsules: Amoxicillin 500 mg
VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK: Carton of 14 daily administration packs for morning, mid-day and evening dosing, each containing the following two drug products (3.2):
-
- Tablets: Vonoprazan 20 mg
- Capsules: Amoxicillin 500 mg
Contraindications
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK:
- Known hypersensitivity to vonoprazan, amoxicillin or any other beta-lactams, clarithromycin or any other macrolide antimicrobial or any component of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. (4.1)
- Known hypersensitivity to vonoprazan, amoxicillin or any other beta-lactams or any component of VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. (4.1)
- Rilpivirine-containing products. (4.1)
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK Due to the Clarithromycin Component:
- Pimozide. (4.2)
- Lomitapide, lovastatin, and simvastatin. (4.2)
- Ergot alkaloids (ergotamine or dihydroergotamine). (4.2)
- Colchicine in renal or hepatic impairment. (4.2)
- History of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic dysfunction with use of clarithromycin. (4.2)
Warnings and Precautions
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious and occasionally fatal reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) have been reported with components of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK and institute immediate therapy (e.g., anaphylaxis management). (5.1)
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCAR): Discontinue VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK at the first signs or symptoms of SCAR or other signs of hypersensitivity and consider further evaluation (5.1).
- Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD): Evaluate if diarrhea occurs with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. (5.1)
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK Due to the Clarithromycin Component:
- QT Prolongation: Avoid VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK in patients with known QT prolongation or receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval, ventricular arrhythmia (torsades de pointes), hypokalemia/hypomagnesemia, significant bradycardia, or taking Class IA or III antiarrhythmics. (5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Discontinue if signs and symptoms of hepatitis occur with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. (5.2)
- Serious adverse reactions due to concomitant use with other drugs: Serious adverse reactions can occur with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK due to drug interactions of clarithromycin with colchicine, some lipid lowering agents, some calcium channel blockers, and other drugs. (5.2)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Based on the findings from animal studies and human observational studies in pregnant women treated with clarithromycin, VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is not recommended for use in pregnant women except in clinical circumstances where no alternative therapy is appropriate. (5.2)
- Myasthenia Gravis: Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis can occur with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK since it has been reported in patients receiving clarithromycin tablets. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK: Most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) were dysgeusia, diarrhea, vulvovaginal candidiasis, headache, abdominal pain, and hypertension. (6.1)
VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK: Most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) were diarrhea, abdominal pain, vulvovaginal candidiasis and nasopharyngitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Phathom Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at toll-free phone 1-888-775-PHAT (7428) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Components of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK have the potential for clinically important drug interactions. See Full Prescribing Information for important drug interactions with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. (4, 5.2, 7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended during treatment, but a lactating woman can pump and discard breast milk during treatment and for 2 days after VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK administration. (8.2)
- Geriatrics: VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK increased risk of torsades de pointes due to the clarithromycin component. (8.5)
- Renal Impairment: Avoid use in severe renal impairment. (8.6)
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in moderate and severe hepatic impairment. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Voquezna Pak
1.1. Helicobacter pylori Infection
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK are indicated for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)].
1.2. Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK, VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK and other antibacterial drugs, VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2. Voquezna Pak Dosage and Administration
2.1. Recommended Dosage for VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK
The recommended adult oral dosage of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is vonoprazan 20 mg plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg plus clarithromycin 500 mg, each given twice daily (in the morning and evening, 12 hours apart), with or without food, for 14 days.
2.2. Recommended Dosage for VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK
The recommended adult oral dose of VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is vonoprazan 20 mg given twice daily (in the morning and evening) plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg three times daily (in the morning, mid-day, and evening), with or without food, for 14 days.
2.3. Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, administer VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK as soon as possible, within 4 hours after the missed dose. If more than 4 hours have passed, skip the missed dose and administer the next dose on the regularly scheduled time. Patients should continue the normal dosing schedule until the medication is completed.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
3.1. VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is a co-package consisting of 14 administration packs for morning and evening dosing. Each administration pack contains the following three drug products:
- Vonoprazan Tablets, 20 mg: pale red, oval, film-coated tablets debossed V20 on one side and plain on the other side.
- Amoxicillin Capsules, 500 mg: yellow, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted with AMOX 500 on one side and GG 849 on the other side.
- Clarithromycin Tablets, 500 mg: white, oval, film-coated debossed GG C9 on one side and plain on the other side.
3.2. VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK
VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is a co-package consisting of 14 administration packs for morning, mid-day and evening dosing. Each administration pack contains the following two drug products:
- Vonoprazan Tablets, 20 mg: pale red, oval, film-coated tablets debossed V20 on one side and plain on the other side.
- Amoxicillin Capsules, 500 mg: yellow, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted with AMOX 500 on one side and GG 849 on the other side.
4. Contraindications
5. Warnings and Precautions
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Concomitant Use with Other Drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Exacerbation of Myasthenia Gravis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1. Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2. Postmarketing Experience with Components of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of vonoprazan (outside of the United States), amoxicillin or clarithromycin (all used separately). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
Collated drug interaction information for the individual components in VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is summarized below. Drug interaction studies with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK have not been conducted.
These recommendations are based on either drug interaction trials or predicted interactions due to the expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious adverse reactions or loss of efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Clarithromycin (a component of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK) is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Concomitant use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with a drug(s) primarily metabolized by CYP3A may cause elevations in CYP3A substrate drug's concentrations that could increase or prolong both therapeutic and adverse effects of the concomitant drug.
| Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan and clarithromycin are CYP3A substrates. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers may decrease exposure of vonoprazan and clarithromycin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce the effectiveness of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Probenecid | ||
| Clinical Effect | Amoxicillin undergoes tubular secretion. Probenecid may increase amoxicillin exposure by blocking its renal tubular secretion, which may increase the risk of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK adverse reactions. | |
| Prevention or Management | Closely monitor for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions associated with amoxicillin when used with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Allopurinol | ||
| Clinical Effect | Increase in the incidence of rashes is reported in patients receiving both allopurinol and amoxicillin together compared to patients receiving amoxicillin alone. It is not known whether this potentiation of amoxicillin rashes is due to allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients. | |
| Prevention or Management | Discontinue allopurinol at the first appearance of skin rash when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Omeprazole | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin concentrations in the gastric tissue and mucus were increased by concomitant administration of omeprazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with omeprazole. | |
| Itraconazole | ||
| Clinical Effect | Both clarithromycin and itraconazole are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A, potentially leading to a bi-directional drug interaction when administered concomitantly. VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK's use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may lead to increases in clarithromycin exposure, which may increase the risk of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK adverse reactions. | |
| Prevention or Management | Patients taking itraconazole with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK should be monitored closely for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions associated with itraconazole and clarithromycin. | |
| Antivirals | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a CYP3A4 substrate and inhibitor. Use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with antivirals that are CYP3A substrates, inducers, or CYP3A inhibitors may potentially lead to bi-directional drug interactions leading to alterations in exposure of clarithromycin and/or CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions or loss of effectiveness. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Saquinavir (CYP3A substrate and inhibitor) | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. See saquinavir prescribing information for instructions when saquinavir (with or without ritonavir) is co-administered with clarithromycin. |
| Ritonavir (CYP3A inhibitor) | Use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with ritonavir is not recommended in patients with decreased renal function. | |
| Etravirine (CYP3A inducer) | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan is a CYP3A substrate. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers may decrease vonoprazan exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce the effectiveness of VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. |
| Probenecid | |
| Clinical Effect | Amoxicillin undergoes tubular secretion. Probenecid may increase amoxicillin exposure by blocking its renal tubular secretion, which may increase the risk of VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK adverse reactions. |
| Prevention or Management | Closely monitor for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions associated with amoxicillin when used with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. |
| Allopurinol | |
| Clinical Effect | Increase in the incidence of rashes is reported in patients receiving both allopurinol and amoxicillin together compared to patients receiving amoxicillin alone. It is not known whether this potentiation of amoxicillin rashes is due to allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients. |
| Prevention or Management | Discontinue allopurinol at the first appearance of skin rash when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. |
| Drugs Dependent on Gastric pH for Absorption | ||
| Antiretrovirals | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which may alter the absorption of antiretroviral drugs leading to changes in their safety and/or effectiveness. | |
| Prevention or Management | Rilpivirine-containing Products | Concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is contraindicated. |
| Atazanavir | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Nelfinavir | ||
| Other Antiretroviral Drugs | See the prescribing information of other antiretroviral drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption prior to concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Other Drugs (e.g., iron salts, erlotinib, dasatinib, nilotinib, mycophenolate mofetil, ketoconazole/itraconazole) | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which may decrease the absorption of drugs reducing their effectiveness. | |
| Prevention or Management | See the prescribing information for other drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption. | |
| Certain CYP3A Substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Vonoprazan is a weak CYP3A inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Clarithromycin and vonoprazan may increase exposure of CYP3A4 substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with tacrolimus and cyclosporine. |
|
| Prevention or Management | Immunosuppressants: Tacrolimus, cyclosporine. | Frequent monitoring for concentrations and/or adverse reactions related to the substrate drugs when used with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. Dosage reduction of substrate drugs may be needed. See prescribing information for the relevant substrate drugs. |
| CYP2C19 Substrates (e.g., clopidogrel, citalopram, cilostazol) | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan is a CYP2C19 inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Vonoprazan may reduce plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and may cause reduction in platelet inhibition. Vonoprazan may increase exposure of CYP2C19 substrate drugs (e.g., citalopram, cilostazol). | |
| Prevention or Management | Clopidogrel | Carefully monitor the efficacy of clopidogrel and may consider alternative anti-platelet therapy. |
| Citaprolam and Cilostazol | Carefully monitor patients for adverse reactions associated with citaprolam and cilostazol. See the prescribing information for dosage adjustments. | |
| Oral Anticoagulants | ||
| Clinical Effect | Abnormal prolongation of prothrombin time (increased INR) has been reported in patients receiving amoxicillin and oral anticoagulants. | |
| Prevention or Management | Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when anticoagulants are prescribed concurrently. Adjustments in the dose of oral anticoagulants may be necessary to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation. | |
| Chromogranin A (CgA) Test for Neuroendocrine Tumors | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which increases chromogranin A (CgA) levels and may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. | |
| Prevention or Management | Assess CgA levels at least 14 days after VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK treatment and repeat the test if initial CgA levels are high. If serial tests are performed (e.g., for monitoring), use the same commercial laboratory for testing, as reference ranges between tests may vary. | |
| Glucose Tests | ||
| Clinical Effect | Amoxicillin is primarily excreted in the urine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. High urine concentrations of ampicillin or amoxicillin may cause false-positive results when using glucose tests based on the Benedict's copper reduction reaction that determines the amount of reducing substances like glucose in the urine. | |
| Prevention or Management | Use a test based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions when testing for glucose in the urine of patients treated with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Itraconazole | ||
| Clinical Effect | Both clarithromycin and itraconazole are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A, potentially leading to a bi-directional drug interaction when administered concomitantly. VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK's use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may lead to increases in clarithromycin exposure, which may increase the risk of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK adverse reactions. | |
| Prevention or Management | Patients taking itraconazole with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK should be monitored closely for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions associated with itraconazole and clarithromycin. | |
| Antiarrhythmics | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of antiarrhythmic drugs that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates including cardiac arrhythmias (e.g., torsades de pointes). There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with disopyramide and quinidine. There have been postmarketing reports of hypoglycemia with the concomitant administration of clarithromycin and disopyramide |
|
| Prevention or Management | Disopyramide | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor patients for QTc prolongation and changes in blood glucose levels. |
| Amiodarone | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor patients for QTc prolongation. | |
| Dofetilide | ||
| Procainamide | ||
| Sotalol | ||
| Quinidine | ||
| Colchicine | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is an inhibitor of CYP3A and the efflux transporter, P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Colchicine is a substrate of CYP3A and P-gp. Clarithromycin increases exposure of colchicine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to colchicine. | |
| Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of colchicine with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. If co-administration of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and colchicine is necessary in patients with normal renal or hepatic function, carefully monitor patients for clinical symptoms of colchicine toxicity and refer to the colchicine prescribing information for recommendations on dosage reduction. | |
| Antipsychotics | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of antipsychotic drugs that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates including the risk of somnolence, orthostatic hypotension, altered state of consciousness, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, or cardiac arrhythmias (QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes). | |
| Prevention or Management | Pimozide | Concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is contraindicated. |
| Quetiapine | Refer to quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on dosage reduction if co-administered with CYP3A4 inhibitors such as clarithromycin. | |
| Tolterodine (patients deficient in CYP2D6 activity) | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. The primary route of metabolism for tolterodine is via CYP2D6. Clarithromycin may increase tolterodine exposure and the risk of adverse reactions related to tolterodine in patients deficient in CYP2D6 activity because tolterodine is metabolized via CYP3A in this subset of population. | |
| Prevention or Management | Tolterodine 1 mg twice daily is recommended in patients deficient in CYP2D6 activity (poor metabolizers) when co-administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as clarithromycin. | |
| Antivirals | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a CYP3A4 substrate and inhibitor. Use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with antivirals that are CYP3A substrates, inducers, or CYP3A inhibitors may potentially lead to bi-directional drug interactions leading to alterations in exposure of clarithromycin and/or CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions or loss of effectiveness [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Saquinavir (CYP3A substrate and inhibitor) | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. See saquinavir prescribing information for instructions when saquinavir (with or without ritonavir) is co-administered with clarithromycin. |
| Maraviroc (CYP3A substrate) | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. See the prescribing information of maraviroc for dosage recommendation when given with strong CYP3A inhibitors such as clarithromycin. | |
| Zidovudine | Administration of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and zidovudine should be separated by at least two hours. | |
| Benzodiazepines | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of benzodiazepines that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Midazolam | Closely monitor patients for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged central nervous system effects s (e.g., somnolence and confusion) and refer to the CYP3A substrate prescribing information for dosage adjustments when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. |
| Alprazolam | ||
| Triazolam | ||
| Calcium Channel Blockers | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of calcium channel blockers that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates including hypotension, acute kidney injury, bradyarrhythmias, lactic acidosis, or peripheral edema. | |
| Prevention or Management | Verapamil | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. |
| Amlodipine | ||
| Diltiazem | ||
| Nifedipine | ||
| Ergot Alkaloids | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of ergot alkaloids that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues including the central nervous system [see Contraindications (4.2)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Ergotamine | Concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is contraindicated. |
| Dihydroergotamine | ||
| Hypoglycemic Agents | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of hypoglycemic agents that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Nateglinide | Closely monitor glucose levels when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. |
| Pioglitazone | ||
| Repaglinide | ||
| Rosiglitazone | ||
| Insulin | ||
| Lipid-lowering Agents | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of lipid-lowering drugs that are CYP3A substrates, thereby increasing the risk of toxicities from these drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Lomitapide | Concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is contraindicated. |
| Lovastatin | ||
| Simvastatin | ||
| Atorvastatin | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. In situations where the concomitant use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with atorvastatin or pravastatin cannot be avoided, atorvastatin dose should not exceed 20 mg daily and pravastatin dose should not exceed 40 mg daily. | |
| Pravastatin | ||
| Fluvastatin | Use of a statin that is not dependent on CYP3A metabolism (e.g., fluvastatin) can be considered. It is recommended to prescribe the lowest registered dose if concomitant use cannot be avoided. | |
| Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of phosphodiesterase inhibitors that are CYP3A substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. | |
| Prevention or Management | Sildenafil | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. If concomitant use is unavoidable, see the prescribing information of the respective phosphodiesterase inhibitors for dosage recommendation when given with strong CYP3A inhibitors such as clarithromycin. |
| Tadalafil | ||
| Vardenafil | ||
| Other CYP3A Based Interactions | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a substrate and strong inhibitor of CYP3A4. Clarithromycin increases exposure of CYP3A substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers may decrease exposure of clarithromycin. There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with alfentanil, methylprednisolone, cilostazol, bromocriptine, vinblastine, phenobarbital, and St. John's Wort. | |
| Prevention or Management | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. | |
| P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Substrates: Digoxin | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin is a P-gp inhibitor. Clarithromycin may increase exposure of P-gp substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates, including potentially fatal arrhythmias. Elevated digoxin serum concentrations in patients receiving clarithromycin and digoxin concomitantly have been reported in postmarketing surveillance. Some patients have shown clinical signs consistent with digoxin toxicity, including potentially fatal arrhythmias. | |
| Prevention or Management | Digoxin | Carefully monitor serum concentrations and refer to the digoxin prescribing information for dosage adjustments when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. |
| Drugs Metabolized by CYP450 Isoforms Other than CYP3A | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin may increase exposure of drugs that are metabolized by CYP450 isoforms other than CYP3A by inhibiting their metabolism. There have been post-marketing reports of interactions of clarithromycin with drugs not thought to be metabolized by CYP3A. | |
| Prevention or Management | Hexobarbital | Use VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK with caution. |
| Phenytoin | ||
| Valproate | ||
| Theophylline | ||
| Clinical Effect | Clarithromycin may increase exposure of theophylline (a xanthine derivative drug) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to theophylline. | |
| Prevention or Management | Closely monitor serum theophylline concentrations in patients receiving high dosages of theophylline or with baseline concentrations in the upper therapeutic range when used concomitantly with VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK. | |
| Drugs Dependent on Gastric pH for Absorption | ||
| Antiretrovirals | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which may alter the absorption of antiretroviral drugs leading to changes in their safety and/or effectiveness. | |
| Prevention or Management | Rilpivirine-containing Products | Concomitant use with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is contraindicated. |
| Atazanavir | Avoid concomitant use with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK | |
| Nelfinavir | ||
| Other Antiretroviral Drugs | See the prescribing information of other antiretroviral drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption prior to concomitant use with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. | |
| Other Drugs (e.g., iron salts, erlotinib, dasatinib, nilotinib, mycophenolate mofetil, ketoconazole/itraconazole) | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which may decrease the absorption of drugs reducing their effectiveness. | |
| Prevention or Management | See the prescribing information for other drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption. | |
| Certain CYP3A Substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan is a weak CYP3A inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Vonoprazan may increase exposure of CYP3A4 substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. |
|
| Prevention or Management | Immunosuppressants: Tacrolimus, cyclosporine. | Frequent monitoring for concentrations and/or adverse reactions related to the substrate drugs when used with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. Dosage reduction of substrate drugs may be needed. See prescribing information for the relevant substrate drugs. |
| Oral Anticoagulants | ||
| Clinical Effect | Abnormal prolongation of prothrombin time (increased INR) has been reported in patients receiving amoxicillin and oral anticoagulants. | |
| Prevention or Management | Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when anticoagulants are prescribed concurrently. Adjustments in the dose of oral anticoagulants may be necessary to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation. | |
| CYP2C19 Substrates (e.g., clopidogrel, citalopram, cilostazol) | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan is a CYP2C19 inhibitor [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Vonoprazan may reduce plasma concentrations of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and may cause reduction in platelet inhibition. Vonoprazan may increase exposure of CYP2C19 substrate drugs (e.g., citalopram, cilostazol). |
|
| Prevention or Management | Clopidogrel | Carefully monitor the efficacy of clopidogrel and may consider alternative anti-platelet therapy |
| Citaprolam and Cilostazol | Carefully monitor patients for adverse reactions associated with citaprolam and cilostazol. See the prescribing information for dosage adjustments. | |
| CgA Test for Neuroendocrine Tumors | ||
| Clinical Effect | Vonoprazan reduces intragastric acidity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)], which increases CgA levels and may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. | |
| Prevention or Management | Assess CgA levels at least 14 days after VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK treatment and repeat the test if initial CgA levels are high. If serial tests are performed (e.g., for monitoring), use the same commercial laboratory for testing, as reference ranges between tests may vary. | |
| Glucose Tests | ||
| Clinical Effect | Amoxicillin is primarily excreted in the urine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. High urine concentrations of ampicillin or amoxicillin may cause false-positive results when using glucose tests based on the Benedict's copper reduction reaction that determines the amount of reducing substances like glucose in the urine. | |
| Prevention or Management | Use a test based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions when testing for glucose in the urine of patients treated with VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK. | |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1. Pregnancy
8.2. Lactation
8.4. Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5. Geriatric Use
8.6. Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is recommended in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 89 mL/min). Avoid the use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7. Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). Avoid the use of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
No information is available on accidental overdosage of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK or VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK in humans.
In case of an overdose, patients should contact a physician, poison control center, or emergency room. The available overdosage information for each of the individual components in VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK are summarized below:
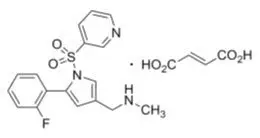
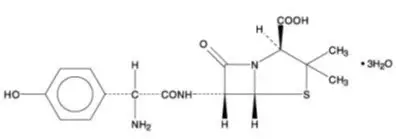
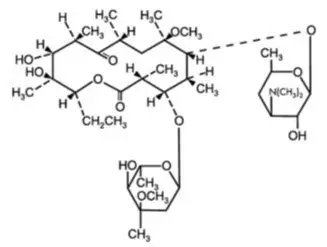
11. Voquezna Pak Description
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK contains vonoprazan tablets, 20 mg, amoxicillin capsules, 500 mg and clarithromycin tablets, 500 mg for oral administration. VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK contains vonoprazan tablets, 20 mg and amoxicillin capsules, 500 mg for oral administration.
12. Voquezna Pak - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Vonoprazan suppresses basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell through inhibition of the H+, K+-ATPase enzyme system in a potassium competitive manner. Because this enzyme is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the parietal cell, vonoprazan has been characterized as a type of gastric proton-pump inhibitor, in that it blocks the final step of acid production. Vonoprazan does not require activation by acid. Vonoprazan may selectively concentrate in the parietal cells in both the resting and stimulated states. Vonoprazan binds to the active proton pumps in a noncovalent and reversible manner. Amoxicillin is an antibacterial drug. Clarithromycin is a macrolide antimicrobial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
Acid suppression enhances the replication of H. pylori bacteria and the stability and effectiveness of antimicrobials in the treatment of H. pylori infection.
12.3. Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters for vonoprazan 20 mg after a single dose (not an approved recommended dosage) and at steady state following twice daily administration are summarized in Table 6.
| PK Parameter | Single Dose (N=10) | Steady State (N=32) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax = Maximum plasma concentration; AUC0-12h =Area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to the end of the 12-hour dosing interval; Tmax = Time to reach Cmax; t1/2 = Elimination half-life, CL/F = Apparent oral clearance, Vz/F = Apparent oral volume of distribution. | ||
| Tmax (h), median (range) | 2.5 (1.0-4.0) | 3.0 (1.0-6.0) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 25.2 (39.7) | 37.8 (36.1) |
| AUC0-12h (ng*hr/mL) | 154.8 (25.2) | 272.5 (30.5) |
| t1/2 (h) | 7.1 (10.1) | 6.8 (22.7) |
| CL/F (L/h) | 97.3 (36.3) | 81.3 (35.7) |
| Vz/F (L) | 1001 (39.6) | 782.7 (34.4) |
Vonoprazan
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No adequate or well-controlled long-term studies have been performed to evaluate the effect of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK on carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
14. Clinical Studies
The effectiveness and safety of VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK were evaluated in a randomized, controlled, double-blind triple therapy/open-label dual therapy study conducted in the United States and Europe in treatment-naÏve H. pylori-positive adult patients with at least one clinical condition: dyspepsia lasting at least 2 weeks, functional dyspepsia, recent/new diagnosis of peptic ulcer, peptic ulcer not treated for H. pylori infection, or a stable dose of long-term NSAID treatment (NCT 04167670). Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg twice daily plus clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily (VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK) or vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg three times daily (VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK) or lansoprazole 30 mg twice daily plus amoxicillin 1,000 mg twice daily plus clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily (LAC) administered for 14 consecutive days.
H. pylori infection at baseline was defined as positive by 13C urea breath test (UBT) and follow-up upper endoscopy (culture or histology). H. pylori eradication was confirmed with a negative 13C UBT test-of-cure at ≥ 27 days post-therapy. Patients with negative test results were considered treatment successes. Patients who tested positive for H. pylori infection and patients with missing results from the test-of-cure visit were considered treatment failures.
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK were shown to be noninferior to LAC in patients who did not have a clarithromycin or amoxicillin resistant strain of H. pylori at baseline. VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK were shown to be superior to LAC in patients who had a clarithromycin resistant strain of H. pylori at baseline and in the overall population.
H. pylori eradication rates are shown in Table 8 for VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK and VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK compared to LAC.
| VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK | VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK | LAC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % (n) | % (n) | % (n) |
|
| LAC = lansoprazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin triple therapy regimen; CI = confidence interval calculated via the Miettinen and Nurminen method | |||
| Modified intent to treat (mITT) population: Patients were included in the MITT analysis if they had documented H. pylori infection at baseline. | |||
|
|||
| Patients with H. pylori infection who did not have a clarithromycin or amoxicillin resistant strain at baseline* | 84.7 (222) | 78.5 (208) | 78.8 (201) |
| Treatment Difference from LAC (95% CI) | 5.9†
(-0.8, 12.6) | -0.3‡
(-7.4, 6.8) | |
| All randomized patients with H. pylori infection at baseline | 80.8 (273) | 77.2 (250) | 68.5 (226) |
| Treatment Difference from LAC (95% CI) | 12.3§
(5.7, 18.8) | 8.7¶
(1.9, 15.4) | |
| Patients with H. pylori infection who had a clarithromycin resistant strain of H. pylori at baseline | 65.8 (48) | 69.6 (39) | 31.9 (23) |
| Treatment Difference from LAC (95% CI) | 33.8#
(17.7, 48.1) | 37.7#
(20.5, 52.6) | |
16. How is Voquezna Pak supplied
VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK is a co-package containing:
- Vonoprazan Tablets, 20 mg: pale red, oval, film-coated tablets debossed V20 on one side and plain on the other side.
- Amoxicillin Capsules, 500 mg: yellow, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted with AMOX 500 on one side and GG 849 on the other side.
- Clarithromycin Tablets, 500 mg: white, oval, film-coated tablets debossed GG C9 on one side and plain on the other side.
Vonoprazan tablets, amoxicillin capsules and clarithromycin tablets are supplied in separate blister cavities within the same blister card.
Each unit of use carton (NDC 81520-255-14) contains 56 tablets and 56 capsules divided into 14 daily dose blister cards.
Each daily blister card contains two vonoprazan tablets (20 mg each), four amoxicillin capsules (500 mg each) and two clarithromycin tablets (500 mg each), and indicates which tablets and capsules need to be taken in the morning and evening.
| VOQUEZNA DUAL PAK
vonoprazan fumarate and amoxicillin kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VOQUEZNA TRIPLE PAK
vonoprazan fumarate, amoxicillin and clarithromycin kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Phathom Pharmaceuticals Inc. (117232216) |